Difference between revisions of "Neuropathology tumours"
m (→Gliosarcoma) |
Jensflorian (talk | contribs) (Minor rearrangement) |
||
| (286 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
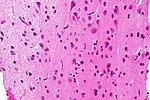
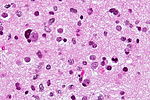
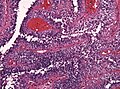
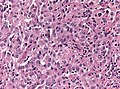
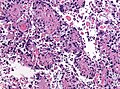
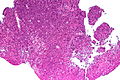
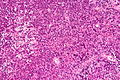
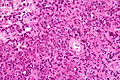
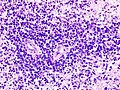
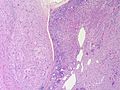
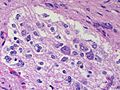
[[Image:Gemistocytic Astrocytoma 003.jpg|thumb|right|A brain stem [[astrocytoma]]. (WC)]] | |||
The article covers '''tumours in neuropathology'''. Tumours are a large part of [[neuropathology]]. [[Cytopathology]] of CNS tumours is dealt with in the article ''[[CNS cytopathology]]''. | The article covers '''tumours in neuropathology'''. Tumours are a large part of [[neuropathology]]. [[Cytopathology]] of CNS tumours is dealt with in the article ''[[CNS cytopathology]]''. | ||
There | There are separate articles for ''[[peripheral nerve sheath tumours]]'' and ''[[pituitary gland|pituitary/peri-pituitary lesions]]''. | ||
==Brain tumours - overview== | ==Brain tumours - overview== | ||
===Adult=== | ===Alphabetical=== | ||
For overview see [[:Category:Neuropathology_tumours|here]] | |||
===By age group=== | |||
====Adult==== | |||
Four most common types of brain tumours:<ref>[http://neurosurgery.mgh.harvard.edu/abta/primer.htm http://neurosurgery.mgh.harvard.edu/abta/primer.htm]</ref> | Four most common types of brain tumours:<ref>[http://neurosurgery.mgh.harvard.edu/abta/primer.htm http://neurosurgery.mgh.harvard.edu/abta/primer.htm]</ref> | ||
# Metastatic brain tumours (barely edges out primary tumours) | # Metastatic brain tumours (barely edges out primary tumours) | ||
#*Lung (most common) | #*[[Lung cancer|Lung]] (most common). | ||
#*Breast | #*[[Invasive breast cancer|Breast]]. | ||
#*Melanoma | #*[[Melanoma]]. | ||
#*[[Renal cell carcinoma]] (RCC). | #*[[Renal cell carcinoma]] (RCC). | ||
# Glioblastoma | # [[Glioblastoma]], IDH-wildtype. | ||
# | # [[Astrocytoma, IDH-mutant]]. | ||
# Meningioma. | # [[Meningioma]]. | ||
===Children=== | ====Children==== | ||
# | # [[Pilocytic astrocytoma]]. | ||
# Medulloblastoma. | # [[Medulloblastoma]]. | ||
# Ependymoma. | # [[Ependymoma]]. | ||
# Pontine glioma, often [[Diffuse midline glioma, H3 K27-altered]]. | |||
=== | ===By location=== | ||
Certain tumours like to hang-out at certain places:<ref>URL: [http://www.msdlatinamerica.com/ebooks/DiagnosticNeuropathologySmears/files/4ce563fb7e8e48fc9ed8b42e296a7747.gif http://www.msdlatinamerica.com/ebooks/DiagnosticNeuropathologySmears/files/4ce563fb7e8e48fc9ed8b42e296a7747.gif] and [http://www.msdlatinamerica.com/ebooks/DiagnosticNeuropathologySmears/sid117213.html http://www.msdlatinamerica.com/ebooks/DiagnosticNeuropathologySmears/sid117213.html]. Accessed on: 2 November 2010.</ref> | Certain tumours like to hang-out at certain places:<ref>URL: [http://www.msdlatinamerica.com/ebooks/DiagnosticNeuropathologySmears/files/4ce563fb7e8e48fc9ed8b42e296a7747.gif http://www.msdlatinamerica.com/ebooks/DiagnosticNeuropathologySmears/files/4ce563fb7e8e48fc9ed8b42e296a7747.gif] and [http://www.msdlatinamerica.com/ebooks/DiagnosticNeuropathologySmears/sid117213.html http://www.msdlatinamerica.com/ebooks/DiagnosticNeuropathologySmears/sid117213.html]. Accessed on: 2 November 2010.</ref> | ||
====Cerebrum==== | |||
*Cortical based - [[oligodendroglioma]]. | |||
*Grey-white junction - metastases. | |||
*White matter - astrocytoma, [[glioblastoma]]. | |||
*Periventricular - CNS lymphoma. | |||
*Cystic - [[ganglioglioma]], [[pilocytic astrocytoma]], [[pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma]]. | |||
====Cerebellum==== | |||
*Midline/central - [[medulloblastoma]]. | |||
*Cystic lesion - pilocytic astrocytoma (younger individual), [[hemangioblastoma]] (older individual). | |||
*Solid lesion (older individual) - [[metastasis]]. | |||
* | ====Sella turcica==== | ||
** | * [[Pituitary adenoma]]. | ||
** | * [[Craniopharyngioma]]. | ||
less common: | |||
* [[Pituicytoma]]. | |||
* [[Granular cell tumour]]. | |||
* [[Germinoma]]. | |||
* [[Chordoma]] | |||
* Rathke cleft cyst. | |||
* Hypophysitis. | |||
* Xanthogranuloma. | |||
====Spinal cord==== | |||
*[[Ependymoma]] | |||
*[[Glioblastoma]] | |||
*[[Meningioma]] | |||
*Carcinoma metastasis | |||
*[[Hemangioblastoma]] | |||
====Filum terminale==== | ====Filum terminale==== | ||
* | *[[Meningioma]]. | ||
*[[Myxopapillary ependymoma]]. | |||
*[[Neurofibroma]]. | |||
* | *[[Schwannoma]]. | ||
* | *[[Paraganglioma]]. | ||
* | ====Meninges==== | ||
* | * [[Meningioma]]. | ||
* | * [[Solitary fibrous tumour]] / Hemangiopericytoma. | ||
* [[Hemangioblastoma]]. | |||
==== | less common: | ||
* [[Melanoma]] / Melanocytoma. | |||
*Schwannoma. | * Lymphoproliferative diseases. | ||
*Meningioma. | * [[Sarcoidosis]] | ||
*Dermoid cyst/epidermoid cyst. | * [[Arachnoid cyst]]. | ||
*Ependymoma. | * Disseminated oligodendroglial-like leptomeningeal tumour. | ||
*Choroid plexus papilloma. | * Desmoplastic infantile astrocytoma / ganglioglioma. | ||
* Meningioangiomatosis. | |||
* Calcifying pseudoneoplasm. | |||
====Skull==== | |||
* [[Fibrous dysplasia]]. | |||
* [[Paget disease]]. | |||
* [[Histiocytosis]]. | |||
* [[Hemangioma]]. | |||
* [[Aneurysmal bone cyst]]. | |||
* [[Plasma_cell_neoplasms#Multiple_myeloma|Multiple myeloma]]. | |||
====Skull base / Cerebellopontine angle==== | |||
* [[Schwannoma]]. | |||
* [[Meningioma]]. | |||
* [[Dermoid cyst]] / epidermoid cyst. | |||
less common: | |||
* [[Ependymoma]]. | |||
* [[Choroid plexus papilloma]]. | |||
* [[Glomus tumour]]. | |||
* [[Chordoma]]. | |||
* [[Chondrosarcoma]]. | |||
* [[Olfactory neuroblastoma]]. | |||
* [[Endolymphatic sac tumour]]. | |||
===Primary | ===Primary versus secondary=== | ||
Glial tumours: | *[[AKA]] (primary) brain tumour versus metastatic cancer. | ||
====Primary==== | |||
[[Glioma|Glial tumours]]: | |||
*Cytoplasmic processes - '''key feature'''. | *Cytoplasmic processes - '''key feature'''. | ||
**Best seen at highest magnification - usu. ~1 micrometer. | **Best seen at highest magnification - usu. ~1 micrometer. | ||
**Processes may branch. | **Processes may branch. | ||
*Ill-defined border/blend with the surrounding brain/. | *Ill-defined border/blend with the surrounding brain. | ||
[[Meningioma]]: | |||
*Lesion often dura-based. | |||
*Mesenchymal tumor (often contains collagen). | |||
[[Lymphoma]]: | |||
*Primary CNS Lymphoma (PCNSL) is usu. a diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. | |||
*Large (lymphoid) cells, ergo usu. not a difficult diagnosis. | |||
**~2x size of resting lymphocyte, nucleoli. | |||
*Lesion predominantly perivascular. | |||
====Secondary==== | |||
*Carcinomas: | |||
**Well-demarcated border between brain and lesion - '''key feature'''. | |||
**No cytoplasmic processes. | |||
**Usu. have nuclear atypia of malignancy. | |||
**Nuclei often ~3-4x the size of a [[RBC]]. | |||
**+/-Glandular arrangement. | |||
**+/-Nucleoli. | |||
*Melanoma. | |||
*Secondary Lymphoma. | |||
*Sarcomas (rare). | |||
===By growth pattern=== | |||
====Infiltrative astrocytomas==== | |||
*[[Astrocytoma, IDH-mutant]]. | |||
*[[Glioblastoma]], IDH-wildtype. | |||
Notes: | |||
**Glial: "blends into brain"/gradual transition to non-tumour brain. | |||
====Non-infiltrative astrocytomas==== | |||
**[[Pilocytic astrocytoma]] | |||
**[[Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma]] | |||
**[[Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma]]. | |||
====Cystic tumours==== | |||
DDx:<ref>URL: [http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case320/dx.html http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case320/dx.html]. Accessed on: 14 January 2012.</ref> | |||
*[[Pilocytic astrocytoma]]. | |||
*[[Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma]]. | |||
*[[Ganglioglioma]]. | |||
*[[Hemangioblastoma]]. | |||
*[[Craniopharyngioma]].<ref>URL: [http://www.pathologyoutlines.com/Cnstumor.html#cystsgeneral http://www.pathologyoutlines.com/Cnstumor.html#cystsgeneral]. Accessed on: 14 January 2012.</ref> | |||
Notes: | |||
**Non-glial: no radiating glial processes. | |||
*Rosenthal fibres within the tumour... often seen in [[pilocytic astrocytoma]]. | |||
