Difference between revisions of "Prostate gland"
(→IHC) |
(→IHC) |
||
| Line 108: | Line 108: | ||
*p63 +ve.<ref name=pmid22076175/> | *p63 +ve.<ref name=pmid22076175/> | ||
*CK34betaE12 -ve.<ref name=pmid22076175/> | *CK34betaE12 -ve.<ref name=pmid22076175/> | ||
*AMACR -ve.<ref name=pmid22076175/> | |||
===Sign out=== | ===Sign out=== | ||
Revision as of 19:58, 15 November 2013
The prostate gland adds juice to the sperm. In old men it creates lotsa problems... nodular hyperplasia (commonly called BPH or benign prostatic hyperplasia) and cancer (adenocarcinoma).
Prostate cancer is such a big topic it is dealt with in its own article.
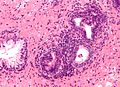
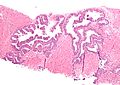
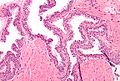
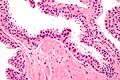
Normal prostate gland
Anatomy
Divided into three zones:[1]
- Peripheral zone - posterior aspect, palpable with digit.
- Classic location for cancer.
- Central zone - considered resistant to disease.
- Transition zone - usual location for nodular hyperplasia.
Histology
- Glands have two cell layers (similar to glands in breast).
- Second cell layer may be difficult to see (like in breast).
- Epithelium in glands is "folded" or "tufted".
- Very important - helps on differentiate from Gleason pattern 3.
- Luminal epithelium often clear cytoplasm.
- Single nucleus.
Benign normal:
- Corpora amylacea.
- Round/ovoid-eosinophilic bodies -- with laminations (layered appearance).
- In gland lumina.
- Usually in benign glands - but cannot be used to exclude cancer.[2]
- Very common.
- These should be differentiated from eosinophilic proteinaceous debris - which is associated with cancer.
Negatives:
- No nucleoli present (if you see nuclei think: cancer, HGPIN, reactive changes, basal cell hyperplasia).
- No mitoses - these are uncommon... even in high grade prostate cancer.
Notes:
- Tufted epithelium is a strong indicator of benignancy; however two uncommon prostate cancer typically have tufted epithelium:
Images
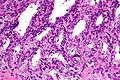
IHC of normal prostate
Normal prostate:
- AMACR -ve (mark epithelial cells).
- CK5/6 +ve,[3] p63 +ve, HMWCK +ve (mark basal cells).
- PSA (prostate-specific antigen) +ve, PSAP (prostatic-specific acid phosphatase) +ve.
Other accessory glands
Bulbourethral gland
- AKA Cowper's gland.
General
- Mucinous glands at the apex of the prostate.
Microscopic
Features:[4]
- Lobular glands with abundant pale cytoplasm.
- Resemble (mucinous) salivary glands.
- Often assocatiated with skeletal muscle.[5]
DDx:
- Foamy gland carcinoma.
- Mucinous metaplasia of the prostate.
Images:
Stains
- Mucicarmine +ve.
- PAS-D +ve.
IHC
Features:[4]
- PSAP -ve.
- PSA +ve.
- HMWCK +ve.
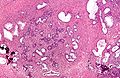
Seminal vesicles
General
- Seen in radical prostatectomies and occasionally in core biopsies.
Microscopic
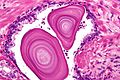
- Fern-like architecture - epithelial component clustered closely, looks like it connects.
- Epithelium surrounded by a thick layer of muscle (>10 cells across ~80 microns).
- Lipofuscin (coarse cytoplasmic yellow granules approximately 1-2 micrometers) - key feature.
- Nucleoli - common.
- Nuclear inclusions - common.[6]
Notes:
- The ejaculatory ducts have the same epithelium as the seminal vesicles.[7]
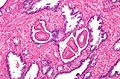
Images
www:
IHC
Sign out
B. PROSTATE, RIGHT MEDIAL SUPERIOR, BIOPSY: - BENIGN PROSTATE TISSUE. - BENIGN SEMINAL VESICLE/EJACULATORY DUCT.
Specimens
- Prostate core biopsy - done transrectal.
