Difference between revisions of "Colon"
(→Spirochetes: tweak) |
|||
| (248 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
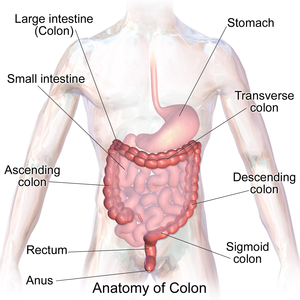
The '''colon''' | [[Image:Blausen_0603_LargeIntestine_Anatomy.png|thumb|right|Anatomy of the colon and rectum. (WC)]] | ||
The '''colon''' is section of the large bowel. This article also covers the '''rectum''' and '''cecum''' as both have a similar mucosa. | |||
It commonly comes to pathologists because there is a suspicion of [[colorectal cancer]] or a known history of [[inflammatory bowel disease]] (IBD). | |||
An introduction to gastrointestinal pathology is found in the ''[[gastrointestinal pathology]]'' article. The ''[[anus]]'' and ''[[ileocecal valve]]'' are dealt with in separate articles. | |||
Technically, the rectum and cecum are ''not'' part of the colon. Thus, inflammation of the rectum should be ''proctitis'' and inflammation of the cecum should be ''cecitis''. | |||
'' | =Anatomy= | ||
*The [[rectum]] has several definition. These are discussed in the ''[[rectum]]'' article. | |||
* | *The large bowel may be submitted with segment names or with the distance to the anal verge. | ||
A conversion between named segments and distance - as per NCI of the United States:<ref>URL: [https://training.seer.cancer.gov/colorectal/anatomy/figure/figure1.html]https://training.seer.cancer.gov/colorectal/anatomy/figure/figure1.html]. Accessed on: 8 February 2018.</ref> | |||
{| class="wikitable sortable" | |||
!Named segment | |||
!Distance to anal verge (cm) | |||
|- | |||
|Anus | |||
|0-4 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Rectum]] | |||
|4-16 | |||
|- | |||
|Rectosigmoid | |||
|15-17 | |||
|- | |||
|Sigmoid | |||
|17-57 | |||
|- | |||
|Descending | |||
|57-82 | |||
|- | |||
|Transverse | |||
|82-132 | |||
|- | |||
|Ascending | |||
|132-147 | |||
|- | |||
|Cecum | |||
|150 | |||
|} | |||
=Common clinical problems= | |||
===Obstruction=== | ===Obstruction=== | ||
Top three (in adults):<ref>[http://www.emedicine.com/EMERG/topic65.htm http://www.emedicine.com/EMERG/topic65.htm]</ref> | Top three (in adults):<ref>URL: [http://www.emedicine.com/EMERG/topic65.htm http://www.emedicine.com/EMERG/topic65.htm]. Accessed on: 28 June 2011.</ref> | ||
*Neoplasia | *Neoplasia. | ||
*Volvulus (cecal, sigmoid) | *[[Volvulus]] (cecal, sigmoid). | ||
*Diverticular disease + stricture formation. | *[[Diverticular disease]] + stricture formation. | ||
===Bleeding=== | ===Bleeding=== | ||
Mnemonic ''CHAND'':<ref>TN 2007 G29.</ref> | Mnemonic ''CHAND'':<ref>TN 2007 G29.</ref> | ||
*Colitis (radiation, infectious, ischemic, IBD (UC >CD), iatrogenic (anticoagulants)) | *Colitis ([[radiation colitis|radiation]], [[infectious colitis|infectious]], [[ischemic colitis|ischemic]], [[IBD]] (UC >CD), iatrogenic (anticoagulants)). | ||
*Hemorrhoids | *[[Hemorrhoids]]. | ||
*Angiodysplasia | *[[Angiodysplasia]]. | ||
*Neoplastic | *Neoplastic. | ||
*Diverticular disease. | *[[Diverticular disease]]. | ||
Infectious colitis with bleeding - causes: | Infectious colitis with bleeding - causes: | ||
*Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) -- commonly 0157:H7 | *Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) -- commonly 0157:H7. | ||
*Campylobacter jejuni | *Campylobacter jejuni. | ||
*Clostridium difficile | *[[Clostridium difficile]]. | ||
*Shigella. | *Shigella. | ||
Infectious colitis in the immunosuppressed: | [[Infectious colitis]] in the immunosuppressed: | ||
*Cytomegalovirus (CMV).<ref name=pmid7934809>{{cite journal |author=Golden MP, Hammer SM, Wanke CA, Albrecht MA |title=Cytomegalovirus vasculitis. Case reports and review of the literature |journal=Medicine (Baltimore) |volume=73 |issue=5 |pages=246–55 |year=1994 |month=September |pmid=7934809 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | *[[Cytomegalovirus]] (CMV).<ref name=pmid7934809>{{cite journal |author=Golden MP, Hammer SM, Wanke CA, Albrecht MA |title=Cytomegalovirus vasculitis. Case reports and review of the literature |journal=Medicine (Baltimore) |volume=73 |issue=5 |pages=246–55 |year=1994 |month=September |pmid=7934809 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | ||
**May afflict patients with IBD and lead to colectomy... as IBD patients are put on immunosuppression.<ref name=pmid17026558>{{cite journal |author=Kandiel A, Lashner B |title=Cytomegalovirus colitis complicating inflammatory bowel disease |journal=Am. J. Gastroenterol. |volume=101 |issue=12 |pages=2857–65 |year=2006 |month=December |pmid=17026558 |doi=10.1111/j.1572-0241.2006.00869.x |url=}}</ref> | **May afflict patients with IBD and lead to colectomy... as IBD patients are put on immunosuppression.<ref name=pmid17026558>{{cite journal |author=Kandiel A, Lashner B |title=Cytomegalovirus colitis complicating inflammatory bowel disease |journal=Am. J. Gastroenterol. |volume=101 |issue=12 |pages=2857–65 |year=2006 |month=December |pmid=17026558 |doi=10.1111/j.1572-0241.2006.00869.x |url=}}</ref> | ||
**Organ transplant recipients. | **Organ transplant recipients. | ||
**[[HIV|HIV/AIDS]]. | **[[HIV|HIV/AIDS]]. | ||
== | Images: | ||
{{ | <gallery> | ||
Image:CMV_colitis_-_high_mag_-_cropped.jpg | CMV colitis - high. mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
Image:CMV_colitis_-_intermed_mag.jpg | CMV colitis - intermed. mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
