Difference between revisions of "Vascular tumours"
(→Hemangioma: +VS) |
|||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
=Distinct entities= | =Distinct entities= | ||
==Hemangioma== | ==Hemangioma== | ||
{{ Infobox external links | |||
| Name = Hemangioma | |||
| EHVSC = 10172 | |||
| pathprotocols = | |||
| wikipedia = | |||
| pathoutlines = | |||
}} | |||
===General=== | ===General=== | ||
*May be found in the liver. | *May be found in the liver. | ||
Revision as of 10:28, 26 July 2013
This article covers soft tissue vascular tumours. Vascular malformations are covered in the vascular malformations article.
Normal histology
Normal blood vessel histology is dealt with in the vascular disease article.
Mimics
Distinct entities
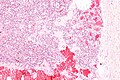
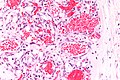
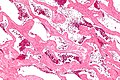
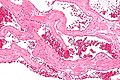
Hemangioma
| Hemangioma | |
|---|---|
| External resources | |
| EHVSC | 10172 |
General
- May be found in the liver.
- Classically subcapsular.
- May rupture and be life-threatening.[1]
- Classically subcapsular.
Hemangiomas to remember - if you're only going remember a few:
- Glomeruloid, infantile, caverous, capillary, arteriovenous, venous and intramuscular.
Childhood
Common childhood hemangiomas:[2]
- Tufted - small clusters of blood vessels.
- Microvenular hemangioma.
- Glomeruloid hemangioma - associated with POEMS syndrome, Castleman disease.[3][4]
- Epithelioid hemangioma - see angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia.
- Targetoid hemosideric hemangioma.
- Infantile hemangioma (AKA juvenile hemangioma[5]) - these tumours are GLUT-1 +ve. They tumours grow and then spontaneously regress.[6]
Soft tissue
Several types are seen in soft tissue:[7]
- Capillary.
- Cavernous.
- Arteriovenous.
- Venous.
- Intramuscular.
- Synovial.
Microscopic
Features:
- Channels lined by benign endothelium containing RBCs.
DDx:
- Lymphangioma.
- Angiokeratoma.
- Lobular capillary hemangioma (pyogenic granuloma).
Images
www:
IHC
- CD31 +ve.
- D2-40 -ve.[8]
Juvenile hemangioma:[5]
- GLUT-1 +ve.
Sign out
SUBCUTANEOUS NECK LESION, LEFT, EXCISION: - CAVERNOUS HEMANGIOMA. - NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
LESION, LEFT SIDE OF FACE, EXCISION: - CAPILLARY HEMANGIOMA. - NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
Micro
The sections show hair-bearing skin with abundant small superficial vascular channels containing red blood cells. The endothelial cells of the vascular channels do not have atypia. No mitotic activity is appreciated. The overlying epidermis is unremarkable. Extensive solar elastosis is present. No nevus is identified.
Lymphangioma
General
- Benign.
- Classically in the left neck.[9]
- May be seen in Turner syndrome.
Treatment:
- Surgical excision.
Microscopic
- Thin-walled channels lined by endothelium.
- +/-Eosinophilic intraluminal material.
- +/-Clusters of intraluminal lymphocytes.
- +/-Occasional RBCs.
DDx:
Images:
IHC
- D2-40 +ve.
Kaposi sarcoma
- Abbreviated KS.
General
- Caused by Human herpesvirus-8 (HHV-8).
- In the North American context, it is often associated with immunodeficiency, e.g. HIV/AIDS.
Interesting note:
- It has been said that KS is not really a sarcoma.[12]
Stages
It is seen in different stages:[13][14]
- Patch stage.
- Plaque stage.
- Nodular stage.
- Exophytic stage.
- Infiltrative stage.
- Lymphadenopathic stage.
Note:
- The first three are the classic ones.
Type or form
Classically divided into four types:[15][16][17]
- Classic = old men Mediterranean or Ashkenazi Jew.
- Endemic = African infants and young males.
- Immunosuppression-associated or transplant-associated - iatrogenic.
- AIDS-associated.
