Difference between revisions of "Chondro-osseous tumours"
m (→Bone tumours: more in table) |
|||
| (180 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
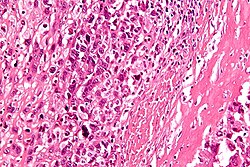
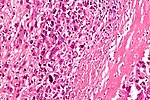
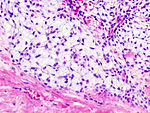
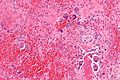
'''Chondro-osseous tumours''' occasionally cross the desk of the pathologist. They are grouped together as [[bone]] may develop from [[cartilage]]. | [[Image:Osteosarcoma - very high mag.jpg|thumb|250px|right|A chondro-osseous tumour ([[osteosarcoma]]). [[H&E stain]].]] | ||
'''Chondro-osseous tumours''' occasionally cross the desk of the pathologist. They are grouped together as [[bone]] may develop from [[cartilage]]. | |||
Primary bone tumours are rare; the most common bone tumour is metastases.<ref name=Ref_WMSP632>{{Ref WMSP|632}}</ref> | Primary bone tumours are rare; the most common bone tumour is [[metastases]].<ref name=Ref_WMSP632>{{Ref WMSP|632}}</ref> | ||
Bone tumours occasionally are lumped with soft tissue tumours. Soft tissue tumours are dealt with in the ''[[soft tissue lesions]]'' article. An introduction to bone is found in the ''[[bone]]'' article. An introduction to cartilage is found in the ''[[cartilage]]'' article. | Bone tumours occasionally are lumped with soft tissue tumours. Soft tissue tumours are dealt with in the ''[[soft tissue lesions]]'' article. An introduction to bone is found in the ''[[bone]]'' article. An introduction to cartilage is found in the ''[[cartilage]]'' article. | ||
| Line 10: | Line 11: | ||
===Common malignant=== | ===Common malignant=== | ||
*Osteosarcoma. | *[[Osteosarcoma]]. | ||
*Chondrosarcoma. | *[[Chondrosarcoma]]. | ||
*Ewing's sarcoma. | *[[Ewing's sarcoma]]. | ||
*Multiple myeloma. | *[[Multiple myeloma]]. | ||
*Metastases. | *[[Metastases]]. | ||
**Most common tumours metastatic to bone (mnemonic: ''BLT with Ketchup & Pickles''): | **Most common tumours metastatic to bone (mnemonic: ''BLT with Ketchup & Pickles''): | ||
***[[Breast]]. | ***[[Breast]]. | ||
| Line 22: | Line 23: | ||
***[[Prostate gland]]. | ***[[Prostate gland]]. | ||
Epidemiology:<ref> | Epidemiology:<ref name=Ref_TN2005_OR42>{{Ref TN2005 |OR42}}</ref> | ||
*Osteosarcoma -> 2nd decade. | *Osteosarcoma -> 2nd decade. | ||
*Ewing's ->5-20 yrs. | *Ewing's ->5-20 yrs. | ||
| Line 29: | Line 30: | ||
===Malignant bone tumours by age=== | ===Malignant bone tumours by age=== | ||
Most common by age:<ref> | Most common by age:<ref name=Ref_TN2005_OR42>{{Ref TN2005 |OR42}}</ref> | ||
*<1 year old - [[neuroblastoma]]. | *<1 year old - [[neuroblastoma]]. | ||
*1-10 years old - Ewing's of tubular bones. | *1-10 years old - [[Ewing sarcoma|Ewing's]] of tubular bones. | ||
*10-30 years old - osteosarcoma, Ewing's of flat bones. | *10-30 years old - osteosarcoma, Ewing's of flat bones. | ||
*30-40 years old - reticulum cell sarcoma, fibrosarcoma, parosteal osteosarcoma, malignant giant cell tumour, lymphoma. | *30-40 years old - [[reticulum cell sarcoma]], [[fibrosarcoma]], parosteal osteosarcoma, [[malignant giant cell tumour]], [[lymphoma]]. | ||
*>40 years old - mets, multiple myeloma, chondrosarcoma. | *>40 years old - mets, [[multiple myeloma]], [[chondrosarcoma]]. | ||
===Benign aggressive bone tumours=== | ===Benign aggressive bone tumours=== | ||
*Giant cell | *[[Giant cell tumour of bone]]. | ||
*Osteoblastoma. | *[[Osteoblastoma]]. | ||
