Difference between revisions of "Ovarian tumours"
m (→Metastatic ovarian tumours: fix link) |
|||
| (253 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
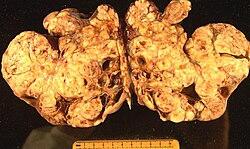
The article examines '''ovarian tumours''' including '''ovarian cancer'''. | [[Image:Ovarian carcinoma.JPG|thumb|250px|right|[[Gross pathology|Gross]] photo of a [[malignant]] ovarian tumour. (WC/Doc James)]] | ||
The article examines '''ovarian tumours''' including '''ovarian cancer'''. | |||
==Classification | An introduction to the ovary is in the ''[[ovary]]'' article, which also deals benign cysts. | ||
What was labeled "ovarian cancer" in the past may really arise from [[fallopian tube]].<ref name=pmid19574767>{{Cite journal | last1 = Hirst | first1 = JE. | last2 = Gard | first2 = GB. | last3 = McIllroy | first3 = K. | last4 = Nevell | first4 = D. | last5 = Field | first5 = M. | title = High rates of occult fallopian tube cancer diagnosed at prophylactic bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy. | journal = Int J Gynecol Cancer | volume = 19 | issue = 5 | pages = 826-9 | month = Jul | year = 2009 | doi = 10.1111/IGC.0b013e3181a1b5dc | PMID = 19574767 }}</ref> The label ''tubo-ovarian cancer'' | |||
has been advocated to address this change. These tumours are dealt with in this article. | |||
=Clinical= | |||
Gynecologists use a scoring system to help decide which patients need surgery and estimate their pre-op risk of malignancy. | |||
===Risk of malignancy index=== | |||
*Abbreviated ''RMI''. | |||
*There are two versions.<ref name=ukguide>URL: [http://www.sign.ac.uk/guidelines/fulltext/75/section3.html http://www.sign.ac.uk/guidelines/fulltext/75/section3.html]. Accessed on: 16 September 2011.</ref> | |||
====Definition==== | |||
:<math>RMI\ score = ultrasound\ score\ *\ menopausal\ score\ *\ CA125\ level\ [U/ml].</math> | |||
====Elements==== | |||
Elements & points (RMI 2):<ref name=ukguide>URL: [http://www.sign.ac.uk/guidelines/fulltext/75/section3.html http://www.sign.ac.uk/guidelines/fulltext/75/section3.html]. Accessed on: 16 September 2011.</ref> | |||
#Ultrasound features. | |||
#*Significant findings: multilocular cyst, solid component, bilateral lesions, ascites, suspected intra-abdominal [[metastases]] (one finding=1 point, two or more findings=4 points). | |||
#Menopause/pre-menopause status (menopausal=4 points, pre-menopausal=1 point). | |||
#CA-125 (blood test) in ''U/ml''. | |||
====Interpretation==== | |||
*RMI > 200 -- predicts malignancy. | |||
=Classification= | |||
===The Latta rule of fives=== | ===The Latta rule of fives=== | ||
Can be divided as follows:<ref>PBoD | Can be divided as follows:<ref name=Ref_PBoD1093>{{Ref PBoD|1093}}</ref><ref>LAE. 22 October 2009.</ref> | ||
# Surface epithelial tumours (most common). | # Surface epithelial tumours (most common). | ||
# Sex cord stromal tumours (SCSTs). | # Sex cord stromal tumours (SCSTs). | ||
# Germ cell tumours (GCTs). | # [[Germ cell tumours]] (GCTs). | ||
# Metastatic tumours. | # Metastatic tumours. | ||
# Rare stuff that doesn't fit in any of the above (e.g. leiomyoma, angiosarcoma). | # Rare stuff that doesn't fit in any of the above (e.g. [[leiomyoma]], [[angiosarcoma]], [[ovarian small cell carcinoma of the hypercalcemic type]]). | ||
Surface epithelial tumours: | Surface epithelial tumours: | ||
# Serous. | # [[Serous carcinoma of the ovary|Serous carcinoma]]. | ||
# Endometrioid. | #* High-grade serous carcinoma. † | ||
# Mucinous. | #* Low-grade serous carcinoma. | ||
# Brenner tumour. | # [[Endometrioid carcinoma of the ovary|Endometrioid carcinoma]]. | ||
# [[Mucinous carcinoma of the ovary|Mucinous carcinoma]]. | |||
# [[Clear cell carcinoma of the ovary|Clear cell carcinoma]]. | |||
# [[Brenner tumour]]. | |||
Note: | |||
* † Transitional cell tumours<ref name=Ref_WMSP401>{{Ref WMSP|401}}</ref> are now grouped with high-grade serous carcinoma.<ref name=pmid23681072>{{Cite journal | last1 = Takeuchi | first1 = T. | last2 = Ohishi | first2 = Y. | last3 = Imamura | first3 = H. | last4 = Aman | first4 = M. | last5 = Shida | first5 = K. | last6 = Kobayashi | first6 = H. | last7 = Kato | first7 = K. | last8 = Oda | first8 = Y. | title = Ovarian transitional cell carcinoma represents a poorly differentiated form of high-grade serous or endometrioid adenocarcinoma. | journal = Am J Surg Pathol | volume = 37 | issue = 7 | pages = 1091-9 | month = Jul | year = 2013 | doi = 10.1097/PAS.0b013e3182834d41 | PMID = 23681072 }}</ref><ref name=pmid23018212>{{Cite journal | last1 = Ali | first1 = RH. | last2 = Seidman | first2 = JD. | last3 = Luk | first3 = M. | last4 = Kalloger | first4 = S. | last5 = Gilks | first5 = CB. | title = Transitional cell carcinoma of the ovary is related to high-grade serous carcinoma and is distinct from malignant brenner tumor. | journal = Int J Gynecol Pathol | volume = 31 | issue = 6 | pages = 499-506 | month = Nov | year = 2012 | doi = 10.1097/PGP.0b013e31824d7445 | PMID = 23018212 }}</ref> | |||
Sex cord stromal tumours: | Sex cord stromal tumours: | ||
#Granulosa cell tumour (adult type, juvenile type). | #[[Granulosa cell tumour]] ([[Adult granulosa cell tumour|adult type]], [[Juvenile granulosa cell tumour|juvenile type]]). | ||
#Sertoli cell tumour. | #[[Sertoli cell tumour]]. | ||
#Leydig cell tumour. | #[[Leydig cell tumour]]. | ||
#Fibroma. | #[[Ovarian fibroma|Fibroma]]. | ||
#Thecoma. | #[[Thecoma]]. | ||
Germ cell tumours: | [[Germ cell tumours]]: | ||
#Dysgerminoma. | #[[Dysgerminoma]]. | ||
#Endodermal sinus tumour (yolk sac tumour). | #Endodermal sinus tumour ([[yolk sac tumour]]). | ||
#Embryonal | #[[Embryonal carcinoma]]. | ||
#Choriocarcinoma. | #[[Choriocarcinoma]]. | ||
#Teratoma. | #[[Teratoma]]. | ||
=Common special tumours= | |||
===Endometriosis-related tumours=== | ===Endometriosis-related tumours=== | ||
Tumours associated with endometriosis:<ref>LAE. 22 October 2009.</ref> | Tumours associated with endometriosis:<ref>LAE. 22 October 2009.</ref> | ||
| Line 52: | Line 84: | ||
**Granulosa-theca cell tumour. | **Granulosa-theca cell tumour. | ||
= | =A morphologic approach= | ||
Where is the tumour arising? | Where is the tumour arising? | ||
*Central location -- think GCTs and SCST. | *Central location -- think GCTs and SCST. | ||
| Line 66: | Line 98: | ||
Gland-like structures? | Gland-like structures? | ||
*Endometrioid carcinoma. | *Endometrioid carcinoma. | ||
* | *Granulosa cell tumour. | ||
"[[Dirty necrosis]]": | "[[Dirty necrosis]]": | ||
* | *Definition: cellular debris within gland lumen.<ref>[http://www.cancer.gov/cancertopics/genetics-terms-alphalist/all#D http://www.cancer.gov/cancertopics/genetics-terms-alphalist/all#D]. Accessed on: 14 September 2011.</ref> | ||