- Prostate chips (from a transurethral resection of the prostate, abbreviated TURP) - usu. done for nodular hyperplasia of the prostate gland; may be done in the context of obstructing cancer.
- Radical prostatectomy - includes the seminal vesicles.
- Radical cystoprostatectomy - includes the urinary bladder and seminal vesicles.[11]
Approach
- Know the common diagnoses well.
- Core biopsies - scan the slides with the 10x objective.
Common diagnoses
- Benign.
- Atrophy - may resemble adenocarcinoma - typically not reported.
- Adenosis - may resemble adenocarcinoma - typically not reported.
- Prostate adenocarcinoma.
- Most common Grade is 3+3=6.
- HGPIN (high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia) - prostate adenocarcinoma precursor lesion.
- ASAP (atypical small acinar proliferation) - used if you have a few abnormal appearing glands... but can't decide between prostate adenocarcinoma & benign.
- Chronic inflammation.
- Acute inflammation - can result in an elevated PSA and may have prompted the biopsy you're looking at.
- Nodular hyperplasia of the prostate; AKA benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH).
- Not diagnosed on needle biopsies.
- BPH is technically incorrect -- the process is a hyperplasia.
- Hyperplasia = proliferation of cells, hypertrophy = enlargement of cells.
- How to remember? A. Prostate... hyperPlasia.
- Hyperplasia = proliferation of cells, hypertrophy = enlargement of cells.
Clinical history
- PSA (serum).
- >10 ng/mL worrisome for prostate cancer.
- Normal is age dependent - increases with age, usu. cut-off ~ 4 ng/mL.
- HIFU = High Intensity Focused Ultrasound - an ablation procedure for prostate cancer.[12]
Specific conditions
Prostatic nodular hyperplasia
- AKA nodular hyperplasia of the prostate.
- AKA benign prostatic hyperplasia (abbreviated BPH).
- AKA benign prostatic hypertrophy.
- This is a misnomer. It is not a hypertrophy.
General
- Very common.
- Incidence increases with age.
Clinical - mnemonic I WISH 2p:[13]
- Intermittency.
- Weak stream.
- Incomplete emptying.
- Straining.
- Hesitancy.
- Post-void dribbling.
- Prolonged voiding.
Treatment:
- Medications.
- Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP).
Microscopic
Features:
- Stromal and/or glandular hyperplasia.
Note:
- Should not be diagnosed on core biopsy!
DDx:
- Urothelial carcinoma - significant nuclear atypia.
Images
Sign out
Urothelium present
PROSTATE TISSUE, TRANSURETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE (TURP): - BENIGN PROSTATIC TISSUE WITH GLANDULAR AND STROMAL PROLIFERATION. - UROTHELIAL MUCOSA WITH A MILD LYMPHOCYTIC INFILTRATE. - NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
PROSTATE TISSUE, TRANSURETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE (TURP) AND URINARY BLADDER NECK: - BENIGN PROSTATIC TISSUE WITH GLANDULAR AND STROMAL PROLIFERATION. - UROTHELIUM WITH THE CHANGES OF CYSTITIS CYSTICA ET GLANDULARIS. - NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
PROSTATE TISSUE, TRANSURETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE (TURP) AND URINARY BLADDER NECK: - BENIGN PROSTATIC TISSUE WITH GLANDULAR AND STROMAL PROLIFERATION, AND FOCAL ACUTE AND CHRONIC INFLAMMATION. - UROTHELIUM WITH THE CHANGES OF CYSTITIS CYSTICA ET GLANDULARIS. - NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
No urothelium present
PROSTATE GLAND, TRANSURETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE (TURP): - BENIGN PROSTATIC TISSUE WITH GLANDULAR AND STROMAL PROLIFERATION.