</gallery> | |||
=Grossing= | |||
==Types of specimens== | |||
Introduction to colorectal surgery: | |||
# Colonic resection - remove a piece of large bowel. | |||
# Total colectomy - leaves rectum and anus.<ref>[http://www.allaboutbowelsurgery.com/shared/stoma_care/stoma_surgery/procedures/surgery_colon/subtotal.htm http://www.allaboutbowelsurgery.com/shared/stoma_care/stoma_surgery/procedures/surgery_colon/subtotal.htm]</ref> | |||
# Subtotal colectomy - part of colon removed --or-- some of the rectum remains. | |||
# Right hemicolectomy - right colon + distal ileum. | |||
# [[Lower anterior resection]] (LAR) - proximal rectum +/- sigmoid (for proximal rectal malignancies). | |||
#* Specimens have should have intact mesorectum - ''[[total mesorectal excision]]'' (TME) - reduces local recurrence.<ref name=pmid8665198>{{Cite journal | last1 = Arbman | first1 = G. | last2 = Nilsson | first2 = E. | last3 = Hallböök | first3 = O. | last4 = Sjödahl | first4 = R. | title = Local recurrence following total mesorectal excision for rectal cancer. | journal = Br J Surg | volume = 83 | issue = 3 | pages = 375-9 | month = Mar | year = 1996 | doi = | PMID = 8665198 }}</ref> | |||
# [[Abdominoperineal resection]] (APR) - anus + rectum - results in a permanent [[stoma]] (for distal rectal malignancies). | |||
# [[Stoma]] - these are often done emergently and then get cut-out after the patient's condition has settled. | |||
#[[Doughnuts]] (also ''donuts'') from an end-to-end anastomosis stapler. | |||
#*Often accompany lower anterior resections. | |||
===Images=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
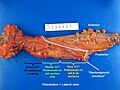
Image:Rectum - anterior view.jpg | APR specimen - anterior (WC) | |||
Image: Rectum - lateral view.jpg | APR specimen - lateral (WC) | |||
Image: Rectum - anterior and lateral - inked.jpg | APR specimen - inked (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
==Identifying the specimen== | |||
*Transverse colon - has [[omentum]]. | |||
*Ascending colon - usu. comes with [[ileocecal valve]] and a bit of ileum. | |||
*Descending colon - has a bare area. | |||
*Rectum - has adventitia. | |||
**Pathologists define it as starting where the adventitia starts/the serosal surface no longer completely surrounds the large intestine.<ref>{{Ref Lester3|339}}</ref> | |||
**Anatomists define it in relation to the third sacral vertebra.<ref>URL: [http://www.bartleby.com/107/249.html http://www.bartleby.com/107/249.html]. Accessed on: 19 October 2012.</ref> | |||
=== | ===Images=== | ||
<gallery> | |||
Image: Rectum - lateral view.jpg | Sigmoid and rectum. APR specimen. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
== | ==Lymph nodes== | ||
=== | *One should get at least 12 [[lymph nodes]] if it is cancer.<ref name=pmid18780863>{{cite journal |author=Bilimoria KY, Bentrem DJ, Stewart AK, ''et al.'' |title=Lymph node evaluation as a colon cancer quality measure: a national hospital report card |journal=J. Natl. Cancer Inst. |volume=100 |issue=18 |pages=1310–7 |year=2008 |month=September |pmid=18780863 |doi=10.1093/jnci/djn293 |url=http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/581463}}</ref> | ||
=== | ==Quirke method== | ||
*Bowel is not opened - it is fixed... then sliced.<ref name=pmid18667357>{{cite journal |author=West NP, Morris EJ, Rotimi O, Cairns A, Finan PJ, Quirke P |title=Pathology grading of colon cancer surgical resection and its association with survival: a retrospective observational study |journal=Lancet Oncol. |volume=9 |issue=9 |pages=857–65 |year=2008 |month=September |pmid=18667357 |doi=10.1016/S1470-2045(08)70181-5 |url=}}</ref><ref name=pmid18541901>{{cite journal |author=West NP, Finan PJ, Anderin C, Lindholm J, Holm T, Quirke P |title=Evidence of the oncologic superiority of cylindrical abdominoperineal excision for low rectal cancer |journal=J. Clin. Oncol. |volume=26 |issue=21 |pages=3517–22 |year=2008 |month=July |pmid=18541901 |doi=10.1200/JCO.2007.14.5961 |url=}}</ref> | |||
==Standard method== | |||
* | *Bowel is prep'ed by [[opening]] it along the antimesenteric side. | ||
* | *Dimensions - length, circumference at both [[margins]]. | ||
*Radial margin/circumferential margin - should be painted. | |||
* | **Rectum starts/sigmoid ends @ place where serosa ends on the posterior aspect of the bowel. | ||
** | ***The proximal, anterior aspect of the rectum has serosa, i.e. it is not painted. | ||
* | |||
**.. | |||
Note: | |||
* | *There are several definitions for the rectum.<ref name=pmid24130630>{{Cite journal | last1 = Kenig | first1 = J. | last2 = Richter | first2 = P. | title = Definition of the rectum and level of the peritoneal reflection - still a matter of debate? | journal = Wideochir Inne Tech Maloinwazyjne | volume = 8 | issue = 3 | pages = 183-6 | month = Sep | year = 2013 | doi = 10.5114/wiitm.2011.34205 | PMID = 24130630 }}</ref> | ||
* | **In a survey of surgeons: | ||
* | **67% defined it by an anatomical landmark | ||
***35% of all respondants considered the peritoneal reflection the proximal boundary of the rectum. | |||
**30% defined the proximal boundary as a distance from the anal verge. | |||
=Common non-neoplastic disease= | |||
==Colorectal polyps== | |||
{{main|Intestinal polyps}} | |||
