Difference between revisions of "Testis"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→Hydrocele testis: +SO) |
(→Epidermoid cyst of the testis: create) |
||
| (43 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
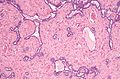
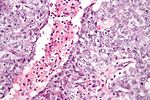
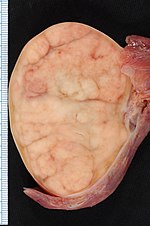
[[Image:Seminoma_of_the_Testis.jpg|thumb|150px|Orchiectomy specimen showing testis replaced by tumour (proven to be [[seminoma]]). (WC/Ed Uthman)]] | |||
The '''testis''', plural '''testes''', are important for survival of the species. Tumours occasionally arise in 'em. They generally are not biopsied. | The '''testis''', plural '''testes''', are important for survival of the species. Tumours occasionally arise in 'em. They generally are not biopsied. | ||
If the testis is biopsied, it is usually for fertility - | If the testis is biopsied, it is usually for [[male infertility|fertility]]. The [[cut-up]] of orchiectomy specimens is dealt with in ''[[orchiectomy grossing]]''. | ||
=Normal testis= | =Normal testis= | ||
==Gross== | ===Gross=== | ||
Anatomy - deep to superficial: | Anatomy - deep to superficial: | ||
*Tunica albuginea - fibrous layer. | *Tunica albuginea - fibrous layer. | ||
*Tunica vaginalis - thin mesothelial layer. | *Tunica vaginalis - thin mesothelial layer. | ||
**This layer is important in the [[cancer staging|staging]] of testicular tumours. | |||
==Microscopic== | ===Microscopic=== | ||
===Seminiferous tubules=== | ====Seminiferous tubules==== | ||
*Sertoli cells ([[AKA]] sustentacular cell [[AKA]] nurse cell). | *Sertoli cells ([[AKA]] sustentacular cell [[AKA]] nurse cell). | ||
**Large cells with oval nucleus. | **Large cells with oval nucleus. | ||
| Line 23: | Line 25: | ||
**You don't see the tail on light microscopy. | **You don't see the tail on light microscopy. | ||
====Images==== | =====Images===== | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
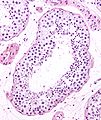
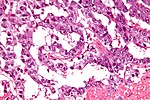
Image:Seminiferous_tubule_and_sperm_low_mag.jpg | Seminiferous tubule and sperm - low mag. (WC/Nephron) | Image:Seminiferous_tubule_and_sperm_low_mag.jpg | Seminiferous tubule and sperm - low mag. (WC/Nephron) | ||
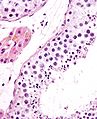
Image:Seminiferous_tubule_and_sperm.jpg | Seminiferous tubule and sperm - high mag. (WC/Nephron) | Image:Seminiferous_tubule_and_sperm.jpg | Seminiferous tubule and sperm - high mag. (WC/Nephron) | ||
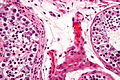
Image:Intratubular_germ_cell_neoplasia_-_2_-_very_high_mag.jpg | Benign seminiferous tubules and ITGCN. (WC/Nephron) | Image:Intratubular_germ_cell_neoplasia_-_2_-_very_high_mag.jpg | Benign seminiferous tubules and GCNIS (ITGCN). (WC/Nephron) | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
===Interstitial=== | ====Interstitial==== | ||
*Leydig cell ([[AKA]] interstitial cell). | *Leydig cell ([[AKA]] interstitial cell). | ||
**Large eosinophilic cell. | **Large eosinophilic cell. | ||
*[[Blood vessel]]s. | *[[Blood vessel]]s. | ||
====Image==== | =====Image===== | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
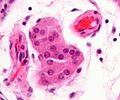