**Thought to be related to osteoid osteoma. | **Thought to be related to [[osteoid osteoma]]. | ||
**If in long bones often diaphyseal. | **If in long bones often diaphyseal. | ||
Ref.:<ref> | |||
Ref.:<ref name=Ref_TN2005_OR41>{{Ref TN2005 |OR41}}</ref><ref>URL: [http://www.emedicine.com/RADIO/topic494.htm http://www.emedicine.com/RADIO/topic494.htm].</ref> | |||
===Summary tables=== | ===Summary tables=== | ||
====Bone tumours==== | ====Bone tumours==== | ||
{| class="wikitable sortable" style="margin-left:auto;margin-right:auto" | {| class="wikitable sortable" style="margin-left:auto;margin-right:auto" | ||
! Entity | |||
! Key feature | |||
| | ! Other features | ||
| | ! Radiology / gross | ||
| | ! Clinical | ||
| | ! Stains / other | ||
| Image | ! Image | ||
|- | |||
| [[Osteoma]] | |||
| normal bone (???) | |||
| other features (???) | |||
| radiology / gross (???) | |||
| ? | |||
| no stains / may be assoc. with [[FAP]] | |||
| [[Image:Osteoma -- intermed mag.jpg |thumb|center|150px| Osteoma. (WC)]] | |||
|- | |- | ||
| [[Osteoid osteoma]] | | [[Osteoid osteoma]] | ||
| osteoblastic rimming | | osteoblastic rimming | ||
| anastomosing bony trabeculae | | anastomosing bony trabeculae | ||
| <= | | must be <2 cm,<ref name=pmid25224389>{{Cite journal | last1 = Yalcinkaya | first1 = U. | last2 = Doganavsargil | first2 = B. | last3 = Sezak | first3 = M. | last4 = Kececi | first4 = B. | last5 = Argin | first5 = M. | last6 = Basdemir | first6 = G. | last7 = Oztop | first7 = F. | title = Clinical and morphological characteristics of osteoid osteoma and osteoblastoma: a retrospective single-center analysis of 204 patients. | journal = Ann Diagn Pathol | volume = 18 | issue = 6 | pages = 319-25 | month = Dec | year = 2014 | doi = 10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2014.08.006 | PMID = 25224389 }}</ref> metaphysis | ||
| painful, NSAIDs remove pain, young | | painful, NSAIDs remove pain, young | ||
| IHC / other | | IHC / other | ||
| [ | | [[Image:Osteoid_osteoma_-_high_mag.jpg |thumb|center|150px| Osteoid osteoma. (WC)]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[Osteoblastoma]] | | [[Osteoblastoma]] | ||
| osteoblastic rimming | | osteoblastic rimming | ||
| anastomosing bony trabeculae | | anastomosing bony trabeculae | ||
| > 1 | | must be >1 cm,<ref name=pmid25224389/> often >=2 cm, metaphysis | ||
| not painful | | not painful | ||
| IHC / other | | IHC / other | ||
| Image | | [[Image:Osteoblastoma_-_high_mag.jpg|thumb|center|150px|Osteoblastoma. (WC)]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[Ewing sarcoma]] | | [[Ewing sarcoma]] | ||
| [[small round blue cell tumour]] | | [[small round blue cell tumour]] | ||
| cytoplasmic clearing (due to glycogen) | | cytoplasmic clearing (due to glycogen) | ||
| | | usu. diaphysis | ||
| pediatric | | pediatric, typically 1-10 years | ||
| | | PAS+, PASD-, [[chromosomal translocations]] (usually t(11;22)(q24;q12)) | ||
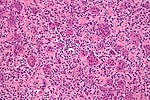
| Image | | [[Image:Ewing_sarcoma_-_PAS_-_high_mag.jpg |thumb|center|150px| Ewing sarcoma. [[PAS stain]]. (WC)]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[Osteosarcoma]] | | [[Osteosarcoma]] | ||
| osteoid | | osteoid | ||
| | | +/-hemorrhage, +/-cartilage | ||
| | | distal femur, prox. tibia, prox. humerous | ||
| | | typically 10-30 years, pain, swelling | ||
| | | no stains; many subtypes | ||
| Image | | [[Image:Osteosarcoma_-_very_high_mag.jpg |thumb|center|150px|Osteosarcoma. (WC)]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[Giant cell tumour of bone]] | | [[Giant cell tumour of bone]] | ||