*Characteristic of colorectal adenocarcinoma, may be absent in ovarian tumours -- limited value.<ref name=pmid9421090>{{cite journal |author=DeCostanzo DC, Elias JM, Chumas JC |title=Necrosis in 84 ovarian carcinomas: a morphologic study of primary versus metastatic colonic carcinoma with a selective immunohistochemical analysis of cytokeratin subtypes and carcinoembryonic antigen |journal=Int. J. Gynecol. Pathol. |volume=16 |issue=3 |pages=245–9 |year=1997 |month=July |pmid=9421090 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | *Characteristic of colorectal adenocarcinoma, may be absent in ovarian tumours -- limited value.<ref name=pmid9421090>{{cite journal |author=DeCostanzo DC, Elias JM, Chumas JC |title=Necrosis in 84 ovarian carcinomas: a morphologic study of primary versus metastatic colonic carcinoma with a selective immunohistochemical analysis of cytokeratin subtypes and carcinoembryonic antigen |journal=Int. J. Gynecol. Pathol. |volume=16 |issue=3 |pages=245–9 |year=1997 |month=July |pmid=9421090 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | ||
=Grading of ovarian cancer= | |||
*Silverberg grading system,<ref>{{cite journal |author=Silverberg SG |title=Histopathologic grading of ovarian carcinoma: a review and proposal |journal=Int. J. Gynecol. Pathol. |volume=19 |issue=1 |pages=7-15 |year=2000 |month=January |pmid=10638449 |doi= |url=http://meta.wkhealth.com/pt/pt-core/template-journal/lwwgateway/media/landingpage.htm?issn=0277-1691&volume=19&issue=1&spage=7}}</ref> aka ''universal grading system''. | *Silverberg grading system,<ref>{{cite journal |author=Silverberg SG |title=Histopathologic grading of ovarian carcinoma: a review and proposal |journal=Int. J. Gynecol. Pathol. |volume=19 |issue=1 |pages=7-15 |year=2000 |month=January |pmid=10638449 |doi= |url=http://meta.wkhealth.com/pt/pt-core/template-journal/lwwgateway/media/landingpage.htm?issn=0277-1691&volume=19&issue=1&spage=7}}</ref> aka ''universal grading system''. | ||
*Based on ''pattern'', ''cytologic atypia'' and ''mitotic rate''. | *Based on ''pattern'', ''cytologic atypia'' and ''mitotic rate''. | ||
*System somewhat similar to [[breast]] grading, which can be remembered as: '' | *System somewhat similar to [[breast]] grading, which can be remembered as: ''TNM'' (tubular formation, [[nuclear atypia]], mitotic rate). | ||
===Silverberg system=== | ===Silverberg system=== | ||
| Line 96: | Line 128: | ||
*Grade III = 8-9. | *Grade III = 8-9. | ||
Note | Note: | ||
*Most resident microscopes have an eyepiece diameter of 22 mm. Thus, the approximate field diameter is 0.55 mm (22 mm/40 X = 0.55 mm), at highest magnification, and the field area is 0.23758 mm^2 (pi*(0.55/2)^2=0.23758 mm^2). | *Most resident microscopes have an eyepiece diameter of 22 mm. Thus, the approximate field diameter is 0.55 mm (22 mm/40 X = 0.55 mm), at highest magnification, and the field area is 0.23758 mm^2 (pi*(0.55/2)^2=0.23758 mm^2). | ||
*The number of HPFs should be adjusted if the area per field is different than 0.345 mm^2. | *The number of HPFs should be adjusted if the area per field is different than 0.345 mm^2. | ||
**If the field diameter is 0.55 mm and the sample area is 3.45 mm^2, this is equivalent to 14.52 HPFs (3.45 mm^2 / 0.23758 mm^2 = 14.52); thus, it would be appropriate to use 15 HPFs and the cut points above. | **If the field diameter is 0.55 mm and the sample area is 3.45 mm^2, this is equivalent to 14.52 HPFs (3.45 mm^2 / 0.23758 mm^2 = 14.52); thus, it would be appropriate to use 15 HPFs and the cut points above. | ||
===Predictive power of Silverberg grading=== | |||
=== | |||
Good correlation with five year survival (rounded values):<ref name=pmid12496698>{{cite journal |author=Sato Y, Shimamoto T, Amada S, Asada Y, Hayashi T |title=Prognostic value of histologic grading of ovarian carcinomas |journal=Int. J. Gynecol. Pathol. |volume=22 |issue=1 |pages=52-6 |year=2003 |month=January |pmid=12496698 |doi= |url=http://meta.wkhealth.com/pt/pt-core/template-journal/lwwgateway/media/landingpage.htm?issn=0277-1691&volume=22&issue=1&spage=52}}</ref> | Good correlation with five year survival (rounded values):<ref name=pmid12496698>{{cite journal |author=Sato Y, Shimamoto T, Amada S, Asada Y, Hayashi T |title=Prognostic value of histologic grading of ovarian carcinomas |journal=Int. J. Gynecol. Pathol. |volume=22 |issue=1 |pages=52-6 |year=2003 |month=January |pmid=12496698 |doi= |url=http://meta.wkhealth.com/pt/pt-core/template-journal/lwwgateway/media/landingpage.htm?issn=0277-1691&volume=22&issue=1&spage=52}}</ref> | ||
*Grade I = 90%. | *Grade I = 90%. | ||
| Line 114: | Line 139: | ||
*Grade III = 40%. | *Grade III = 40%. | ||
==Surface epithelial tumours | ==Peritoneal implants== | ||
Most common subtypes - in short:<ref>PBoD | ===General=== | ||
Applies only to: | |||
*[[Serous borderline tumour]]. | |||
*[[Seromucinous borderline tumour]]. | |||
====Classification==== | |||
There are two types:<ref name=pmid17727474>{{Cite journal | last1 = Stewart | first1 = CJ. | last2 = Brennan | first2 = BA. | last3 = Crook | first3 = ML. | last4 = Russell | first4 = P. | title = Value of elastin staining in the assessment of peritoneal implants associated with ovarian serous borderline tumours. | journal = Histopathology | volume = 51 | issue = 3 | pages = 313-21 | month = Sep | year = 2007 | doi = 10.1111/j.1365-2559.2007.02789.x | PMID = 17727474 }}</ref> | |||
#Non-invasive implants. | |||
#*Subdivided into: | |||
#*#Epithelial. | |||
#*#Desmoplastic. | |||
#Invasive implants -- malignant cells within the stroma. | |||
Notes: | |||
*Invasive implants are significant clinically. | |||
*Non-invasive implants have little clinical significance. | |||
===Microscopic=== | |||
====Non-invasive implant==== | |||
Features (non-invasive implant epithelial-type):<ref name=pmid3179935>{{Cite journal | last1 = Bell | first1 = DA. | last2 = Weinstock | first2 = MA. | last3 = Scully | first3 = RE. | title = Peritoneal implants of ovarian serous borderline tumors. Histologic features and prognosis. | journal = Cancer | volume = 62 | issue = 10 | pages = 2212-22 | month = Nov | year = 1988 | doi = | PMID = 3179935 }}</ref> | |||
*Papillary proliferation on surface. | |||
*+/-Smooth contoured invagination into: | |||
**Submesothelium. | |||
**Omental fat lobules. | |||
*No "stromal response": | |||
**Fibrosis. | |||
*+/-[[Psammoma bodies]]. | |||