Image:Leydig_cells_-_very_high_mag.jpg | Leydig cells - very high mag. (WC/Nephron) | Image:Leydig_cells_-_very_high_mag.jpg | Leydig cells - very high mag. (WC/Nephron) | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
===Associated structures=== | ====Associated structures==== | ||
*Epididymis - stores the sperm. | *[[Epididymis]] - stores the sperm. | ||
**Pseudostratified epithelium with cilia. | **Pseudostratified epithelium with cilia. | ||
| Line 45: | Line 47: | ||
*[http://www.webpathology.com/image.asp?n=3&Case=27 Epididymis (webpathology.com)]. | *[http://www.webpathology.com/image.asp?n=3&Case=27 Epididymis (webpathology.com)]. | ||
===Rete testis=== | ====Rete testis==== | ||
*Receives stuff from the tubules. | *Receives stuff from the tubules. | ||
*Occasionally afflicted by ''[[adenomatous hyperplasia of the rete testis]]''. | |||
*Very rarely give rise to an ''[[adenocarcinoma of the rete testis]]''. | *Very rarely give rise to an ''[[adenocarcinoma of the rete testis]]''. | ||
*May be involved by [[seminoma]] | *May be involved by [[seminoma]]. | ||
**Increases risk of relapse in a univariate analysis.<Ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Soper | first1 = MS. | last2 = Hastings | first2 = JR. | last3 = Cosmatos | first3 = HA. | last4 = Slezak | first4 = JM. | last5 = Wang | first5 = R. | last6 = Lodin | first6 = K. | title = Observation Versus Adjuvant Radiation or Chemotherapy in the Management of Stage I Seminoma: Clinical Outcomes and Prognostic Factors for Relapse in a Large US Cohort. | journal = Am J Clin Oncol | volume = | issue = | pages = | month = Dec | year = 2012 | doi = 10.1097/COC.0b013e318277d839 | PMID = 23275274 }}</ref> | |||
**More common with (sometimes subtle) intertubular pattern of seminoma.<ref name=pmid16021570>{{Cite journal | last1 = Browne | first1 = TJ. | last2 = Richie | first2 = JP. | last3 = Gilligan | first3 = TD. | last4 = Rubin | first4 = MA. | title = Intertubular growth in pure seminomas: associations with poor prognostic parameters. | journal = Hum Pathol | volume = 36 | issue = 6 | pages = 640-5 | month = Jun | year = 2005 | doi = 10.1016/j.humpath.2005.03.011 | PMID = 16021570 }}</ref> | |||
Microscopic: | Microscopic: | ||
*Delicate anastomosing channels lined by cuboid epithelium. | *Delicate anastomosing channels lined by cuboid epithelium. | ||
====Images==== | =====Images===== | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
Image:Rete_testis_high_mag.jpg | Rete testis (WC/Nephron) | Image:Rete_testis_high_mag.jpg | Rete testis (WC/Nephron) | ||
| Line 61: | Line 66: | ||
*[http://www.webpathology.com/image.asp?case=27&n=5 Rete testis (webpathology.com)]. | *[http://www.webpathology.com/image.asp?case=27&n=5 Rete testis (webpathology.com)]. | ||
===Appendix of testis=== | ====Appendix of testis==== | ||
Muellerian duct remnant. | *Muellerian duct remnant. | ||
Microscopic: | Microscopic: | ||
| Line 71: | Line 76: | ||
*[http://www.webpathology.com/image.asp?case=27&n=7 Appendix of testis (webpathology.com)]. | *[http://www.webpathology.com/image.asp?case=27&n=7 Appendix of testis (webpathology.com)]. | ||
==Sign out== | ===Sign out=== | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
TESTICLE, RIGHT, ORCHIECTOMY: | |||
- TESTICLE WITHOUT APPARENT PATHOLOGY. | - TESTICLE WITHOUT APPARENT PATHOLOGY. | ||
- NEGATIVE FOR INTRATUBULAR GERM CELL NEOPLASIA. | |||
- NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY. | |||
</pre> | |||
====Alternate==== | |||
<pre> | |||
RIGHT TESTICLE, ORCHIDECTOMY: | |||
- BENIGN TESTIS WITH SPERMATOGENESIS. | |||
- NEGATIVE FOR INTRATUBULAR GERM CELL NEOPLASIA. | - NEGATIVE FOR INTRATUBULAR GERM CELL NEOPLASIA. | ||
- NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY. | - NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY. | ||
| Line 106: | Line 119: | ||
*Beta-hCG - choriocarcinoma. | *Beta-hCG - choriocarcinoma. | ||
*CD30 - embryonal carcinoma. | *CD30 - embryonal carcinoma. | ||
*D2-40 - seminoma. | *[[D2-40]] - seminoma. | ||
===Tabular summary of GCTs=== | ===Tabular summary of GCTs=== | ||
| Line 117: | Line 130: | ||
! Image | ! Image | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[ | | [[Germ cell neoplasia in situ]] (GCNIS) | ||
| nests of small fried egg cells | | nests of small fried egg cells | ||
| large central nucleus, clear <br>cytoplasm, round ''or'' polygonal nuclear membrane, [[nucleoli]]<ref name=Ref_GUP538>{{Ref GUP|538}}</ref> | | large central nucleus, clear <br>cytoplasm, round ''or'' polygonal nuclear membrane, [[nucleoli]]<ref name=Ref_GUP538>{{Ref GUP|538}}</ref> | ||
| CD117 | | CD117 | ||
| appearance similar to seminoma | | appearance similar to seminoma | ||
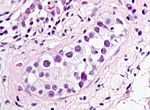
| [[Image:Intratubular_germ_cell_neoplasia_high_mag_cropped.jpg|thumb|center|150px| | | [[Image:Intratubular_germ_cell_neoplasia_high_mag_cropped.jpg|thumb|center|150px|GCNIS (WC)]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
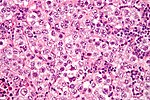
| [[Seminoma]] | | [[Seminoma]] | ||
| Line 159: | Line 172: | ||
| [[Image:Teratoma_2_low_mag.jpg|thumb|center|150px|Teratoma (WC)]] | | [[Image:Teratoma_2_low_mag.jpg|thumb|center|150px|Teratoma (WC)]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[Spermatocytic | | [[Spermatocytic tumour]] (previously ''spermatocytic seminoma'') | ||
| population of 3 cells | | population of 3 cells | ||
| pop.: (1) small cell with high [[NC ratio]] (mature lymphocyte-like), (2) medium with nucleoli, (3) large cells with filamentous chromatin - few present | | pop.: (1) small cell with high [[NC ratio]] (mature lymphocyte-like), (2) medium with nucleoli, (3) large cells with filamentous chromatin - few present | ||
| ? | | ? | ||
| does not arise from | | does not arise from GCNIS, no lymphocytic infiltrate (like in seminoma) | ||
| [[Image:Spermatocytic_seminoma_high_mag.jpg|thumb|center|150px|Spermatocytic | | [[Image:Spermatocytic_seminoma_high_mag.jpg|thumb|center|150px|Spermatocytic tumour (WC)]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[Mixed germ cell tumour]] | | [[Mixed germ cell tumour]] | ||
| Line 200: | Line 213: | ||
=Benign= | =Benign= | ||
==Testicular atrophy== | ==Testicular atrophy== | ||
*[[AKA]] ''atrophic testis''. | *[[AKA]] ''atrophic testis''. | ||
*[[AKA]] ''atrophy of the testis''. | *[[AKA]] ''atrophy of the testis''. | ||
{{Main|Testicular atrophy}} | |||
==Male infertility== | |||
*This is a [[clinical diagnosis]]. | |||
{{Main|Male infertility}} | |||
==Spermatocele== | ==Spermatocele== | ||
{{Main|Spermatocele}} | |||
==Hydrocele testis== | ==Hydrocele testis== | ||
*[[AKA]] ''hydrocele''. | *[[AKA]] ''hydrocele''. | ||
{{Main|Hydrocele testis}} | |||