**Rosenthal fibres may be seen around a (very) slow growing tumour and represent a reactive process. | |||
*Inflammatory cells and macrophages should prompt consideration of an alternate diagnosis (e.g. [[cerebral infarct]], [[multiple sclerosis]]) - esp. if this is a primary lesion.<ref>URL: [http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case79/dx.html http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case79/dx.html]. Accessed on: 2 January 2012.</ref> | |||
====Grading==== | |||
Nuclear pleomorphism present: | |||
*At least grade II (diffuse astrocytoma). | |||
Mitotic figures present: | |||
*At least grade III (anaplastic astrocytoma). | |||
Microvascular proliferation ''or'' necrosis with pseudopalisading tumour cells: | |||
*Grade IV (glioblastoma [[AKA]] glioblastoma multiforme). | |||
Notes: | |||
*Pseudopalisading tumour cells = high tumour cell density adjacent to regions of necrosis; palisade = a fence of poles forming a defensive barrier or fortification. | |||
*WHO Grading is currently based on expected biologiocal behaviour without treatment. | |||
**Grading does not reflect molecular divergent groups within a tumor class or response to therapy (Currently controversies in grading for IDH-mutant astrocytoma vs. IDH-wildtype astrocytoma).<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Louis | first1 = DN. | last2 = von Deimling | first2 = A. | title = Grading of diffuse astrocytic gliomas: Broders, Kernohan, Zülch, the WHO… and Shakespeare. | journal = Acta Neuropathol | volume = | issue = | pages = | month = Aug | year = 2017 | doi = 10.1007/s00401-017-1765-z | PMID = 28801693 }}</ref> | |||
===By IHC=== | |||
*GFAP - should stain cytoplasm of tumour cells and the perikaryon (nuclear membrane) of most [[Astrocytoma]]s. | |||
*[[IDH-1]](R132H) (isocitrate dehydrogenase 1) in [[Astrocytoma, IDH-mutant]].<ref name=pmid19228619>{{cite journal |author=Yan H, Parsons DW, Jin G, ''et al.'' |title=IDH1 and IDH2 mutations in gliomas |journal=N. Engl. J. Med. |volume=360 |issue=8 |pages=765–73 |year=2009 |month=February |pmid=19228619 |pmc=2820383 |doi=10.1056/NEJMoa0808710 |url=}}</ref><ref name=pmid20975057>{{cite journal |author=Houillier C, Wang X, Kaloshi G, ''et al.'' |title=IDH1 or IDH2 mutations predict longer survival and response to temozolomide in low-grade gliomas |journal=Neurology |volume=75 |issue=17 |pages=1560–6 |year=2010 |month=October |pmid=20975057 |doi=10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181f96282 |url=}}</ref> | |||
*[[H3F3A|H3F3A K27M]] in [[Diffuse midline glioma, H3 K27-altered]]. | |||
*[[ATRX]] -ve in [[Astrocytoma, IDH-mutant]] or [[Diffuse hemispheric glioma, H3 G34-mutant]]. | |||
*[[CD20]] in PCNSL. | |||
*Cytokeratins in Carcinoma brain metastases, Plexus choroid tumours, [[AT/RT]], [[Papillary tumour of the pineal region]], [[Craniopharyngioma]]. | |||
*[[EMA]] in [[Meningioma]] and carcinoma brain metastases. | |||
*PrgR in [[Meningioma]] and carcinoma metastases. | |||
*[[Synaptophysin]] in glioneuronal tumours and Pituitary adenoma and embryonal tumours. | |||
===Common | ===Common neuropathology tumours in a table=== | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|'''Type''' | |'''Type''' | ||
| Line 72: | Line 190: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Normal tissue | |Normal tissue | ||
| | |cells regularly spaced, no nuc. atypia | ||
|small lesion? | |small lesion? / deep lesion? | ||
|variable | |variable | ||
|missed lesion? | |missed lesion? | ||
|nil | |nil | ||
|[ | |[[Image:Grey_matter_and_white_matter_-_very_high_mag.jpg |thumb|center|150px|Normal. (WC)]] | ||
|- | |||
|[[Reactive astrocytes]] | |||
|astrocytes with well-demarcated eosinophilic cytoplasm, regular spacing, no nuc. atypia | |||
|small lesion? / deep lesion? | |||
|variable | |||
|missed lesion / close to a lesion; non-specific pathologic process - need more tissue | |||
|GFAP | |||
|[[Image:Reactive_astrocytes_-_lfb_-_high_mag.jpg|thumb|center|150px|Reactive astrocytes. (WC)]] | |||
|- | |||
|[[Schwannoma]] | |||
|cellular areas (Antoni A), paucicelluar areas (Antoni B), palisading of nuclei (Verocay bodies) | |||
|extra-axial + intradural | |||
|old or young | |||
|need frozen section to Dx, DDx: [[meningioma]] | |||
|S100, SOX10 | |||
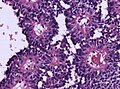
|[[Image:Schwannoma_-_Antoni_A_and_B_-_very_high_mag.jpg|thumb|center|150px|Schwannoma. (WC)]] | |||
|- | |||
|[[Meningioma]] | |||
|whorls, psammomatous calcs, nuclear inclusions | |||
|extra-axial + intradural | |||
|old or young | |||
|may be diagnosed on smear, DDx: [[schwannoma]], choroid plexus | |||
|EMA, PR, Ki-67 | |||
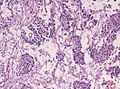
|[[Image:Meningioma_intermed_mag.jpg |thumb|center|150px|Meningioma. (WC)]] | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | |[[Astrocytoma, IDH-mutant]] (CNS [[WHO]] grade 2 or grade 3) | ||
| | |glial processes (esp. on smear), nuclear atypia (typical size var. ~3x, irreg. nuc. membrane, hyperchromasia), no Rosenthal fibres in the core of the lesion †, no microvascular proliferation, no necrosis | ||
| | |often enhancing (suggests high grade), usu. supratentorial, usu. white matter | ||
| | |usu. old, occ. young | ||
| | |common | ||
| | |IDH-1(R132H)+/-, GFAP+ | ||
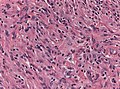
|[ | | [[Image:Anaplastic_astrocytoma_-_very_high_mag_-_cropped.jpg | thumb| center| 150px|High-grade astrocytoma. (WC)]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |[[Glioblastoma]], IDH-wildtype (CNS [[WHO]] grade 4) | ||
|glial processes (on smear), nuclear atypia (size var. ~3x, irreg. nuc. membrane, hyperchromasia) | |glial processes (esp. on smear), nuclear atypia (typical size var. ~3x, irreg. nuc. membrane, hyperchromasia), no Rosenthal fibres in the core of the lesion †, microvascular proliferation or necrosis | ||
|enhancing, usu. supratentorial, usu. white matter | |often enhancing (suggests high grade), usu. supratentorial, usu. white matter | ||
|usu. old, occ. young | |usu. old, occ. young | ||
|very common, esp. glioblastoma | |very common, esp. glioblastoma | ||
|IDH-1+/- | |IDH-1+/-, GFAP+ | ||
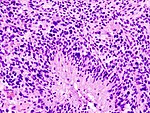
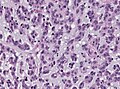
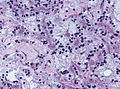
|[ | | [[Image:Glioblastoma (1).jpg | thumb| center| 150px|Glioblastoma. (WC)]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Metastasis | |[[Metastatic brain tumours|Metastasis]] | ||
|sharp interface with brain, often glandular, +/-nucleoli, no glial processes | |sharp interface with brain, often glandular, +/-nucleoli, no glial processes | ||
|often cerebellular, well-circumscribed | |often cerebellular, well-circumscribed | ||
|usu. old | |usu. old | ||
|often suspected to have metastatic disease | |often suspected to have metastatic disease | ||
|TTF-1, CK7, CK20 | |[[TTF-1]], CK7, [[CK20]], BRST-2 | ||
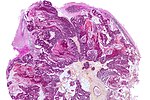
|[ | |[[Image:Metastatic_adenocarcinoma_-_cerebellum_-_very_low_mag.jpg | thumb| center|150px |Metastasis. (WC)]] | ||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|} | |} | ||
† Rosenthal fibres at the periphery of a lesion are a non-specific finding seen in chronic processes. | |||
==Brain metastasis== | |||
{{Main|Brain metastasis}} | |||
===Molecular=== | |||
See also: [[Molecular_pathology_tests#Neuropathology|Molecular Neuropathology]] | |||
== | ==Gliomas== | ||
{{Main|Glioma}} | |||
Gliomas, glioneuronal tumours and neuronal tumours are often categorized together. | |||
===Astrocytic tumours=== | |||
{{Main|Astrocytoma}} | |||
* [[Astrocytoma]], IDH-mutant. | |||
* [[Glioblastoma]], IDH-wildtype. | |||
* | ** [[Gliosarcoma]] (a glioblastoma subtype) | ||
* | |||
* | |||
* | |||
Features:<ref name=pmid>{{cite journal |author=Rong Y, Durden DL, Van Meir EG, Brat DJ |title='Pseudopalisading' necrosis in glioblastoma: a familiar morphologic feature that links vascular pathology, hypoxia, and angiogenesis |journal=J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. |volume=65 |issue=6 |pages=529–39 |year=2006 |month=June |pmid=16783163 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref>[http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/palisading http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/palisading]</ref> | Features:<ref name=pmid>{{cite journal |author=Rong Y, Durden DL, Van Meir EG, Brat DJ |title='Pseudopalisading' necrosis in glioblastoma: a familiar morphologic feature that links vascular pathology, hypoxia, and angiogenesis |journal=J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. |volume=65 |issue=6 |pages=529–39 |year=2006 |month=June |pmid=16783163 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref>[http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/palisading http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/palisading]</ref> | ||
