Breast pathology
The breast is an important organ for the continuance of the species and one that pathologists see quite often because it is often afflicted by cancer. Before women started smoking in large numbers, it was the number one cause of cancer death in women (in Canada).
Fortunately, breast cancer, these days, has a relatively good prognosis if it is detected early... and this is why there are week-ends to end breast cancer -- there are large numbers of breast cancer survivors that are well, wealthy and can advocate for better care and research into breast cancer.
Clinical
Classic presentation:
- Nipple discharge.
- Pain.
- Breast lump/mass.
- New nipple inversion.
- Skin changes, e.g. peau d'orange.
Most common presentation:
- Abnormal/suspicious screening mammogram - suspicious microcalcifications and/or suspicious mass.
Breast cancer screening
Breast cancer screening, for normal risk individuals, starts at age 50 in Canada. In the USA, breast screening starts at age 40.
Radiologic screening is less effective in younger individual as:
- The breast is more dense and thus radiologically more difficult to interpret, and
- The incidence of breast cancer is lower.
Breast radiology
BI-RADS = Breast Imaging Reporting And Data System:[1]
- 0: Incomplete - come back for more imaging (radiologist cha-ching).
- 1: Negative.
- 2: Benign finding(s).
- 3: Probably benign -- often short follow-up.
- 4: Suspicious abnormality -- needs biopsy.
- 5: Highly suggestive of malignancy.
- 6: Pathologist says there is a malignancy.
Specimens
Breast comes in three main flavours:
- Core needle biopsy (CNB).
- Lumpectomy.
- Modified radical mastectomy.
Note:
- Breast cytopathology is dealt with in the breast cytopathology article. It is almost dead, as it is not as sensitive and specific as CNB.
Core needle biopsy
Work-up of CNBs is dependent on the clinical abnormality:[2]
- Mass lesion - usu. obvious what is going on; typically 3 levels.
- Calcifications - abnormality may be very small; typically 10 levels.
Lumpectomy
Lumpectomies are usually oriented with short and long suture; short is typically superior (aspect) and long is typically lateral (aspect).
Modified radical mastectomy
- Usually done with sentinel lymph node biopsy - as one cannot go back later to do this.
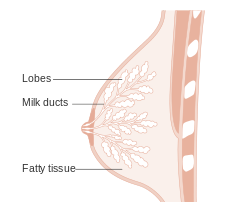
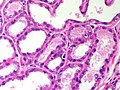
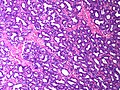
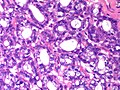
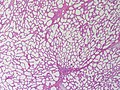
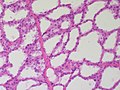
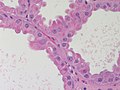
Normal
Resting
- Glands -- normally has two cell layers (like the prostate).
- Myoepithelial cells
- Frequently spindle-like, often hard to see.
- Secretory cells.
- Myoepithelial cells
- Stroma:
- Not cellular.
- Not myxoid.
May be present:
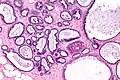
- Calcification:
- Purple globs (with concentric rings) on H&E = calcium phosphate.
- Q. How to remember? A. Purple = Phosphate.
- Calcium oxalate visible with (light) polarization - not assoc. with malignancy.
- Often in the lumen of a gland, may be in the stroma.
- Calcific material typically has a well-demarcated border +/- "sharp corners".
- Radiologists can pick-up calcs (calcifications) that are approximately 100 micrometers; if "calcs" is on the requisition one needs to find calcs this size.[3]
- The large calcs seen on radiology are approximately 1/5 - 1/6 the size of a HPF, if the field of view (FOV) is ~0.55 mm (as is the case with 22 mm-10x eye pieces and a 40x objective).
- Purple globs (with concentric rings) on H&E = calcium phosphate.
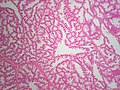
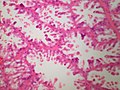
Image:
Notes:
- The architecture is more important than the cytologic features in the diagnosis of malignancy in the breast;[4] low grade tumours have distorted architecture but normal/near normal cytology.