==Idiopathic granulomatous orchitis== | ==Idiopathic granulomatous orchitis== | ||
| Line 310: | Line 241: | ||
DDx: | DDx: | ||
*[[ | *[[GCNIS]] (ITGCN). | ||
*[[Seminoma]]. | *[[Seminoma]]. | ||
*Tertiary [[syphilis]] - classically, plasma cell rich.<ref name=pmid22343746>{{Cite journal | last1 = Sekita | first1 = N. | last2 = Nishikawa | first2 = R. | last3 = Fujimura | first3 = M. | last4 = Sugano | first4 = I. | last5 = Mikami | first5 = K. | title = [Syphilitic orchitis: a case report]. | journal = Hinyokika Kiyo | volume = 58 | issue = 1 | pages = 53-5 | month = Jan | year = 2012 | doi = | PMID = 22343746 }}</ref> | *Tertiary [[syphilis]] - classically, plasma cell rich.<ref name=pmid22343746>{{Cite journal | last1 = Sekita | first1 = N. | last2 = Nishikawa | first2 = R. | last3 = Fujimura | first3 = M. | last4 = Sugano | first4 = I. | last5 = Mikami | first5 = K. | title = [Syphilitic orchitis: a case report]. | journal = Hinyokika Kiyo | volume = 58 | issue = 1 | pages = 53-5 | month = Jan | year = 2012 | doi = | PMID = 22343746 }}</ref> | ||
| Line 317: | Line 248: | ||
*[[Lymphoma]].<ref name=pmid21458170/> | *[[Lymphoma]].<ref name=pmid21458170/> | ||
*[[Malakoplakia]].<ref name=pmid21458170/> | *[[Malakoplakia]].<ref name=pmid21458170/> | ||
*BCG-associated orchitis.<ref name=pmid23856256>{{Cite journal | last1 = Parker | first1 = SG. | last2 = Kommu | first2 = SS. | title = Post-intravesical BCG epididymo-orchitis: Case report and a review of the literature. | journal = Int J Surg Case Rep | volume = 4 | issue = 9 | pages = 768-70 | month = | year = 2013 | doi = 10.1016/j.ijscr.2013.05.017 | PMID = 23856256 }}</ref><ref name=pmid12841318>{{Cite journal | last1 = Bulbul | first1 = MA. | last2 = Hijaz | first2 = A. | last3 = Beaini | first3 = M. | last4 = Araj | first4 = GF. | last5 = Tawil | first5 = A. | title = Tuberculous epididymo-orchitis following intravesical BCG for superficial bladder cancer. | journal = J Med Liban | volume = 50 | issue = 1-2 | pages = 67-9 | month = | year = | doi = | PMID = 12841318 }}</ref> | |||
===Stains=== | ===Stains=== | ||
| Line 322: | Line 254: | ||
*[[Dieterle stain]] -ve -- for syphilis. | *[[Dieterle stain]] -ve -- for syphilis. | ||
= | ==Testicular scar== | ||
== | {{Main|Testicular scar}} | ||
==Testicular abscess== | |||
{{Main|Testicular abscess}} | |||
==Testicular torsion== | |||
{{Main|Testicular torsion}} | |||
==Adenomatous hyperplasia of the rete testis== | |||
{{Main|Adenomatous hyperplasia of the rete testis}} | |||
==Epidermoid cyst of the testis== | |||
{{Main|Epidermoid cyst of the testis}} | |||
==Testicular trauma== | |||
===General=== | ===General=== | ||
* | *May lead to orchitectomy. | ||
===Gross=== | |||
*Hemorrhagic. | |||
* | |||
===Microscopic=== | ===Microscopic=== | ||
Features: | Features: | ||
* | *Necrotic seminiferous tubules. | ||
* | *Intratubular blood in keeping with hemorrhage. | ||
Note: | |||
* | *Normal spermatogenesis in background - if viable tissue present. | ||
=== | ===Sign out=== | ||
< | <pre> | ||
Right Testicle Tissue, Debridement: | |||
- Hemorrhagic testicular tissue and necrotic seminiferous tubules. | |||
- Small amount of viable seminiferous tubules with spermatogenesis. | |||
- NEGATIVE for germ cell neoplasia in situ. | |||
- NEGATIVE for malignancy. | |||
