Difference between revisions of "Kidney tumours"
| Line 250: | Line 250: | ||
*[[ALK translocation renal cell carcinoma]]. | *[[ALK translocation renal cell carcinoma]]. | ||
An entity proposed after Vancouver | ==An entity proposed after Vancouver== | ||
*[[Eosinophilic, solid and cystic renal cell carcinoma]]. | *[[Eosinophilic, solid and cystic renal cell carcinoma]]. | ||
Revision as of 21:08, 26 February 2016
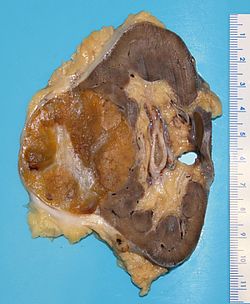
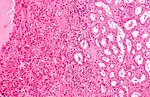
Kidney tumours - includes malignant kidney tumours (kidney cancer) and benign kidney tumours. Medical renal diseases are dealt with in the medical renal diseases article.
Pediatric kidney tumours are dealt with in the pediatric kidney tumours article.
Renal specimens
- Renal biopsy - usually for renal oncocytoma vs. renal cell carcinoma (RCC) or medical diseases - see medical kidney.
- Partial nephrectomy.
- Nephrectomy.
- Nephroureterectomy (includes ureter) - done for urothelial cell carcinoma (UCC) of the renal pelvis and ureteric UCC.
- Radical nephrectomy - includes Gerota's fascia.
- May include the adrenal gland.[1]
In excisions done for tumours, a comment should be made about kidney distant from the tumour. People with less renal mass, i.e. less kidney, are predisposed to focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS).
Anatomy
Layers (superficial to deep):
- Renal fascia (Gerota's fascia).
- Perinephric fat.
- Renal capsule.
- Renal parenchyma (cortex).
Sign out
Missed renal biopsy
KIDNEY (LESION), LEFT, CORE BIOPSY: - RENAL PARENCHYMA. - NEGATIVE FOR MASS LESION, SEE COMMENT. COMMENT: No mass lesion is apparent in the tissue sampled. A re-biopsy should be considered. Renal parenchyma: - Glomeruli: seven glomeruli sampled, no apparent glomerular pathology on the H&E sections. - Interstitium: interstitial fibrosis is not identified. - Tubules: no pathology is apparent. - Vessels: mild atherosclerosis, no hyalinization of arterioles apparent.
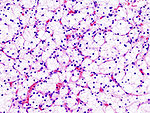
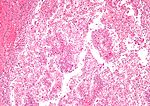
Tabular comparison (selected tumours)
Selected common tumours of the kidney:[2][3]
| Clear cell RCC | Papillary RCC type 1 |
Papillary RCC type 2 |
Chromophobe RCC classic variant |
Chromophobe RCC eosinophilic variant |
Oncocytoma | |
| Gross | Golden yellow, solid | friable | friable | light brown | light brown | mahogany/brown, +/-central scar |
| Architecture | nests, sheets | papillary, simple | papillary, pseudostratified |
nests, sheets | nests, sheets | nests, sheets |
| Nuclear atypia | low-high typically medium-high |
low-medium | medium-high | low-high, "raisinoid" nuc. membrane |
low-high, "raisinoid" nuc. membrane |
low-medium, round nuclei |
| Cytoplasm | clear | eosinophilic | eosinophilic | cobwebs/clear | eosinophilic/cobwebs | eosinophilic/ granular & abundant |
| Other | delicate vessels, necrosis common |
histiocytes in fibrovascular cores, >0.5 cm |
histiocytes in fibrovascular cores, >0.5 cm |
perinuclear clearing, thick vessels | perinuclear clearing, thick vessels | in loose fibrous/hyaline stroma |
| IHC | CK7-, EMA+ | AMACR+, EMA+, CK7+ | AMACR+, E-cadherin+, CK7- | CD117+, CK7+ (membrane) | CD117+, CK7+ (membrane) | Vimentin-, EMA+ |
| Main DDx | chromophobe classic variant |
PaRCC type 2, mets | PaRCC type 1, mets | clear cell RCC | oncocytoma | chromophobe eosinophilic variant |
| Key features | clear cells, vascular | papillae, histiocytes simple epithelium |
papillae, histiocytes, stratified |
perinuc. clearing, wispy cytoplasm |
perinuc. clearing, wispy eosinophilic cytoplasm |
eosinophilic, granular cytoplasm |
| Image(s) | , |
Notes:
- Cell shape: all have epithelioid morphology.