Post-TURP granuloma present
PROSTATE TISSUE, TRANSURETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE (TURP): - BENIGN PROSTATIC TISSUE WITH GLANDULAR AND STROMAL PROLIFERATION WITH PROMINENT BLOOD VESSELS AND SQUAMOUS METAPLASIA. - PALISADING GRANULOMA WITH NECROTIC CORE, SEE COMMENT. - UROTHELIAL MUCOSA WITH A MILD INFLAMMATORY INFILTRATE. - NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY. COMMENT: This is morphologically consistent with a post-TURP granuloma.
Acute inflammation of the prostate gland
| Prostate gland | |
|---|---|
| External resources | |
| EHVSC | 10176 |
- AKA prostate gland with acute inflammation.
General
- A may lead to an increase in the PSA and prompt biopsy.
Note:
- "Prostatitis" is considered a clinical diagnosis.
- Cases are signed out as "acute inflammation".
- Some pathologists do not comment on the presence (or absence) of inflammation.
- Cases are signed out as "acute inflammation".
Microscopic
Features:
- Neutrophils within the glands, between the epithelial cells or within the stroma - key feature.
- +/-Chronic inflammation (lymphocytes) within the surrounding stroma.
DDx:
Image
Sign out
G. PROSTATE, LEFT LATERAL SUPERIOR, BIOPSY: - BENIGN PROSTATE TISSUE; - FOCAL ACUTE INFLAMMATION.
G. PROSTATE, LEFT LATERAL SUPERIOR, BIOPSY: - BENIGN PROSTATE TISSUE; - FOCAL ACUTE AND CHRONIC INFLAMMATION.
Chronic inflammation not otherwise specified
General
- Common.
- Non-specific finding.
- Etiology usually not apparent on histomorphology.
Microscopic
Features:
- Lymphocytes within the glands, between the epithelial cells or within the stroma - key feature.
Notes:
- Rare scattered lymphocytes are common, especially in the central portion of the gland.
- "Focal" one field with a 2.2 mm diameter involved.
Image
Sign out
G. PROSTATE, LEFT LATERAL SUPERIOR, BIOPSY: - BENIGN PROSTATE TISSUE; - FOCAL CHRONIC INFLAMMATION.
F. PROSTATE, RIGHT MEDIAL MIDZONE, BIOPSY: - BENIGN PROSTATE TISSUE; - CHRONIC INFLAMMATION.
Note:
- Opinion is divided on whether this finding should be reported.
- Advocates for reporting inflammation say "[i]t is just reporting what you see and may explain the bump in PSA."
- Naysayers opine that "[i]t may provide false assurance that no cancer is present."
Granulomatous prostatitis
Atrophy of the prostate
General
- Small glands (may mimic Gleason score 3 pattern).
Microscopic
Features:
- Glands often have a jagged edges/prows (in cancer the glands tend to have round edges) - key feature.
- Prow = forward most part of a ship's bow that cuts through the water.[14]
- You may have come across prow in the context of breast cancer, i.e. tubular carcinoma.
- Prow = forward most part of a ship's bow that cuts through the water.[14]
- Gland density is usually lower than in prostate carcinoma, i.e. glands are not back-to-back - key feature.
- Atrophic glands are often hyperchromatic.[15]
- Scant cytoplasm - usually.
Negatives:
- Nuclei like normal, i.e. nucleoli uncommon.
- Should have two cell layers, i.e. epithelial and myoepithelial (may be difficult to see).
Notes:
- Atrophic glands may be scattered with non-atrophic ones.
- IHC may be misleading - basal cell loss.
DDx:
Atrophy versus cancer
| Histologic feature | Atrophy | Cancer |
|---|---|---|
| Glandular architecture/ arrangement |
angulated glands, may look like they originate from one large duct |
round glands, often back-to-back |
| Nuclear hyperchromasia |
marked | moderate |
| Cytoplasm | scant/minimal | moderate, may be amphophilic |
| Basal cells | may be visible | absent |
| Nucleoli | absent | present |
| Secretions in glands |
no | yes - eosinophilic or blue |
Sign out
Generally, this finding is not reported; it is considered a normal finding.