*Glial processes - '''key feature'''. | *Glial processes - '''key feature'''. | ||
**Thin stringy cytoplasmic processes - best seen at high power in less cellular areas. | **Thin stringy cytoplasmic processes - best seen at high power in less cellular areas. | ||
*No Rosenthal fibres within the tumour itself. | |||
Images: | Images: | ||
*[http://moon.ouhsc.edu/kfung/jty1/opaq/PathQuiz/N0A002-PQ01-M.htm Endothelial proliferation in a GBM (ouhsc.edu)]. | *[http://moon.ouhsc.edu/kfung/jty1/opaq/PathQuiz/N0A002-PQ01-M.htm Endothelial proliferation in a GBM (ouhsc.edu)]. | ||
*[http://moon.ouhsc.edu/kfung/jty1/neurotest/Q05-Ans.htm Endothelial proliferation (ouhse.edu)]. | *[http://moon.ouhsc.edu/kfung/jty1/neurotest/Q05-Ans.htm Endothelial proliferation (ouhse.edu)]. | ||
*[http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case368.html Gemistocytic astrocytoma - several images (upmc.edu)]. | |||
Depreceated: | |||
* | * Diffuse [[Astrocytoma]] | ||
** | * [[Anaplastic astrocytoma]] | ||
* | * [[Gliomatosis cerebri]] | ||
* Spongioblastoma | |||
==== | ===Oligodendroglial tumours=== | ||
* [[Oligodendroglioma]], IDH-mutant and 1p/19q codeleted. | |||
* | |||
Depreceated: | |||
* | * Anaplastic oligodendroglioma | ||
* [[Oligoastrocytoma]] | |||
* Anaplastic oligoastrocytoma | |||
===Pediatric-type diffuse high-grade glioma=== | |||
{{Main|Pediatric-type diffuse high-grade glioma}} | |||
* | * [[Astrocytoma#Diffuse_midline_glioma.2C_H3_K27M_mutant|Diffuse midline glioma H3 K27-mutant]] | ||
=== | ===Pediatric-type diffuse low-grade glioma=== | ||
{{Main|Pediatric-type diffuse low-grade glioma}} | |||
== | ===Circumscribed astrocytic gliomas=== | ||
= | * [[Pilocytic astrocytoma]] (PA) | ||
* | ** [[Pilomyxoid astrocytoma]] (PMA) | ||
* | * [[Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma]] (PXA) | ||
* | * [[Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma]] (SEGA) | ||
* | * [[Neuropathology_tumours#Astroblastoma|Astroblastoma MN1-altered]]. | ||
* [[Neuropathology_tumours#Chordoid glioma of the third ventricl|Chordoid glioma]]. | |||
=== | ====Astroblastoma==== | ||
*No WHO grade yet.<ref>{{Ref WHOCNS|88}}</ref> | |||
* | *Very rare superficial tumor of young age.<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Narayan | first1 = S. | last2 = Kapoor | first2 = A. | last3 = Singhal | first3 = MK. | last4 = Jakhar | first4 = SL. | last5 = Bagri | first5 = PK. | last6 = Rajput | first6 = PS. | last7 = Kumar | first7 = HS. | title = Astroblastoma of cerebrum: A rare case report and review of literature. | journal = J Cancer Res Ther | volume = 11 | issue = 3 | pages = 667 | month = | year = | doi = 10.4103/0973-1482.140800 | PMID = 26458709 }}</ref> | ||
* | *Large, cystic. Pushing margin towards CNS. | ||
* | *Vasocentric growth, plump cells with absence of fibrillary pattern. | ||
* | *GFAP+ve, Synaptohysin-ve, Olig-2-ve, focally EMA/panCK+ve. MIB-1: 1-18 %. | ||
* | *Molecular profile overlaps with classical [[CNS-PNET]]. | ||
* | **Gene fusions invoving meningioma gene (MN1)<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Sturm | first1 = D. | last2 = Orr | first2 = BA. | last3 = Toprak | first3 = UH. | last4 = Hovestadt | first4 = V. | last5 = Jones | first5 = DT. | last6 = Capper | first6 = D. | last7 = Sill | first7 = M. | last8 = Buchhalter | first8 = I. | last9 = Northcott | first9 = PA. | title = New Brain Tumor Entities Emerge from Molecular Classification of CNS-PNETs. | journal = Cell | volume = 164 | issue = 5 | pages = 1060-72 | month = Feb | year = 2016 | doi = 10.1016/j.cell.2016.01.015 | PMID = 26919435 }}</ref> | ||
** | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Astroblastoma_HE_Specimen.jpg | HE. (WC/jensflorian) | |||
File:Astroblastoma_HE_papillae.jpg | HE. (WC/jensflorian) | |||
File:Astroblastoma.jpg | Astroblastoma (AFIP) | |||
</gallery> | |||
=== | ====Chordoid glioma of the third ventricle==== | ||
* WHO grade II. | |||
* Slowly growing, non-invasive, in adults. | |||
* Clusters of epithelioid cells in mucinous stroma. | |||
* Lymphocytic infiltrates, adjacent Rosenthal fibers. | |||
* Fibrosis may be present. | |||
* Few mitoses. | |||
* [[GFAP]]+ve, MIB-1 1-3%. | |||
* [[TTF-1]]+ve. | |||
* CD34+ve. | |||
* [[IDH-1]]-ve, [[p53]]-ve. | |||
* PRKCA D463H mutations.<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Goode | first1 = B. | last2 = Mondal | first2 = G. | last3 = Hyun | first3 = M. | last4 = Ruiz | first4 = DG. | last5 = Lin | first5 = YH. | last6 = Van Ziffle | first6 = J. | last7 = Joseph | first7 = NM. | last8 = Onodera | first8 = C. | last9 = Talevich | first9 = E. | title = A recurrent kinase domain mutation in PRKCA defines chordoid glioma of the third ventricle. | journal = Nat Commun | volume = 9 | issue = 1 | pages = 810 | month = 02 | year = 2018 | doi = 10.1038/s41467-018-02826-8 | PMID = 29476136 }}</ref> | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:NP op 20201028 009.jpg | Chordoid Glioma. (WC/jensflorian) | |||
</gallery> | |||
===Ependymal tumours=== | |||
*[ | * [[Subependymoma]] | ||
*[ | * [[Myxopapillary Ependymoma]] | ||
* [[Ependymoma]] | |||
* Anaplastic ependymoma | |||
==Choroid plexus tumours== | |||
* | * [[Choroid plexus papilloma]] | ||
* | * Atypical choroid plexus papilloma | ||
* | * [[Choroid plexus carcinoma]] | ||
==Other neuroepithelial tumours== | |||
* | * [[Neuropathology_tumours#Cribiform_neuroepithelial_tumour|Cribifiorm neuroepithelial tumour]]. | ||
=== | ===Cribiform neuroepithelial tumour=== | ||
AKA: '''CRINET'''. | |||
*Not listed in the current WHO classification. | |||
== | *First description in 2009.<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Hasselblatt | first1 = M. | last2 = Oyen | first2 = F. | last3 = Gesk | first3 = S. | last4 = Kordes | first4 = U. | last5 = Wrede | first5 = B. | last6 = Bergmann | first6 = M. | last7 = Schmid | first7 = H. | last8 = Frühwald | first8 = MC. | last9 = Schneppenheim | first9 = R. | title = Cribriform neuroepithelial tumor (CRINET): a nonrhabdoid ventricular tumor with INI1 loss and relatively favorable prognosis. | journal = J Neuropathol Exp Neurol | volume = 68 | issue = 12 | pages = 1249-55 | month = Dec | year = 2009 | doi = 10.1097/NEN.0b013e3181c06a51 | PMID = 19915490 }}</ref> | ||
=== | *Around ventricles.<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Arnold | first1 = MA. | last2 = Stallings-Archer | first2 = K. | last3 = Marlin | first3 = E. | last4 = Grondin | first4 = R. | last5 = Olshefski | first5 = R. | last6 = Biegel | first6 = JA. | last7 = Pierson | first7 = CR. | title = Cribriform neuroepithelial tumor arising in the lateral ventricle. | journal = Pediatr Dev Pathol | volume = 16 | issue = 4 | pages = 301-7 | month = | year = | doi = 10.2350/12-12-1287-CR.1 | PMID = 23495723 }}</ref> | ||
*Young children.<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Park | first1 = JY. | last2 = Kim | first2 = E. | last3 = Kim | first3 = DW. | last4 = Chang | first4 = HW. | last5 = Kim | first5 = SP. | title = Cribriform neuroepithelial tumor in the third ventricle: a case report and literature review. | journal = Neuropathology | volume = 32 | issue = 5 | pages = 570-6 | month = Oct | year = 2012 | doi = 10.1111/j.1440-1789.2011.01293.x | PMID = 22239490 }}</ref> | |||
* | *Small undifferentiated cells arranged in cribriform strands and trabeculae of varying thickness. | ||
*MAP2+ve, Synaptophysin+ve, CK+/-ve. MIB-1: 30%. | |||
* | *INI-1 loss, but no rhabdoid features and good prognosis. | ||
*Stable genomic profile.<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Gessi | first1 = M. | last2 = Japp | first2 = AS. | last3 = Dreschmann | first3 = V. | last4 = Zur Mühlen | first4 = A. | last5 = Goschzik | first5 = T. | last6 = Dörner | first6 = E. | last7 = Pietsch | first7 = T. | title = High-Resolution Genomic Analysis of Cribriform Neuroepithelial Tumors of the Central Nervous System. | journal = J Neuropathol Exp Neurol | volume = 74 | issue = 10 | pages = 970-4 | month = Oct | year = 2015 | doi = 10.1097/NEN.0000000000000239 | PMID = 26352987 }}</ref> | |||
=== | |||
=== | |||
* | |||
* | |||
** | |||
==Neuronal and mixed neuronal/glial tumours== | |||
* | * [[Desmoplastic infantile astrocytoma]] / ganglioglioma (DIA/DIG) | ||