| abundant giant cells | | abundant giant cells | ||
| | | nuclei of surrounding cells similar to those in giant cells | ||
| | | growth plate of long bones | ||
| | | 20-45 years old, +/-joint pain, +/-immobility | ||
| IHC / other | | IHC / other | ||
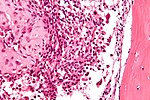
| Image | | [[Image:Giant_cell_tumour_of_bone_-_high_mag.jpg|thumb|center|150px|Giant cell tumour. (WC)]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 98: | Line 108: | ||
====Cartilage tumours==== | ====Cartilage tumours==== | ||
{| class="wikitable sortable" style="margin-left:auto;margin-right:auto" | {| class="wikitable sortable" style="margin-left:auto;margin-right:auto" | ||
! Entity | |||
! Key feature | |||
! Other features | |||
! Radiology / gross | |||
! Clinical | |||
! Stains / other | |||
! Image | |||
|- | |- | ||
| [[ | | [[Chondroma]] | ||
| | | ctyologically benign cells | ||
| | | equally spaced nests | ||
| | | usu. diaphysis | ||
| | | benign / DDx: chondroma, well-diff. chondrosarcoma | ||
| IHC / | | IHC / bone marrow cavity chondroma = ''enchondroma'' | ||
| Image | | [[Image:Enchondroma_-_very_high_mag.jpg |thumb|center|150px| Enchondroma. (WC)]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[Chondroblastoma]] | | [[Chondroblastoma]] | ||
| | | abundant extracellular material, abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm | ||
| | | calcifications surround cells nests ("chickenwire" appearance) - '''classic''' | ||
| | | epiphysis | ||
| | | DDx: [[giant cell tumour of bone]] | ||
| | | S100+ve, vimentin +ve | ||
| Image | | [[Image:Chondroblastoma_-_very_high_mag.jpg |thumb|center|150px| Chondroblastoma. (WC)]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[Chondrosarcoma]] | | [[Chondrosarcoma]] | ||
| | | cartilaginous appearance +/- nuclear atypia | ||
| | | lack osteoid, if present -> osteosarcoma | ||
| | | usu. diaphysis, classically hip; almost never distal extremity | ||
| | | >40 years old | ||
| IHC / | | IHC / may be histologically benign looking | ||
| Image | | [[Image:Chondrosarcoma_%282%29.jpg |thumb|center|150px|Chondrosarcoma. (WC)]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 134: | Line 144: | ||
====Other==== | ====Other==== | ||
{| class="wikitable sortable" style="margin-left:auto;margin-right:auto" | {| class="wikitable sortable" style="margin-left:auto;margin-right:auto" | ||
! Entity | |||
! Key feature | |||
! Other features | |||
! Radiology / gross | |||
! Clinical | |||
! Stains / other | |||
! Image | |||
|- | |- | ||
| [[Osteochondroma]] | | [[Osteochondroma]] | ||
| | | benign bone and cartilage | ||
| Other features | | Other features | ||
| | | metaphyseal lesions | ||
| Clinical | | Clinical | ||
| IHC / other | | IHC / other | ||
| Line 151: | Line 161: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[Adamantinoma]] | | [[Adamantinoma]] | ||
| | | bisphasic - stroma & epithelium | ||
| Other features | | Other features | ||
| | | tibia, fibula, intracortical, radiolucent | ||
| Clinical | | Clinical | ||
| IHC / other | | IHC / other | ||
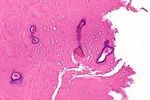
| Image | | [[Image:Adamantinoma_-_intermed_mag.jpg |thumb|center|150px|Adamantinoma. (WC)]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[Diffuse tenosynovial giant-cell tumour]] | | [[Diffuse tenosynovial giant-cell tumour]] ([[AKA]] [[PVNS]]) | ||
| | | pigmented giant cells | ||
| | | nodules | ||