Comment: | |||
The clinical history of trauma is noted. | |||
</pre> | |||
=Premalignant= | |||
==Germ cell neoplasia in situ== | |||
*Previously ''intratubular germ cell neoplasia'' (abbreviated ''ITGCN''). | |||
{{Main|Germ cell neoplasia in situ}} | |||
=Germ cell tumours= | =Germ cell tumours= | ||
| Line 378: | Line 306: | ||
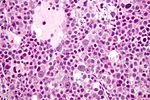
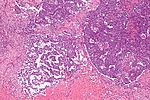
{{Main|Seminoma}} | {{Main|Seminoma}} | ||
==Spermatocytic | ==Spermatocytic tumour== | ||
{{Main|Spermatocytic | *Previously ''spermatocytic seminoma''. | ||
{{Main|Spermatocytic tumour}} | |||
==Yolk sac tumour== | ==Yolk sac tumour== | ||
| Line 395: | Line 324: | ||
{{Main|Embryonal carcinoma}} | {{Main|Embryonal carcinoma}} | ||
These often look like a poorly differentiated carcinoma. | These often look like a poorly differentiated carcinoma. | ||
==Choriocarcinoma== | ==Choriocarcinoma== | ||
{{Main|Choriocarcinoma}} | {{Main|Choriocarcinoma}} | ||
These are aggressive tumours. | These are aggressive tumours. | ||
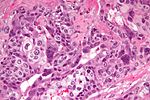
==Teratoma of the testis== | ==Teratoma of the testis== | ||
| Line 441: | Line 336: | ||
==Leydig cell tumour== | ==Leydig cell tumour== | ||
*[[AKA]] ''interstitial cell tumour''. | *[[AKA]] ''interstitial cell tumour''. | ||
{{Main|Leydig cell tumour}} | |||
==Sertoli cell nodule== | ==Sertoli cell nodule== | ||
*Abbreviated ''SCN''. | |||
*[[AKA]] ''Pick's adenoma''. | *[[AKA]] ''Pick's adenoma''. | ||
*AKA ''testicular tubular adenoma''. | *AKA ''testicular tubular adenoma''. | ||
*AKA ''tubular adenoma of the testis''. | *AKA ''tubular adenoma of the testis''. | ||
{{Main|Sertoli cell nodule}} | |||
==Sertoli cell tumour== | ==Sertoli cell tumour== | ||
{{Main|Sertoli cell tumour}} | |||
=Other= | =Other= | ||
| Line 555: | Line 352: | ||
==Adenocarcinoma of the rete testis== | ==Adenocarcinoma of the rete testis== | ||
{{Main|Adenocarcinoma of the rete testis}} | |||
==Testicular adrenal rest tumour== | |||
:Abbreviated ''TART''. | |||
{{Main|Testicular adrenal rest tumour}} | |||
==Fibrous pseudotumour of the paratesticular region== | |||
{{Main|Fibrous pseudotumour of the paratesticular region}} | |||
=== | ==Testicular metastasis== | ||
{{Main|Testicular metastasis}} | |||
=See also= | =See also= | ||
*[[Genitourinary pathology]]. | *[[Genitourinary pathology]]. | ||
| Line 576: | Line 370: | ||
*[[Vas deferens]]. | *[[Vas deferens]]. | ||
*[[Spermatic cord]]. | *[[Spermatic cord]]. | ||
*[[Paratesticular region]]. | |||
=References= | =References= | ||
| Line 584: | Line 379: | ||
[[Category: Genitourinary pathology]] | [[Category: Genitourinary pathology]] | ||
[[Category: Testis]] | |||
Latest revision as of 19:26, 9 September 2021

Orchiectomy specimen showing testis replaced by tumour (proven to be seminoma). (WC/Ed Uthman)
The testis, plural testes, are important for survival of the species. Tumours occasionally arise in 'em. They generally are not biopsied.
If the testis is biopsied, it is usually for fertility. The cut-up of orchiectomy specimens is dealt with in orchiectomy grossing.
Normal testis
Gross
Anatomy - deep to superficial:
- Tunica albuginea - fibrous layer.
- Tunica vaginalis - thin mesothelial layer.
- This layer is important in the staging of testicular tumours.