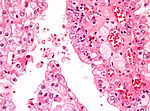
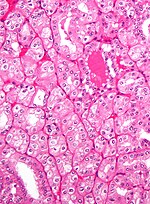
Tabular comparison of oncocytoma and chromophobe RCC
Histomorphologic features useful to distinguish chromophobe RCC (eosinophilic variant) and oncocytoma:[4]
| Morphologic feature | ChRCC (eosinophilic variant) |
Renal oncocytoma |
|---|---|---|
| Nuclear morphology | "raisinoid"/wrinkled appearance | round with small nucleolus, usu. little size variation |
| Multinucleation | common - binucleation | uncommon |
| Chromatin | coarse | fine |
| Architecture | solid, crowded nests | spaced nests / archipelago-like, solid |
| Cytoplasm | perinuclear halo, may be focal | no perinuclear halo |
| Degenerative foci (focal atypia & pleomorphism) |
absent | present in ~20% of cases |
| Image |
Common DDx
Spindle cell tumours
Malignant spindle cell tumours of the kidney:
- Renal cell carcinoma with sarcomatoid differentiation.
- Renal mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma.
- Wilms tumour.
- Renal cell carcinoma, unclassified.
Benign spindle cell tumours of the kidney:
Renal tumours with eosinophilic cytoplasm
WHO classification of renal neoplasia
- Based on 2004 iteration - as per WMSP, slightly modified.[5] Online, the classification can found here.
Renal cell tumours
Common:
- Clear cell renal cell carcinoma.
- Papillary renal cell carcinoma.
- Papillary adenoma.
- Chromophobe renal cell carcinoma.
- Oncocytoma.
Less common:
- Multilocular clear cell renal cell carcinoma.
- Carcinoma of the collecting ducts of Bellini.
- Renal cell carcinoma, unclassified.
- Renal medullary carcinoma.
- Xp11 translocation carcinoma.
- Mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma.
- Carcinoma associated with neuroblastoma.
Metanephric tumours
Nephroblastic tumours
- Nephrogenic rests.
- Nephroblastoma.
Mesenchymal tumours
Childhood:
Adults:
- Unique to kidney:
Other:
- Angiomyolipoma.
- Epithelioid angiomyolipoma.
- Leiomyosarcoma.
- Angiosarcoma.
- Pleomorphic undifferentiated sarcoma.
- Hemangiopericytoma.
- Solitary fibrous tumour.
- Osteosarcoma.
- Schwannoma.
Mixed mesenchymal and epithelial tumours
Others
- Neuroendocrine tumours.
- Hematologic tumours.
- Germ cell tumours.
- Metastases.
Vancouver modification of WHO classification
In 2012/2013, several additions were made:[6]
- Tubulocystic renal cell carcinoma.
- Acquired cystic disease associated renal cell carcinoma.
- Clear cell papillary renal cell carcinoma (clear cell tubulopapillary renal cell carcinoma).
- Hereditary leiomyomatosis renal cell carcinoma syndrome associated renal cell carcinoma.
- MiT family translocation renal cell carcinoma - includes:
"Emerging" entities (as per Vancouver) are:
- Thyroid-like follicular renal cell carcinoma.
- Succinate dehydrogenase-deficient renal cell carcinoma.
- ALK translocation renal cell carcinoma.
An entity proposed after Vancouver
Renal cell carcinoma
Overview
General
- Relatively common form of cancer.
- Often abbreviated RCC.
- AKA hypernephroma.[7]
- RCC represents approx. 90% of malignancies in kidneys of adults.[8]
Origin
- Proximal renal tubule.
Clinical
- Classically described as a triad:[9]
- Hematuria (most common symptom).
- Abdominal mass.
- Flank pain.
- Frequently picked-up on imaging (incidentaloma) ~ 1/3 of cases.
Risk factors
- Smoking - most important.[8]
- Chemical exposures (arsenic, asbestos, cadmium, organic solvents, pesticides, fungal toxins).[8]
- Chronic renal failure.
- Male>female (~2:1).
- Hereditary - familial syndromes (see Hereditary RCC).