* | * [[Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumour]] | ||
* | * [[Central Neurocytoma]] / Extraventricular [[neurocytoma]] | ||
* Cerebellar liponeurocytoma | |||
* [[Papillary glioneuronal tumour]] (PGNT) | |||
* [[Rosette-forming glioneuronal tumour of the fourth ventricle]] (RGNT) | |||
* Gangliocytoma / Ganglioglioma | |||
* Dysplastic ganglioglioma of the cerebellum ([[Lhermitte-Duclos disease]]) | |||
* [[Paraganglioma]] | |||
=== | ===Desmoplastic infantile astrocytoma / Desmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma=== | ||
*'' | * Abbreviated ''DIA'' or ''DIG''. | ||
* ICD-O code: 9412/1 | |||
* Large, superficial, cystic tumor of the infancy. | |||
* Biologic course corresponds to WHO grade I. | |||
* Very rare, included in the WHO since 1993. | |||
* Prominent desmoplastic stroma. | |||
* Astrocytic cells within stroma. | |||
**GFAP+. | |||
**MIB-1 usu. 1%. | |||
* Frequent BRAF V600E or V600D mutations.<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Wang | first1 = AC. | last2 = Jones | first2 = DTW. | last3 = Abecassis | first3 = IJ. | last4 = Cole | first4 = BL. | last5 = Leary | first5 = SES. | last6 = Lockwood | first6 = CM. | last7 = Chavez | first7 = L. | last8 = Capper | first8 = D. | last9 = Korshunov | first9 = A. | title = Desmoplastic Infantile Ganglioglioma/Astrocytoma (DIG/DIA) are Distinct Entities with Frequent BRAFV600 Mutations. | journal = Mol Cancer Res | volume = | issue = | pages = | month = Jul | year = 2018 | doi = 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-17-0507 | PMID = 30006355 }}</ref> | |||
*Single case with BRAF indel or BRAF fusion. | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:DIG-histology.jpg | Histopathology of DIG (HE stain) | |||
File:DIG-histology2.jpg | Prominent ganglioid cells in DIG (HE stain) | |||
</gallery> | |||
== | ===Cerebellar liponeurocytoma=== | ||
* | * Previously called ''lipomatous medulloblastoma'' (name changed in WHO 2000). | ||
* | * Mean age: 50 years. | ||
* As the name states: A tumour of the cerebellum. | |||
** But cases outside cerebellum reported that would qualify.<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Gupta | first1 = K. | last2 = Salunke | first2 = P. | last3 = Kalra | first3 = I. | last4 = Vasishta | first4 = RK. | title = Central liponeurocytoma: case report and review of literature. | journal = Clin Neuropathol | volume = 30 | issue = 2 | pages = 80-5 | month = | year = | doi = | PMID = 21329617 }}</ref> | |||
* WHO grade II <ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Nishimoto | first1 = T. | last2 = Kaya | first2 = B. | title = Cerebellar liponeurocytoma. | journal = Arch Pathol Lab Med | volume = 136 | issue = 8 | pages = 965-9 | month = Aug | year = 2012 | doi = 10.5858/arpa.2011-0337-RS | PMID = 22849747 }}</ref> (upgraded from WHO grade I in 2007)<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Brat | first1 = DJ. | last2 = Parisi | first2 = JE. | last3 = Kleinschmidt-DeMasters | first3 = BK. | last4 = Yachnis | first4 = AT. | last5 = Montine | first5 = TJ. | last6 = Boyer | first6 = PJ. | last7 = Powell | first7 = SZ. | last8 = Prayson | first8 = RA. | last9 = McLendon | first9 = RE. | title = Surgical neuropathology update: a review of changes introduced by the WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system, 4th edition. | journal = Arch Pathol Lab Med | volume = 132 | issue = 6 | pages = 993-1007 | month = Jun | year = 2008 | doi = 10.1043/1543-2165(2008)132[993:SNUARO]2.0.CO;2 | PMID = 18517285 }}</ref> | |||
*ICD-O code: 9506/1 | |||
=== | ====Histo==== | ||
* | * Advanced neuronal and lipomatous differentiation. | ||
* Neurocytes: round to oval nuclei with clear cytoplasm. | |||
* Quite cellular. | |||
* Mitoses almost absent. | |||
=== | ====IHC==== | ||
* [[GFAP]] +/-ve (focal). | |||
* | * [[MAP2]] +ve. | ||
* | * Synaptophysin +ve. | ||
* | * NeuN +ve. | ||
* | * MIB-1: usu 1-3%. | ||
* | |||
====Molecular==== | |||
* | * Distinct methylation profile. | ||
* Recurent losses on 2p and Chr. 14.<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Capper | first1 = D. | last2 = Stichel | first2 = D. | last3 = Sahm | first3 = F. | last4 = Jones | first4 = DTW. | last5 = Schrimpf | first5 = D. | last6 = Sill | first6 = M. | last7 = Schmid | first7 = S. | last8 = Hovestadt | first8 = V. | last9 = Reuss | first9 = DE. | title = Practical implementation of DNA methylation and copy-number-based CNS tumor diagnostics: the Heidelberg experience. | journal = Acta Neuropathol | volume = | issue = | pages = | month = Jul | year = 2018 | doi = 10.1007/s00401-018-1879-y | PMID = 29967940 }}</ref> | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Cerebellar liponeurocytoma.jpg | Liponeurocytoma, HE (WC/Marvin101). | |||
File:Liponeurocytoma Synaptophysin.jpg | Liponeurocytoma, Synapto (WC/Marvin101). | |||
File:Cerebellar Liponeurocytoma HE.jpg | Liponeurocytoma, HE (WC/jensflorian). | |||
File:Cerebellar Liponeurocytoma Synaptophysin.jpg | Liponeurocytoma, Synapto (WC/jensflorian). | |||
</gallery> | |||
=== | ====DDx==== | ||
* | * [[Medulloblastoma]] | ||
* | * [[Neurocytoma]] | ||
===Gangliocytoma=== | |||
* | * Grade I WHO neuronal tumour. | ||
* | ** ICD-O code: 9492/0 | ||
* | * Groups of irregular large neurons. | ||
* Non-neoplastic, reticulin-rich glial stroma. | |||
== | ===Ganglioglioma=== | ||
===General=== | :'''Not''' to be confused with ''[[ganglioneuroma]]''. | ||
* | ====General==== | ||
** | *Gangliolioma: Grade I WHO mixed neuronal-glial tumour (ICD-O code: 9505/1). | ||
*Anaplastic ganglioglioma: Grade III (ICD-O: 9505/3) | |||
*Rare (approx. 0.5% of all CNS tumors). | |||
*Usu. temporal lobe. | |||
*Predominantly children (mean age: 9 years). | |||
*Recognized as a cause of [[epilepsy]].<ref name=pmid12125968>{{Cite journal | last1 = Im | first1 = SH. | last2 = Chung | first2 = CK. | last3 = Cho | first3 = BK. | last4 = Lee | first4 = SK. | title = Supratentorial ganglioglioma and epilepsy: postoperative seizure outcome. | journal = J Neurooncol | volume = 57 | issue = 1 | pages = 59-66 | month = Mar | year = 2002 | doi = | PMID = 12125968 }}</ref> | |||
*Favourable prognosis (survival rates up to 97%) | |||
**Insufficient data für anaplastic ganglioglioma. | |||
====Macroscopic==== | |||
* | *Circumscribed lesion. | ||
* | *Usu. contrast enhancing. | ||
*Solid, but intracortical cysts may be present. | |||
*Little mass effect. | |||
===Microscopic=== | ====Microscopic==== | ||
Features: | Features: | ||
* | *Dysplastic neurons. | ||
** | **Out of regular architecture / abnormal location. | ||
**Cytomegaly | |||
** | **Clustering | ||
** | **Binucleated (very occassionally). | ||
** | *Atypical glia. | ||
*** | *Eosinophilic granular bodies. | ||
* | *Calcification. | ||
*** | *Prominent capillary network. | ||
* | *Lymphocytic cuffing. | ||
*May contain some reticulin. | |||
*Glial component may resemble: | |||
**Fibrillary astrocytoma. | |||
**Oligodendroglioma. | |||
**Pilocytic astrocytoma. | |||
Anaplastic ganglioglioma: | |||
* | *Brisk mitotic activity | ||
* | *Necrosis | ||
====IHC==== | |||
* | *Neurons: | ||
** | **[[MAP2]] +ve | ||
** | **Synaptophysin +ve | ||
** | ** Neurofilament +ve | ||
** | *Glia: | ||
**CD34+/-ve | |||
*BRAF V600E +ve (approx. 25%, mainly ganglion cells). | |||
==== | ====Molecular==== | ||
*BRAF V600E-mutated(approx. 25%). | |||
*IDH1/2 wt. | |||
*No 1p/19q codeletion. | |||
*Usu. Chr. 7 gain. | |||
*CDKN2A deletions in anaplastic ganglioglioma. | |||
=== | ====DDx:==== | ||
*[[DNT]]. | |||
*[[Oligodendroglioma]]. | |||
* | *Trapped cortical neurons in diffuse astrocytoma. | ||
* | *Papillary glioneuronal tumor. | ||
* | *Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor. | ||
* | |||
* | |||
=== | ====Images==== | ||
<gallery> | |||
* | File:Ganglioglioma lymphocytic cuffing PAS.jpg | Lymphocytic cuffing in ganglioglioma (WC/jensflorian) | ||
* | File:Ganglioglioma calcification.jpg | Calcification in ganglioglioma (WC/jensflorian) | ||
File:Ganglioglioma Cd34 x200.jpg | CD34 immunostain in ganglioglioma (WC/jensflorian) | |||
File:Anaplastic ganglioglioma HE.jpg | Pleomorphic ganglion cells in ganglioglioma (WC/jensflorian) | |||
</gallery> | |||
*[http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case142.html Ganglioglioma - case 1 (upmc.edu)]. | |||
*[http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case282.html Ganglioglioma - case 2 (upmc.edu)]. | |||
== | ===Lhermitte-Duclos disease=== | ||
=== | *Abbreviated ''LDD''. | ||