| Radiology / gross | | Radiology / gross | ||
| Clinical | | Clinical | ||
| IHC / other | | IHC / other | ||
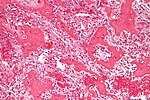
| Image | | [[Image:Pigmented_villonodular_synovitis_low_mag.jpg |thumb|center|150px| PVNS. (WC)]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[Brown tumour]] | | [[Brown tumour]] | ||
| | | fibrosis, +/-giant cells | ||
| | | unaffected bone incr. osteoblasts and osteoclasts | ||
| Radiology / gross | | Radiology / gross | ||
| | | due to hypercalcemia; not a neoplasm | ||
| IHC / other | | IHC / other | ||
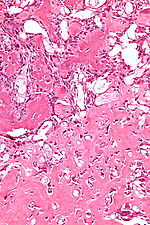
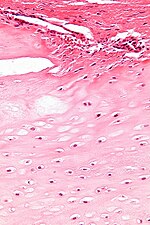
| Image | | [[Image:Brown_tumour_-_low_mag.jpg |thumb|center|150px| Brown tumour. (WC)]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
= | ====Radiology==== | ||
== | =====Radiologic features===== | ||
=== | {| class="wikitable sortable" style="margin-left:auto;margin-right:auto" | ||
! Features | |||
! Benign | |||
! Malignant | |||
|- | |||
| Bone changes | |||
| sclerotic rim | |||
| tumour perforation | |||
|- | |||
| Circumscription | |||
| pushing margins | |||
| ill-defined/moth-eaten | |||
|- | |||
| Soft tissue involvement | |||
| no | |||
| common | |||
|- | |||
| Periosteal reaction | |||
| no | |||
| "hair-on-end" or "sunburst",<br> "onion skin", Codman's triangle | |||
|} | |||
=====Location===== | |||
{| class="wikitable sortable" style="margin-left:auto;margin-right:auto" | |||
! Diagnosis | |||
! [[Epiphysis]] | |||
! [[Metaphysis]] | |||
! [[Diaphysis]] | |||
! Type of lesion | |||
|- | |||
| [[Aneurysmal bone cyst]] | |||
| common | |||
| most common | |||
| rare | |||
| [[bone]] | |||
|- | |||
| [[Chondroblastoma]] | |||
| most common | |||
| rare | |||
| extremely rare | |||
| [[cartilage]] | |||
|- | |||
| [[Chondrosarcoma]] | |||
| uncommon | |||
| common | |||
| most common | |||
| [[cartilage]] | |||
|- | |||
| [[Chondromyxoid fibroma]] | |||
| rare | |||
| most common | |||
| common | |||
| other | |||
|- | |||
| [[Enchondroma]] | |||
| rare | |||
| common | |||
| common | |||
| [[cartilage]] | |||
|- | |||
| [[Ewing sarcoma]] | |||
| rare | |||
| common | |||
| most common | |||
| [[bone]] | |||
|- | |||
| [[Giant cell tumour of bone|Giant cell tumour]] | |||
| most common | |||
| rare | |||
| extremely rare | |||
| [[bone]] | |||
|- | |||
| Metastatic carcinoma | |||
| rare | |||
| common | |||
| most common | |||
| other | |||
|- | |||
| Non-ossifying fibroma | |||
| extremely rare | |||
| most common | |||
| common | |||
| other | |||
|- | |||
| [[Osteoblastoma]] | |||
| rare | |||
| most common | |||
| uncommon | |||
| [[bone]] | |||
|- | |||
| [[Osteochondroma]] | |||
| extremely rare{{fact}} <!-- PMID 12873205 questions this --> | |||
| most common | |||
| common | |||
| [[bone]]/[[cartilage]] | |||
|- | |||
| [[Osteoid osteoma]] | |||
| uncommon | |||
| common | |||
| common<ref name=wheelessonline>URL: [http://www.wheelessonline.com/ortho/osteoid_osteoma http://www.wheelessonline.com/ortho/osteoid_osteoma]. Accessed on: 7 May 2012</ref> | |||
| [[bone]] | |||
|- | |||
| [[Osteosarcoma]] | |||
| rare | |||
| most common | |||
| uncommon | |||
| [[bone]] | |||
|} | |||
How to remember the primary bone lesions: | |||
* | #''Ewing sarcoma'' is the only malignant primary bone tumour of the diaphysis. | ||
#''Giant cell tumour of bone'' is the only primary bone lesion of the epiphysis. | |||
#The rest of the primary bone lesions are metaphyseal. | |||