Lactational changes
General
- Lactational adenoma generally arises in during or in the few weeks after pregnancy.
- May be present focally in non-pregnant females.
- "Lactational adenoma"- circumscribed mass displacing the normal breast architecture (hyperplasia plus functional/physiologic change)
- "Lactational change"- normal breast tissue architecture preserved (functional/physiologic change).
ASIDE:
- Some believe lactational change and secretory change aren't the same...
- Lactational change = only in lactation.
- Secretory change = other times.
- This hair splitting is clinically irrelevant-- both are benign. Also, experts use the terms interchangeably.[6]
Microscopic
Features:[7]
- Glands dilated.
- Increased number of lobules.
- Relative decrease in intralobular and extralobular stroma.
- Luminal cells enlarged.
- Vacuolated cytoplasm.
- Hobnail morphology - hang into the lumen.
- Myoepithelial cells indistinct - after second trimester.
- Lactational "adenoma" may undergo infarction - Imagine what an infarcted lactational adenoma could look like in a FNA specimen!
DDx:
Images
www:
- Lactational changes (gfmer.ch).
- Lactational changes in an angiosarcoma of the breast (webpathology.com).
- Lactating breast (uwa.edu.au).
Where to start
The following entities are a starting point for understanding routine breast pathology & some of challenges in breast pathology:
- Apocrine change.
- Columnar cell change.
- Columnar cells with blebs ("snouts") - often have calcifications (purple).
- If the columnar cells shows low to intermediate grade atypia the process is termed "flat epithelial atypia"
- If higher grade atyia is present the lesion is termed "flat DCIS" (clinging carcinoma)
- Duct ectasia
- Dilation of large ducts secondary to luminal obstruction by inspissated secretions
- Presentation
- ~age 40-50, possibly with cheesy nipple discharge
- Pathology
- Duct lumen dilated and containing foamy macrophages
- Necrosis/shedding of epithelium
- If duct rupture: chronic and granulomatous inflammation of periductal region
- Fibrotic thickening of duct wall
- Fibroadenoma.
- Abundant myxoid (light/blanched) stroma - very common.
- Florid epithelial hyperplasia.
- Too many cells in a duct, cells overlap & form slit-like spaces.
- Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS).
- Too many cells in a duct, nuclei do not touch - "cells are spaced".
- Cells line-up around ovoid/circular spaces - "punch-out" appearance/"cookie cutter" look.
- Myoepithelial cells present.
- Invasive ductal carcinoma.
- Bread & butter cancer - in sheets or glands.
- Lobular carcinoma.
- Dyscohesive cells - can easily be missed.
- Tubular carcinoma.
- Glands have one cell layer... but near normal appearance.
The key to breast pathology is... seeing the two cell layers (at low power). The myoepithelial layer is hard to see at times and that is the challenge.
Additional resources
- Breast Pathology Info [1]
- Digital Atlas of Breast Pathology [2]
- Pathology Outlines - Breast Nonmalignant [3]
- Pathology Outlines - Breast Malignant [4]
- WebPathology - Breast [5]
Common diagnoses - overview
- Normal.
- Benign.
- Columnar cell change.
- Calcification often in lumen.
- Columnar cell change.
- Neoplastic.
- Benign neoplastic:
- Epithelial/myoepithelial - intraductal papilloma.
- Stromal - fibroadenoma, benign phyllodes.
- Malignant neoplastic:
- Epithelial/myoepithelial - most common, e.g. ductal carcinoma, lobular carcinoma.
- Breast stroma - malignant phyllodes tumour.
- Stromal, e.g. angiosarcoma - quite rare.
