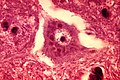
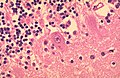
Viruses
(Redirected from CMV)
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
This article deals with viruses. The more general topic of infective things is dealt with in microorganisms. Many viruses afflict humans. Only a few of them can be diagnosed histologically.
Several viruses cause cancer and seen directly or indirectly by pathologists frequently.
Viral inclusions - types
Cowdry types:[1]
- Cowdry type A inclusion:[2]
- Round eosinophilic material surrounded by a clear halo.
- Cowdry type B inclusion:[3]
- Neuropathology thingy. (???)
Images:
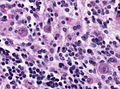
Viruses
Herpes simplex virus
- In the context of gynecologic cytopathology see: Gynecologic_cytopathology#Herpes_simplex_virus.
- Abbreviated HSV.
General
Several subtypes:
- Canker sores - usually HSV-1.
- Genital herpes - usually HSV-2.
Histology/cytology
Features:[4]
- Clear "ground glass" nuclei.
- Rim of peripheral chromatin.
- Nuclear inclusions.
- Multinucleation with nuclear molding, i.e. multiple nuclei that touch over a large surface area.
Mnemonic - 3 Ms: Margination, Multinucleation, Molding.
Images
www:
IHC
- HSV-1 +ve (cytoplasmic and strong nuclear).
- HSV-2 +ve.
Images:
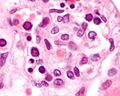
Cytomegalovirus
- Abbreviated CMV.
- For pneumonia caused by CMV - see Cytomegalovirus pneumonia.
- For colitis caused by CMV - see Cytomegalovirus colitis.
General
- The name comes from the microscopic appearance.
- One of the TORCH infections.
- May cause fetal hydrops and intracerebral hemorrhage.[7]
Microscopic
Features:
- Very large nucleus (as the name implies) with clearing.
- Classically described as owl's eye-like.
- Granular cytoplasmic inclusions (red on H&E sections).
Notes:
- Classically in endothelial cells.
- In the context of esophageal ulcers, it is therefore useful to biopsy the base of the ulcer - if this is suspected.
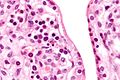
Images
CMV placentitis. (WC)
CMV encephalitis. (WC)
www:
- CMV - owl's eye-like (asm.org).
- CMV - case 1 - several images (upmc.edu).
- CMV - case 2 - several images (upmc.edu).
IHC
- IHC for CMV is available - highlights granular cytoplasmic inclusions; increases sensitivity.
Human papillomavirus
- Abbreviated HPV.
Main article: Human papillomavirus
Adenovirus
General
- Common in kids - usually a mild respiratory infection with fever and pharyngitis.
- Can cause post-infectious bronchiolitis obliterans.[8]
- May be seen in the context of (adenovirus) appendicitis.
Microscopic
Features:
- "Smudge" cells[9] - black/blue blob ~ 10-15 micrometers. (???)
Notes:
Images:
- Adenovirus (medscape.com).[10]
- Smudge cell (medpedia.com).
- Necrosis in germinal centre - low mag. (flickr.com).
- Viral inclusions - high mag. (flickr.com).
- IHC for adenovirus (flickr.com)
- Adenovirus encephalitis - several images (upmc.edu).
Parvovirus
- AKA Parvovirus B19.
General
- Most significant in pregnant women.
- Parvovirus attacks the nucleated RBCs of the fetus - causes an aplastic anemia.
- May cause collapsing glomerulopathy.[11]
Trivia:
Microscopic
Features:
- Glassy (red) nuclear inclusions.[14]
- Nuclear enlargement.
Images
www:
- Parvovirus (fujita-hu.ac.jp).[15]
- Parvovirus - placenta - (scielo.br).[16]
- Parvovirus - several images (fujita-hu.ac.jp).
Epstein-Barr virus
Main article: Epstein-Barr virus
Polyomavirus
Main article: Polyomavirus
Human herpesvirus-8
Main article: Human herpesvirus-8
West Nile virus
- Abbreviated WNV.
General
- Uncommon pathologen.
Clinical:
- Fever.
- Muscle weakness.
Microscopic
Features:[17]
- Perivascular clusters in grey and white matter:
- Mononuclear infiltrates (lymphocytes, plasma cells).
- Microglial nodules (macrophage clusters).
Measles virus
General
- Causes Measles.
- Should not be confused with Rubella (AKA German measles).
- Uncommon due to widespread MMR vaccine.
- However increasing in the last years most likely due to insufficient vaccination.
- May develop weeks to years after infection.