Microscopic
Features:[18]
- Vascular lesion (abundant RBCs) with:
- +/-"Promontory sign" - small vessel protruding into an abnormal vascular space.[19]
- Not pathognomonic for KS.[20]
- +/-Spindle cells with minimal nuclear atypia.
- RBC extravasation - very useful - important feature.[21]
- +/-"Promontory sign" - small vessel protruding into an abnormal vascular space.[19]
- +/-Intracytoplasmic hyaline globules - uncommon - one usu. needs to search for 'em.[22]
- Pale pink globs (that are paler than RBCs) - important feature.
- +/-Hemosiderin deposits.
- +/-Plasma cells.[23]
Notes:
- Hyaline globules have a DDx (hepatocellular carcinoma, lung adenocarcinoma, chondrosarcomas + others).[22]
DDx:
- Angiosarcoma - have many mitoses, nuclear atypia, RBC extravasation not common.
- Masson's hemangioma - AKA intravascular papillary endothelial hyperplasia.
- Benign lymphangioendothelioma.[24]
- Histologically very similar.[25]
Images
www:
Stains
- PAS +ve -- hyaline globules.
IHC
- CD31 +ve.
- CD34 +ve.
- HHV-8 +ve.
Masson hemangioma
General
- Benign non-neoplastic lesion - a vessel that has thrombosed and recanalized.
- Histomorphologically may be confused with low-grade angiosarcoma or other soft tissue sarcomas.[26]
Microscopic
Features:
- Well-circumscribed - key (low power) feature.
- Abundant small vascular channels with benign endothelium.
- +/-Papillary formation with a fibrotic core covered by benign endothelium.[28]
Notes:
- Looks like Kaposi sarcoma at high power.
Images:
Angiosarcoma
General
- Malignant tumour - general has a poor prognosis.[29]
Epidemiology:
- May arise secondary to chronic lymphedema related to breast carcinoma.
- Known as Stewart–Treves syndrome.[30]
- Liver angiosarcomas are associated with vinyl chloride exposure.[31]
- Cutaneous angiosarcomas are classically seen on the head and neck of whites over 60 years old.[32]
Microscopic
Features:
- Very many small capillaries of irregular shape lined with:
- Pleomorphic nuclei.
- May have hobnail morphology.
- Pleomorphic nuclei.
- Mitoses.
- Cytoplasmic vacuoles.
- Cells trying to form lumina - embryologic.
Notes:
- Epithelioid variant (with abundant cytoplasm & sheeting architecture) may resemble melanoma or hepatocellular carcinoma.
DDx:
- Atypical vascular lesion.
- Kaposi sarcoma.
- Poorly differentiated carcinoma.
Images
IHC
Kaposiform hemangioendothelioma
General
- Locally aggressive.[34]
- Childhood tumour.[35]
- Approximately half have Kasabach–Merritt phenomenon[35] = vascular tumour --> coagulopathy.
Microscopic
Features:[36]
- Spindle cells lesions in sheets or nodules.
- +/-Round tumour nodules - "cannon ball" appearance.
DDx:
IHC
Features:[36]
- Vimentin +ve.
- C31 +ve.
- CD34 +ve.
- UEA-1 lectin +ve.
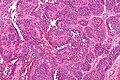
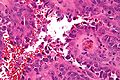
Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma
- Should not be confused with epithelioid hemangioma.
General
Microscopic
Features:[37]
- Large epithelioid perivascular cells with:
- Abundant pale eosinophilic cytoplasm.
- Cytoplasmic vacuolation (some cells) - AKA "blister cells" - key feature.
- May form lumen and have RBC within.
- Vesicular nucleus with prominent nucleolus in some cells.
- Tuft-like projections into capillaries.
- Tumour cells may be in well-circumscribed paucicellular nodules or more cellular poorly formed aggregates.
DDx:
- Angiosarcoma, epithelioid.
- Hemangioma.
Images:
- Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma (WP).
- Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma - low mag. (flickr.com/Rosen).
- Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma - high mag. (flickr.com/Rosen).
- Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma (surgicalpathologyatlas.com).
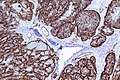
IHC
Features:[37]
- CD31 +ve.
- CD34 +ve.
- Factor VIII +ve.