Polyps are the bread & butter of [[GI pathology]]. They are very common. | |||
Main types: | |||
*Hyperplastic - most common, benign. | |||
* | *Adenomatous - quite common, pre-malignant. | ||
* | *[[Hamartomatous polyps|Hamartomatous]] - rare, weird & wonderful. | ||
* | *Inflammatory, [[AKA]] inflammatory pseudopolyps - associated with [[IBD]]. | ||
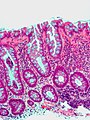
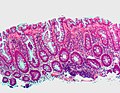
== | Most common (images): | ||
* | <gallery> | ||
Image:Hyperplastic_polyp1.jpg | Hyperplastic polyp image - intermed. mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
Image:Hyperplastic_polyp2.jpg | Hyperplastic polyp image - low mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
</gallery> | |||
==Ischemic colitis== | |||
*[[AKA]] ''colonic ischemia''. | |||
*[[AKA]] ''ischemia of the colon''. | |||
{{Main|Ischemic colitis}} | |||
== | ==Diverticular disease== | ||
{{Main|Diverticular disease}} | |||
== | ==Pseudomembranous colitis== | ||
{{Main|Pseudomembranous colitis}} | |||
== | ==Volvulus== | ||
{{Main|Volvulus}} | |||
==== | =Inflammatory diseases= | ||
==Inflammatory bowel disease== | |||
{{main|Inflammatory bowel disease}} | |||
The bread 'n butter of gastroenterology. A detailed discussion of '''IBD''' is in the ''[[inflammatory bowel disease]]'' article. It comes in two main flavours (Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis). | |||
===Microscopic=== | ===Microscopic=== | ||
Features: | Features helpful for the diagnosis of IBD - as based on a study:<ref name=pmid10048734>{{cite journal |author=Tanaka M, Riddell RH, Saito H, Soma Y, Hidaka H, Kudo H |title=Morphologic criteria applicable to biopsy specimens for effective distinction of inflammatory bowel disease from other forms of colitis and of Crohn's disease from ulcerative colitis |journal=Scand. J. Gastroenterol. |volume=34 |issue=1 |pages=55–67 |year=1999 |month=January |pmid=10048734 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | ||
* | *Basal, i.e. crypt base, plasmacytosis with severe chronic inflammation, | ||
** | *Crypt architectural abnormalities, and | ||
*Distal [[Paneth cell]] metaplasia. | |||
**Paneth cells should ''not'' be in the left colon<ref name=pmid11851832>{{cite journal |author=Tanaka M, Saito H, Kusumi T, ''et al'' |title=Spatial distribution and histogenesis of colorectal Paneth cell metaplasia in idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease |journal=J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. |volume=16 |issue=12 |pages=1353–9 |year=2001 |month=December |pmid=11851832 |doi= |url=http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/resolve/openurl?genre=article&sid=nlm:pubmed&issn=0815-9319&date=2001&volume=16&issue=12&spage=1353}}</ref> - if you see 'em think of IBD and other long-standing injurious processes. | |||
**Some claim that (friendly right colonic) paneth cells and paneth cell metaplasia look quite different and can be distinguished.<ref name=pmid12655793>{{cite journal |author=Rubio CA, Nesi G |title=A simple method to demonstrate normal and metaplastic Paneth cells in tissue sections |journal=In Vivo |volume=17 |issue=1 |pages=67–71 |year=2003 |pmid=12655793 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | |||
==Microscopic colitis== | |||
:''Microscopic colitis'' may refer to a microscopic manifestation of an unspecified disease process that can be apparent macroscopically. This section links to a pair of diseases (''lymphocytic colitis'' and ''collagenous colitis'') that are considered to only have microscopic manifestations and characteristic clinical presentation. | |||
{{Main|Lymphocytic colitis}} | |||
{{Main|Collagenous colitis}} | |||
==Diversion colitis== | |||
{{Main|Diversion colitis}} | |||
== | ==Eosinophilic colitis== | ||
* | *Abbreviated ''EC''. | ||
{{Main|Eosinophilic colitis}} | |||
== | =Infectious= | ||
==Infectious colitis== | |||
:This section covers non-specific colitides that appear to have an infective etiology. | |||
===General=== | ===General=== | ||
*Common. | |||
* | *Diarrhea - typical symptom. | ||
===Gross=== | |||
* | *+/-Erythema on endoscopy. | ||
===Microscopic=== | |||
* | Features: | ||
*Neutrophils predominant - '''key feature'''.<ref name=Ref_GLP324>{{Ref GLP|324}}</ref> | |||
**The neutrophils are often superficial - they go to were the bad guys are. | |||
*No architectural distortion - if acute. | |||
= | DDx: | ||
*Lymphocytic colitis | *[[Inflammatory bowel disease]] - lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate predominant,<ref name=Ref_GLP324>{{Ref GLP|324}}</ref> usually has chronic changes. | ||
* | *[[Ischemic colitis]]. | ||
*Medications - focal neutrophils. | |||
*[[Lymphocytic colitis]] - lymphocytes with a squiggly nucleus, may be confused with neutrophils. | |||
*Specific causes of infective colitis - with a distinctive morphology. | |||
**[[CMV colitis]] - esp. in the immunodeficient. | |||
**[[Pseudomembranous colitis]] - usu. due to ''C. difficle'', has characteristic gross & microscopic appearance. | |||
**[[Intestinal spirochetes]]. | |||
**[[Amebiasis]]. | |||
**[[Strongyloidiasis]]. | |||
**[[Cryptosporidiosis]]. | |||
===IHC=== | |||
Done if the patient is immunosuppressed, or there is clinical or morphological suspicion: | |||
*[[CMV]]. | |||
*HSV-1. | |||
*HSV-2. | |||