* | *[[AKA]] ''dysplastic cerebellar gangliocytoma''.<ref name=pmid20060133>{{Cite journal | last1 = Yağci-Küpeli | first1 = B. | last2 = Oguz | first2 = KK. | last3 = Bilen | first3 = MA. | last4 = Yalçin | first4 = B. | last5 = Akalan | first5 = N. | last6 = Büyükpamukçu | first6 = M. | title = An unusual cause of posterior fossa mass: Lhermitte-Duclos disease. | journal = J Neurol Sci | volume = 290 | issue = 1-2 | pages = 138-41 | month = Mar | year = 2010 | doi = 10.1016/j.jns.2009.12.010 | PMID = 20060133 }}</ref> | ||
*[[AKA]] ''dysplastic gangliocytoma of the cerebellum''. | |||
{{Main|Lhermitte-Duclos disease}} | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Dysplastic_gangliocytoma_lhermitte_duclos.jpg | Dysplastic gangliocytoma (low mag). | |||
</gallery> | |||
=== | ===Papillary glioneuronal tumour=== | ||
* Abbreviated ''PGNT''. | |||
* | * A benign, supratentorial tumor of childhood. | ||
* | ** Biologic course corresponds to WHO grade I. | ||
* | ** Before WHO 2000, considered a [[Ganglioglioma]] variant. | ||
*Prominent pseudopapillary architecture. | |||
*Neurocytes to medium-sized ganglion cells. | |||
*GFAP+ core, GFAP- layer | |||
*Rosenthal fibers, Eosinophilic Granular bodies and lymphocytic cuffing may be present. | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:PGNT_HE_stain.jpg | PGNT (HE) (WC/jensflorian) | |||
</gallery> | |||
===Rosette-forming glioneuronal tumour of the fourth ventricle=== | |||
* | * Abbreviated ''RGNT''. | ||
* | * Provisional ICD-O code: 9509/1 | ||
* A rare benign infratentorial tumour of the midline of children and adults. | |||
* Biologic course corresponds to WHO grade I. | |||
* Glial component corresponds to [[pilocytic astrocytoma]]. | |||
* Neurocytic rosettes. | |||
* Eosinopil fibrillary cores / pseudorosettes. | |||
* GFAP+ in fibrillary areas, Syn+ in rosettes. | |||
* Neurocytic cells: MAP2+ | |||
* MIB-1 usu. below 3%. | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Histology RGNT HE.jpg | RGNT, HE stain (WC/jensflorian). | |||
File:RGNT HE 2.jpg | RGNT, higher magnification (WC/jensflorian). | |||
</gallery> | |||
=== | ===Polymorphous low-grade tumor of the young (PLNTY)=== | ||
* | * [[Pediatric-type diffuse low-grade glioma#Diffuse low-grade glioma, MAPK pathway-altered|Polymorphous low-grade tumor of the young (PLNTY)]] | ||
==Pineal tumours== | |||
{{Main|Pineal gland}} | |||
* [[Pineocytoma]] | |||
* [[Pineal parenchymal tumour of intermediate differentiation]] | |||
* [[Pineoblastoma]] | |||
* | * [[Papillary tumour of the pineal region]] | ||
* | |||
== | ==Embryonal tumours== | ||
* [[Atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumour]] (AT/RT) or (AT-RT) | |||
* | * [[Medulloblastoma]] | ||
* | * [[Primitive neuroectodermal tumour]] (PNET) | ||
* [[Embryonal tumour with abundant neuropil and true rosettes]] (ETANTR) | |||
DDx: | |||
* [[Ewing sarcoma]] | |||
* [[Sarcoma with CIC-rearrangement]] | |||
==Peripheral nerve sheath tumours== | ==Peripheral nerve sheath tumours== | ||
{{Main|Peripheral nerve sheath tumours}} | {{Main|Peripheral nerve sheath tumours}} | ||
A classification:<ref name=pmid17893219>{{cite journal |author=Wippold FJ, Lubner M, Perrin RJ, Lämmle M, Perry A |title=Neuropathology for the neuroradiologist: Antoni A and Antoni B tissue patterns |journal=AJNR Am J Neuroradiol |volume=28 |issue=9 |pages=1633–8 |year=2007 |month=October |pmid=17893219 |doi=10.3174/ajnr.A0682 |url=http://www.ajnr.org/cgi/reprint/28/9/1633}}</ref> | A classification:<ref name=pmid17893219>{{cite journal |author=Wippold FJ, Lubner M, Perrin RJ, Lämmle M, Perry A |title=Neuropathology for the neuroradiologist: Antoni A and Antoni B tissue patterns |journal=AJNR Am J Neuroradiol |volume=28 |issue=9 |pages=1633–8 |year=2007 |month=October |pmid=17893219 |doi=10.3174/ajnr.A0682 |url=http://www.ajnr.org/cgi/reprint/28/9/1633}}</ref> | ||
'''Benign:''' | |||
* | *[[Schwannoma]]. | ||
* | *[[Neurofibroma]]. | ||
** | *[[Perineurioma]]. | ||
**Traumatic neuroma. | *Ganglioneuroma. | ||
**[[Traumatic neuroma]]. | |||
* | '''Malignant:''' | ||
*[[Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumour]] (MPNST). | |||
===Ganglioneuroma=== | |||
=== | :'''Not''' to be confused with ''[[ganglioglioma]]''. | ||
*[[AKA]] ganglioma.<ref>URL: [http://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/ganglioma http://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/ganglioma]. Accessed on: 8 November 2010.</ref> | *[[AKA]] ganglioma.<ref>URL: [http://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/ganglioma http://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/ganglioma]. Accessed on: 8 November 2010.</ref> | ||
{{Main|Ganglioneuroma}} | |||
==Meningioma== | |||
{{Main|Meningioma}} | |||
=== | |||
==Chordoma== | ==Chordoma== | ||
{{Main|Chordoma}} | |||
==Hemangioblastoma== | ==Hemangioblastoma== | ||
{{Main|Hemangioblastoma}} | |||
==CNS lymphoma== | ==CNS lymphoma== | ||
| Line 679: | Line 613: | ||
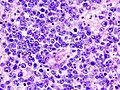
**Nucleolus - common. | **Nucleolus - common. | ||
*Perivascular clustering. | *Perivascular clustering. | ||
====Images==== | |||
www: | |||
*[http://frontalcortex.com/?page=image&topic=1&qid=1237 CNS lymphoma (frontalcortex.com)]. | |||
*[http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case403.html Primary CNS lymphoma - several images (upmc.edu)]. | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Primary CNS lymphoma - low mag.jpg | CNS lymphoma - low mag. (WC) | |||
Image:Primary CNS lymphoma - intermed mag.jpg | CNS lymphoma - intermed. mag. (WC) | |||
Image:Primary CNS lymphoma - high mag.jpg | CNS lymphoma - high mag. (WC) | |||
Image:Primary CNS lymphoma - very high mag.jpg | CNS lymphoma - very high mag. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image: CNS lymphoma (1) B-cell type.jpg | CNS lymphoma. (WC/KGH) | |||
Image: CNS lymphoma (2) B-cell type.jpg | CNS lymphoma. (WC/KGH) | |||
</gallery> | |||
===IHC=== | ===IHC=== | ||
| Line 684: | Line 633: | ||
Common pattern: | Common pattern: | ||
*CD20 +ve - key stain. | *[[CD20]] +ve - key stain. | ||
*CD3 -ve. | *CD3 -ve. | ||
*Ki-67 ~40%. | *Ki-67 ~40%. | ||
*Bcl-6 +ve. | *Bcl-6 +ve. | ||
*Bcl-1 -ve. | *Bcl-1 -ve. | ||
==Ganglioneuroblastoma== | |||
{{Main|Neuroblastoma}} | |||
===General=== | |||
*Uncommon. | |||
*Part of the ''neuroblastic tumours'' group which includes:<ref name=pmid10421272>{{cite journal |author=Shimada H, Ambros IM, Dehner LP, Hata J, Joshi VV, Roald B |title=Terminology and morphologic criteria of neuroblastic tumors: recommendations by the International Neuroblastoma Pathology Committee |journal=Cancer |volume=86 |issue=2 |pages=349–63 |year=1999 |month=July |pmid=10421272 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | |||
**[[Ganglioneuroma]] (benign). | |||
**Ganglioneuroblastoma (intermediate). | |||
**[[Neuroblastoma]] (aggressive). | |||
===Microscopic=== | |||
Features: | |||
*Ganglion-like cells with a prominent nucleolus. | |||
*Small undifferentiated cells with scant cytoplasm. | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Adrenal Ganglioneuroblastoma LP CTR.jpg|thumb|Adrenal Ganglioneuroblastoma - Low power (SKB) | |||
Image:Adrenal Ganglioneuroblastoma MP CTR.jpg|thumb|Adrenal Ganglioneuroblastoma - Medium power (SKB) | |||
Image:Adrenal Ganglioneuroblastoma HP CTR.jpg|thumb|Adrenal Ganglioneuroblastoma - High power (SKB) | |||
Image:Adrenal Ganglioneuroblastoma HP3 CTR.jpg|thumb|Adrenal Ganglioneuroblastoma - High power (SKB) | |||
Image:Adrenal Ganglioneuroblastoma HP2 CTR.jpg|thumb|Adrenal Ganglioneuroblastoma - High power (SKB) | |||
</gallery> | |||
Images: | |||
*[http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case530.html Ganglioneuroblastoma - several images (upmc.edu)]. | |||
===IHC=== | |||
*NSE +ve -- small cells. | |||
==Lesions of the sella turcica== | |||
{{Main|Pituitary gland}} | |||
Lesions of the sella turcica, the pituitary gland environs, is a topic for it self. The differential diagnosis for lesions in this area includes: | |||
*[[Pituitary adenoma]]. | |||
*[[Craniopharyngioma]]. | |||
*[[Rathke cleft cyst]]. | |||
*[[Germ cell tumour]]. | |||
*[[Meningioma]]. | |||
*[[Pilomyxoid astrocytoma]] - in children. | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
Latest revision as of 09:04, 14 April 2022
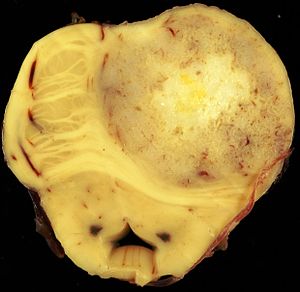
The article covers tumours in neuropathology. Tumours are a large part of neuropathology. Cytopathology of CNS tumours is dealt with in the article CNS cytopathology.