- Benign neoplastic:
Major Pathologic Patterns
General classification
| Breast pathology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stromal pathology | Miscellaneous | Glandular pathology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Myxoid | Long slit-like spaces | Simple epithelium | Dilated | Cellular lesions | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fibroadenoma | Malignant features | Benign features | Tubular carcinoma | FEA, FCC, CCC | FEHUT, Neoplastic, Malignant | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Malignant phyllodes | Benign phyllodes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Notes:
- The challenges in breast pathology are in: the Simple epithelium category and the Cellular lesions category.
- Neoplastic includes: ADH and LDH.
- Malignant includes: DCIS, LCIS, ductal carcinoma (DC) and lobular carcinoma (LC), some papillary lesions.
- Lobular carcinoma (a pitfall) may appear to be a stromal problem, i.e. the stroma looks too cellular.
- Miscellaneous includes rare tumours of the breast that do not fit into another category, i.e. metastases, lymphomas, melanoma, sarcomas. Skin-related pathology is dealt within the dermatologic neoplasms article. Paget disease of the breast, which may be seen in the context of malignant breast lesions, is discussed in its own article.
Cellular lesions
| Cellular lesions (Glandular) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Equal spacing, punched-out | Streaming, periph. slit-like spaces. | Discohesive cells, expanded gl. | Single cells or single file | Fibrovascular cores | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ductal lesion | FEHUT | Lobular lesion | Lobular carcinoma | Papillary lesions | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Two cell layers | One cell layer | <50% of gl. | >50% of gl. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ductal non-inv. neoplasm | Ductal carcinoma | ALH | LCIS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Large extent | Small extent | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DCIS | ADH | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Notes:
- The largest challenge is: differentiating between the first two categories on level 2, i.e. equal spacing' vs. streaming.
- The fibrovascular cores must arise from a tuft, i.e. if they are arising directly from the wall of glands only it is likely papillary DCIS.
Papillary lesions
| Papillary lesions | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Myoepithelial cells present | Myoepithelial cells absent | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unremarkable papillae | Atypia or arch. abnorm. or cellular proliferation | Neoplastic cells present | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Benign intraductal papilloma | High grade atypia | Low grade atypia or abnorm. arch. | Only cellular proliferation | Intracystic (encapsulated) papillary ca. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DCIS in papilloma | FEHUT in papilloma | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| >3 mm extent | <3 mm extent | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DCIS in papilloma | ADH in papilloma | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Notes:
- Adapted from Mulligan & O'Malley.[8]
- The most important decision is the first one: myoepithelial cells present vs. absent.
- abnorm. arch. = abnormal architecture present.
- DCIS = ductal carcinoma in situ.
- FEHUT = florid epithelial hyperplasia of the usual type.
- extent refers to the size of the abnormal cell population within the papillary lesion.
Basaloid Lesions
- Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma of the Breast
- Intracystic Papillary Breast Carcinoma, Solid Variant
- Medullary Breast Carcinoma
- Medullary-like Breast Carcinoma
Know when to start a discussion about BRCA mutations, triple negativity and the 'basal-like molecular phenotype'.
Spindle Cell Lesions
- Metaplastic Breast Carcinoma
- Mammary Myofibroblastoma
- Phyllodes Tumor - stromal component
Malignant lesions
Non-invasive breast cancer
This includes the in situ lesions - DCIS and LCIS.
Invasive breast cancer
This is includes descriptions of the usual types... and the not so common ones.
Common benign lesions
The breast has lots of benign things. Unlike the prostate, the where benign is called benign, everything has a name. It is more common among breast pathologists to sign-out things like: apocrine metaplasia (benign), columnar cell change (benign), and florid epithelial hyperplasia of the usual type (FEHUT) - instead of - benign breast tissue.
Mild epithelial hyperplasia
General
- No increased risk of malignancy.
- Often not reported - as it has not clinical signficance.
- Has to be separated from moderate epithelial hyperplasia / florid epithelial hyperplasia.
Microscopic
Features:[9]
- Breast glands with three or four cell layers above the basement membrane.
- Variable cells.
Note:
- No nuclear atypia.
DDx:
- Flat epithelial atypia.