#*''Osteochondroma'' is bone first and cartilage second. It behaves like most primary bone lesions; it is usually metaphyseal. | |||
How to remember the primary cartilaginous lesions: | |||
#''Chondroblastoma'' is epiphyseal. The chicken wire goes around the chicken coop. | |||
#The others are diaphyseal. | |||
=Cartilage= | |||
==Chondroma== | |||
{{Main|Chondroma}} | |||
==Chondroblastoma== | ==Chondroblastoma== | ||
{{Main|Chondroblastoma}} | |||
==Chondromyxoid fibroma== | |||
{{Main|Chondromyxoid fibroma}} | |||
==Chondrosarcoma== | ==Chondrosarcoma== | ||
{{Main|Chondrosarcoma}} | |||
=Bone= | |||
==Osteoma== | |||
{{Main|Osteoma}} | |||
==== | |||
==Osteoid osteoma== | ==Osteoid osteoma== | ||
{{Main|Osteoid osteoma}} | |||
==Osteoblastoma== | ==Osteoblastoma== | ||
{{Main|Osteoblastoma}} | |||
==Ewing sarcoma== | ==Ewing sarcoma== | ||
{{Main|Ewing sarcoma}} | |||
==Osteosarcoma== | ==Osteosarcoma== | ||
{{Main|Osteosarcoma}} | |||
== | ==Giant cell tumour of bone== | ||
{{Main|Giant cell tumour of bone}} | |||
=Other= | |||
This section collects stuff that doesn't neatly fit into the ''bone'' or ''cartilage'' category. | |||
==Notochordal tumors== | |||
Notochordal tumors arise from notochordal remnants and thus are seen in the clivus or sacrum. | |||
{{Main|Chordoma}} | |||
==Osteochondroma== | ==Osteochondroma== | ||
{{Main|Osteochondroma}} | |||
==Diffuse tenosynovial giant-cell tumour== | ==Diffuse tenosynovial giant-cell tumour== | ||
*[[AKA]] ''tenosynovial giant-cell tumour, diffuse type''. | *[[AKA]] ''tenosynovial giant-cell tumour, diffuse type''. | ||
*Previously known as ''pigmented villonodular synovitis'' (PVNS).<ref>{{Ref PBoD8|1247}}</ref> | *Previously known as ''pigmented villonodular synovitis'' (PVNS).<ref>{{Ref PBoD8|1247}}</ref> | ||
{{Main|Diffuse tenosynovial giant-cell tumour}} | |||
=== | ==Giant cell tumour of tendon sheath== | ||
*Abbreviated ''GCT of tendon sheath''. | |||
*'' | {{Main|Giant cell tumour of tendon sheath}} | ||
==Adamantinoma== | ==Adamantinoma== | ||
{{Main|Adamantinoma}} | |||
==Brown tumour== | ==Brown tumour== | ||
===General=== | ===General=== | ||
*''Not'' a true neoplasm | *''Not'' a true neoplasm.<ref name=pmid16775919>{{cite journal |author=Meydan N, Barutca S, Guney E, ''et al.'' |title=Brown tumors mimicking bone metastases |journal=J Natl Med Assoc |volume=98 |issue=6 |pages=950–3 |year=2006 |month=June |pmid=16775919 |pmc=2569361 |doi= |url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2569361/?page=1 }}</ref> | ||
**If ''tumour'' is understood as a synonym for ''neoplasm'', the name is a misnomer. | |||
**May (clinically) mimic a true neoplasm. | **May (clinically) mimic a true neoplasm. | ||
*Due to hyperparathyroidism - usually parathyroid adenoma. | *Due to hyperparathyroidism - usually [[parathyroid adenoma]]. | ||
**Usually secondary to chronic renal failure. | **Usually secondary to chronic renal failure. | ||
====Hypercalcemia DDx==== | ====Hypercalcemia DDx==== | ||
Mnemonic ''GRIMED'':<ref> | Mnemonic ''GRIMED'':<ref>{{Ref TN2006 |Emerg.}}</ref> | ||
*Granulomatous disease (tuberculosis, [[sarcoidosis]]). | *Granulomatous disease (tuberculosis, [[sarcoidosis]]). | ||
*Renal disease. | *Renal disease. | ||
*Immobility. | *Immobility. | ||
*Malignancy (esp. squamous cell carcinoma, [[plasmacytoma]]). | *Malignancy (esp. [[squamous cell carcinoma]], [[plasmacytoma]]). | ||
*Endocrine (primary hyperparathyroidism - leads to brown | *Endocrine ([[parathyroid gland|primary hyperparathyroidism]] - leads to [[brown tumour]]). | ||