See also
References
- ↑ Vokaer, B.; Kothonidis, K.; Delatte, P.; De Cooman, S.; Pector, JC.; Liberale, G.. "Should ruptured liver haemangioma be treated by surgery or by conservative means? A case report.". Acta Chir Belg 108 (6): 761-4. PMID 19241936.
- ↑ Prieto VG, Shea CR (July 1999). "Selected cutaneous vascular neoplasms. A review". Dermatol Clin 17 (3): 507–20, viii. PMID 10410855.
- ↑ Uthup S, Balachandran K, Ammal VA, et al. (August 2006). "Renal involvement in multicentric Castleman disease with glomeruloid hemangioma of skin and plasmacytoma". Am. J. Kidney Dis. 48 (2): e17–24. doi:10.1053/j.ajkd.2006.04.089. PMID 16860182.
- ↑ Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 618. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 North, PE.; Waner, M.; Mizeracki, A.; Mihm, MC. (Jan 2000). "GLUT1: a newly discovered immunohistochemical marker for juvenile hemangiomas.". Hum Pathol 31 (1): 11-22. PMID 10665907.
- ↑ Dadras, SS.; North, PE.; Bertoncini, J.; Mihm, MC.; Detmar, M. (Sep 2004). "Infantile hemangiomas are arrested in an early developmental vascular differentiation state.". Mod Pathol 17 (9): 1068-79. doi:10.1038/modpathol.3800153. PMID 15143338.
- ↑ Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 602. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Kahn, HJ.; Bailey, D.; Marks, A. (Apr 2002). "Monoclonal antibody D2-40, a new marker of lymphatic endothelium, reacts with Kaposi's sarcoma and a subset of angiosarcomas.". Mod Pathol 15 (4): 434-40. doi:10.1038/modpathol.3880543. PMID 11950918.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 12. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 489. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ Kalof, AN.; Cooper, K. (Jan 2009). "D2-40 immunohistochemistry--so far!". Adv Anat Pathol 16 (1): 62-4. doi:10.1097/PAP.0b013e3181915e94. PMID 19098468.
- ↑ Pérez, A.; Sánchez, JL.; Almodóvar, PI. (Oct 2003). "Kaposi's sarcoma is not a neoplasm let alone a sarcoma.". Int J Dermatol 42 (10): 844-5. PMID 14521707.
- ↑ URL: http://www.histopathology-india.net/KS.htm. Accessed on: 31 January 2010.
- ↑ URL: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1083998-clinical#a0217. Accessed on: 17 November 2011.
- ↑ Szajerka, T.; Jablecki, J.. "Kaposi's sarcoma revisited.". AIDS Rev 9 (4): 230-6. PMID 18219366.
- ↑ Morand, JJ.; Lightburn, E.; Simon, F.; Patte, JH. (Apr 2007). "[Update on Kaposi's sarcoma].". Med Trop (Mars) 67 (2): 123-30. PMID 17691428.
- ↑ Antman, K.; Chang, Y. (Apr 2000). "Kaposi's sarcoma.". N Engl J Med 342 (14): 1027-38. doi:10.1056/NEJM200004063421407. PMID 10749966.
- ↑ Klatt, Edward C. (2006). Robbins and Cotran Atlas of Pathology (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 23. ISBN 978-1416002741.
- ↑ Lazova R, McNiff JM, Glusac EJ, Godic A (April 2009). "Promontory sign--present in patch and plaque stage of angiosarcoma!". Am J Dermatopathol 31 (2): 132–6. doi:10.1097/DAD.0b013e3181951045. PMID 19318797.
- ↑ Fernandez-Flores A, Rodriguez R (June 2010). "Promontory Sign in a Reactive Benign Vascular Proliferation". Am J Dermatopathol. doi:10.1097/DAD.0b013e3181cf0ae5. PMID 20577080.
- ↑ Kato, H.; Hamada, T.; Tsuji, T.; Baba, T.; Seki, J.; Kobayashi, Y. (Jul 1990). "Kaposi's sarcoma: a light and electron microscopic study.". J Dermatol 17 (7): 414-22. PMID 2229644.