Prostatic infarct
- AKA prostatic infarction.
General
- Rare < 0.1% of core biopsies.[16]
- Can mimic cancer - urothelial carcinoma.[16]
- Prostate usually large.
Microscopic
Features:
- Classic findings of necrosis:
- Karyolysis (loss of nuclei), karyorrhexis (frag. of nuclei), pyknosis (small shrunken nuclei).
- +/-Squamous metaplasia of prostate gland epithelium.
Notes:
- Corpora amylacea - help... call it benign.
- Glands maintain normal spacing.
DDx:
- Urothelial carcinoma with squamous differentiation.
Image:
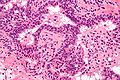
Basal cell hyperplasia of the prostate
General
- Benign lesion that can be misdiagnosed as cancer.[17]
Microscopic
Features:[18]
- Low power gland architecture near normal.[19][20]
- Glands not as small as cancer.
- Folds in gland lumina.
- No nuclear hyperchromasia.
- Two cell populations (as in normal prostate glands).
- Basal cells may have nucleoli.
DDx:
- High-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia - has nuclear hyperchromasia, architecture usually different (micropapillary, tufted, cribriform or flat).
- Prostatic adenocarcinoma.
Image:
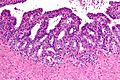
High-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia
- Abbreviated as HGPIN.
- May be referred to as prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia, abbreviated PIN.
General
- Thought to be a precursor lesion for prostate adenocarcinoma.
Low-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia:
- Not reported and generally believed to be irrelevant biologically/clinically.
- PIN not otherwise specified refers to HGPIN.
- Low-grade PIN has the architecture of HGPIN but lacks the nuclear atypia.
Microscopic
- Medium to large glands with architectural changes - see HGPIN architecture below.
- Described as "epithelial hyperplasia".
- Diagnosed on basis of nuclear changes.
- Hyperchromatic nuclei - key (low power) feature.
- Nucleoli present - key (high power) feature.
- Often increased NC ratio.
- Nuclear enlargement.
Notes:
- Nucleoli should be visible with the 20x objective.
- If one uses the 40x objective... one over calls.
- May need IHC for cancer versus HGPIN.
- Nucleoli should be present in >= 10% of cells in a gland to call it HGPIN.[25]
- This criterium is not required by all pathologists.
DDx:
- Basal cell hyperplasia of the prostate.
- Intraductal carcinoma of the prostate.
- Prostatic adenocarcinoma - glands with HGPIN have two or more distinct cells layers.
- PIN-like prostatic ductal adenocarcinoma - glands crowded.
- Benign prostate - HPGIN has nuclear changes.
HGPIN architecture
There are several forms:[26][27]
- Flat - uncommon.
- Tufting - common.
- Micropapillary - common.
- Cribriform - rare.
Note:
- The architectural pattern is not thought to have any prognostic significance; however, it may be useful for differentiating it from benign prostate.
Images
IHC
- HGPIN: AMACR +ve, p63 +ve, HMWCK +ve.
- Cancer: AMACR +ve, p63 -ve, HMWCK -ve.
- Normal: AMACR -ve, p63 +ve, HMWCK +ve.
Sign out
A. PROSTATE, RIGHT LATERAL SUPERIOR, BIOPSY: - HIGH-GRADE PROSTATIC INTRAEPITHELIAL NEOPLASIA; - NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
Atypical small acinar proliferation
- Abbreviated ASAP.
- AKA suspicious for carcinoma.[28]
- ASAP is preferred as it does not contain the word carcinoma and, thus, cannot be misread as carcinoma, i.e. positive for malignancy.
General
- It is a waffle diagnosis, i.e. it is not considered an entity with a distinct pathobiology.[29]
- Analogous to ASCUS on a pap test.