Microscopic
Seminiferous tubules
- Sertoli cells (AKA sustentacular cell AKA nurse cell).
- Large cells with oval nucleus.
- Primary spermatocyte.
- Small cells with dark nucleus on basement membrane.
- Secondary spermatocyte.
- Rarely seen on light microscopy.
- Spermatids.
- Round small.
- Usually close to the centre of the lumen.
- Spermatozoa.
- You don't see the tail on light microscopy.
Images
Interstitial
- Leydig cell (AKA interstitial cell).
- Large eosinophilic cell.
- Blood vessels.
Image
Associated structures
- Epididymis - stores the sperm.
- Pseudostratified epithelium with cilia.
Image:
Rete testis
- Receives stuff from the tubules.
- Occasionally afflicted by adenomatous hyperplasia of the rete testis.
- Very rarely give rise to an adenocarcinoma of the rete testis.
- May be involved by seminoma.
Microscopic:
- Delicate anastomosing channels lined by cuboid epithelium.
Images
www:
Appendix of testis
- Muellerian duct remnant.
Microscopic:
- Polypoid structure.
Images:
Sign out
TESTICLE, RIGHT, ORCHIECTOMY: - TESTICLE WITHOUT APPARENT PATHOLOGY. - NEGATIVE FOR INTRATUBULAR GERM CELL NEOPLASIA. - NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
Alternate
RIGHT TESTICLE, ORCHIDECTOMY: - BENIGN TESTIS WITH SPERMATOGENESIS. - NEGATIVE FOR INTRATUBULAR GERM CELL NEOPLASIA. - NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
Diagnoses (overview)
- Benign.
- Spermatid present/not present.
- Infertility - azoospermic.
- No sperm present.
- Germ cell tumours (GCTs).
- Intratubular germ cell neoplasia.
- Seminoma.
- Spermatocytic seminoma.
- Yolk sac tumour (endodermal sinus tumour).
- Embryonal carcinoma.
- Choriocarcinoma.
- Teratoma.
- Mixed GCT - 60% of GCTs are mixed.
- Common combinations:
- teratoma + embryonal carcinoma + endodermal sinus tumour (yolk sac tumour) (TEE).
- seminoma + embryonal (SE).
- embryonal + teratoma (TE).
- Common combinations:
- Sex-cord stromal tumour.
IHC for GCTs
ABCDs of GCTs:
- AFP - yolk sac tumour.
- Beta-hCG - choriocarcinoma.
- CD30 - embryonal carcinoma.
- D2-40 - seminoma.
Tabular summary of GCTs
| Tumour | Key feature | Microscopic | IHC | Other | Image |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Germ cell neoplasia in situ (GCNIS) | nests of small fried egg cells | large central nucleus, clear cytoplasm, round or polygonal nuclear membrane, nucleoli[3] |
CD117 | appearance similar to seminoma | |
| Seminoma | fried egg cells | fried egg-like cells (central nucleus, clear cytoplasm) with squared-off nuclear membrane, nucleoli, lymphocytic infiltrate, granulomata, syncytiotrophoblastic giant cells[4] |
D2-40 | Dysgerminoma = female version of this tumour | |
| Yolk sac tumour (endodermal sinus tumour) | Schiller-Duval bodies | Schiller-Duval b. = central blood vessel surrounded by epithelial-like cells a space and more epithelial-like cells, variable arch. | AFP | patterns: microcystic, solid, hepatoid | |
| Embryonal carcinoma | prominent nucleoli, vescicular nuclei | var. arch.: tubulopapillary, glandular, solid, embryoid bodies (ball of cells in surrounded by empty space on three sides), +/-nuclear overlap, mitoses common | CD30 | usu. part of a mixed GCT | |
| Choriocarcinoma | marked nuclear atypia | cells with clear cytoplasm (cytotrophoblast), multinucleated cells (syncytiotrophoblast) | beta-hCG | not commonly pure, usu. a component of a mixed GCT | |
| Teratoma | skin, GI tract-like epithelium | skin (epidermis, adnexal structures - sebaceous glands, hair follicles), GI tract-like glands (simple tall columnar epithelium), fat +/-primitive neuroepithelium (pseudostratified epithelium in rosettes) | None | testicular teratomas in post-pubertal males are all considered malignant[5] | |