- Moderate epithelial hyperplasia / florid epithelial hyperplasia.
- Atypical ductal hyperplasia.
Apocrine metaplasia
General
- Benign/not significant. Can be considered to be pretty wallpaper in the house of breast pathology.
Etiology
- Increased number of mitochondria.
- In other body sites this has different names, e.g. Hurthle cell change (thyroid), oncocytic change (kidney - oncocytoma, thyroid).
Microscopic
Features:
- Eosinophilic cytoplasm - key feature.
Note:
- Apocrine changes, i.e. cytoplasmic eosinophilia, can appear in malignant tumours; eosinophilia doesn't make something benign.
- Apocrine snouts may be present. (???)
- Small globules at the apical aspect of the cell (composed of cytoplasm and plasma membrane).
Images
Fibrocystic change
- Abbreviated FCC.
- AKA fibrocystic changes.
General
- Really common.
- Benign.
Microscopic
Features:
- Dilated glands - key change.
- Glands normal: two cell layers present.
- Often seen together with apocrine metaplasia.
Images
Columnar cell change
General
- Columnar cell change is associated with (benign) calcification - key point.
Microscopic
Features:
- Secretory cells (line gland lumen) have columnar morphology.
- May have "apical snouts".
- Blebs or round balls eosinophilic material appear to be adjacent to the cell at their luminal surface.
- The snouts are attached to the cell-- appear as round ball only in the plane of section.
- Cytoplasm +/-eosinophilia.
DDx:
- Flat epithelial atypia (>2 cell layers).[citation needed]
Image:
Gynecomastoid hyperplasia
- AKA gynecomastia.
Lesions with increased risk of malignancy
Florid epithelial hyperplasia
- AKA florid epithelial hyperplasia, abbreviated FEH.
- AKA florid epithelial hyperplasia of the usual type, abbreviated FEHUT.
- AKA epithelial hyperplasia - term should be avoid as it could lead to confusion with mild epithelial hyperplasia.
General
- Mild increased risk of malignancy ~ 1.5-2x.[10]
- Has to be separated from mild epithelial hyperplasia.
Note:
- Moderate epithelial hyperplasia redirects to this section.
- It is generally not separated from FEH, as the prognosis is thought to be the same.
Microscopic
Features:[11]
- Breast glands with more than four cell layers above the basement membrane - key feature.
- Irregular cell spacing; streaming.
- Slit-like lumina, esp. at the periphery of the duct.
- No DCIS-like architecture (not cribriform, not papillary, not micropapillary, not solid).
- No nuclear atypia - usually no nucleoli.
Memory device CLEAN:
- Cell spacing is irregular, Lumina are slit-like, Extent is less than 2 mm or 2 ducts, Architecture not DCIS-like, Nuclear atypia not present.
DDx:
Sclerosing adenosis
General
- Can be scary... can look like ductal carcinoma.
- Derived from sclerosing[12] (hardening) and adenosis (glandular enlargement).
- Think scaring + lotsa glands and you're pretty close.
- Management: follow-up, no further treatment.[13]
Microscopic
Features:
- Acini are smaller than usual and there are more of them.
- Acini often slit-like.
- Fibrosis (scleroses) - pink on H&E surrounds the acini.
- Can mimic a desmoplastic reaction.
Notes:
- The acini should:
- Be in lobular arrangements, i.e. in groups (benign appearance at low power) - key feature.
- Have two cell layers like well-behaved breast glands do.
DDx:
- Low-grade ductal carcinoma.
- Tubular adenoma of the breast.
- Adenomyoepithelioma.[14]
Flat epithelial atypia
General
Epidemiology:
- Associated with ADH & DCIS; may represent a non-obligate precursor lesion of ADH & DCIS.[15]
- Low risk of progression to invasive malignancy.[16]
Management:
- Excision.
Microscopic
Features:
- "Flat" ~ three cells thick.
- Hypercellular gland -- several layers.
- Columnar cell morphology.
- +/-Apical snouts.
DDx:
- Columnar cell change.