There are separate articles for peripheral nerve sheath tumours and pituitary/peri-pituitary lesions.
Brain tumours - overview
Alphabetical
For overview see here
By age group
Adult
Four most common types of brain tumours:[1]
- Metastatic brain tumours (barely edges out primary tumours)
- Lung (most common).
- Breast.
- Melanoma.
- Renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
- Glioblastoma, IDH-wildtype.
- Astrocytoma, IDH-mutant.
- Meningioma.
Children
- Pilocytic astrocytoma.
- Medulloblastoma.
- Ependymoma.
- Pontine glioma, often Diffuse midline glioma, H3 K27-altered.
By location
Certain tumours like to hang-out at certain places:[2]
Cerebrum
- Cortical based - oligodendroglioma.
- Grey-white junction - metastases.
- White matter - astrocytoma, glioblastoma.
- Periventricular - CNS lymphoma.
- Cystic - ganglioglioma, pilocytic astrocytoma, pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma.
Cerebellum
- Midline/central - medulloblastoma.
- Cystic lesion - pilocytic astrocytoma (younger individual), hemangioblastoma (older individual).
- Solid lesion (older individual) - metastasis.
Sella turcica
less common:
- Pituicytoma.
- Granular cell tumour.
- Germinoma.
- Chordoma
- Rathke cleft cyst.
- Hypophysitis.
- Xanthogranuloma.
Spinal cord
- Ependymoma
- Glioblastoma
- Meningioma
- Carcinoma metastasis
- Hemangioblastoma
Filum terminale
Meninges
- Meningioma.
- Solitary fibrous tumour / Hemangiopericytoma.
- Hemangioblastoma.
less common:
- Melanoma / Melanocytoma.
- Lymphoproliferative diseases.
- Sarcoidosis
- Arachnoid cyst.
- Disseminated oligodendroglial-like leptomeningeal tumour.
- Desmoplastic infantile astrocytoma / ganglioglioma.
- Meningioangiomatosis.
- Calcifying pseudoneoplasm.
Skull
- Fibrous dysplasia.
- Paget disease.
- Histiocytosis.
- Hemangioma.
- Aneurysmal bone cyst.
- Multiple myeloma.
Skull base / Cerebellopontine angle
- Schwannoma.
- Meningioma.
- Dermoid cyst / epidermoid cyst.
less common:
- Ependymoma.
- Choroid plexus papilloma.
- Glomus tumour.
- Chordoma.
- Chondrosarcoma.
- Olfactory neuroblastoma.
- Endolymphatic sac tumour.
Primary versus secondary
- AKA (primary) brain tumour versus metastatic cancer.
Primary
- Cytoplasmic processes - key feature.
- Best seen at highest magnification - usu. ~1 micrometer.
- Processes may branch.
- Ill-defined border/blend with the surrounding brain.
- Lesion often dura-based.
- Mesenchymal tumor (often contains collagen).
- Primary CNS Lymphoma (PCNSL) is usu. a diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.
- Large (lymphoid) cells, ergo usu. not a difficult diagnosis.
- ~2x size of resting lymphocyte, nucleoli.
- Lesion predominantly perivascular.
Secondary
- Carcinomas:
- Well-demarcated border between brain and lesion - key feature.
- No cytoplasmic processes.
- Usu. have nuclear atypia of malignancy.
- Nuclei often ~3-4x the size of a RBC.
- +/-Glandular arrangement.
- +/-Nucleoli.
- Melanoma.
- Secondary Lymphoma.
- Sarcomas (rare).
By growth pattern
Infiltrative astrocytomas
- Astrocytoma, IDH-mutant.
- Glioblastoma, IDH-wildtype.
Notes:
- Glial: "blends into brain"/gradual transition to non-tumour brain.
Non-infiltrative astrocytomas
Cystic tumours
DDx:[3]
- Pilocytic astrocytoma.
- Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma.
- Ganglioglioma.
- Hemangioblastoma.
- Craniopharyngioma.[4]
Notes:
- Non-glial: no radiating glial processes.
- Rosenthal fibres within the tumour... often seen in pilocytic astrocytoma.
- Rosenthal fibres may be seen around a (very) slow growing tumour and represent a reactive process.
- Inflammatory cells and macrophages should prompt consideration of an alternate diagnosis (e.g. cerebral infarct, multiple sclerosis) - esp. if this is a primary lesion.[5]
Grading
Nuclear pleomorphism present:
- At least grade II (diffuse astrocytoma).
Mitotic figures present:
- At least grade III (anaplastic astrocytoma).
Microvascular proliferation or necrosis with pseudopalisading tumour cells:
- Grade IV (glioblastoma AKA glioblastoma multiforme).
Notes:
- Pseudopalisading tumour cells = high tumour cell density adjacent to regions of necrosis; palisade = a fence of poles forming a defensive barrier or fortification.
- WHO Grading is currently based on expected biologiocal behaviour without treatment.
- Grading does not reflect molecular divergent groups within a tumor class or response to therapy (Currently controversies in grading for IDH-mutant astrocytoma vs. IDH-wildtype astrocytoma).[6]
By IHC
- GFAP - should stain cytoplasm of tumour cells and the perikaryon (nuclear membrane) of most Astrocytomas.
- IDH-1(R132H) (isocitrate dehydrogenase 1) in Astrocytoma, IDH-mutant.[7][8]
- H3F3A K27M in Diffuse midline glioma, H3 K27-altered.
- ATRX -ve in Astrocytoma, IDH-mutant or Diffuse hemispheric glioma, H3 G34-mutant.
- CD20 in PCNSL.
- Cytokeratins in Carcinoma brain metastases, Plexus choroid tumours, AT/RT, Papillary tumour of the pineal region, Craniopharyngioma.
- EMA in Meningioma and carcinoma brain metastases.
- PrgR in Meningioma and carcinoma metastases.
- Synaptophysin in glioneuronal tumours and Pituitary adenoma and embryonal tumours.
Common neuropathology tumours in a table
| Type | Key feature(s) | Imaging | History | Notes | IHC | Images |
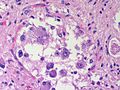
| Normal tissue | cells regularly spaced, no nuc. atypia | small lesion? / deep lesion? | variable | missed lesion? | nil | |
| Reactive astrocytes | astrocytes with well-demarcated eosinophilic cytoplasm, regular spacing, no nuc. atypia | small lesion? / deep lesion? | variable | missed lesion / close to a lesion; non-specific pathologic process - need more tissue | GFAP | |
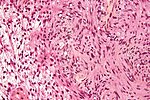
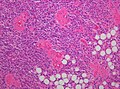
| Schwannoma | cellular areas (Antoni A), paucicelluar areas (Antoni B), palisading of nuclei (Verocay bodies) | extra-axial + intradural | old or young | need frozen section to Dx, DDx: meningioma | S100, SOX10 | |
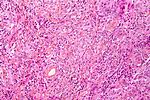
| Meningioma | whorls, psammomatous calcs, nuclear inclusions | extra-axial + intradural | old or young | may be diagnosed on smear, DDx: schwannoma, choroid plexus | EMA, PR, Ki-67 | |
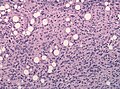
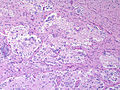
| Astrocytoma, IDH-mutant (CNS WHO grade 2 or grade 3) | glial processes (esp. on smear), nuclear atypia (typical size var. ~3x, irreg. nuc. membrane, hyperchromasia), no Rosenthal fibres in the core of the lesion †, no microvascular proliferation, no necrosis | often enhancing (suggests high grade), usu. supratentorial, usu. white matter | usu. old, occ. young | common | IDH-1(R132H)+/-, GFAP+ | |
| Glioblastoma, IDH-wildtype (CNS WHO grade 4) | glial processes (esp. on smear), nuclear atypia (typical size var. ~3x, irreg. nuc. membrane, hyperchromasia), no Rosenthal fibres in the core of the lesion †, microvascular proliferation or necrosis | often enhancing (suggests high grade), usu. supratentorial, usu. white matter | usu. old, occ. young | very common, esp. glioblastoma | IDH-1+/-, GFAP+ | |
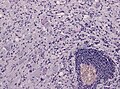
| Metastasis | sharp interface with brain, often glandular, +/-nucleoli, no glial processes | often cerebellular, well-circumscribed | usu. old | often suspected to have metastatic disease | TTF-1, CK7, CK20, BRST-2 |
† Rosenthal fibres at the periphery of a lesion are a non-specific finding seen in chronic processes.