Features (non-invasive implant desmoplastic-type):<ref name=pmid3179935>{{Cite journal | last1 = Bell | first1 = DA. | last2 = Weinstock | first2 = MA. | last3 = Scully | first3 = RE. | title = Peritoneal implants of ovarian serous borderline tumors. Histologic features and prognosis. | journal = Cancer | volume = 62 | issue = 10 | pages = 2212-22 | month = Nov | year = 1988 | doi = | PMID = 3179935 }}</ref> | |||
*Stromal reaction restricted to the: | |||
**Serosal surface. | |||
**Fibrous septae. | |||
*+/-[[Psammoma bodies]]. | |||
Note: | |||
*No "destructive invasion". | |||
**Irregular infiltration. | |||
====Invasive implant==== | |||
Features (invasive implant):<ref name=pmid3179935/> | |||
*Irregular infiltration of tumour into the submesothelial tissue - '''key feature''' - characterized by: | |||
**+/-Solid nests. | |||
**+/-Small glands +/- irregular "bridging" connections between glands - '''common'''. | |||
*Nuclear atypia - '''common'''. | |||
*+/-[[Psammoma bodies]]. | |||
===Stains=== | |||
*Elastin stain:<ref name=pmid17727474/> | |||
**Non-invasive implants are sit superficial to the peritoneal elastic lamina (PEL). | |||
**Invasive implants are deep to the PEL. | |||
Note: | |||
*Elastin layer is '''not''' present in the omentum. | |||
===IHC=== | |||
*Elastin stain. | |||
=Staging of ovarian cancer= | |||
*The CAP protocol talks of in the pelvis and outside the pelvis - pT2 versus pT3. | |||
*Omental involvement is considered outside the pelvis; it is pT3.<ref>URL: [http://ovariancancer.about.com/od/testsdiagnosis/a/FIGO_stages.htm http://ovariancancer.about.com/od/testsdiagnosis/a/FIGO_stages.htm]. Accessed on: 8 July 2013.</ref> | |||
=Surface epithelial tumours= | |||
Most common subtypes - in short:<ref>{{Ref PBoD|1096-7}}</ref> | |||
*Serous: | *Serous: | ||
**Columnar cells | **Columnar cells. | ||
**Cilia | **Cilia. | ||
**Psammoma bodies | **[[Psammoma bodies]]. | ||
**Papillae | **Papillae. | ||
*Endometrioid: | *Endometrioid: | ||
**Tubular glands | **Tubular glands. | ||
**Squamous differentiation (eosinophilic cytoplasm, well-defined cell borders, +/-keratin). | |||
*Mucinous: | *Mucinous: | ||
**Tall columnar cells with mucin | **Tall columnar cells with mucin. | ||
**Glands with mucin. | **Glands with mucin. | ||
'''Where to start when considering a malignant (epithelial) tumour of the ovary:''' | '''Where to start when considering a malignant (epithelial) tumour of the ovary:''' | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable sortable" | ||
!Features | |||
! Serous | |||
! Endometrioid | |||
! Mucinous | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | |Histology | ||
| low grade: cilia, columnar cells, [[psammoma bodies]], papillary arch.; high grade: marked nuclear pleomorphism, prominent [[red nucleoli]], [[psammoma bodies]] | |||
| gland forming - esp. cribriforming, endometrium-like | |||
| mucinous glands, colon-like | |||
|- | |- | ||
|Differentiators | |Differentiators | ||
| cilia, [[psammoma bodies]] | |||
| squamous metaplasia | |||
| mucin, often lack of [[necrosis]] | |||
|- | |- | ||
|Associations | |Associations | ||
| atrophy | |||
| [[endometriosis]], [[endometrial hyperplasia]] | |||
| (?) | |||
|- | |- | ||
|Typical age | |Typical age | ||
| usually 60s+ | |||
| 40-60 | |||
| varies (?) | |||
|- | |- | ||
|Grade | |Grade | ||
| typically high grade | |||
| typically low grade | |||
| often low | |||
|- | |- | ||
|IHC | |IHC | ||
| p53 +ve (diffuse), WT-1 +ve, CA-125 +ve, D2-40 +ve | |||
| WT-1 -ve | |||
| CK7 +ve, CK20 +ve (other tumours CK7 +ve, CK20 -ve) | |||
|- | |- | ||
|Main DDx | |Main DDx | ||
| poorly diff. endometrioid | |||
| serous | |||
| metastatic tumour (usually GI) | |||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
==Serous tumours== | ==Serous tumours - overview== | ||
===Classification<ref>PBoD | ===General=== | ||
*Most common malignant ovarian tumour. | |||
====Classification==== | |||
Based on features predictive of behaviour:<ref name=Ref_PBoD1096>{{Ref PBoD |1096}}</ref> | |||
*Benign. | *Benign. | ||
*Borderline. | *Borderline. | ||
**May have pseudostratification of epithelial cells. | **May have pseudostratification of epithelial cells. | ||
**"Usually, ''borderline'' if first impression is ''borderline''."<ref>LAE 19 | **"Usually, ''borderline'' if first impression is ''borderline''."<ref>LAE. 19 February 2009.</ref> | ||
*Malignant. | *Malignant. | ||
**Cytologic atypia. | **Cytologic atypia. | ||
** | **+/-Papillae. | ||
=== | ===Microscopic=== | ||
Features:<ref name=Ref_PBoD1096>{{Ref PBoD |1096}}</ref> | |||
*Tubal like epithelium: | *Tubal like epithelium: | ||
**Ciliated. | **Ciliated. | ||
**Columnar. | **Columnar. | ||
*Papillae. | *Papillae. | ||
*Psammoma bodies (concentric | *[[Psammoma bodies]] (concentric [[calcification]]s). | ||
Note: | Note: | ||
*In ''serous borderline tumours'', ''micropapillae'' are thought to have significance -- assoc. with increased risk of distant recurrence<ref> | *In ''serous borderline tumours'', ''micropapillae'' are thought to have significance -- assoc. with increased risk of distant recurrence<ref>LAE. 19 February 2009.</ref><ref name=pmid15897738>URL: [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15897738 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15897738]. Accessed on: 7 April 2011.</ref><ref>{{cite journal |author=Piura B, Rabinovich A, Yanai-Inbar I |title=Micropapillary serous carcinoma of the ovary: case report and review of literature |journal=Eur. J. Gynaecol. Oncol. |volume=21 |issue=4 |pages=374–6 |year=2000 |pmid=11055486 |doi= |url=}}</ref> - though is disputed.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Prat J, De Nictolis M |title=Serous borderline tumors of the ovary: a long-term follow-up study of 137 cases, including 18 with a micropapillary pattern and 20 with microinvasion |journal=Am. J. Surg. Pathol. |volume=26 |issue=9 |pages=1111-28 |year=2002 |month=September |pmid=12218568 |doi= |url=http://meta.wkhealth.com/pt/pt-core/template-journal/lwwgateway/media/landingpage.htm?issn=0147-5185&volume=26&issue=9&spage=1111}}</ref> | ||
*Psammoma bodies may be seen in [[endosalpingiosis]].<ref name=pmid1774734>{{cite journal |author=Hallman KB, Nahhas WA, Connelly PJ |title=Endosalpingiosis as a source of psammoma bodies in a Papanicolaou smear. A case report |journal=J Reprod Med |volume=36 |issue=9 |pages=675–8 |year=1991 |month=September |pmid=1774734 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | |||
==Serous carcinoma of the ovary== | |||
*[[AKA]] ''ovarian [[serous carcinoma]]''. | |||
{{Main|Serous carcinoma of the ovary}} | |||
== | ==Serous cystadenoma of the ovary== | ||
* | *[[AKA]] ''ovarian serous cystadenoma''. | ||
