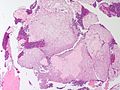
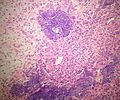
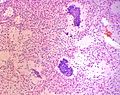
Chondromyxoid fibroma
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Chondromyxoid fibroma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
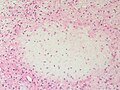
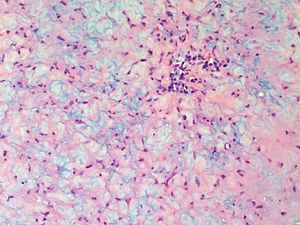 Chondromyxoid fibroma. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
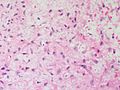
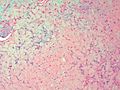
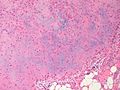
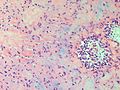
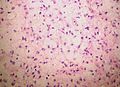
| LM | spindle cells or stellate cells in a myxoid or chondroid stroma, lobules with hypocellular centers and hypercellular peripheries, +/-giant cells in the hypercellular periphery, scattered calcifications, no true hyaline cartilage formation, no mitotic activity |
| LM DDx | chondroblastoma, chondrosarcoma, phosphaturic mesenchymal tumour (case report) |
| Site | bone (metaphysis) - see bone tumours |
|
| |
| Clinical history | teenager/young adult |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
| Prognosis | benign |
Chondromyxoid fibroma is a rare benign chondro-osseous tumour typically found in the metaphysis of teenagers or young adults.
General
- Uncommon and benign.[1]
- Teenagers or young adults.
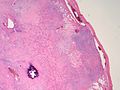
Gross
- Metaphyseal lesion - classic location.[2]
- Well-circumscribed.
- Fragments of white-grey rubbery tissue.
Microscopic
Features:[3]
- Spindle cells or stellate cells in a myxoid or chondroid stroma.
- Lobules with hypocellular centers and hypercellular peripheries.
- Giant cells in the hypercellular periphery.
- Scattered calcifications.
- No true hyaline cartilage formation.
- No mitotic activity.
IHC
SOX9 positive
DDx:
- Chondroblastoma.
- Likewise has immature cartilage but (1) epiphyseal location, (2) chickenwire-like calcifications.
- Chondrosarcoma.
- Different age group.
- Mature hyaline cartilage formation.
- Tumour permeation of the surrounding bone.
- Mitotic activity.
- Phosphaturic mesenchymal tumour - case report.[4]
Images
www:
- Chondromyxoid fibroma - low mag. (webpathology.com).
- Chondromyxoid fibroma - high mag. (webpathology.com).
- Tumor Library [1].
- Tumor Library [2].
- Tumor Library [3].
- Tumor Library [4].
- Tumor Library [5].
- Tumor Library [6].
- Diagnostic Pathology [7].
Molecular
- Activating rearrangements of GRM1 (metabotropic glutamate receptor 1).[5]
See also
References
- ↑ Bhamra, JS.; Al-Khateeb, H.; Dhinsa, BS.; Gikas, PD.; Tirabosco, R.; Pollock, RC.; Skinner, JA.; Aston, WJ. et al. (2014). "Chondromyxoid fibroma management: a single institution experience of 22 cases.". World J Surg Oncol 12: 283. doi:10.1186/1477-7819-12-283. PMID 25217119.
- ↑ Budny, AM.; Ismail, A.; Osher, L.. "Chondromyxoid fibroma.". J Foot Ankle Surg 47 (2): 153-9. doi:10.1053/j.jfas.2007.08.013. PMID 18312923.
- ↑ Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 642. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ Suryawanshi, P.; Agarwal, M.; Dhake, R.; Desai, S.; Rekhi, B.; Reddy, KB.; Jambhekar, NA. (Nov 2011). "Phosphaturic mesenchymal tumor with chondromyxoid fibroma-like feature: an unusual morphological appearance.". Skeletal Radiol 40 (11): 1481-5. doi:10.1007/s00256-011-1159-6. PMID 21533894.
- ↑ Nord, KH.; Lilljebjörn, H.; Vezzi, F.; Nilsson, J.; Magnusson, L.; Tayebwa, J.; de Jong, D.; Bovée, JV. et al. (May 2014). "GRM1 is upregulated through gene fusion and promoter swapping in chondromyxoid fibroma.". Nat Genet 46 (5): 474-7. doi:10.1038/ng.2927. PMID 24658000.