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 del Rosario AD, Bui HX, Singh J, Ginsburg R, Ross JS (December 1994). "Intracytoplasmic eosinophilic hyaline globules in cartilaginous neoplasms: a surgical, pathological, ultrastructural, and electron probe x-ray microanalytic study". Hum. Pathol. 25 (12): 1283–9. PMID 7528163.
- ↑ Douglas, JL.; Gustin, JK.; Dezube, B.; Pantanowitz, JL.; Moses, AV. (Sep 2007). "Kaposi's sarcoma: a model of both malignancy and chronic inflammation.". Panminerva Med 49 (3): 119-38. PMID 17912148.
- ↑ Guillou, L.; Fletcher, CD. (Aug 2000). "Benign lymphangioendothelioma (acquired progressive lymphangioma): a lesion not to be confused with well-differentiated angiosarcoma and patch stage Kaposi's sarcoma: clinicopathologic analysis of a series.". Am J Surg Pathol 24 (8): 1047-57. PMID 10935645.
- ↑ URL: http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case134/dx.html. Accessed on: 5 January 2012.
- ↑ 26.0 26.1 Korkolis DP, Papaevangelou M, Koulaxouzidis G, Zirganos N, Psichogiou H, Vassilopoulos PP (2005). "Intravascular papillary endothelial hyperplasia (Masson's hemangioma) presenting as a soft-tissue sarcoma". Anticancer Res. 25 (2B): 1409–12. PMID 15865098.
- ↑ URL: http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case544/dx.html. Accessed on: 25 January 2012.
- ↑ URL: http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case544.html. Accessed on: 25 January 2012.
- ↑ Young RJ, Brown NJ, Reed MW, Hughes D, Woll PJ (May 2010). "Angiosarcoma". Lancet Oncol. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(10)70023-1. PMID 20537949.
- ↑ Pincus, LB.; Fox, LP. (Aug 2008). "Images in clinical medicine. The Stewart-Treves syndrome.". N Engl J Med 359 (9): 950. doi:10.1056/NEJMicm071344. PMID 18753651. http://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMicm071344.
- ↑ Mitchell, Richard; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Abbas, Abul K.; Aster, Jon (2011). Pocket Companion to Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 212. ISBN 978-1416054542.
- ↑ Albores-Saavedra, J.; Schwartz, AM.; Henson, DE.; Kostun, L.; Hart, A.; Angeles-Albores, D.; Chablé-Montero, F. (Apr 2011). "Cutaneous angiosarcoma. Analysis of 434 cases from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program, 1973-2007.". Ann Diagn Pathol 15 (2): 93-7. doi:10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2010.07.012. PMID 21190880.
- ↑ Rossi, S.; Orvieto, E.; Furlanetto, A.; Laurino, L.; Ninfo, V.; Dei Tos, AP. (May 2004). "Utility of the immunohistochemical detection of FLI-1 expression in round cell and vascular neoplasm using a monoclonal antibody.". Mod Pathol 17 (5): 547-52. doi:10.1038/modpathol.3800065. PMID 15001993.
- ↑ 34.0 34.1 Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 603. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ 35.0 35.1 Lyons, LL.; North, PE.; Mac-Moune Lai, F.; Stoler, MH.; Folpe, AL.; Weiss, SW. (May 2004). "Kaposiform hemangioendothelioma: a study of 33 cases emphasizing its pathologic, immunophenotypic, and biologic uniqueness from juvenile hemangioma.". Am J Surg Pathol 28 (5): 559-68. PMID 15105642.
- ↑ 36.0 36.1 36.2 Miller, K. (Mar 1991). "Sister-chromatid exchange in human B- and T-lymphocytes exposed to bleomycin, cyclophosphamide, and ethyl methanesulfonate.". Mutat Res 247 (1): 175-82. PMID 1706068. http://www.nature.com/modpathol/journal/v14/n11/full/3880441a.html.
- ↑ 37.0 37.1 37.2 Gupta, R.; Mathur, SR.; Gupta, SD.; Durgapal, P.; Iyer, VK.; Das, CJ.; Shalimar, SK.; Acharya, . (2010). "Hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: A diagnostic pitfall in aspiration cytology.". Cytojournal 6: 25. doi:10.4103/1742-6413.58951. PMID 20165548.