*Related to ''adenofibroma'' and ''serous cystadenofibroma''. | |||
{{Main|Serous cystadenoma of the ovary}} | |||
== | ==Ovarian serous borderline tumour== | ||
* | *[[AKA]] ''serous borderline tumour of the ovary''. | ||
* | *[[AKA]] ''serous tumour of low malignant potential of the ovary'', abbreviated ''SLMP''.<ref name=pmid10836293>{{Cite journal | last1 = Seidman | first1 = JD. | last2 = Kurman | first2 = RJ. | title = Ovarian serous borderline tumors: a critical review of the literature with emphasis on prognostic indicators. | journal = Hum Pathol | volume = 31 | issue = 5 | pages = 539-57 | month = May | year = 2000 | doi = | PMID = 10836293 }}</ref><ref name=pmid10881733>{{Cite journal | last1 = Dietel | first1 = M. | last2 = Hauptmann | first2 = S. | title = Serous tumors of low malignant potential of the ovary. 1. Diagnostic pathology. | journal = Virchows Arch | volume = 436 | issue = 5 | pages = 403-12 | month = May | year = 2000 | doi = | PMID = 10881733 }}</ref> | ||
{{Main|Serous borderline tumour}} | |||
=== | ==Mucinous ovarian tumours== | ||
* | |||
* | ==General== | ||
* | *Common. | ||
*Tumours may be heterogenous; benign appearing epithelium may be beside clearly malignant epithelium. | |||
*Good sampling of mucinous tumours, i.e. many blocks, is important to lessen the chance of undercalling them. | |||
===Subtypes=== | ===Subtypes=== | ||
| Line 195: | Line 318: | ||
Comparison of mucosa: | Comparison of mucosa: | ||
*Normal endocervical mucosa: [http://pathology.mc.duke.edu/research/Histo_course/endocx.jpg endocervical mucosa]. | *Normal endocervical mucosa: [http://pathology.mc.duke.edu/research/Histo_course/endocx.jpg endocervical mucosa (duke.edu)]. | ||
*Normal | *Normal gastric mucosa: [http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Normal_gastric_mucosa_intermed_mag.jpg gastric mucosa (WC)]. | ||
===Classification=== | ===Classification=== | ||
*Benign. (Dx: mucinous cystadenoma) | *Benign. (Dx: [[Mucinous_cystadenoma_of_the_ovary|mucinous cystadenoma]] ''or'' mucinous adenofibroma ''or'' mucinous cystadenofibroma) | ||
**Single layer of cells. | **Single layer of cells. | ||
*Borderline. (Dx: ''mucinous tumour of uncertain malignant potential'' or ''borderline mucinous tumour'') | *Borderline. (Dx: ''mucinous tumour of uncertain malignant potential'' or ''borderline mucinous tumour'') | ||
| Line 206: | Line 329: | ||
**Usually intestinal subtype. | **Usually intestinal subtype. | ||
==Seromucinous borderline tumour of the ovary== | |||
* | *[[AKA]] ''endocervical-type mucinous and mixed cell-type tumour''.<ref name=pmid12459620>{{Cite journal | last1 = Shappell | first1 = HW. | last2 = Riopel | first2 = MA. | last3 = Smith Sehdev | first3 = AE. | last4 = Ronnett | first4 = BM. | last5 = Kurman | first5 = RJ. | title = Diagnostic criteria and behavior of ovarian seromucinous (endocervical-type mucinous and mixed cell-type) tumors: atypical proliferative (borderline) tumors, intraepithelial, microinvasive, and invasive carcinomas. | journal = Am J Surg Pathol | volume = 26 | issue = 12 | pages = 1529-41 | month = Dec | year = 2002 | doi = | PMID = 12459620 }}</ref> | ||
===General=== | |||
*Rare. | |||
== | *Associated with [[endometriosis]]. | ||
=== | ===Gross=== | ||
*Associated with [[endometriosis]] | *Mucin-filled cysts. | ||
Image: | |||
* | *[http://alf3.urz.unibas.ch/pathopic/e/getpic-fra.cfm?id=009520 Seromucinous borderline tumor of the ovary (unibas.ch)]. | ||
== | ===Microscopic=== | ||
Features: | |||
#Simple mucinous epithelium - endocervical type.<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Shappell | first1 = HW. | last2 = Riopel | first2 = MA. | last3 = Smith Sehdev | first3 = AE. | last4 = Ronnett | first4 = BM. | last5 = Kurman | first5 = RJ. | title = Diagnostic criteria and behavior of ovarian seromucinous (endocervical-type mucinous and mixed cell-type) tumors: atypical proliferative (borderline) tumors, intraepithelial, microinvasive, and invasive carcinomas. | journal = Am J Surg Pathol | volume = 26 | issue = 12 | pages = 1529-41 | month = Dec | year = 2002 | doi = | PMID = 12459620 }}</ref> | |||
#*Tall columnar epithelium with apical pale cytoplasm. | |||
#Simple serous epithelium - with cilia. | |||
== | ==Mucinous cystadenoma of the ovary== | ||
* [[ | *[[AKA]] ''ovarian mucinous cystadenoma''. | ||
{{Main|Mucinous cystadenoma of the ovary}} | |||
==Mucinous borderline tumour of the ovary== | |||
* | *[[AKA]] ''ovarian mucinous borderline tumour''. | ||
*[[AKA]] ''ovarian mucinous tumour of low malignant potential''.<ref name=pmid21464732>{{Cite journal | last1 = Khunamornpong | first1 = S. | last2 = Settakorn | first2 = J. | last3 = Sukpan | first3 = K. | last4 = Suprasert | first4 = P. | last5 = Siriaunkgul | first5 = S. | title = Mucinous tumor of low malignant potential (borderline or atypical proliferative tumor) of the ovary: a study of 171 cases with the assessment of intraepithelial carcinoma and microinvasion. | journal = Int J Gynecol Pathol | volume = 30 | issue = 3 | pages = 218-30 | month = May | year = 2011 | doi = 10.1097/PGP.0b013e3181fcf01a | PMID = 21464732 }}</ref> | |||
{{Main|Mucinous borderline tumour of the ovary}} | |||
== | ==Mucinous adenocarcinoma of the ovary== | ||
*[[AKA]] ''ovarian mucinous adenocarcinoma''. | |||
* | *[[AKA]] ''ovarian mucinous carcinoma''. | ||
* | {{Main|Mucinous adenocarcinoma of the ovary}} | ||
== | ==Endometrioid carcinoma of the ovary== | ||
* | *[[AKA]] ''endometrioid ovarian carcinoma''. | ||
*[[AKA]] ''endometrioid adenocarcinoma of the ovary''. | |||
*[[AKA]] ''ovarian endometrioid adenocarcinoma''. | |||
{{Main|Endometrioid carcinoma of the ovary}} | |||
== | ==Clear cell carcinoma of the ovary== | ||
* | *[[AKA]] ''ovarian clear cell adenocarcinoma'', abbreviated ''OCCC''. | ||
* | *[[AKA]] ''ovarian clear cell carcinoma''. | ||
* | *[[AKA]] ''clear cell adenocarcinoma of the ovary''. | ||
{{Main|Clear cell carcinoma of the ovary}} | |||
==Transitional cell carcinoma of the ovary== | |||
{{Main|Transitional cell carcinoma of the ovary}} | |||
==Brenner tumour== | |||
{{Main|Brenner tumour}} | |||
==Germ cell tumours | =Germ cell tumours= | ||
These tumour are relatively uncommon, though are the most common grouping for young women. | {{Main|Germ cell tumours}} | ||
These tumour are relatively uncommon, though are the most common grouping for young women. | |||
==Overview== | |||
*Dysgerminoma (most common). | *Dysgerminoma (most common). | ||
**Female version of [[seminoma]]. | **Female version of [[seminoma]]. | ||
| Line 277: | Line 398: | ||