Brain metastasis
Molecular
See also: Molecular Neuropathology
Gliomas
Gliomas, glioneuronal tumours and neuronal tumours are often categorized together.
Astrocytic tumours
- Astrocytoma, IDH-mutant.
- Glioblastoma, IDH-wildtype.
- Gliosarcoma (a glioblastoma subtype)
- Glial processes - key feature.
- Thin stringy cytoplasmic processes - best seen at high power in less cellular areas.
- No Rosenthal fibres within the tumour itself.
Images:
- Endothelial proliferation in a GBM (ouhsc.edu).
- Endothelial proliferation (ouhse.edu).
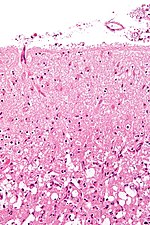
- Gemistocytic astrocytoma - several images (upmc.edu).
Depreceated:
- Diffuse Astrocytoma
- Anaplastic astrocytoma
- Gliomatosis cerebri
- Spongioblastoma
Oligodendroglial tumours
- Oligodendroglioma, IDH-mutant and 1p/19q codeleted.
Depreceated:
- Anaplastic oligodendroglioma
- Oligoastrocytoma
- Anaplastic oligoastrocytoma
Pediatric-type diffuse high-grade glioma
Pediatric-type diffuse low-grade glioma
Circumscribed astrocytic gliomas
- Pilocytic astrocytoma (PA)
- Pilomyxoid astrocytoma (PMA)
- Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma (PXA)
- Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma (SEGA)
- Astroblastoma MN1-altered.
- Chordoid glioma.
Astroblastoma
- No WHO grade yet.[11]
- Very rare superficial tumor of young age.[12]
- Large, cystic. Pushing margin towards CNS.
- Vasocentric growth, plump cells with absence of fibrillary pattern.
- GFAP+ve, Synaptohysin-ve, Olig-2-ve, focally EMA/panCK+ve. MIB-1: 1-18 %.
- Molecular profile overlaps with classical CNS-PNET.
- Gene fusions invoving meningioma gene (MN1)[13]
Chordoid glioma of the third ventricle
- WHO grade II.
- Slowly growing, non-invasive, in adults.
- Clusters of epithelioid cells in mucinous stroma.
- Lymphocytic infiltrates, adjacent Rosenthal fibers.
- Fibrosis may be present.
- Few mitoses.
- GFAP+ve, MIB-1 1-3%.
- TTF-1+ve.
- CD34+ve.
- IDH-1-ve, p53-ve.
- PRKCA D463H mutations.[14]
Ependymal tumours
- Subependymoma
- Myxopapillary Ependymoma
- Ependymoma
- Anaplastic ependymoma
Choroid plexus tumours
- Choroid plexus papilloma
- Atypical choroid plexus papilloma
- Choroid plexus carcinoma
Other neuroepithelial tumours
Cribiform neuroepithelial tumour
AKA: CRINET.
- Not listed in the current WHO classification.
- First description in 2009.[15]
- Around ventricles.[16]
- Young children.[17]
- Small undifferentiated cells arranged in cribriform strands and trabeculae of varying thickness.
- MAP2+ve, Synaptophysin+ve, CK+/-ve. MIB-1: 30%.
- INI-1 loss, but no rhabdoid features and good prognosis.
- Stable genomic profile.[18]
Neuronal and mixed neuronal/glial tumours
- Desmoplastic infantile astrocytoma / ganglioglioma (DIA/DIG)
- Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumour
- Central Neurocytoma / Extraventricular neurocytoma
- Cerebellar liponeurocytoma
- Papillary glioneuronal tumour (PGNT)
- Rosette-forming glioneuronal tumour of the fourth ventricle (RGNT)
- Gangliocytoma / Ganglioglioma
- Dysplastic ganglioglioma of the cerebellum (Lhermitte-Duclos disease)
- Paraganglioma
Desmoplastic infantile astrocytoma / Desmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma
- Abbreviated DIA or DIG.
- ICD-O code: 9412/1
- Large, superficial, cystic tumor of the infancy.
- Biologic course corresponds to WHO grade I.
- Very rare, included in the WHO since 1993.
- Prominent desmoplastic stroma.
- Astrocytic cells within stroma.
- GFAP+.
- MIB-1 usu. 1%.
- Frequent BRAF V600E or V600D mutations.[19]
- Single case with BRAF indel or BRAF fusion.
Cerebellar liponeurocytoma
- Previously called lipomatous medulloblastoma (name changed in WHO 2000).
- Mean age: 50 years.
- As the name states: A tumour of the cerebellum.
- But cases outside cerebellum reported that would qualify.[20]
- WHO grade II [21] (upgraded from WHO grade I in 2007)[22]
- ICD-O code: 9506/1
Histo
- Advanced neuronal and lipomatous differentiation.
- Neurocytes: round to oval nuclei with clear cytoplasm.
- Quite cellular.
- Mitoses almost absent.
IHC
Molecular
- Distinct methylation profile.
- Recurent losses on 2p and Chr. 14.[23]
DDx
Gangliocytoma
- Grade I WHO neuronal tumour.
- ICD-O code: 9492/0
- Groups of irregular large neurons.
- Non-neoplastic, reticulin-rich glial stroma.
Ganglioglioma
- Not to be confused with ganglioneuroma.
General
- Gangliolioma: Grade I WHO mixed neuronal-glial tumour (ICD-O code: 9505/1).
- Anaplastic ganglioglioma: Grade III (ICD-O: 9505/3)
- Rare (approx. 0.5% of all CNS tumors).
- Usu. temporal lobe.
- Predominantly children (mean age: 9 years).
- Recognized as a cause of epilepsy.[24]
- Favourable prognosis (survival rates up to 97%)
- Insufficient data für anaplastic ganglioglioma.
Macroscopic
- Circumscribed lesion.
- Usu. contrast enhancing.
- Solid, but intracortical cysts may be present.
- Little mass effect.
Microscopic
Features:
- Dysplastic neurons.
- Out of regular architecture / abnormal location.
- Cytomegaly
- Clustering
- Binucleated (very occassionally).
- Atypical glia.
- Eosinophilic granular bodies.
- Calcification.
- Prominent capillary network.
- Lymphocytic cuffing.
- May contain some reticulin.
- Glial component may resemble:
- Fibrillary astrocytoma.
- Oligodendroglioma.
- Pilocytic astrocytoma.
Anaplastic ganglioglioma:
- Brisk mitotic activity
- Necrosis
IHC
- Neurons:
- MAP2 +ve
- Synaptophysin +ve
- Neurofilament +ve
- Glia:
- CD34+/-ve
- BRAF V600E +ve (approx. 25%, mainly ganglion cells).
Molecular
- BRAF V600E-mutated(approx. 25%).
- IDH1/2 wt.
- No 1p/19q codeletion.
- Usu. Chr. 7 gain.
- CDKN2A deletions in anaplastic ganglioglioma.
DDx:
- DNT.
- Oligodendroglioma.
- Trapped cortical neurons in diffuse astrocytoma.
- Papillary glioneuronal tumor.
- Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor.
Images
Lhermitte-Duclos disease
- Abbreviated LDD.
- AKA dysplastic cerebellar gangliocytoma.[25]
- AKA dysplastic gangliocytoma of the cerebellum.
Papillary glioneuronal tumour
- Abbreviated PGNT.
- A benign, supratentorial tumor of childhood.
- Biologic course corresponds to WHO grade I.
- Before WHO 2000, considered a Ganglioglioma variant.
- Prominent pseudopapillary architecture.
- Neurocytes to medium-sized ganglion cells.
- GFAP+ core, GFAP- layer
- Rosenthal fibers, Eosinophilic Granular bodies and lymphocytic cuffing may be present.
Rosette-forming glioneuronal tumour of the fourth ventricle
- Abbreviated RGNT.
- Provisional ICD-O code: 9509/1
- A rare benign infratentorial tumour of the midline of children and adults.
- Biologic course corresponds to WHO grade I.
- Glial component corresponds to pilocytic astrocytoma.
- Neurocytic rosettes.
- Eosinopil fibrillary cores / pseudorosettes.
- GFAP+ in fibrillary areas, Syn+ in rosettes.
- Neurocytic cells: MAP2+
- MIB-1 usu. below 3%.
Polymorphous low-grade tumor of the young (PLNTY)
Pineal tumours
- Pineocytoma
- Pineal parenchymal tumour of intermediate differentiation
- Pineoblastoma
- Papillary tumour of the pineal region
Embryonal tumours
- Atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumour (AT/RT) or (AT-RT)
- Medulloblastoma
- Primitive neuroectodermal tumour (PNET)
- Embryonal tumour with abundant neuropil and true rosettes (ETANTR)
DDx:
Peripheral nerve sheath tumours
A classification:[26] Benign:
- Schwannoma.
- Neurofibroma.
- Perineurioma.
- Ganglioneuroma.
Malignant:
Ganglioneuroma
- Not to be confused with ganglioglioma.
Meningioma
Chordoma
Hemangioblastoma
CNS lymphoma
Classification:
- Primary CNS lymphoma.