Subtypes of RCC
RCC (renal cell carcinoma) comes in different subtypes:[10]
- Clear cell carcinoma (70-80% of RCC) -- abbrev. CCRCC.
- Papillary renal cell carcinoma (10-15% of RCC) -- abbrev. PRCC.
- Chromophobe renal carcinoma (5% of RCC) -- abbrev. ChRCC.
- Collecting duct (Bellini duct) carcinoma (1% of RCC).
Notes:
- Subtype is an independent predictor of mortality - but adds very little to multivariate models with staging information.[11]
- CCRCC tends to be worse than ChRCC and PRCC, probably due to higher incidence of mets.[12]
- The exam answer (worst to best): clear cell RCC, papillary RCC, chromophobe RCC.
IHC - is it RCC?
- RCC Ma (+), CD10 (+) -- specific for RCC[13]
IHC - differentiation of types
- Clear cell RCC vs. papillary RCC:
- CK7 (-ve CCRCC), AMACR (+ve in PRCC).[14]
- Papillary RCC type 1 vs. papillary RCC type 2:
- ChRCC vs. oncocytoma (ONC):
- CK7 (ChRCC +ve membrane), CK20, CD15.[14]
- CK7 -- ChRCC 86% +ve vs. ONC 0% +ve.[16]
- CD15 -- ChRCC 11% +ve vs. ONC 57% +ve.[17]
- Hale's colloidal iron +ve in ChRCC, usually neg. in ONC.[18]
- PAX2 -- ChRCC (1/11) +ve vs. ONC (20/23) +ve.[19]
- Kidney-specific cadherin (Ksp-cadherin) -- ChRCC 97% +ve (distinctive membrane pattern) vs. ONC only 3% +ve.[20]
- ChRCC & renal oncocytoma vs. others:
- CD117 (ckit) +ve (100% membrane, ~75% cytoplasmic).[21]
- Clear cell RCC vs. chromophobe RCC:
- Hale's colloidal iron (+ve in ChRCC).[18]
- CK7 (cell membrane +ve in ChRCC).
Notes:
- One paper[22] describes CD10, parvalbumin, AMACR, CK7 and S100A1 as being useful.
- Another paper I came across:[23]
- c-kit (CD117) not useful for differentiating ONC and ChRCC.[19]
- E-cadherin not useful for differentiating ChRCC and ONC.[24]
RCC vs. Urothelial cell carcinoma
- Clinically/radiologically, it may not be possible to differentiate renal pelvis UCC and RCC if the tumour is large.
- Pathologically, this is not very difficult.
- On gross specimens, it is almost always obvious what one is dealing with:
- UCC = nephroureterectomy.
- RCC = partial nephrectomy, nephrectomy or radical nephrectomy.
Renal cell carcinoma with sarcomatoid differentiation
- AKA sarcomatoid renal cell carcinoma.
Renal cell carcinoma with rhabdoid morphology
- AKA renal cell carcinoma with rhabdoid change.
Hereditary renal cell carcinoma
The classics - which are all autosomal dominant:[10]
- Von Hippel-Lindau syndrome.
- VHL gene mutation.
- Clear cell RCC.
- Hereditary clear cell renal cell carcinoma.
- VHL gene mutation.
- Hereditary papillary renal cell carcinoma.
- MET proto-oncogene mutation.
- PaRCC type 1.[25]
- Hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell cancer:[25]
- FH (fumarate hydratase) gene mutation.[26]
- PaRCC type 2.
- Benign leiomyomas skin/uterus.
- Uterine leiomyosarcoma.
- Birt–Hogg–Dubé syndrome:[25]
- FLCN (folliculin) gene mutation.[27]
- Skin lesions (fibrofolliculoma, trichodiscoma, acrochordon).
- ChRCC most common, other types seen (e.g. oncocytoma).
- Variable penetrance (autosomal dominant).
Others:
- Hereditary papillary carcinoma (TFE3 related translocations).[28]
Notes:
- A total of ten hereditary renal cancer syndromes have been described. In eight of the ten the gene is known.[29]
Molecular
Recurrent molecular changes in RCC:
- Clear cell RCC:
- Loss of 3p - contains the VHL gene.
- Papillary RCC:
- Sporadic:
- Trisomy 7, 16, 17.
- Loss of Y.