==Teratoma== | ==Teratoma== | ||
{{Main|Teratoma}} | |||
*May be benign or malignant. | |||
*Skin component ''only'' called "dermoid". | |||
* | |||
==Dysgerminoma== | ==Dysgerminoma== | ||
===General=== | ===General=== | ||
* Female counterpart of [[seminoma]]<ref>PBoD | *Female counterpart of [[seminoma]]<ref>{{Ref PBoD|1101}}</ref> -- look the same. | ||
Epidemiology: | |||
* Most common [[GCT]] in females. | |||
* Prognosis usually good. | |||
=== | ===Microscopic=== | ||
Features: | |||
* Fried egg appearance (clear cytoplasm, central nucleus). | * Fried egg appearance (clear cytoplasm, central nucleus). | ||
* Nuclear membrane has "corners", i.e. is "squared-off" - or "polygonal". | * Nuclear membrane has "corners", i.e. is "squared-off" - or "polygonal". | ||
| Line 298: | Line 417: | ||
* +/- Granulomata. | * +/- Granulomata. | ||
=== | Dysgerminoma vs lymphoma: | ||
* | * Dysgerminoma has "squared-off" nuclei,<ref>{{cite journal |author=Baker P, Oliva E |title=A practical approach to intraoperative consultation in gynecological pathology |journal=Int. J. Gynecol. Pathol. |volume=27 |issue=3 |pages=353?65 |year=2008 |month=July |pmid=18580313 |doi=10.1097/PGP.0b013e31815c24fe |url=}}</ref> i.e. the nuclei look are polygonal-shaped. | ||
*[http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case356.html Dysgerminoma - several cases (upmc.edu)]. | |||
==Gonadoblastoma== | |||
{{Main|Gonadoblastoma}} | |||
Details dealt with in the main article. | |||
== | ===Microscopic=== | ||
Features:<ref name=Ref_PBoD1104>{{Ref PBoD|1104}}</ref><ref>URL: [http://www.pathconsultddx.com/pathCon/diagnosis?pii=S1559-8675%2806%2970245-5 http://www.pathconsultddx.com/pathCon/diagnosis?pii=S1559-8675%2806%2970245-5]. Accessed on: 8 April 2011.</ref> | |||
* | *Immature germ cells resembling Sertoli cells or granulosa cells. | ||
**Cells with moderate cytoplasm is a trabecular or tubular architecture. | |||
*Primitive germ cells resemble those of a [[dysgerminoma]]. | |||
**Polygonal cells with a central nucleus, squared-off nuclear membrane and clear cytoplasm. | |||
*+/-Calcification (very common). | |||
= | =Metastatic ovarian tumours= | ||
{{Main|Ovarian metastasis}} | |||
= | =Sex cord stromal tumours= | ||
===General=== | ===General=== | ||
* | *Most are unilateral.<ref name=pmid16810055/> | ||
* | |||
* | ===IHC=== | ||
* | *Most are positive for alpha-inhibin.<ref name=pmid16810055>{{cite journal |author=Roth LM |title=Recent advances in the pathology and classification of ovarian sex cord-stromal tumors |journal=Int. J. Gynecol. Pathol. |volume=25 |issue=3 |pages=199–215 |year=2006 |month=July |pmid=16810055 |doi=10.1097/01.pgp.0000192271.22289.e6 |url=}}</ref> | ||
*Most are positive for calretinin -- considered more sensitive than alpha-inhibin.<ref name=pmid12409724>{{Cite journal | last1 = Movahedi-Lankarani | first1 = S. | last2 = Kurman | first2 = RJ. | title = Calretinin, a more sensitive but less specific marker than alpha-inhibin for ovarian sex cord-stromal neoplasms: an immunohistochemical study of 215 cases. | journal = Am J Surg Pathol | volume = 26 | issue = 11 | pages = 1477-83 | month = Nov | year = 2002 | doi = | PMID = 12409724 }}</ref> | |||
*Melan A +ve. | |||
*CD99 +ve. | |||
= | Memory device ''MAC'' = '''m'''elan A, '''a'''lpha-inhibin, '''c'''alretinin. | ||
== | ==Sex cord tumour with annular tubules== | ||
* | *Abbreviated ''SCTAT''. | ||
* | *'''NOT''' ''sex cord tumour with angulated tubules''. | ||
{{Main|Sex cord tumour with annular tubules}} | |||
== | ==Juvenile granulosa cell tumour== | ||
{{Main|Juvenile granulosa cell tumour}} | |||
==Adult granulosa cell tumour== | |||
* | *[[AKA]] ''granulosa cell tumour''. | ||
** | **Should '''not''' be confused with ''[[granular cell tumour]]''. | ||
* | **Ideally, it should be called ''adult granulosa cell tumour'' to avoid confusion with ''[[juvenile granulosa cell tumour]]''. | ||
{{Main| Adult granulosa cell tumour}} | |||
==Fibroma-thecoma group== | ==Fibroma-thecoma group== | ||
| Line 340: | Line 468: | ||
Note: | Note: | ||
*Some discourage the use of the term ''fibrothecoma'' and sugguest calling tumours in the | *Some discourage the use of the term ''fibrothecoma'' and sugguest calling tumours in the fibroma-thecoma group ''fibroma'' unless there are lipid-laden cells and more than minimal alpha-inhibin positivity.<ref name=pmid16810055/> | ||
== | ==Ovarian fibroma== | ||
{{Main|Ovarian fibroma}} | |||
==Thecoma== | ==Thecoma== | ||
{{Main|Thecoma}} | |||
== | ==Sertoli-Leydig cell tumour== | ||
*[[AKA]] ''androblastoma''. | |||
{{Main|Sertoli-Leydig cell tumour}} | |||
* | |||
== | ==Hilus cell tumour== | ||
{{Main|Leydig cell tumour}} | |||
*[[AKA]] ''Leydig cell tumour''.<ref name=pmid19697637>{{Cite journal | last1 = Zafrakas | first1 = M. | last2 = Venizelos | first2 = ID. | last3 = Theodoridis | first3 = TD. | last4 = Zepiridis | first4 = L. | last5 = Agorastos | first5 = T. | last6 = Bontis | first6 = JN. | title = Virilizing ovarian hilus (Leydig) cell tumor with concurrent contralateral hilus cell hyperplasia: a rare diagnosis. | journal = Eur J Gynaecol Oncol | volume = 30 | issue = 3 | pages = 338-40 | month = | year = 2009 | doi = | PMID = 19697637 }}</ref> | |||
===General=== | ===General=== | ||
* | *Rare.<ref name=pmid19697637/> | ||
*May cause virilization. | |||
**Development of male (sexual) characteristics in a female. | |||
*Arise from [[hilus cells]]. | |||
=== | ===Microscopic=== | ||
* | Features - see ''[[Leydig cell tumour]]'': | ||
* +/- | *Moderate eosinophilic cytoplasm. | ||
*+/-Reinke crystalloids (cytoplasmic inclusions). | |||
DDx: | |||
*Hilus hyperplasia. | |||
* | *[[Sertoli-Leydig tumour]]. | ||
* | |||
= | =Benign= | ||
*[[ | *[[Benign mesothelial inclusion cyst]] - may mimic a tumour. | ||
=See also= | |||
*[[Ovary]]. | *[[Ovary]]. | ||
*[[Gynecologic pathology]]. | *[[Gynecologic pathology]]. | ||
=References= | |||
{{reflist|2}} | {{reflist|2}} | ||
[[Category:Gynecologic pathology]] | [[Category:Gynecologic pathology]] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:35, 1 March 2018
The article examines ovarian tumours including ovarian cancer.
An introduction to the ovary is in the ovary article, which also deals benign cysts.
What was labeled "ovarian cancer" in the past may really arise from fallopian tube.[1] The label tubo-ovarian cancer has been advocated to address this change. These tumours are dealt with in this article.
Clinical
Gynecologists use a scoring system to help decide which patients need surgery and estimate their pre-op risk of malignancy.
Risk of malignancy index
- Abbreviated RMI.