*[[EBV]] - may mimic IBD.<ref name=pmid21119609>{{Cite journal | last1 = Karlitz | first1 = JJ. | last2 = Li | first2 = ST. | last3 = Holman | first3 = RP. | last4 = Rice | first4 = MC. | title = EBV-associated colitis mimicking IBD in an immunocompetent individual. | journal = Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol | volume = 8 | issue = 1 | pages = 50-4 | month = Jan | year = 2011 | doi = 10.1038/nrgastro.2010.192 | PMID = 21119609 }}</ref> | |||
=== | ===Sign out=== | ||
<pre> | |||
ASCENDING COLON, BIOPSY: | |||
- MILD ACTIVE COLITIS, SEE COMMENT. | |||
COMMENT: | |||
There is are no granulomas. The crypt architecture is normal. A benign lymphoid nodule is | |||
present. | |||
The differential diagnosis includes infective etiologies, early inflammatory | |||
bowel disease and ischemia. The histomorphology is more in keeping with an infective | |||
etiology as neutrophils are a predominant feature; however, clinical correlation is | |||
required. | |||
</pre> | |||
== | ==Cytomegalovirus colitis== | ||
{{Main|CMV}} | |||
*Abbreviated ''CMV colitis''. | |||
* | {{Main|Cytomegalovirus colitis}} | ||
==Intestinal spirochetosis== | ==Intestinal spirochetosis== | ||
*[[AKA]] ''intestinal spirochetes''; more specifically ''colonic spirochetes'', ''colonic spirochetosis''. | |||
* | {{Main|Intestinal spirochetosis}} | ||
==Amebiasis== | ==Amebiasis== | ||
*May also be spelled ''amoebiasis''. | |||
{{Main|Amebiasis}} | |||
*May also be | |||
==Cryptosporidiosis== | ==Cryptosporidiosis== | ||
| Line 251: | Line 259: | ||
**Bluish staining of brush border '''key feature''' - low power. | **Bluish staining of brush border '''key feature''' - low power. | ||
== | =Rectal pathology= | ||
{{ | ==Solitary rectal ulcer== | ||
*[[AKA]] ''solitary ulcer syndrome of the rectum'', abbreviated ''SUS''. | |||
*[[AKA]] ''solitary rectal ulcer syndrome''. | |||
*''[[Mucosal prolapse syndrome]]'' may be used as a synonym; however, it encompasses other entities.<ref name=pmid22697798>{{Cite journal | last1 = Abid | first1 = S. | last2 = Khawaja | first2 = A. | last3 = Bhimani | first3 = SA. | last4 = Ahmad | first4 = Z. | last5 = Hamid | first5 = S. | last6 = Jafri | first6 = W. | title = The clinical, endoscopic and histological spectrum of the solitary rectal ulcer syndrome: a single-center experience of 116 cases. | journal = BMC Gastroenterol | volume = 12 | issue = | pages = 72 | month = | year = 2012 | doi = 10.1186/1471-230X-12-72 | PMID = 22697798 }}</ref> | |||
{{Main|Solitary rectal ulcer}} | |||
Main | ==Rectal prolapse== | ||
{{Main|Rectal prolapse}} | |||
=Neoplastic disease= | |||
==Colorectal Tumours== | ==Colorectal Tumours== | ||
{{main|Colorectal tumours}} | {{main|Colorectal tumours}} | ||
These are very common. The are covered in a separate article entitled ''[[colorectal tumours]]''. | These are very common. The are covered in a separate article entitled ''[[colorectal tumours]]''. | ||
== | ==Neuroendocrine tumour== | ||
{{Main|Neuroendocrine neoplasms#GI tract}} | |||
*[[AKA]] ''carcinoid''. | |||
==Goblet cell carcinoid== | |||
:Described in detail in the ''[[appendix]]'' article. | |||
*AKA ''crypt cell carcinoma''. | |||
*Biphasic tumour; features of ''carcinoid tumour'' and ''adenocarcinoma''. | |||
==== | =Other= | ||
==Colonic pseudo-obstruction== | |||
{{Main|Colonic pseudo-obstruction}} | |||
== | ==Pseudomelanosis coli== | ||
* | *[[AKA]] ''melanosis coli''. | ||
{{Main|Pseudomelanosis coli}} | |||
=== | ==Angiodysplasia== | ||
{{Main|Angiodysplasia}} | |||
== | ==Drugs== | ||
* | {{Main|Drug toxicity}} | ||
===Sodium polystyrene sulfonate=== | |||
*AKA ''Kayexalate''. | |||
====General==== | |||
*Used to treat hyperkalemia - as may be seen in renal failure. | |||
== | ====Microscopic==== | ||
= | Features:<ref name=pmid11342776>{{cite journal |author=Abraham SC, Bhagavan BS, Lee LA, Rashid A, Wu TT |title=Upper gastrointestinal tract injury in patients receiving kayexalate (sodium polystyrene sulfonate) in sorbitol: clinical, endoscopic, and histopathologic findings |journal=Am. J. Surg. Pathol. |volume=25 |issue=5 |pages=637-44 |year=2001 |month=May |pmid=11342776 |doi= |url=http://meta.wkhealth.com/pt/pt-core/template-journal/lwwgateway/media/landingpage.htm?issn=0147-5185&volume=25&issue=5&spage=637}}</ref> | ||
*Purple blobs on H&E stain - look somewhat like [[calcium phosphate]]. | *Purple blobs on H&E stain - look somewhat like [[calcium phosphate]]. | ||
*Can cause focal [[necrosis]]. | *Can cause focal [[necrosis]]. | ||
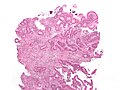
Image | =====Image===== | ||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Cecal_adenocarcinoma.jpg | Adenocarcinoma and sodium polystyrene crystals (WC/Nephron) | |||
</gallery> | |||
==Graft-versus host disease== | |||
{{Main|Graft-versus-host disease}} | {{Main|Graft-versus-host disease}} | ||
*Abbreviated as ''GVHD''. | *Abbreviated as ''GVHD''. | ||
*Seen in the context of bone marrow transplants. | *Seen in the context of bone marrow transplants. | ||
==Bowel transplant== | |||
The histology of bowel transplant rejection is identical to GVHD - see ''[[GVHD]]''. | The histology of bowel transplant rejection is identical to GVHD - see ''[[GVHD]]''. | ||
==Chronic constipation== | ==Chronic constipation== | ||
This is occasionally an indication for colectomy. | :This section deals with ''chronic constipation'' that has no apparent cause. | ||