- Familial:
- Trisomy 7 - contains MET gene.[30]
- Sporadic:
Renal cell carcinoma grading
General
There are two systems:
- Fuhrman grading:
- Older and more complicated.
- Based on nuclear size and shape, chromatin pattern and nucleolar size.[31]
- ISUP grading:[32]
- Newer and less complicated.
- Mostly based on nucleolar size and to a much lesser degree on size and morphology
- Developed based on Fuhrman grading.
ISUP grading
Criteria:[32]
- Grade 1 - nucleoli absent/very small at 400x. §
- Grade 2 - nucleoli seen with 400x, but not at 100x. §§
- Grade 3 - nucleoli seen at 100x, i.e. with the 10x objective.
- Grade 4 - extreme nuclear pleomorphism (esp. nuclear enlargement) or sarcomatoid differentiation (spindle cells[33] or rhabdoid cells).
Cavets:[32]
- Higher grade component trumps lower grade component.
- No agreed upon minimum quantity of high grade component for upgrading.
- 37% use 1 field of view with the x10 objective. †
- 41% use 1 field of view with the x40 objective. ‡
- No agreed upon minimum quantity of high grade component for upgrading.
- Grading system not used for chromophobe RCC.
- The experience with the Fuhrman grading system showed it is not prognostic for chromophobe RCC.[34]
Notes:
- † Suffers from IPFitis.
- ‡ Suffers from HPFitis.
- § Some describe Grade 1 nuclei as lymphocyte-like.[citation needed]
- §§ Some suggest the following relationship between grading/nucleoli:[citation needed]
- Grade 1 = nucleoli seen at 400x.
- Grade 2 = nucleoli seen at 200x.
- Grade 3 = nucleoli seen at 100x.
Renal cell carcinoma staging
Renal sinus invasion
Clear cell renal cell carcinoma
Multilocular cystic renal cell carcinoma
Papillary renal cell carcinoma
Chromophobe renal cell carcinoma
Clear cell papillary renal cell carcinoma
Unclassified renal cell carcinoma
- Abbreviated URCC.
Renal translocation carcinomas
Renal tumour with Xp11.2 translocation
Renal tumour with t(6;11) translocation
- AKA t(6;11) renal cell carcinoma.
Benign tumours
Papillary adenoma of the kidney
- AKA renal papillary adenoma.
Renal oncocytoma
Angiomyolipoma
- Abbreviated AML.
Mimics
Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis
- Abbreviated XGP.
Malakoplakia
Rare stuffs
Juxtaglomerular cell tumour
Renomedullary interstitial cell tumour
Metanephric adenoma
- Should not be confused mesonephric adenoma, another term for nephrogenic adenoma.
- Memory device: metanephric adenoma is a tumour.
Renal epithelial and stromal tumour
- Abbreviated REST.
The lumping term for both:[37]
Mixed epithelial and stromal tumour
- Abbreviated MEST.
Cystic nephroma
Renal mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma
- AKA renal mucinous tubular spindle cell carcinoma.
- AKA mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma of the kidney.[38]
Collecting duct carcinoma
Renal medullary carcinoma
Tubulocystic carcinoma of the kidney
Acquired cystic disease-associated renal cell carcinoma
Kidney metastasis
- AKA renal metastasis, metastatic kidney disease.
Pediatric
The most common is nephroblastoma (Wilms tumour).
Others include:
- Metanephric stromal tumour.
- Metanephric adenofibroma
- Metanephric adenoma.
- Clear cell sarcoma of the kidney.
See also
- Urinary bladder.
- Medical kidney.
- Malakoplakia - yellow lesion on gross; may mimic RCC.
References
- ↑ Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 288. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ Zhou, Ming; Magi-Galluzzi, Cristina (2006). Genitourinary Pathology: A Volume in Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 281-304. ISBN 978-0443066771.
- ↑ Srigley, JR.; Delahunt, B. (Jun 2009). "Uncommon and recently described renal carcinomas.". Mod Pathol 22 Suppl 2: S2-S23. doi:10.1038/modpathol.2009.70. PMID 19494850.
- ↑ Tickoo, SK.; Amin, MB. (Dec 1998). "Discriminant nuclear features of renal oncocytoma and chromophobe renal cell carcinoma. Analysis of their potential utility in the differential diagnosis.". Am J Clin Pathol 110 (6): 782-7. PMID 9844591.