*Drugs (thiazides ... others). | *Drugs (thiazides ... others). | ||
=== | ===Microscopic=== | ||
Features: | Features: | ||
*Fibrosis. | *Fibrosis. | ||
*+/-Giant cells. | *+/-Giant cells with round to oval nuclei and nucleoli.<ref>URL: [http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case139/micro.html http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case139/micro.html]. Accessed on: 6 January 2012.</ref> | ||
*Bone unaffected by tumour - increased numbers of the following: | |||
**Multinucleated cells (osteoclasts). | |||
**Mononuclear cells around the bony trabeculae (osteoblasts). | |||
DDx: | DDx: | ||
*[[Giant cell tumour of bone]] and other [[giant cell lesions]]. | *[[Giant cell tumour of bone]] and other [[giant cell lesions]]. | ||
== | ====Images==== | ||
= | <gallery> | ||
Image:Brown_tumour_-_low_mag.jpg | Brown tumour - low mag. (WC) | |||
Image:Brown_tumour_-_intermed_mag.jpg | Brown tumour - intermed. mag. (WC) | |||
Image:Brown_tumour_-_high_mag.jpg | Brown tumour - high mag. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
www: | |||
*[http://wwwold.path.utah.edu/classes/webpath/bonehtml/bone053.htm Brown tumour (utah.edu)]. | |||
*[http://www.mda-sy.com/pathology/BONEHTML/BONE054.HTM Brown tumour (mda-sy.com)]. | |||
*[http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case139/micro.html Brown tumour - several images (upmc.edu)]. | |||
*[http:// | |||
*[http:// | |||
* | |||
=See also= | =See also= | ||
| Line 622: | Line 410: | ||
=External links= | =External links= | ||
*[http://www.medpath.info/MainContent/Skeletal/Bone_07.html Bone lesions (medpath.info)]. | *[http://www.medpath.info/MainContent/Skeletal/Bone_07.html Bone lesions (medpath.info)]. | ||
*[http://www.radiologyassistant.nl/en/494e15cbf0d8d Bone radiology (radiologyassistant.nl)]. | |||
[[Category:Chondro-osseous tumours]] | |||
[[Category:Weird stuff]] | [[Category:Weird stuff]] | ||
Latest revision as of 01:46, 20 June 2016
Chondro-osseous tumours occasionally cross the desk of the pathologist. They are grouped together as bone may develop from cartilage.
Primary bone tumours are rare; the most common bone tumour is metastases.[1]
Bone tumours occasionally are lumped with soft tissue tumours. Soft tissue tumours are dealt with in the soft tissue lesions article. An introduction to bone is found in the bone article. An introduction to cartilage is found in the cartilage article.
General
- Diagnosis of a primary bone tumour should not be made without radiologic & clinical information!
- Metastasis:primary bone tumours = >20:1.[1]
Common malignant
- Osteosarcoma.
- Chondrosarcoma.
- Ewing's sarcoma.
- Multiple myeloma.
- Metastases.
- Most common tumours metastatic to bone (mnemonic: BLT with Ketchup & Pickles):
Epidemiology:[2]
- Osteosarcoma -> 2nd decade.
- Ewing's ->5-20 yrs.
- Chondrosarcoma -> from enchondroma or osteochrondroma -- patients over 40 yrs.
- Multiple myeloma -> most common primary bone tumour in adults.
Malignant bone tumours by age
Most common by age:[2]
- <1 year old - neuroblastoma.
- 1-10 years old - Ewing's of tubular bones.
- 10-30 years old - osteosarcoma, Ewing's of flat bones.
- 30-40 years old - reticulum cell sarcoma, fibrosarcoma, parosteal osteosarcoma, malignant giant cell tumour, lymphoma.
- >40 years old - mets, multiple myeloma, chondrosarcoma.
Benign aggressive bone tumours
- Giant cell tumour of bone.
- Osteoblastoma.
- Thought to be related to osteoid osteoma.