| Spermatocytic tumour (previously spermatocytic seminoma) | population of 3 cells | pop.: (1) small cell with high NC ratio (mature lymphocyte-like), (2) medium with nucleoli, (3) large cells with filamentous chromatin - few present | ? | does not arise from GCNIS, no lymphocytic infiltrate (like in seminoma) | |
| Mixed germ cell tumour | NA | common combinations: teratoma + embryonal carcinoma + endodermal sinus tumour (yolk sac tumour) (TEE); seminoma + embryonal (SE); embryonal + teratoma (TE) | NA | - |
Tabular summary of (male) SCSTs
| Tumour | Key feature | Microscopic | IHC | Other | Image |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leydig cell tumour | intersitial cell cluster with eosinophilic cytoplasm | cytoplasmic vacuolization, uniform nuclei with nucleoli | MART-1, calretinin, inhibin | +/-Reinke crystals (cylindrical crystalloid eosinophilic cytoplasmic bodies) | |
| Sertoli cell tumour | cells in cords or trabeculae | light staining bubbly cytoplasm +/- large cytoplasmic vacuoles, granular chromatin | ? | usu. no significant nuclear atypia, no mitoses |
Benign
Testicular atrophy
Main article: Testicular atrophy
Male infertility
- This is a clinical diagnosis.
Main article: Male infertility
Spermatocele
Main article: Spermatocele
Hydrocele testis
- AKA hydrocele.
Main article: Hydrocele testis
Idiopathic granulomatous orchitis
- Granulomatous orchitis redirects here.
General
- Rare.
- Unknown etiology -- possibly trauma + immune reaction to sperm.[6]
Microscopic
Features:[6]
- Granulomas +/- necrosis.
- +/-Destruction of seminiferous tubules.
- Prominent collagen fibrosis.
DDx:
- GCNIS (ITGCN).
- Seminoma.
- Tertiary syphilis - classically, plasma cell rich.[7]
- Syphilis, unlike other infections of the GU tract, is said to affect the testis before the epididymis.[8]
- Tuberculosis.
- Lymphoma.[6]
- Malakoplakia.[6]
- BCG-associated orchitis.[9][10]
Stains
- AFB -ve -- for tuberculosis.
- Dieterle stain -ve -- for syphilis.
Testicular scar
Main article: Testicular scar
Testicular abscess
Main article: Testicular abscess
Testicular torsion
Main article: Testicular torsion
Adenomatous hyperplasia of the rete testis
Main article: Adenomatous hyperplasia of the rete testis
Epidermoid cyst of the testis
Main article: Epidermoid cyst of the testis
Testicular trauma
General
- May lead to orchitectomy.
Gross
- Hemorrhagic.
Microscopic
Features:
- Necrotic seminiferous tubules.
- Intratubular blood in keeping with hemorrhage.
Note:
- Normal spermatogenesis in background - if viable tissue present.
Sign out
Right Testicle Tissue, Debridement:
- Hemorrhagic testicular tissue and necrotic seminiferous tubules.
- Small amount of viable seminiferous tubules with spermatogenesis.
- NEGATIVE for germ cell neoplasia in situ.
- NEGATIVE for malignancy.
Comment:
The clinical history of trauma is noted.
Premalignant
Germ cell neoplasia in situ
- Previously intratubular germ cell neoplasia (abbreviated ITGCN).
Main article: Germ cell neoplasia in situ
Germ cell tumours
Main article: Germ cell tumours
Seminoma
Main article: Seminoma
Spermatocytic tumour
- Previously spermatocytic seminoma.
Main article: Spermatocytic tumour
Yolk sac tumour
Main article: Yolk sac tumour
- Most common GCT in infants and young boys.
Microscopic
Classic feature:
- Schiller-Duval bodies.
- Look like glomerulus - central blood vessel surrounded by epithelial-like cells a space and more epithelial-like cells
- Architecure - variable.