- Non-primary CNS lymphoma - see lymphoma article.
General - primary CNS
- Classically periventicular distribution.
- Usually large B cell; can be considered a type of diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
- Prognosis of CNS (DLBCL) lymphomas worse than nodal (non-CNS) DLBCL.[28]
Microscopic
Features:
- Large cell lymphoma.
- Size = 2x diameter normal lymphocyte.
- Nucleolus - common.
- Perivascular clustering.
Images
www:
IHC
Can be subclassified in GCB (germinal centre B-cell-like) and non-GCB by CD10, Bcl-6, MUM1/IRF-4, and Bcl-2.[28]
Common pattern:
- CD20 +ve - key stain.
- CD3 -ve.
- Ki-67 ~40%.
- Bcl-6 +ve.
- Bcl-1 -ve.
Ganglioneuroblastoma
General
- Uncommon.
- Part of the neuroblastic tumours group which includes:[29]
- Ganglioneuroma (benign).
- Ganglioneuroblastoma (intermediate).
- Neuroblastoma (aggressive).
Microscopic
Features:
- Ganglion-like cells with a prominent nucleolus.
- Small undifferentiated cells with scant cytoplasm.
Images:
IHC
- NSE +ve -- small cells.
Lesions of the sella turcica
Lesions of the sella turcica, the pituitary gland environs, is a topic for it self. The differential diagnosis for lesions in this area includes:
- Pituitary adenoma.
- Craniopharyngioma.
- Rathke cleft cyst.
- Germ cell tumour.
- Meningioma.
- Pilomyxoid astrocytoma - in children.
See also
References
- ↑ http://neurosurgery.mgh.harvard.edu/abta/primer.htm
- ↑ URL: http://www.msdlatinamerica.com/ebooks/DiagnosticNeuropathologySmears/files/4ce563fb7e8e48fc9ed8b42e296a7747.gif and http://www.msdlatinamerica.com/ebooks/DiagnosticNeuropathologySmears/sid117213.html. Accessed on: 2 November 2010.
- ↑ URL: http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case320/dx.html. Accessed on: 14 January 2012.
- ↑ URL: http://www.pathologyoutlines.com/Cnstumor.html#cystsgeneral. Accessed on: 14 January 2012.
- ↑ URL: http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case79/dx.html. Accessed on: 2 January 2012.
- ↑ Louis, DN.; von Deimling, A. (Aug 2017). "Grading of diffuse astrocytic gliomas: Broders, Kernohan, Zülch, the WHO… and Shakespeare.". Acta Neuropathol. doi:10.1007/s00401-017-1765-z. PMID 28801693.
- ↑ Yan H, Parsons DW, Jin G, et al. (February 2009). "IDH1 and IDH2 mutations in gliomas". N. Engl. J. Med. 360 (8): 765–73. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0808710. PMC 2820383. PMID 19228619. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2820383/.
- ↑ Houillier C, Wang X, Kaloshi G, et al. (October 2010). "IDH1 or IDH2 mutations predict longer survival and response to temozolomide in low-grade gliomas". Neurology 75 (17): 1560–6. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181f96282. PMID 20975057.
- ↑ Rong Y, Durden DL, Van Meir EG, Brat DJ (June 2006). "'Pseudopalisading' necrosis in glioblastoma: a familiar morphologic feature that links vascular pathology, hypoxia, and angiogenesis". J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 65 (6): 529–39. PMID 16783163.
- ↑ http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/palisading
- ↑ The International Agency for Research on Cancer (Editors: Louis, D.N.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Cavenee, W.K.) (2007). Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of Tumors of the Central Nervous System (IARC WHO Classification of Tumours) (4th ed.). Lyon: World Health Organization. pp. 88. doi:10.1007/s00401-007-0243-4. ISBN 978-9283224303.
- ↑ Narayan, S.; Kapoor, A.; Singhal, MK.; Jakhar, SL.; Bagri, PK.; Rajput, PS.; Kumar, HS.. "Astroblastoma of cerebrum: A rare case report and review of literature.". J Cancer Res Ther 11 (3): 667. doi:10.4103/0973-1482.140800. PMID 26458709.
- ↑ Sturm, D.; Orr, BA.; Toprak, UH.; Hovestadt, V.; Jones, DT.; Capper, D.; Sill, M.; Buchhalter, I. et al. (Feb 2016). "New Brain Tumor Entities Emerge from Molecular Classification of CNS-PNETs.". Cell 164 (5): 1060-72. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2016.01.015. PMID 26919435.
- ↑ Goode, B.; Mondal, G.; Hyun, M.; Ruiz, DG.; Lin, YH.; Van Ziffle, J.; Joseph, NM.; Onodera, C. et al. (02 2018). "A recurrent kinase domain mutation in PRKCA defines chordoid glioma of the third ventricle.". Nat Commun 9 (1): 810. doi:10.1038/s41467-018-02826-8. PMID 29476136.
- ↑ Hasselblatt, M.; Oyen, F.; Gesk, S.; Kordes, U.; Wrede, B.; Bergmann, M.; Schmid, H.; Frühwald, MC. et al. (Dec 2009). "Cribriform neuroepithelial tumor (CRINET): a nonrhabdoid ventricular tumor with INI1 loss and relatively favorable prognosis.". J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 68 (12): 1249-55. doi:10.1097/NEN.0b013e3181c06a51. PMID 19915490.
- ↑ Arnold, MA.; Stallings-Archer, K.; Marlin, E.; Grondin, R.; Olshefski, R.; Biegel, JA.; Pierson, CR.. "Cribriform neuroepithelial tumor arising in the lateral ventricle.". Pediatr Dev Pathol 16 (4): 301-7. doi:10.2350/12-12-1287-CR.1. PMID 23495723.
- ↑ Park, JY.; Kim, E.; Kim, DW.; Chang, HW.; Kim, SP. (Oct 2012). "Cribriform neuroepithelial tumor in the third ventricle: a case report and literature review.". Neuropathology 32 (5): 570-6. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1789.2011.01293.x. PMID 22239490.
- ↑ Gessi, M.; Japp, AS.; Dreschmann, V.; Zur Mühlen, A.; Goschzik, T.; Dörner, E.; Pietsch, T. (Oct 2015). "High-Resolution Genomic Analysis of Cribriform Neuroepithelial Tumors of the Central Nervous System.". J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 74 (10): 970-4. doi:10.1097/NEN.0000000000000239. PMID 26352987.
- ↑ Wang, AC.; Jones, DTW.; Abecassis, IJ.; Cole, BL.; Leary, SES.; Lockwood, CM.; Chavez, L.; Capper, D. et al. (Jul 2018). "Desmoplastic Infantile Ganglioglioma/Astrocytoma (DIG/DIA) are Distinct Entities with Frequent BRAFV600 Mutations.". Mol Cancer Res. doi:10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-17-0507. PMID 30006355.
- ↑ Gupta, K.; Salunke, P.; Kalra, I.; Vasishta, RK.. "Central liponeurocytoma: case report and review of literature.". Clin Neuropathol 30 (2): 80-5. PMID 21329617.
- ↑ Nishimoto, T.; Kaya, B. (Aug 2012). "Cerebellar liponeurocytoma.". Arch Pathol Lab Med 136 (8): 965-9. doi:10.5858/arpa.2011-0337-RS. PMID 22849747.
- ↑ Brat, DJ.; Parisi, JE.; Kleinschmidt-DeMasters, BK.; Yachnis, AT.; Montine, TJ.; Boyer, PJ.; Powell, SZ.; Prayson, RA. et al. (Jun 2008). "Surgical neuropathology update: a review of changes introduced by the WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system, 4th edition.". Arch Pathol Lab Med 132 (6): 993-1007. doi:10.1043/1543-2165(2008)132[993:SNUARO]2.0.CO;2. PMID 18517285.
- ↑ Capper, D.; Stichel, D.; Sahm, F.; Jones, DTW.; Schrimpf, D.; Sill, M.; Schmid, S.; Hovestadt, V. et al. (Jul 2018). "Practical implementation of DNA methylation and copy-number-based CNS tumor diagnostics: the Heidelberg experience.". Acta Neuropathol. doi:10.1007/s00401-018-1879-y. PMID 29967940.
- ↑ Im, SH.; Chung, CK.; Cho, BK.; Lee, SK. (Mar 2002). "Supratentorial ganglioglioma and epilepsy: postoperative seizure outcome.". J Neurooncol 57 (1): 59-66. PMID 12125968.
- ↑ Yağci-Küpeli, B.; Oguz, KK.; Bilen, MA.; Yalçin, B.; Akalan, N.; Büyükpamukçu, M. (Mar 2010). "An unusual cause of posterior fossa mass: Lhermitte-Duclos disease.". J Neurol Sci 290 (1-2): 138-41. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2009.12.010. PMID 20060133.
- ↑ Wippold FJ, Lubner M, Perrin RJ, Lämmle M, Perry A (October 2007). "Neuropathology for the neuroradiologist: Antoni A and Antoni B tissue patterns". AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28 (9): 1633–8. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A0682. PMID 17893219. http://www.ajnr.org/cgi/reprint/28/9/1633.
- ↑ URL: http://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/ganglioma. Accessed on: 8 November 2010.
- ↑ 28.0 28.1 Raoux D, Duband S, Forest F, et al. (June 2010). "Primary central nervous system lymphoma: Immunohistochemical profile and prognostic significance". Neuropathology 30 (3): 232–40. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1789.2009.01074.x. PMID 19925562.
- ↑ Shimada H, Ambros IM, Dehner LP, Hata J, Joshi VV, Roald B (July 1999). "Terminology and morphologic criteria of neuroblastic tumors: recommendations by the International Neuroblastoma Pathology Committee". Cancer 86 (2): 349–63. PMID 10421272.