- If in long bones often diaphyseal.
Summary tables
Bone tumours
| Entity | Key feature | Other features | Radiology / gross | Clinical | Stains / other | Image |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Osteoma | normal bone (???) | other features (???) | radiology / gross (???) | ? | no stains / may be assoc. with FAP | |
| Osteoid osteoma | osteoblastic rimming | anastomosing bony trabeculae | must be <2 cm,[5] metaphysis | painful, NSAIDs remove pain, young | IHC / other | |
| Osteoblastoma | osteoblastic rimming | anastomosing bony trabeculae | must be >1 cm,[5] often >=2 cm, metaphysis | not painful | IHC / other | |
| Ewing sarcoma | small round blue cell tumour | cytoplasmic clearing (due to glycogen) | usu. diaphysis | pediatric, typically 1-10 years | PAS+, PASD-, chromosomal translocations (usually t(11;22)(q24;q12)) | 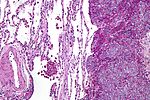 Ewing sarcoma. PAS stain. (WC) |
| Osteosarcoma | osteoid | +/-hemorrhage, +/-cartilage | distal femur, prox. tibia, prox. humerous | typically 10-30 years, pain, swelling | no stains; many subtypes | |
| Giant cell tumour of bone | abundant giant cells | nuclei of surrounding cells similar to those in giant cells | growth plate of long bones | 20-45 years old, +/-joint pain, +/-immobility | IHC / other |
Cartilage tumours
| Entity | Key feature | Other features | Radiology / gross | Clinical | Stains / other | Image |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chondroma | ctyologically benign cells | equally spaced nests | usu. diaphysis | benign / DDx: chondroma, well-diff. chondrosarcoma | IHC / bone marrow cavity chondroma = enchondroma | |
| Chondroblastoma | abundant extracellular material, abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm | calcifications surround cells nests ("chickenwire" appearance) - classic | epiphysis | DDx: giant cell tumour of bone | S100+ve, vimentin +ve | |
| Chondrosarcoma | cartilaginous appearance +/- nuclear atypia | lack osteoid, if present -> osteosarcoma | usu. diaphysis, classically hip; almost never distal extremity | >40 years old | IHC / may be histologically benign looking |
Other
| Entity | Key feature | Other features | Radiology / gross | Clinical | Stains / other | Image |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Osteochondroma | benign bone and cartilage | Other features | metaphyseal lesions | Clinical | IHC / other | Image |
| Adamantinoma | bisphasic - stroma & epithelium | Other features | tibia, fibula, intracortical, radiolucent | Clinical | IHC / other | |
| Diffuse tenosynovial giant-cell tumour (AKA PVNS) | pigmented giant cells | nodules | Radiology / gross | Clinical | IHC / other | |
| Brown tumour | fibrosis, +/-giant cells | unaffected bone incr. osteoblasts and osteoclasts | Radiology / gross | due to hypercalcemia; not a neoplasm | IHC / other |
Radiology
Radiologic features
| Features | Benign | Malignant |
|---|---|---|
| Bone changes | sclerotic rim | tumour perforation |
| Circumscription | pushing margins | ill-defined/moth-eaten |
| Soft tissue involvement | no | common |
| Periosteal reaction | no | "hair-on-end" or "sunburst", "onion skin", Codman's triangle |
Location
| Diagnosis | Epiphysis | Metaphysis | Diaphysis | Type of lesion |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aneurysmal bone cyst | common | most common | rare | bone |
| Chondroblastoma | most common | rare | extremely rare | cartilage |
| Chondrosarcoma | uncommon | common | most common | cartilage |
| Chondromyxoid fibroma | rare | most common | common | other |
| Enchondroma | rare | common | common | cartilage |
| Ewing sarcoma | rare | common | most common | bone |
| Giant cell tumour | most common | rare | extremely rare | bone |
| Metastatic carcinoma | rare | common | most common | other |
| Non-ossifying fibroma | extremely rare | most common | common | other |
| Osteoblastoma | rare | most common | uncommon | bone |
| Osteochondroma | extremely rare[citation needed] | most common | common | bone/cartilage |
| Osteoid osteoma | uncommon | common | common[6] | bone |
| Osteosarcoma | rare | most common | uncommon | bone |
How to remember the primary bone lesions:
- Ewing sarcoma is the only malignant primary bone tumour of the diaphysis.