===General=== | |||
*This is occasionally an indication for [[colectomy]].<ref name=pmid21382578>{{Cite journal | last1 = Knowles | first1 = CH. | last2 = Farrugia | first2 = G. | title = Gastrointestinal neuromuscular pathology in chronic constipation. | journal = Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol | volume = 25 | issue = 1 | pages = 43-57 | month = Feb | year = 2011 | doi = 10.1016/j.bpg.2010.12.001 | PMID = 21382578 }} | |||
</ref> | |||
General differential diagnosis for constipation: | |||
*Tumour. | *Tumour. | ||
*Adhesions - due to previous surgery. | *Adhesions - due to previous surgery. | ||
*Neuropathy. | *Neuropathy.<ref name=pmid21382578/> | ||
*Congenital defect (Hirschsprung's disease). | **[[Parkinson disease]]. | ||
*Congenital defect ([[Hirschsprung's disease]]). | |||
*Myopathy.<ref name=pmid21382578/> | |||
*Medications/substance use. | *Medications/substance use. | ||
*Idiopathic. | *Idiopathic. | ||
Work-up if no tumour is identified:<ref>IAV. 15 December 2009.</ref> | ===Gross=== | ||
*No changes. | |||
===Microscopic=== | |||
Features: | |||
*Colon within normal limits. | |||
**Look for the Ganglion cells (submucosal plexus, myenteric plexus). | |||
**Look for interstitial cells of Cajal (with CD117) - typically most common around the myenteric plexus.<ref name=pmid17222246>{{Cite journal | last1 = Streutker | first1 = CJ. | last2 = Huizinga | first2 = JD. | last3 = Driman | first3 = DK. | last4 = Riddell | first4 = RH. | title = Interstitial cells of Cajal in health and disease. Part I: normal ICC structure and function with associated motility disorders. | journal = Histopathology | volume = 50 | issue = 2 | pages = 176-89 | month = Jan | year = 2007 | doi = 10.1111/j.1365-2559.2006.02493.x | PMID = 17222246 | url = http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1365-2559.2006.02493.x/pdf }}</ref> | |||
Negatives: | |||
*No significant vascular disease. | |||
*No fibrosis. | |||
*No loss of muscle. | |||
===Stains & IHC=== | |||
Work-up if no tumour is identified:<ref>IAV. 15 December 2009.</ref><ref name=pmid19360428/> | |||
*Routine H&E. | *Routine H&E. | ||
* | *Smooth muscle actin - confirm myocyte loss. | ||
*Gomori trichrome. | *Gomori trichrome - examine connective tissue. | ||
*CD117 - to look for the ''interstitial cells of Cajal''. | *CD117 - to look for the ''interstitial cells of Cajal''. | ||
**<50% the expected = abnormal.<ref name=pmid19360428/> | |||
***Normal numbers not defined. | |||
*HU - neuronal marker.<ref name=pmid8586967>{{cite journal |author=Barami K, Iversen K, Furneaux H, Goldman SA |title=Hu protein as an early marker of neuronal phenotypic differentiation by subependymal zone cells of the adult songbird forebrain |journal=J. Neurobiol. |volume=28 |issue=1 |pages=82–101 |year=1995 |month=September |pmid=8586967 |doi=10.1002/neu.480280108 |url=}}</ref> | *HU - neuronal marker.<ref name=pmid8586967>{{cite journal |author=Barami K, Iversen K, Furneaux H, Goldman SA |title=Hu protein as an early marker of neuronal phenotypic differentiation by subependymal zone cells of the adult songbird forebrain |journal=J. Neurobiol. |volume=28 |issue=1 |pages=82–101 |year=1995 |month=September |pmid=8586967 |doi=10.1002/neu.480280108 |url=}}</ref> | ||
== | ===Sign out=== | ||
: | *A long list of things to report is contained the recommendation of a working group.<ref name=pmid19360428>{{Cite journal | last1 = Knowles | first1 = CH. | last2 = De Giorgio | first2 = R. | last3 = Kapur | first3 = RP. | last4 = Bruder | first4 = E. | last5 = Farrugia | first5 = G. | last6 = Geboes | first6 = K. | last7 = Gershon | first7 = MD. | last8 = Hutson | first8 = J. | last9 = Lindberg | first9 = G. | title = Gastrointestinal neuromuscular pathology: guidelines for histological techniques and reporting on behalf of the Gastro 2009 International Working Group. | journal = Acta Neuropathol | volume = 118 | issue = 2 | pages = 271-301 | month = Aug | year = 2009 | doi = 10.1007/s00401-009-0527-y | PMID = 19360428 }}</ref> | ||
* | **Most pathology practises do not report much. | ||
<pre> | |||
TERMINAL ILEUM, CECUM, COLON (ASCENDING, TRANSVERSE AND SIGMOID), COLECTOMY: | |||
- SMALL BOWEL, CECUM, AND COLON WITHIN NORMAL LIMITS. | |||
- FOUR LYMPH NODES NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY ( 0 POSITIVE / 4 ). | |||
- NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA AND NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY. | |||
COMMENT: | |||
Several stains were done: | |||
CD117: interstitial cells of Cajal present, no apparent decrease. | |||
SMA: no significant myocyte loss. | |||
Gomori trichrome: no abnormal fibrosis apparent. | |||
Tau: no abnormalities apparent. | |||
</pre> | |||
=See also= | |||
*[[GIST]]. | *[[GIST]]. | ||
*[[Gastrointestinal pathology]]. | *[[Gastrointestinal pathology]]. | ||
*[[Intestinal polyps]]. | *[[Intestinal polyps]]. | ||
*[[Small bowel]]. | *[[Small bowel]]. | ||
*[[Doughnuts]]. | |||
=References= | |||
{{reflist|2}} | {{reflist|2}} | ||
[[Category:Gastrointestinal pathology]] | [[Category:Gastrointestinal pathology]] | ||
[[Category:Colon|Colon]] | |||
Latest revision as of 14:46, 5 October 2023
The colon is section of the large bowel. This article also covers the rectum and cecum as both have a similar mucosa.