- ↑ Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 291. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ Srigley, JR.; Delahunt, B.; Eble, JN.; Egevad, L.; Epstein, JI.; Grignon, D.; Hes, O.; Moch, H. et al. (Oct 2013). "The International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) Vancouver Classification of Renal Neoplasia.". Am J Surg Pathol 37 (10): 1469-89. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e318299f2d1. PMID 24025519.
- ↑ URL:http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0001544/. Accessed on: 14 July 2011.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 289. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ Schmid HP, Szabo J (May 1997). "[Renal cell carcinoma--a current review]" (in German). Praxis (Bern 1994) 86 (20): 837?3. PMID 9312811.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Cotran, Ramzi S.; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Nelso Fausto; Robbins, Stanley L.; Abbas, Abul K. (2005). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (7th ed.). St. Louis, Mo: Elsevier Saunders. pp. 1016. ISBN 0-7216-0187-1.
- ↑ Capitanio, U.; Cloutier, V.; Zini, L.; Isbarn, H.; Jeldres, C.; Shariat, SF.; Perrotte, P.; Antebi, E. et al. (Jun 2009). "A critical assessment of the prognostic value of clear cell, papillary and chromophobe histological subtypes in renal cell carcinoma: a population-based study.". BJU Int 103 (11): 1496-500. doi:10.1111/j.1464-410X.2008.08259.x. PMID 19076149.
- ↑ Delahunt, B.; Bethwaite, PB.; Nacey, JN. (Oct 2007). "Outcome prediction for renal cell carcinoma: evaluation of prognostic factors for tumours divided according to histological subtype.". Pathology 39 (5): 459-65. doi:10.1080/00313020701570061. PMID 17886093.
- ↑ Zhou M, Roma A, Magi-Galluzzi C (June 2005). "The usefulness of immunohistochemical markers in the differential diagnosis of renal neoplasms". Clin. Lab. Med. 25 (2): 247?7. doi:10.1016/j.cll.2005.01.004. PMID 15848735.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 Zhou M, Roma A, Magi-Galluzzi C (June 2005). "The usefulness of immunohistochemical markers in the differential diagnosis of renal neoplasms". Clin. Lab. Med. 25 (2): 247?7. doi:10.1016/j.cll.2005.01.004. PMID 15848735.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 Langner C, Ratschek M, Rehak P, Schips L, Zigeuner R (February 2004). "Expression of MUC1 (EMA) and E-cadherin in renal cell carcinoma: a systematic immunohistochemical analysis of 188 cases". Mod. Pathol. 17 (2): 180?. doi:10.1038/modpathol.3800032. PMID 14657952.
- ↑ Liu L, Qian J, Singh H, Meiers I, Zhou X, Bostwick DG (August 2007). "Immunohistochemical analysis of chromophobe renal cell carcinoma, renal oncocytoma, and clear cell carcinoma: an optimal and practical panel for differential diagnosis". Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 131 (8): 1290?. PMID 17683191. http://journals.allenpress.com/jrnlserv/?request=get-abstract&issn=0003-9985&volume=131&page=1290.
- ↑ Pan CC, Chen PC, Ho DM (November 2004). "The diagnostic utility of MOC31, BerEP4, RCC marker and CD10 in the classification of renal cell carcinoma and renal oncocytoma: an immunohistochemical analysis of 328 cases". Histopathology 45 (5): 452?. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2559.2004.01962.x. PMID 15500648.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 Geramizadeh B, Ravanshad M, Rahsaz M (2008). "Useful markers for differential diagnosis of oncocytoma, chromophobe renal cell carcinoma and conventional renal cell carcinoma". Indian J Pathol Microbiol 51 (2): 167?1. PMID 18603673. http://www.ijpmonline.org/article.asp?issn=0377-4929;year=2008;volume=51;issue=2;spage=167;epage=171;aulast=Geramizadeh.
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 Memeo L, Jhang J, Assaad AM, et al. (February 2007). "Immunohistochemical analysis for cytokeratin 7, KIT, and PAX2: value in the differential diagnosis of chromophobe cell carcinoma". Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 127 (2): 225–9. doi:10.1309/9KWEA4W9Y94D1AEE. PMID 17210525. http://ajcp.ascpjournals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=17210525.