- Giant cell tumour of bone is the only primary bone lesion of the epiphysis.
- The rest of the primary bone lesions are metaphyseal.
- Osteochondroma is bone first and cartilage second. It behaves like most primary bone lesions; it is usually metaphyseal.
How to remember the primary cartilaginous lesions:
- Chondroblastoma is epiphyseal. The chicken wire goes around the chicken coop.
- The others are diaphyseal.
Cartilage
Chondroma
Chondroblastoma
Chondromyxoid fibroma
Chondrosarcoma
Bone
Osteoma
Osteoid osteoma
Osteoblastoma
Ewing sarcoma
Osteosarcoma
Giant cell tumour of bone
Other
This section collects stuff that doesn't neatly fit into the bone or cartilage category.
Notochordal tumors
Notochordal tumors arise from notochordal remnants and thus are seen in the clivus or sacrum.
Osteochondroma
Diffuse tenosynovial giant-cell tumour
- AKA tenosynovial giant-cell tumour, diffuse type.
- Previously known as pigmented villonodular synovitis (PVNS).[7]
Giant cell tumour of tendon sheath
- Abbreviated GCT of tendon sheath.
Adamantinoma
Brown tumour
General
- Not a true neoplasm.[8]
- If tumour is understood as a synonym for neoplasm, the name is a misnomer.
- May (clinically) mimic a true neoplasm.
- Due to hyperparathyroidism - usually parathyroid adenoma.
- Usually secondary to chronic renal failure.
Hypercalcemia DDx
Mnemonic GRIMED:[9]
- Granulomatous disease (tuberculosis, sarcoidosis).
- Renal disease.
- Immobility.
- Malignancy (esp. squamous cell carcinoma, plasmacytoma).
- Endocrine (primary hyperparathyroidism - leads to brown tumour).
- Drugs (thiazides ... others).
Microscopic
Features:
- Fibrosis.
- +/-Giant cells with round to oval nuclei and nucleoli.[10]
- Bone unaffected by tumour - increased numbers of the following:
- Multinucleated cells (osteoclasts).
- Mononuclear cells around the bony trabeculae (osteoblasts).
DDx:
- Giant cell tumour of bone and other giant cell lesions.
Images
www:
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 632. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Yeung, J.C.; Leonard, Blair J. N. (2005). The Toronto Notes 2005 - Review for the MCCQE and Comprehensive Medical Reference (2005 ed.). The Toronto Notes Inc. for Medical Students Inc.. pp. OR42. ISBN 978-0968592854.
- ↑ Yeung, J.C.; Leonard, Blair J. N. (2005). The Toronto Notes 2005 - Review for the MCCQE and Comprehensive Medical Reference (2005 ed.). The Toronto Notes Inc. for Medical Students Inc.. pp. OR41. ISBN 978-0968592854.
- ↑ URL: http://www.emedicine.com/RADIO/topic494.htm.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Yalcinkaya, U.; Doganavsargil, B.; Sezak, M.; Kececi, B.; Argin, M.; Basdemir, G.; Oztop, F. (Dec 2014). "Clinical and morphological characteristics of osteoid osteoma and osteoblastoma: a retrospective single-center analysis of 204 patients.". Ann Diagn Pathol 18 (6): 319-25. doi:10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2014.08.006. PMID 25224389.
- ↑ URL: http://www.wheelessonline.com/ortho/osteoid_osteoma. Accessed on: 7 May 2012
- ↑ Kumar, Vinay; Abbas, Abul K.; Fausto, Nelson; Aster, Jon (2009). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 1247. ISBN 978-1416031215.
- ↑ Meydan N, Barutca S, Guney E, et al. (June 2006). "Brown tumors mimicking bone metastases". J Natl Med Assoc 98 (6): 950–3. PMC 2569361. PMID 16775919. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2569361/?page=1.
- ↑ Shiau, Carolyn; Toren, Andrew (2006). Toronto Notes 2006: Comprehensive Medical Reference (Review for MCCQE 1 and USMLE Step 2) (22nd edition (2006) ed.). Toronto Notes for Medical Students, Inc.. pp. Emerg.. ISBN 978-0968592861.
- ↑ URL: http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case139/micro.html. Accessed on: 6 January 2012.