It commonly comes to pathologists because there is a suspicion of colorectal cancer or a known history of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
An introduction to gastrointestinal pathology is found in the gastrointestinal pathology article. The anus and ileocecal valve are dealt with in separate articles.
Technically, the rectum and cecum are not part of the colon. Thus, inflammation of the rectum should be proctitis and inflammation of the cecum should be cecitis.
Anatomy
- The rectum has several definition. These are discussed in the rectum article.
- The large bowel may be submitted with segment names or with the distance to the anal verge.
A conversion between named segments and distance - as per NCI of the United States:[1]
| Named segment | Distance to anal verge (cm) |
|---|---|
| Anus | 0-4 |
| Rectum | 4-16 |
| Rectosigmoid | 15-17 |
| Sigmoid | 17-57 |
| Descending | 57-82 |
| Transverse | 82-132 |
| Ascending | 132-147 |
| Cecum | 150 |
Common clinical problems
Obstruction
Top three (in adults):[2]
- Neoplasia.
- Volvulus (cecal, sigmoid).
- Diverticular disease + stricture formation.
Bleeding
Mnemonic CHAND:[3]
- Colitis (radiation, infectious, ischemic, IBD (UC >CD), iatrogenic (anticoagulants)).
- Hemorrhoids.
- Angiodysplasia.
- Neoplastic.
- Diverticular disease.
Infectious colitis with bleeding - causes:
- Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) -- commonly 0157:H7.
- Campylobacter jejuni.
- Clostridium difficile.
- Shigella.
Infectious colitis in the immunosuppressed:
- Cytomegalovirus (CMV).[4]
Images:
Grossing
Types of specimens
Introduction to colorectal surgery:
- Colonic resection - remove a piece of large bowel.
- Total colectomy - leaves rectum and anus.[6]
- Subtotal colectomy - part of colon removed --or-- some of the rectum remains.
- Right hemicolectomy - right colon + distal ileum.
- Lower anterior resection (LAR) - proximal rectum +/- sigmoid (for proximal rectal malignancies).
- Specimens have should have intact mesorectum - total mesorectal excision (TME) - reduces local recurrence.[7]
- Abdominoperineal resection (APR) - anus + rectum - results in a permanent stoma (for distal rectal malignancies).
- Stoma - these are often done emergently and then get cut-out after the patient's condition has settled.
- Doughnuts (also donuts) from an end-to-end anastomosis stapler.
- Often accompany lower anterior resections.
Images
Identifying the specimen
- Transverse colon - has omentum.
- Ascending colon - usu. comes with ileocecal valve and a bit of ileum.
- Descending colon - has a bare area.
- Rectum - has adventitia.
Images
Lymph nodes
- One should get at least 12 lymph nodes if it is cancer.[10]
Quirke method
Standard method
- Bowel is prep'ed by opening it along the antimesenteric side.
- Dimensions - length, circumference at both margins.
- Radial margin/circumferential margin - should be painted.
- Rectum starts/sigmoid ends @ place where serosa ends on the posterior aspect of the bowel.
- The proximal, anterior aspect of the rectum has serosa, i.e. it is not painted.
- Rectum starts/sigmoid ends @ place where serosa ends on the posterior aspect of the bowel.
Note:
- There are several definitions for the rectum.[13]
- In a survey of surgeons:
- 67% defined it by an anatomical landmark
- 35% of all respondants considered the peritoneal reflection the proximal boundary of the rectum.
- 30% defined the proximal boundary as a distance from the anal verge.
Common non-neoplastic disease
Colorectal polyps
Polyps are the bread & butter of GI pathology. They are very common.
Main types:
- Hyperplastic - most common, benign.
- Adenomatous - quite common, pre-malignant.
- Hamartomatous - rare, weird & wonderful.
- Inflammatory, AKA inflammatory pseudopolyps - associated with IBD.
Most common (images):
Ischemic colitis
Diverticular disease
Pseudomembranous colitis
Volvulus
Inflammatory diseases
Inflammatory bowel disease
The bread 'n butter of gastroenterology. A detailed discussion of IBD is in the inflammatory bowel disease article. It comes in two main flavours (Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis).
Microscopic
Features helpful for the diagnosis of IBD - as based on a study:[14]
- Basal, i.e. crypt base, plasmacytosis with severe chronic inflammation,
- Crypt architectural abnormalities, and
- Distal Paneth cell metaplasia.