- Columnar cell hyperplasia.
- ADH.
- Low grade DCIS.
- Apocrine cyst - granular cytoplasm.
- Tubular carcinoma - should be considered due to the association.
Molecular
- Loss of 16q.
- Not used for diagnosis.
Complex sclerosing lesion
- AKA radial scar.
General
- The term radial scar is a misnomer. It isn't a scar. It isn't associated with prior trauma or surgery.[17]
- May appear malignant on imaging.[18]
- Associated with subsequent elevated risk of breast cancer.[19]
- Management - usu. surgical excision.[20]
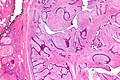
Gross
- Spiculated mass.
- Usually small - 3-7 mm.
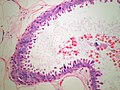
Image
Microscopic
- Stellate appearance (low magnification).
- Center of lesion has "fibroelastosis" - stroma light pink (on H&E) - key feature.
- Scar like stroma with entrapped normal breast ducts and lobules.
- Glands appear to enlarge with distance from center of lesion.
Notes:
- Histomorphologic appearance may mimic a desmoplastic reaction of the stroma - leading to a misdiagnosis of malignancy.
- "Hyaline - pink stuff on H&E - is the key."
DDx:
- Invasive ductal carcinoma - should be considered if the lesion is asymmetrical or glands are dilated centrally.
Images
IHC
Features:
- p63 +ve.
- Calponin +ve.
Note:
- HMWK +ve/-ve. (???)
Stromal lesions
This section (below) covers stromal lesions of the breast, which vary from benign to malignant. The most common is (the benign) fibroadenoma.
Non-breast stroma stromal lesions are covered in the soft tissue lesions article. Angiosarcoma (dealt with in the vascular tumours article) is the most common (non-breast stroma) sarcoma of the breast, and classically arises after treatment for a breast carcinoma.
Fibroadenoma
Phyllodes tumour
- Previously cystosarcoma phyllodes.
Pseudoangiomatous stromal hyperplasia
Weird stuff
Like in all niches of pathology... there is weird stuff.
Mammary hamartoma
- AKA breast hamartoma.
Collagenous spherulosis
Nipple adenoma
- AKA nipple duct adenoma.
- AKA nipple adenoma of breast.
- AKA adenoma of the nipple.
- AKA florid papillomatosis of the nipple.[24]
Intraductal papilloma
- AKA papilloma.
Lymphocytic mastitis
- If the individual has diabetes mellitus it is diabetic mastopathy.
Microglandular adenosis
- Not to be confused with microglandular hyperplasia.
- Abbreviated MGA.
Adenomyoepithelioma
Mammary myofibroblastoma
Squamous metaplasia of lactiferous ducts
- Abbreviated SMOLD.
Granular cell tumour of the breast
General
- Uncommon.
Gross
- May be a spiculated mass and thus mimic malignancy radiologically.[25]
Microscopic
- See granular cell tumour.
DDx:
See also
References
- ↑ URL: http://breastcancer.about.com/od/diagnosis/a/birads.htm. Accessed on: 16 March 2011.
- ↑ MUA. 1 October 2010.
- ↑ MUA. 1 October 2010.
- ↑ RS. 4 May 2010.
- ↑ URL: [Breast_pathology#Lactational_changes Breast_pathology#Lactational_changes. Accessed on: 3 October 2011.
- ↑ Tavassoli, FA.; Yeh, IT. (Jan 1987). "Lactational and clear cell changes of the breast in nonlactating, nonpregnant women.". Am J Clin Pathol 87 (1): 23-9. PMID 2879437.
- ↑ URL: http://flylib.com/books/en/2.953.1.9/1/. Accessed on: 6 August 2011.
- ↑ Mulligan AM, O'Malley FP (March 2007). "Papillary lesions of the breast: a review". Adv Anat Pathol 14 (2): 108–19. doi:10.1097/PAP.0b013e318032508d. PMID 17471117.