- Illness may be complicated by subacute sclerosing panencephalitis (SSPE) - a chronic neurodegenerative condition.[18]
Microscopic
Features:
- +/-Intranuclear Cowdry type A inclusions.
- Glassy (pink) nucleus.
- Lymphocytes and macrophages (microglial cells).
- May be mild in in measles inclusion body encephalitis.
- Multinucleated cells.
- Microglial nodules.
- Demyelination.
- Gliosis.
Notes:
- Measles inclusions are intranuclear. RSV inclusions are intracytoplasmic.[citation needed]
Images
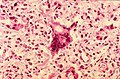
Rabies virus
General
- Causes rabies.
Virus affects:[19]
- Cerebral cortex.
- Hippocamus pyramidal cells.
- Purkinje cells.
Microscopic
Features:
- Negri bodies:
- Dense-appearing eosinophilic cytoplasmic bodies with a pale halo.
Images
www:
See also
References
- ↑ URL: http://www.pathconsultddx.com/pathCon/largeImage?pii=S1559-8675%2806%2970864-6&figureId=fig3&ecomponentId=mmc3. Accessed: 12 January 2010.
- ↑ URL: http://www.whonamedit.com/synd.cfm/3495.html. Accessed on: 22 January 2010.
- ↑ http://www.whonamedit.com/synd.cfm/3496.html. Accessed on: 22 January 2010.
- ↑ SM. 11 January 2010.
- ↑ URL: http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case120/dx.html. Accessed on: 28 February 2013.
- ↑ URL: http://www.antibodies-online.com/antibody/100405/anti-Herpes+Simplex+Virus+1+HSV1/. Accessed on: 28 February 2013.
- ↑ Tongsong, T.; Sukpan, K.; Wanapirak, C.; Phadungkiatwattna, P. (2008). "Fetal cytomegalovirus infection associated with cerebral hemorrhage, hydrops fetalis, and echogenic bowel: case report.". Fetal Diagn Ther 23 (3): 169-72. doi:10.1159/000116737. PMID 18417974.
- ↑ Aguerre, V.; Castaños, C.; Pena, HG.; Grenoville, M.; Murtagh, P. (Dec 2010). "Postinfectious bronchiolitis obliterans in children: clinical and pulmonary function findings.". Pediatr Pulmonol 45 (12): 1180-5. doi:10.1002/ppul.21304. PMID 20717912.
- ↑ URL: http://www.pathguy.com/lectures/infect.htm. Accessed on: 8 July 2010.
- ↑ URL:http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/438534_2. Accessed on: 8 July 2010.
- ↑ Schwimmer, JA.; Markowitz, GS.; Valeri, A.; Appel, GB. (Mar 2003). "Collapsing glomerulopathy.". Semin Nephrol 23 (2): 209-18. doi:10.1053/snep.2003.50019. PMID 12704581.
- ↑ Cossart, YE.; Field, AM.; Cant, B.; Widdows, D. (Jan 1975). "Parvovirus-like particles in human sera.". Lancet 1 (7898): 72-3. PMID 46024.
- ↑ Servey JT, Reamy BV, Hodge J (February 2007). "Clinical presentations of parvovirus B19 infection". Am Fam Physician 75 (3): 373–6. PMID 17304869. http://www.aafp.org/afp/991001ap/1455.html.
- ↑ URL: http://www.pathguy.com/lectures/infect.htm. Accessed on: 8 July 2010.
- ↑ URL:http://info.fujita-hu.ac.jp/~tsutsumi/case/case210.htm. Accessed on: 8 February 2011.
- ↑ URL: http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?pid=S0036-46652007000200007&script=sci_arttext. Accessed on: 18 August 2011.
- ↑ Sampson, BA.; Ambrosi, C.; Charlot, A.; Reiber, K.; Veress, JF.; Armbrustmacher, V. (May 2000). "The pathology of human West Nile Virus infection.". Hum Pathol 31 (5): 527-31. PMID 10836291.
- ↑ URL: http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case595/dx.html. Accessed on: 26 January 2012.
- ↑ Lefkowitch, Jay H. (2006). Anatomic Pathology Board Review (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 424 Q36. ISBN 978-1416025887.
- ↑ Nuovo, GJ.; Defaria, DL.; Chanona-Vilchi, JG.; Zhang, Y. (Jan 2005). "Molecular detection of rabies encephalitis and correlation with cytokine expression.". Mod Pathol 18 (1): 62-7. doi:10.1038/modpathol.3800274. PMID 15389258. http://www.nature.com/modpathol/journal/v18/n1/full/3800274a.html.