- There are two versions.[2]
Definition
Elements
Elements & points (RMI 2):[2]
- Ultrasound features.
- Significant findings: multilocular cyst, solid component, bilateral lesions, ascites, suspected intra-abdominal metastases (one finding=1 point, two or more findings=4 points).
- Menopause/pre-menopause status (menopausal=4 points, pre-menopausal=1 point).
- CA-125 (blood test) in U/ml.
Interpretation
- RMI > 200 -- predicts malignancy.
Classification
The Latta rule of fives
Can be divided as follows:[3][4]
- Surface epithelial tumours (most common).
- Sex cord stromal tumours (SCSTs).
- Germ cell tumours (GCTs).
- Metastatic tumours.
- Rare stuff that doesn't fit in any of the above (e.g. leiomyoma, angiosarcoma, ovarian small cell carcinoma of the hypercalcemic type).
Surface epithelial tumours:
- Serous carcinoma.
- High-grade serous carcinoma. †
- Low-grade serous carcinoma.
- Endometrioid carcinoma.
- Mucinous carcinoma.
- Clear cell carcinoma.
- Brenner tumour.
Note:
Sex cord stromal tumours:
- Granulosa cell tumour (adult type, juvenile type).
- Sertoli cell tumour.
- Leydig cell tumour.
- Fibroma.
- Thecoma.
- Dysgerminoma.
- Endodermal sinus tumour (yolk sac tumour).
- Embryonal carcinoma.
- Choriocarcinoma.
- Teratoma.
Common special tumours
Tumours associated with endometriosis:[8]
- Endometrioid.
- Clear cell carcinoma.
- Endocervical mucinous (AKA Seroumucinous type and Muellerian type).
Solid ovarian tumours
Simple version: basically anything sex cord stromal.
List:[9]
- Brenner tumour.
- SCSTs:
- Fibroma.
- Thecoma.
- Fibrothecoma.
- Leydig tumour.
- Sertoli cell tumour.
- Sertoli-Leydig tumour.
- Granulosa cell tumour.
- Granulosa-theca cell tumour.
A morphologic approach
Where is the tumour arising?
- Central location -- think GCTs and SCST.
- Surface of ovary -- think surface epithelial tumour.
- If no surface is apparent... possibly obliterated by tumour.
Spindle cell morphology?
- Consider sex cord stromal tumours.
Nests of cells?
- Consider Brenner tumour.
Gland-like structures?
- Endometrioid carcinoma.
- Granulosa cell tumour.
- Definition: cellular debris within gland lumen.[10]
- Characteristic of colorectal adenocarcinoma, may be absent in ovarian tumours -- limited value.[11]
Grading of ovarian cancer
- Silverberg grading system,[12] aka universal grading system.
- Based on pattern, cytologic atypia and mitotic rate.
- System somewhat similar to breast grading, which can be remembered as: TNM (tubular formation, nuclear atypia, mitotic rate).
Silverberg system
- Pattern:
- Glandular = 1.
- Papillary = 2.
- Solid = 3.
- Cytologic atypia:
- Slight = 1.
- Moderate = 2.
- Marked = 3.
- Mitoses (see note below):
- 0-9/(0.345 x10 mm^2) = 1.
- 10-24/(0.345 x10 mm^2) = 2.
- >=25/(0.345 x10 mm^2) = 3.
Composite score (pattern score + cytologic score + mitotic score):
- Grade I = 3-5.
- Grade II = 6-7.
- Grade III = 8-9.
Note:
- Most resident microscopes have an eyepiece diameter of 22 mm. Thus, the approximate field diameter is 0.55 mm (22 mm/40 X = 0.55 mm), at highest magnification, and the field area is 0.23758 mm^2 (pi*(0.55/2)^2=0.23758 mm^2).
- The number of HPFs should be adjusted if the area per field is different than 0.345 mm^2.
- If the field diameter is 0.55 mm and the sample area is 3.45 mm^2, this is equivalent to 14.52 HPFs (3.45 mm^2 / 0.23758 mm^2 = 14.52); thus, it would be appropriate to use 15 HPFs and the cut points above.
Predictive power of Silverberg grading
Good correlation with five year survival (rounded values):[13]
- Grade I = 90%.
- Grade II = 65%.
- Grade III = 40%.
Peritoneal implants
General
Applies only to:
Classification
There are two types:[14]
- Non-invasive implants.
- Subdivided into:
- Epithelial.
- Desmoplastic.
- Subdivided into:
- Invasive implants -- malignant cells within the stroma.
Notes:
- Invasive implants are significant clinically.
- Non-invasive implants have little clinical significance.
Microscopic
Non-invasive implant
Features (non-invasive implant epithelial-type):[15]
- Papillary proliferation on surface.
- +/-Smooth contoured invagination into:
- Submesothelium.
- Omental fat lobules.
- No "stromal response":
- Fibrosis.
- +/-Psammoma bodies.
Features (non-invasive implant desmoplastic-type):[15]
- Stromal reaction restricted to the:
- Serosal surface.
- Fibrous septae.
- +/-Psammoma bodies.
Note:
- No "destructive invasion".
- Irregular infiltration.
Invasive implant
Features (invasive implant):[15]
- Irregular infiltration of tumour into the submesothelial tissue - key feature - characterized by:
- +/-Solid nests.
- +/-Small glands +/- irregular "bridging" connections between glands - common.
- Nuclear atypia - common.
- +/-Psammoma bodies.
Stains
- Elastin stain:[14]
- Non-invasive implants are sit superficial to the peritoneal elastic lamina (PEL).
- Invasive implants are deep to the PEL.
Note:
- Elastin layer is not present in the omentum.
IHC
- Elastin stain.
Staging of ovarian cancer
- The CAP protocol talks of in the pelvis and outside the pelvis - pT2 versus pT3.
- Omental involvement is considered outside the pelvis; it is pT3.[16]
Surface epithelial tumours
Most common subtypes - in short:[17]
- Serous:
- Columnar cells.
- Cilia.
- Psammoma bodies.
- Papillae.
- Endometrioid:
- Tubular glands.
- Squamous differentiation (eosinophilic cytoplasm, well-defined cell borders, +/-keratin).
- Mucinous:
- Tall columnar cells with mucin.
- Glands with mucin.
Where to start when considering a malignant (epithelial) tumour of the ovary:
| Features | Serous | Endometrioid | Mucinous |
|---|---|---|---|
| Histology | low grade: cilia, columnar cells, psammoma bodies, papillary arch.; high grade: marked nuclear pleomorphism, prominent red nucleoli, psammoma bodies | gland forming - esp. cribriforming, endometrium-like | mucinous glands, colon-like |
| Differentiators | cilia, psammoma bodies | squamous metaplasia | mucin, often lack of necrosis |
| Associations | atrophy | endometriosis, endometrial hyperplasia | (?) |
| Typical age | usually 60s+ | 40-60 | varies (?) |
| Grade | typically high grade | typically low grade | often low |
| IHC | p53 +ve (diffuse), WT-1 +ve, CA-125 +ve, D2-40 +ve | WT-1 -ve | CK7 +ve, CK20 +ve (other tumours CK7 +ve, CK20 -ve) |
| Main DDx | poorly diff. endometrioid | serous | metastatic tumour (usually GI) |
Serous tumours - overview
General
- Most common malignant ovarian tumour.
Classification
Based on features predictive of behaviour:[18]
- Benign.
- Borderline.
- May have pseudostratification of epithelial cells.
- "Usually, borderline if first impression is borderline."[19]
- Malignant.
- Cytologic atypia.
- +/-Papillae.
Microscopic
Features:[18]
- Tubal like epithelium:
- Ciliated.
- Columnar.
- Papillae.
- Psammoma bodies (concentric calcifications).
Note:
- In serous borderline tumours, micropapillae are thought to have significance -- assoc. with increased risk of distant recurrence[20][21][22] - though is disputed.[23]
- Psammoma bodies may be seen in endosalpingiosis.[24]
Serous carcinoma of the ovary
- AKA ovarian serous carcinoma.