- ↑ O'Malley, Frances P.; Pinder, Sarah E. (2006). Breast Pathology: A Volume in Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology series (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 159-160. ISBN 978-0443066801.
- ↑ Mitchell, Richard; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Abbas, Abul K.; Aster, Jon (2011). Pocket Companion to Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 542. ISBN 978-1416054542.
- ↑ O'Malley, Frances P.; Pinder, Sarah E. (2006). Breast Pathology: A Volume in Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology series (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 159-160. ISBN 978-0443066801.
- ↑ URL: http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/sclerosis. Accessed on: 16 March 2011.
- ↑ URL: http://www.breastcancercare.org.uk/breast-cancer-information/breast-awareness/benign-breast-conditions/sclerosing-lesions. Accessed on: 30 April 2012.
- ↑ Chu et al. (2006). Adenomyoepithelioma of the Breast — A Case Report. Tzu Chi Med J. Vol. 18 No. 1. URL:URL: http://www.tzuchi.com.tw/file/tcmj/95-1/2-8.pdf. Accessed on: 28 April 2012.
- ↑ Lerwill, MF. (Apr 2008). "Flat epithelial atypia of the breast.". Arch Pathol Lab Med 132 (4): 615-21. doi:10.1043/1543-2165(2008)132[615:FEAOTB]2.0.CO;2. PMID 18384213.
- ↑ Schnitt, SJ. (2003). "The diagnosis and management of pre-invasive breast disease: flat epithelial atypia--classification, pathologic features and clinical significance.". Breast Cancer Res 5 (5): 263-8. doi:10.1186/bcr625. PMID 12927037.
- ↑ Kumar, Vinay; Abbas, Abul K.; Fausto, Nelson; Aster, Jon (2009). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 1072. ISBN 978-1416031215.
- ↑ Ung OA, Lee WB, Greenberg ML, Bilous M (January 2001). "Complex sclerosing lesion: the lesion is complex, the management is straightforward". ANZ J Surg 71 (1): 35–40. PMID 11167596.
- ↑ URL: http://www.cancer.org/docroot/NWS/content/NWS_1_1x_Radial_Scars.asp. Accessed on: 4 May 2010.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 Kennedy M, Masterson AV, Kerin M, Flanagan F (October 2003). "Pathology and clinical relevance of radial scars: a review". J. Clin. Pathol. 56 (10): 721–4. PMC 1770086. PMID 14514771. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1770086/.
- ↑ O'Malley, Frances P.; Pinder, Sarah E. (2006). Breast Pathology: A Volume in Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology series (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 91. ISBN 978-0443066801.
- ↑ Leon, ME.; Leon, MA.; Ahuja, J.; Garcia, FU.. "Nodular myofibroblastic stromal hyperplasia of the mammary gland as an accurate name for pseudoangiomatous stromal hyperplasia of the mammary gland.". Breast J 8 (5): 290-3. PMID 12199757.
- ↑ URL: http://surgpathcriteria.stanford.edu/breast/collspher/. Accessed on: 4 September 2011.
- ↑ Boutayeb, S.; Benomar, S.; Sbitti, Y.; Harroudi, T.; Hassam, B.; Errihani, H. (2012). "Nipple adenoma in a man: An unusual case report.". Int J Surg Case Rep 3 (5): 190-2. doi:10.1016/j.ijscr.2011.05.008. PMID 22342578.
- ↑ Yang, WT.; Edeiken-Monroe, B.; Sneige, N.; Fornage, BD. (May 2006). "Sonographic and mammographic appearances of granular cell tumors of the breast with pathological correlation.". J Clin Ultrasound 34 (4): 153-60. doi:10.1002/jcu.20227. PMID 16615051.
- ↑ Tan, PH.; Harada, O.; Thike, AA.; Tse, GM. (Aug 2011). "Histiocytoid breast carcinoma: an enigmatic lobular entity.". J Clin Pathol 64 (8): 654-9. doi:10.1136/jcp.2011.088930. PMID 21398688.