- Most common microcystic pattern.[11]
Embryonal carcinoma
Main article: Embryonal carcinoma
These often look like a poorly differentiated carcinoma.
Choriocarcinoma
Main article: Choriocarcinoma
These are aggressive tumours.
Teratoma of the testis
Main article: Teratoma
In post-pubertal males these (testicular) tumours are considered malignant. They usually consist of all three germ layers.[12]
Sex cord stromal tumours
Leydig cell tumour
- AKA interstitial cell tumour.
Main article: Leydig cell tumour
Sertoli cell nodule
- Abbreviated SCN.
- AKA Pick's adenoma.
- AKA testicular tubular adenoma.
- AKA tubular adenoma of the testis.
Main article: Sertoli cell nodule
Sertoli cell tumour
Main article: Sertoli cell tumour
Other
These tumours are rare.
Adenocarcinoma of the rete testis
Main article: Adenocarcinoma of the rete testis
Testicular adrenal rest tumour
- Abbreviated TART.
Main article: Testicular adrenal rest tumour
Fibrous pseudotumour of the paratesticular region
Main article: Fibrous pseudotumour of the paratesticular region
Testicular metastasis
Main article: Testicular metastasis
See also
- Genitourinary pathology.
- Ovary.
- Ovarian tumours.
- Vas deferens.
- Spermatic cord.
- Paratesticular region.
References
- ↑ Soper, MS.; Hastings, JR.; Cosmatos, HA.; Slezak, JM.; Wang, R.; Lodin, K. (Dec 2012). "Observation Versus Adjuvant Radiation or Chemotherapy in the Management of Stage I Seminoma: Clinical Outcomes and Prognostic Factors for Relapse in a Large US Cohort.". Am J Clin Oncol. doi:10.1097/COC.0b013e318277d839. PMID 23275274.
- ↑ Browne, TJ.; Richie, JP.; Gilligan, TD.; Rubin, MA. (Jun 2005). "Intertubular growth in pure seminomas: associations with poor prognostic parameters.". Hum Pathol 36 (6): 640-5. doi:10.1016/j.humpath.2005.03.011. PMID 16021570.
- ↑ Zhou, Ming; Magi-Galluzzi, Cristina (2006). Genitourinary Pathology: A Volume in Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 538. ISBN 978-0443066771.
- ↑ Zhou, Ming; Magi-Galluzzi, Cristina (2006). Genitourinary Pathology: A Volume in Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 542. ISBN 978-0443066771.
- ↑ Carver, BS.; Al-Ahmadie, H.; Sheinfeld, J. (May 2007). "Adult and pediatric testicular teratoma.". Urol Clin North Am 34 (2): 245-51; abstract x. doi:10.1016/j.ucl.2007.02.013. PMID 17484929.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 Roy, S.; Hooda, S.; Parwani, AV. (May 2011). "Idiopathic granulomatous orchitis.". Pathol Res Pract 207 (5): 275-8. doi:10.1016/j.prp.2011.02.005. PMID 21458170.
- ↑ Sekita, N.; Nishikawa, R.; Fujimura, M.; Sugano, I.; Mikami, K. (Jan 2012). "[Syphilitic orchitis: a case report].". Hinyokika Kiyo 58 (1): 53-5. PMID 22343746.
- ↑ Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 364. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ Parker, SG.; Kommu, SS. (2013). "Post-intravesical BCG epididymo-orchitis: Case report and a review of the literature.". Int J Surg Case Rep 4 (9): 768-70. doi:10.1016/j.ijscr.2013.05.017. PMID 23856256.
- ↑ Bulbul, MA.; Hijaz, A.; Beaini, M.; Araj, GF.; Tawil, A.. "Tuberculous epididymo-orchitis following intravesical BCG for superficial bladder cancer.". J Med Liban 50 (1-2): 67-9. PMID 12841318.
- ↑ URL: http://webpathology.com/image.asp?case=34&n=1. Accessed on: March 8, 2010.
- ↑ Moore, Keith L.; Persaud, T.V.N. (2002). The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology (7th ed.). Saunders. pp. 83. ISBN 978-0721694122.