Serous cystadenoma of the ovary
- AKA ovarian serous cystadenoma.
- Related to adenofibroma and serous cystadenofibroma.
Ovarian serous borderline tumour
- AKA serous borderline tumour of the ovary.
- AKA serous tumour of low malignant potential of the ovary, abbreviated SLMP.[25][26]
Mucinous ovarian tumours
General
- Common.
- Tumours may be heterogenous; benign appearing epithelium may be beside clearly malignant epithelium.
- Good sampling of mucinous tumours, i.e. many blocks, is important to lessen the chance of undercalling them.
Subtypes
- Endocervical type.
- Less likely to be malignant.
- More common than malignant type.
- Intestinal type.
- More likely to be malignant.
- Goblet cells. (???)
- One large clear apical vacuole.
- If it doesn't look like intestine to you... it probably isn't.
- May vaguely resemble colorectal adenocarcinoma (hyperchromatic, columnar nuclei, nuclear pleomorphism).
- Image: [1]
Comparison of mucosa:
- Normal endocervical mucosa: endocervical mucosa (duke.edu).
- Normal gastric mucosa: gastric mucosa (WC).
Classification
- Benign. (Dx: mucinous cystadenoma or mucinous adenofibroma or mucinous cystadenofibroma)
- Single layer of cells.
- Borderline. (Dx: mucinous tumour of uncertain malignant potential or borderline mucinous tumour)
- Papillae.
- Malignant. (Dx: mucinous adenocarcinoma)
- Usually intestinal subtype.
Seromucinous borderline tumour of the ovary
General
- Rare.
- Associated with endometriosis.
Gross
- Mucin-filled cysts.
Image:
Microscopic
Features:
- Simple mucinous epithelium - endocervical type.[28]
- Tall columnar epithelium with apical pale cytoplasm.
- Simple serous epithelium - with cilia.
Mucinous cystadenoma of the ovary
- AKA ovarian mucinous cystadenoma.
Mucinous borderline tumour of the ovary
Mucinous adenocarcinoma of the ovary
Endometrioid carcinoma of the ovary
- AKA endometrioid ovarian carcinoma.
- AKA endometrioid adenocarcinoma of the ovary.
- AKA ovarian endometrioid adenocarcinoma.
Clear cell carcinoma of the ovary
- AKA ovarian clear cell adenocarcinoma, abbreviated OCCC.
- AKA ovarian clear cell carcinoma.
- AKA clear cell adenocarcinoma of the ovary.
Transitional cell carcinoma of the ovary
Brenner tumour
Germ cell tumours
These tumour are relatively uncommon, though are the most common grouping for young women.
Overview
- Dysgerminoma (most common).
- Female version of seminoma.
- Yolk sac tumour (endodermal sinus tumour).
- Embryonal carcinoma.
- Choriocarcinoma.
- Teratoma.
- Mixed GCT - 60% of GCTs are mixed.
- Common combinations:
- Teratoma + embryonal carcinoma + endodermal sinus tumour (yolk sac tumour) (TEE).
- Seminoma + embryonal (SE).
- Embryonal + teratoma (TE).
- Common combinations:
Mnemonic: SEE CT, S=Seminoma, Embryonal carcinoma, Endodermal Sinus Tumour, Choriocarcinoma, Teratoma.
Teratoma
- May be benign or malignant.
- Skin component only called "dermoid".
Dysgerminoma
General
Epidemiology:
- Most common GCT in females.
- Prognosis usually good.
Microscopic
Features:
- Fried egg appearance (clear cytoplasm, central nucleus).
- Nuclear membrane has "corners", i.e. is "squared-off" - or "polygonal".
- +/- Lymphocytes - often prominent.
- +/- Granulomata.
Dysgerminoma vs lymphoma:
- Dysgerminoma has "squared-off" nuclei,[31] i.e. the nuclei look are polygonal-shaped.
Gonadoblastoma
Details dealt with in the main article.
Microscopic
- Immature germ cells resembling Sertoli cells or granulosa cells.
- Cells with moderate cytoplasm is a trabecular or tubular architecture.
- Primitive germ cells resemble those of a dysgerminoma.
- Polygonal cells with a central nucleus, squared-off nuclear membrane and clear cytoplasm.
- +/-Calcification (very common).
Metastatic ovarian tumours
Sex cord stromal tumours
General
- Most are unilateral.[34]
IHC
- Most are positive for alpha-inhibin.[34]
- Most are positive for calretinin -- considered more sensitive than alpha-inhibin.[35]
- Melan A +ve.
- CD99 +ve.
Memory device MAC = melan A, alpha-inhibin, calretinin.
Sex cord tumour with annular tubules
- Abbreviated SCTAT.
- NOT sex cord tumour with angulated tubules.
Juvenile granulosa cell tumour
Adult granulosa cell tumour
- AKA granulosa cell tumour.
- Should not be confused with granular cell tumour.
- Ideally, it should be called adult granulosa cell tumour to avoid confusion with juvenile granulosa cell tumour.
Fibroma-thecoma group
- Some say fibromas and thecomas are related,[36] while others believe they should be considered distinct entities.[37]
- A combination of a fibroma and a thecoma is known as a fibrothecoma.
Note:
- Some discourage the use of the term fibrothecoma and sugguest calling tumours in the fibroma-thecoma group fibroma unless there are lipid-laden cells and more than minimal alpha-inhibin positivity.[34]
Ovarian fibroma
Thecoma
Sertoli-Leydig cell tumour
- AKA androblastoma.
Hilus cell tumour
General
- Rare.[38]
- May cause virilization.
- Development of male (sexual) characteristics in a female.
- Arise from hilus cells.
Microscopic
Features - see Leydig cell tumour:
- Moderate eosinophilic cytoplasm.
- +/-Reinke crystalloids (cytoplasmic inclusions).
DDx:
- Hilus hyperplasia.
- Sertoli-Leydig tumour.
Benign
- Benign mesothelial inclusion cyst - may mimic a tumour.
See also
References
- ↑ Hirst, JE.; Gard, GB.; McIllroy, K.; Nevell, D.; Field, M. (Jul 2009). "High rates of occult fallopian tube cancer diagnosed at prophylactic bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy.". Int J Gynecol Cancer 19 (5): 826-9. doi:10.1111/IGC.0b013e3181a1b5dc. PMID 19574767.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 URL: http://www.sign.ac.uk/guidelines/fulltext/75/section3.html. Accessed on: 16 September 2011.
- ↑ Cotran, Ramzi S.; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Nelso Fausto; Robbins, Stanley L.; Abbas, Abul K. (2005). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (7th ed.). St. Louis, Mo: Elsevier Saunders. pp. 1093. ISBN 0-7216-0187-1.
- ↑ LAE. 22 October 2009.
- ↑ Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 401. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ Takeuchi, T.; Ohishi, Y.; Imamura, H.; Aman, M.; Shida, K.; Kobayashi, H.; Kato, K.; Oda, Y. (Jul 2013). "Ovarian transitional cell carcinoma represents a poorly differentiated form of high-grade serous or endometrioid adenocarcinoma.". Am J Surg Pathol 37 (7): 1091-9. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e3182834d41. PMID 23681072.
- ↑ Ali, RH.; Seidman, JD.; Luk, M.; Kalloger, S.; Gilks, CB. (Nov 2012). "Transitional cell carcinoma of the ovary is related to high-grade serous carcinoma and is distinct from malignant brenner tumor.". Int J Gynecol Pathol 31 (6): 499-506. doi:10.1097/PGP.0b013e31824d7445. PMID 23018212.
- ↑ LAE. 22 October 2009.
- ↑ NEED REF.
- ↑ http://www.cancer.gov/cancertopics/genetics-terms-alphalist/all#D. Accessed on: 14 September 2011.