Microscopic colitis
- Microscopic colitis may refer to a microscopic manifestation of an unspecified disease process that can be apparent macroscopically. This section links to a pair of diseases (lymphocytic colitis and collagenous colitis) that are considered to only have microscopic manifestations and characteristic clinical presentation.
Diversion colitis
Eosinophilic colitis
- Abbreviated EC.
Infectious
Infectious colitis
- This section covers non-specific colitides that appear to have an infective etiology.
General
- Common.
- Diarrhea - typical symptom.
Gross
- +/-Erythema on endoscopy.
Microscopic
Features:
- Neutrophils predominant - key feature.[17]
- The neutrophils are often superficial - they go to were the bad guys are.
- No architectural distortion - if acute.
DDx:
- Inflammatory bowel disease - lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate predominant,[17] usually has chronic changes.
- Ischemic colitis.
- Medications - focal neutrophils.
- Lymphocytic colitis - lymphocytes with a squiggly nucleus, may be confused with neutrophils.
- Specific causes of infective colitis - with a distinctive morphology.
- CMV colitis - esp. in the immunodeficient.
- Pseudomembranous colitis - usu. due to C. difficle, has characteristic gross & microscopic appearance.
- Intestinal spirochetes.
- Amebiasis.
- Strongyloidiasis.
- Cryptosporidiosis.
IHC
Done if the patient is immunosuppressed, or there is clinical or morphological suspicion:
Sign out
ASCENDING COLON, BIOPSY: - MILD ACTIVE COLITIS, SEE COMMENT. COMMENT: There is are no granulomas. The crypt architecture is normal. A benign lymphoid nodule is present. The differential diagnosis includes infective etiologies, early inflammatory bowel disease and ischemia. The histomorphology is more in keeping with an infective etiology as neutrophils are a predominant feature; however, clinical correlation is required.
Cytomegalovirus colitis
- Abbreviated CMV colitis.
Intestinal spirochetosis
- AKA intestinal spirochetes; more specifically colonic spirochetes, colonic spirochetosis.
Amebiasis
- May also be spelled amoebiasis.
Cryptosporidiosis
General
- Usually in immune incompetent individuals, e.g. HIV/AIDS.
Microscopic
Features:
- Uniform spherical nodules 2-4 micrometres in diameter, typical location - GI tract brush border.
- Bluish staining of brush border key feature - low power.
Rectal pathology
Solitary rectal ulcer
- AKA solitary ulcer syndrome of the rectum, abbreviated SUS.
- AKA solitary rectal ulcer syndrome.
- Mucosal prolapse syndrome may be used as a synonym; however, it encompasses other entities.[19]
Rectal prolapse
Neoplastic disease
Colorectal Tumours
These are very common. The are covered in a separate article entitled colorectal tumours.
Neuroendocrine tumour
- AKA carcinoid.
Goblet cell carcinoid
- Described in detail in the appendix article.
- AKA crypt cell carcinoma.
- Biphasic tumour; features of carcinoid tumour and adenocarcinoma.
Other
Colonic pseudo-obstruction
Pseudomelanosis coli
- AKA melanosis coli.
Angiodysplasia
Drugs
Sodium polystyrene sulfonate
- AKA Kayexalate.
General
- Used to treat hyperkalemia - as may be seen in renal failure.
Microscopic
Features:[20]
- Purple blobs on H&E stain - look somewhat like calcium phosphate.
- Can cause focal necrosis.
Image
Graft-versus host disease
- Abbreviated as GVHD.
- Seen in the context of bone marrow transplants.
Bowel transplant
The histology of bowel transplant rejection is identical to GVHD - see GVHD.
Chronic constipation
- This section deals with chronic constipation that has no apparent cause.
General
General differential diagnosis for constipation:
- Tumour.
- Adhesions - due to previous surgery.
- Neuropathy.[21]
- Congenital defect (Hirschsprung's disease).
- Myopathy.[21]
- Medications/substance use.
- Idiopathic.
Gross
- No changes.
Microscopic
Features:
- Colon within normal limits.
- Look for the Ganglion cells (submucosal plexus, myenteric plexus).
- Look for interstitial cells of Cajal (with CD117) - typically most common around the myenteric plexus.[22]
Negatives:
- No significant vascular disease.
- No fibrosis.
- No loss of muscle.
Stains & IHC
Work-up if no tumour is identified:[23][24]
- Routine H&E.
- Smooth muscle actin - confirm myocyte loss.
- Gomori trichrome - examine connective tissue.
- CD117 - to look for the interstitial cells of Cajal.
- <50% the expected = abnormal.[24]
- Normal numbers not defined.
- <50% the expected = abnormal.[24]
- HU - neuronal marker.[25]
Sign out
- A long list of things to report is contained the recommendation of a working group.[24]
- Most pathology practises do not report much.
TERMINAL ILEUM, CECUM, COLON (ASCENDING, TRANSVERSE AND SIGMOID), COLECTOMY: - SMALL BOWEL, CECUM, AND COLON WITHIN NORMAL LIMITS. - FOUR LYMPH NODES NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY ( 0 POSITIVE / 4 ). - NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA AND NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY. COMMENT: Several stains were done: CD117: interstitial cells of Cajal present, no apparent decrease. SMA: no significant myocyte loss. Gomori trichrome: no abnormal fibrosis apparent. Tau: no abnormalities apparent.
See also
References
- ↑ URL: [1]https://training.seer.cancer.gov/colorectal/anatomy/figure/figure1.html]. Accessed on: 8 February 2018.
- ↑ URL: http://www.emedicine.com/EMERG/topic65.htm. Accessed on: 28 June 2011.
- ↑ TN 2007 G29.
- ↑ Golden MP, Hammer SM, Wanke CA, Albrecht MA (September 1994). "Cytomegalovirus vasculitis. Case reports and review of the literature". Medicine (Baltimore) 73 (5): 246–55. PMID 7934809.