- ↑ Mazal PR, Exner M, Haitel A, et al. (January 2005). "Expression of kidney-specific cadherin distinguishes chromophobe renal cell carcinoma from renal oncocytoma". Hum. Pathol. 36 (1): 22–8. doi:10.1016/j.humpath.2004.09.011. PMID 15712178.
- ↑ Krueger S, Sotlar K, Kausch I, Horny HP (2005). "Expression of KIT (CD117) in renal cell carcinoma and renal oncocytoma". Oncology 68 (2-3): 269-75. doi:10.1159/000086783. PMID 16015044.
- ↑ Martignoni G, Brunelli M, Gobbo S, et al (February 2007). "Role of molecular markers in diagnosis and prognosis of renal cell carcinoma". Anal. Quant. Cytol. Histol. 29 (1): 41?. PMID 17375873.
- ↑ Avery AK, Beckstead J, Renshaw AA, Corless CL (February 2000). "Use of antibodies to RCC and CD10 in the differential diagnosis of renal neoplasms". Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 24 (2): 203?0. PMID 10680888. http://meta.wkhealth.com/pt/pt-core/template-journal/lwwgateway/media/landingpage.htm?issn=0147-5185&volume=24&issue=2&spage=203.
- ↑ Kim MK, Kim S (December 2002). "Immunohistochemical profile of common epithelial neoplasms arising in the kidney". Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 10 (4): 332–8. PMID 12613443.
- ↑ 25.0 25.1 25.2 Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 290. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 136850
- ↑ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 135150
- ↑ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 314310
- ↑ Verine, J.; Pluvinage, A.; Bousquet, G.; Lehmann-Che, J.; de Bazelaire, C.; Soufir, N.; Mongiat-Artus, P. (Nov 2010). "Hereditary renal cancer syndromes: an update of a systematic review.". Eur Urol 58 (5): 701-10. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2010.08.031. PMID 20817385.
- ↑ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 164860
- ↑ Zhou, Ming; Magi-Galluzzi, Cristina (2006). Genitourinary Pathology: A Volume in Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 282. ISBN 978-0443066771.
- ↑ 32.0 32.1 32.2 Delahunt B, Cheville JC, Martignoni G, et al. (October 2013). "The International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) grading system for renal cell carcinoma and other prognostic parameters". Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 37 (10): 1490–504. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e318299f0fb. PMID 24025520.
- ↑ Dall'Oglio, MF.; Lieberknecht, M.; Gouveia, V.; Sant'Anna, AC.; Leite, KR.; Srougi, M.. "Sarcomatoid differentiation in renal cell carcinoma: prognostic implications.". Int Braz J Urol 31 (1): 10-6. PMID 15763002.
- ↑ Delahunt, B.; Sika-Paotonu, D.; Bethwaite, PB.; McCredie, MR.; Martignoni, G.; Eble, JN.; Jordan, TW. (Jun 2007). "Fuhrman grading is not appropriate for chromophobe renal cell carcinoma.". Am J Surg Pathol 31 (6): 957-60. doi:10.1097/01.pas.0000249446.28713.53. PMID 17527087.
- ↑ Wong, L.; Hsu, TH.; Perlroth, MG.; Hofmann, LV.; Haynes, CM.; Katznelson, L. (Feb 2008). "Reninoma: case report and literature review.". J Hypertens 26 (2): 368-73. doi:10.1097/HJH.0b013e3282f283f3. PMID 18192852.
- ↑ Bircan, S.; Orhan, D.; Tulunay, O.; Safak, M. (2000). "Renomedullary interstitial cell tumor.". Urol Int 65 (3): 163-6. PMID 11054036.
- ↑ Turbiner, J.; Amin, MB.; Humphrey, PA.; Srigley, JR.; De Leval, L.; Radhakrishnan, A.; Oliva, E. (Apr 2007). "Cystic nephroma and mixed epithelial and stromal tumor of kidney: a detailed clinicopathologic analysis of 34 cases and proposal for renal epithelial and stromal tumor (REST) as a unifying term.". Am J Surg Pathol 31 (4): 489-500. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e31802bdd56. PMID 17414095.
- ↑ Brandal, P.; Lie, AK.; Bassarova, A.; Svindland, A.; Risberg, B.; Danielsen, H.; Heim, S. (Feb 2006). "Genomic aberrations in mucinous tubular and spindle cell renal cell carcinomas.". Mod Pathol 19 (2): 186-94. doi:10.1038/modpathol.3800499. PMID 16258504.