- ↑ DeCostanzo DC, Elias JM, Chumas JC (July 1997). "Necrosis in 84 ovarian carcinomas: a morphologic study of primary versus metastatic colonic carcinoma with a selective immunohistochemical analysis of cytokeratin subtypes and carcinoembryonic antigen". Int. J. Gynecol. Pathol. 16 (3): 245–9. PMID 9421090.
- ↑ Silverberg SG (January 2000). "Histopathologic grading of ovarian carcinoma: a review and proposal". Int. J. Gynecol. Pathol. 19 (1): 7-15. PMID 10638449. http://meta.wkhealth.com/pt/pt-core/template-journal/lwwgateway/media/landingpage.htm?issn=0277-1691&volume=19&issue=1&spage=7.
- ↑ Sato Y, Shimamoto T, Amada S, Asada Y, Hayashi T (January 2003). "Prognostic value of histologic grading of ovarian carcinomas". Int. J. Gynecol. Pathol. 22 (1): 52-6. PMID 12496698. http://meta.wkhealth.com/pt/pt-core/template-journal/lwwgateway/media/landingpage.htm?issn=0277-1691&volume=22&issue=1&spage=52.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 Stewart, CJ.; Brennan, BA.; Crook, ML.; Russell, P. (Sep 2007). "Value of elastin staining in the assessment of peritoneal implants associated with ovarian serous borderline tumours.". Histopathology 51 (3): 313-21. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2559.2007.02789.x. PMID 17727474.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 15.2 Bell, DA.; Weinstock, MA.; Scully, RE. (Nov 1988). "Peritoneal implants of ovarian serous borderline tumors. Histologic features and prognosis.". Cancer 62 (10): 2212-22. PMID 3179935.
- ↑ URL: http://ovariancancer.about.com/od/testsdiagnosis/a/FIGO_stages.htm. Accessed on: 8 July 2013.
- ↑ Cotran, Ramzi S.; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Nelso Fausto; Robbins, Stanley L.; Abbas, Abul K. (2005). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (7th ed.). St. Louis, Mo: Elsevier Saunders. pp. 1096-7. ISBN 0-7216-0187-1.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 Cotran, Ramzi S.; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Nelso Fausto; Robbins, Stanley L.; Abbas, Abul K. (2005). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (7th ed.). St. Louis, Mo: Elsevier Saunders. pp. 1096. ISBN 0-7216-0187-1.
- ↑ LAE. 19 February 2009.
- ↑ LAE. 19 February 2009.
- ↑ URL: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15897738. Accessed on: 7 April 2011.
- ↑ Piura B, Rabinovich A, Yanai-Inbar I (2000). "Micropapillary serous carcinoma of the ovary: case report and review of literature". Eur. J. Gynaecol. Oncol. 21 (4): 374–6. PMID 11055486.
- ↑ Prat J, De Nictolis M (September 2002). "Serous borderline tumors of the ovary: a long-term follow-up study of 137 cases, including 18 with a micropapillary pattern and 20 with microinvasion". Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 26 (9): 1111-28. PMID 12218568. http://meta.wkhealth.com/pt/pt-core/template-journal/lwwgateway/media/landingpage.htm?issn=0147-5185&volume=26&issue=9&spage=1111.
- ↑ Hallman KB, Nahhas WA, Connelly PJ (September 1991). "Endosalpingiosis as a source of psammoma bodies in a Papanicolaou smear. A case report". J Reprod Med 36 (9): 675–8. PMID 1774734.
- ↑ Seidman, JD.; Kurman, RJ. (May 2000). "Ovarian serous borderline tumors: a critical review of the literature with emphasis on prognostic indicators.". Hum Pathol 31 (5): 539-57. PMID 10836293.
- ↑ Dietel, M.; Hauptmann, S. (May 2000). "Serous tumors of low malignant potential of the ovary. 1. Diagnostic pathology.". Virchows Arch 436 (5): 403-12. PMID 10881733.
- ↑ Shappell, HW.; Riopel, MA.; Smith Sehdev, AE.; Ronnett, BM.; Kurman, RJ. (Dec 2002). "Diagnostic criteria and behavior of ovarian seromucinous (endocervical-type mucinous and mixed cell-type) tumors: atypical proliferative (borderline) tumors, intraepithelial, microinvasive, and invasive carcinomas.". Am J Surg Pathol 26 (12): 1529-41. PMID 12459620.
- ↑ Shappell, HW.; Riopel, MA.; Smith Sehdev, AE.; Ronnett, BM.; Kurman, RJ. (Dec 2002). "Diagnostic criteria and behavior of ovarian seromucinous (endocervical-type mucinous and mixed cell-type) tumors: atypical proliferative (borderline) tumors, intraepithelial, microinvasive, and invasive carcinomas.". Am J Surg Pathol 26 (12): 1529-41. PMID 12459620.
- ↑ Khunamornpong, S.; Settakorn, J.; Sukpan, K.; Suprasert, P.; Siriaunkgul, S. (May 2011). "Mucinous tumor of low malignant potential (borderline or atypical proliferative tumor) of the ovary: a study of 171 cases with the assessment of intraepithelial carcinoma and microinvasion.". Int J Gynecol Pathol 30 (3): 218-30. doi:10.1097/PGP.0b013e3181fcf01a. PMID 21464732.
- ↑ Cotran, Ramzi S.; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Nelso Fausto; Robbins, Stanley L.; Abbas, Abul K. (2005). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (7th ed.). St. Louis, Mo: Elsevier Saunders. pp. 1101. ISBN 0-7216-0187-1.
- ↑ Baker P, Oliva E (July 2008). "A practical approach to intraoperative consultation in gynecological pathology". Int. J. Gynecol. Pathol. 27 (3): 353?65. doi:10.1097/PGP.0b013e31815c24fe. PMID 18580313.
- ↑ Cotran, Ramzi S.; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Nelso Fausto; Robbins, Stanley L.; Abbas, Abul K. (2005). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (7th ed.). St. Louis, Mo: Elsevier Saunders. pp. 1104. ISBN 0-7216-0187-1.
- ↑ URL: http://www.pathconsultddx.com/pathCon/diagnosis?pii=S1559-8675%2806%2970245-5. Accessed on: 8 April 2011.
- ↑ 34.0 34.1 34.2 Roth LM (July 2006). "Recent advances in the pathology and classification of ovarian sex cord-stromal tumors". Int. J. Gynecol. Pathol. 25 (3): 199–215. doi:10.1097/01.pgp.0000192271.22289.e6. PMID 16810055.
- ↑ Movahedi-Lankarani, S.; Kurman, RJ. (Nov 2002). "Calretinin, a more sensitive but less specific marker than alpha-inhibin for ovarian sex cord-stromal neoplasms: an immunohistochemical study of 215 cases.". Am J Surg Pathol 26 (11): 1477-83. PMID 12409724.
- ↑ http://www.pathologyoutlines.com/ovarytumor.html#fibroma
- ↑ Nocito AL, Sarancone S, Bacchi C, Tellez T (February 2008). "Ovarian thecoma: clinicopathological analysis of 50 cases". Ann Diagn Pathol 12 (1): 12–6. doi:10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2007.01.011. PMID 18164409.
- ↑ 38.0 38.1 Zafrakas, M.; Venizelos, ID.; Theodoridis, TD.; Zepiridis, L.; Agorastos, T.; Bontis, JN. (2009). "Virilizing ovarian hilus (Leydig) cell tumor with concurrent contralateral hilus cell hyperplasia: a rare diagnosis.". Eur J Gynaecol Oncol 30 (3): 338-40. PMID 19697637.
![{\displaystyle RMI\ score=ultrasound\ score\ *\ menopausal\ score\ *\ CA125\ level\ [U/ml].}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/ceca9c0133d58c2dd4b95eb62c31e68a12bb64b2)