- ASAP should be used sparingly.
- One benchmark is < 3-5% of biopsies.[30]
- Never diagnosed on excision, i.e. prostatectomy specimen.
Association with adenocarcinoma
- On subsequent biopsy - chance of finding adenocarcinoma is approximately 40%; this is higher than if there is high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (HGPIN).[31]
Management
- ASAP is considered an indication for re-biopsy;[32] in one survey of urologists[33] 41/42 (~98%) of respondents considered it a sufficient reason to re-biopsy.
Microscopic
Features:
- Atypical appearing acini.
- Limited extent, e.g. 2-3 glands.
Notes:
- IHC not contributory.
- Deeper cuts didn't yield anything - important.
DDx:
Prostate cancer
This is a big topic that is dealt with in its own article.
See also
References
- ↑ McNeal, JE. (Aug 1988). "Normal histology of the prostate.". Am J Surg Pathol 12 (8): 619-33. PMID 2456702.
- ↑ Christian JD, Lamm TC, Morrow JF, Bostwick DG (January 2005). "Corpora amylacea in adenocarcinoma of the prostate: incidence and histology within needle core biopsies". Mod. Pathol. 18 (1): 36–9. doi:10.1038/modpathol.3800250.
- ↑ Trpkov, K.; Bartczak-McKay, J.; Yilmaz, A. (Aug 2009). "Usefulness of cytokeratin 5/6 and AMACR applied as double sequential immunostains for diagnostic assessment of problematic prostate specimens.". Am J Clin Pathol 132 (2): 211-20; quiz 307. doi:10.1309/AJCPGFJP83IXZEUR. PMID 19605815.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Cina, SJ.; Silberman, MA.; Kahane, H.; Epstein, JI. (May 1997). "Diagnosis of Cowper's glands on prostate needle biopsy.". Am J Surg Pathol 21 (5): 550-5. PMID 9158679.
- ↑ URL: http://webpathology.com/image.asp?case=21&n=4. Accessed on: 3 June 2013.
- ↑ URL: http://surgpathcriteria.stanford.edu/prostate/adenocarcinoma/benign-vs-carcinoma.html. Accessed on: 10 January 2013.
- ↑ Leroy X, Ballereau C, Villers A, et al. (April 2003). "MUC6 is a marker of seminal vesicle-ejaculatory duct epithelium and is useful for the differential diagnosis with prostate adenocarcinoma". Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 27 (4): 519–21. PMID 12657938.
- ↑ Itami, Y.; Nagai, Y.; Kobayashi, Y.; Shimizu, N.; Yamamoto, Y.; Minami, T.; Hayashi, T.; Nozawa, M. et al. (Jul 2012). "[A case of prostatic cancer with a low PSA level accompanied with cystic formation requiring differentiation from adenocarcinoma of the seminal vesicle].". Hinyokika Kiyo 58 (7): 349-53. PMID 22895132.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Tarján, M.; Ottlecz, I.; Tot, T. (Jan 2009). "Primary adenocarcinoma of the seminal vesicle.". Indian J Urol 25 (1): 143-5. doi:10.4103/0970-1591.45557. PMID 19468449.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 Terada, T. (2011). "Monstrous epithelial cell clusters in the seminal vesicle.". Int J Clin Exp Pathol 4 (7): 727-30. PMID 22076175.
- ↑ URL: http://www.cancer.gov/dictionary?cdrid=446218. Accessed on: 23 February 2012.
- ↑ URL: http://www.internationalhifu.com/what-is-hifu-mainmenu-132.html. Accessed on: 15 June 2010.
- ↑ Shiau, Carolyn; Toren, Andrew (2006). Toronto Notes 2006: Comprehensive Medical Reference (Review for MCCQE 1 and USMLE Step 2) (22nd edition (2006) ed.). Toronto Notes for Medical Students, Inc.. pp. U5. ISBN 978-0968592861.