- ↑ Kandiel A, Lashner B (December 2006). "Cytomegalovirus colitis complicating inflammatory bowel disease". Am. J. Gastroenterol. 101 (12): 2857–65. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.2006.00869.x. PMID 17026558.
- ↑ http://www.allaboutbowelsurgery.com/shared/stoma_care/stoma_surgery/procedures/surgery_colon/subtotal.htm
- ↑ Arbman, G.; Nilsson, E.; Hallböök, O.; Sjödahl, R. (Mar 1996). "Local recurrence following total mesorectal excision for rectal cancer.". Br J Surg 83 (3): 375-9. PMID 8665198.
- ↑ Lester, Susan Carole (2010). Manual of Surgical Pathology (3rd ed.). Saunders. pp. 339. ISBN 978-0-323-06516-0.
- ↑ URL: http://www.bartleby.com/107/249.html. Accessed on: 19 October 2012.
- ↑ Bilimoria KY, Bentrem DJ, Stewart AK, et al. (September 2008). "Lymph node evaluation as a colon cancer quality measure: a national hospital report card". J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 100 (18): 1310–7. doi:10.1093/jnci/djn293. PMID 18780863. http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/581463.
- ↑ West NP, Morris EJ, Rotimi O, Cairns A, Finan PJ, Quirke P (September 2008). "Pathology grading of colon cancer surgical resection and its association with survival: a retrospective observational study". Lancet Oncol. 9 (9): 857–65. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(08)70181-5. PMID 18667357.
- ↑ West NP, Finan PJ, Anderin C, Lindholm J, Holm T, Quirke P (July 2008). "Evidence of the oncologic superiority of cylindrical abdominoperineal excision for low rectal cancer". J. Clin. Oncol. 26 (21): 3517–22. doi:10.1200/JCO.2007.14.5961. PMID 18541901.
- ↑ Kenig, J.; Richter, P. (Sep 2013). "Definition of the rectum and level of the peritoneal reflection - still a matter of debate?". Wideochir Inne Tech Maloinwazyjne 8 (3): 183-6. doi:10.5114/wiitm.2011.34205. PMID 24130630.
- ↑ Tanaka M, Riddell RH, Saito H, Soma Y, Hidaka H, Kudo H (January 1999). "Morphologic criteria applicable to biopsy specimens for effective distinction of inflammatory bowel disease from other forms of colitis and of Crohn's disease from ulcerative colitis". Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 34 (1): 55–67. PMID 10048734.
- ↑ Tanaka M, Saito H, Kusumi T, et al (December 2001). "Spatial distribution and histogenesis of colorectal Paneth cell metaplasia in idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease". J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 16 (12): 1353–9. PMID 11851832. http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/resolve/openurl?genre=article&sid=nlm:pubmed&issn=0815-9319&date=2001&volume=16&issue=12&spage=1353.
- ↑ Rubio CA, Nesi G (2003). "A simple method to demonstrate normal and metaplastic Paneth cells in tissue sections". In Vivo 17 (1): 67–71. PMID 12655793.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 Iacobuzio-Donahue, Christine A.; Montgomery, Elizabeth A. (2005). Gastrointestinal and Liver Pathology: A Volume in the Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 324. ISBN 978-0443066573.
- ↑ Karlitz, JJ.; Li, ST.; Holman, RP.; Rice, MC. (Jan 2011). "EBV-associated colitis mimicking IBD in an immunocompetent individual.". Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 8 (1): 50-4. doi:10.1038/nrgastro.2010.192. PMID 21119609.
- ↑ Abid, S.; Khawaja, A.; Bhimani, SA.; Ahmad, Z.; Hamid, S.; Jafri, W. (2012). "The clinical, endoscopic and histological spectrum of the solitary rectal ulcer syndrome: a single-center experience of 116 cases.". BMC Gastroenterol 12: 72. doi:10.1186/1471-230X-12-72. PMID 22697798.
- ↑ Abraham SC, Bhagavan BS, Lee LA, Rashid A, Wu TT (May 2001). "Upper gastrointestinal tract injury in patients receiving kayexalate (sodium polystyrene sulfonate) in sorbitol: clinical, endoscopic, and histopathologic findings". Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 25 (5): 637-44. PMID 11342776. http://meta.wkhealth.com/pt/pt-core/template-journal/lwwgateway/media/landingpage.htm?issn=0147-5185&volume=25&issue=5&spage=637.
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 21.2 Knowles, CH.; Farrugia, G. (Feb 2011). "Gastrointestinal neuromuscular pathology in chronic constipation.". Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 25 (1): 43-57. doi:10.1016/j.bpg.2010.12.001. PMID 21382578.
- ↑ Streutker, CJ.; Huizinga, JD.; Driman, DK.; Riddell, RH. (Jan 2007). "Interstitial cells of Cajal in health and disease. Part I: normal ICC structure and function with associated motility disorders.". Histopathology 50 (2): 176-89. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2559.2006.02493.x. PMID 17222246. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1365-2559.2006.02493.x/pdf.
- ↑ IAV. 15 December 2009.
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 24.2 Knowles, CH.; De Giorgio, R.; Kapur, RP.; Bruder, E.; Farrugia, G.; Geboes, K.; Gershon, MD.; Hutson, J. et al. (Aug 2009). "Gastrointestinal neuromuscular pathology: guidelines for histological techniques and reporting on behalf of the Gastro 2009 International Working Group.". Acta Neuropathol 118 (2): 271-301. doi:10.1007/s00401-009-0527-y. PMID 19360428.
- ↑ Barami K, Iversen K, Furneaux H, Goldman SA (September 1995). "Hu protein as an early marker of neuronal phenotypic differentiation by subependymal zone cells of the adult songbird forebrain". J. Neurobiol. 28 (1): 82–101. doi:10.1002/neu.480280108. PMID 8586967.