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Prow
- ↑ SN. June 3, 2009.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 Milord, RA.; Kahane, H.; Epstein, JI. (Oct 2000). "Infarct of the prostate gland: experience on needle biopsy specimens.". Am J Surg Pathol 24 (10): 1378-84. PMID 11023099.
- ↑ Cleary, KR.; Choi, HY.; Ayala, AG. (Dec 1983). "Basal cell hyperplasia of the prostate.". Am J Clin Pathol 80 (6): 850-4. PMID 6195916.
- ↑ URL: http://pathologyoutlines.com/prostate.html#bch. Accessed on: 28 June 2010.
- ↑ URL: http://www.nature.com/modpathol/journal/v16/n6/fig_tab/3880810f1.html. Accessed on: 28 June 2010.
- ↑ URL: http://www.nature.com/modpathol/journal/v16/n6/fig_tab/3880810f2.html. Accessed on: 28 June 2010.
- ↑ Srigley, JR.; Merrimen, JL.; Jones, G.; Jamal, M. (Dec 2010). "Multifocal high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia is still a significant risk factor for adenocarcinoma.". Can Urol Assoc J 4 (6): 434. PMID 21191509.
- ↑ Herawi, M.; Kahane, H.; Cavallo, C.; Epstein, JI. (Jan 2006). "Risk of prostate cancer on first re-biopsy within 1 year following a diagnosis of high grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia is related to the number of cores sampled.". J Urol 175 (1): 121-4. doi:10.1016/S0022-5347(05)00064-9. PMID 16406886.
- ↑ Amin, Mahul B. (2010). Diagnostic Pathology: Genitourinary (1st ed.). Amirsys. pp. 3-56. ISBN 978-1931884280.
- ↑ Chin, AI.; Dave, DS.; Rajfer, J. (2007). "Is repeat biopsy for isolated high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia necessary?". Rev Urol 9 (3): 124-31. PMC 2002502. PMID 17934569. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2002502/.
- ↑ Amin, Mahul B. (2010). Diagnostic Pathology: Genitourinary (1st ed.). Amirsys. pp. 3-55. ISBN 978-1931884280.
- ↑ Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 380. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ Bostwick, DG.; Qian, J. (Mar 2004). "High-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia.". Mod Pathol 17 (3): 360-79. doi:10.1038/modpathol.3800053. PMID 14739906. http://www.nature.com/modpathol/journal/v17/n3/pdf/3800053a.pdf.
- ↑ THvdK. 19 June 2010.
- ↑ Flury SC, Galgano MT, Mills SE, Smolkin ME, Theodorescu D (January 2007). "Atypical small acinar proliferation: biopsy artefact or distinct pathological entity". BJU International 99 (4): 780-5. PMID 17378841. http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/journal/118508438/abstract.
- ↑ THvdK. 19 June 2010.
- ↑ Leite KR, Camara-Lopes LH, Cury J, Dall'oglio MF, Sañudo A, Srougi M (June 2008). "Prostate cancer detection at rebiopsy after an initial benign diagnosis: results using sextant extended prostate biopsy". Clinics 63 (3): 339–42. PMID 18568243. http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1807-59322008000300009&lng=en&nrm=iso&tlng=en.
- ↑ Bostwick DG, Meiers I (July 2006). "Atypical small acinar proliferation in the prostate: clinical significance in 2006". Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 130 (7): 952–7. PMID 16831049. http://journals.allenpress.com/jrnlserv/?request=get-abstract&issn=0003-9985&volume=130&page=952.
- ↑ Rubin MA, Bismar TA, Curtis S, Montie JE (July 2004). "Prostate needle biopsy reporting: how are the surgical members of the Society of Urologic Oncology using pathology reports to guide treatment of prostate cancer patients?". Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 28 (7): 946–52. PMID 15223967.
External links
- CAP prostate check list - cap.org.
- CAP prostate protocol - cap.org.
- Gleason score quiz - Johns Hopkins Prostate Center.