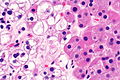
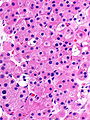
Parathyroid adenoma
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Parathyroid adenoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
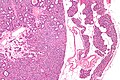
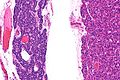
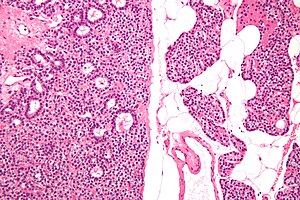 Chief cell parathyroid adenoma (left of image) and unremarkable parathyroid gland (right of image). H&E stain. (WC) | |
|
| |
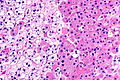
| LM | proliferation of parathyroid cells (chief cells, oxyphils or both) usually lacking adipose tissue, +/-rimmed by normal parathyroid gland, lack of destructive invasion of surround structures, lack of metastatic disease |
| Subtypes | chief cell, oxyphil, mixed |
| LM DDx | parathyroid hyperplasia, parathyroid carcinoma, lymph node, thyroid gland, Hürthle cell adenoma of thyroid (for oxyphil subtype) |
| IHC | Ki-67 low |
| Site | parathyroid gland (neck/mediastinum) |
|
| |
| Associated Dx | renal stones, osteitis fibrosa cystica |
| Syndromes | multiple endocrine neoplasia 1, multiple endocrine neoplasia 2A |
|
| |
| Signs | constipation |
| Symptoms | bone pain, abdominal pain, lethargy, fatigue, memory loss |
| Blood work | increased parathyroid hormone, serum calcium increased |
| Prognosis | benign |
| Other | depression, psychosis, delirium, coma, ataxia |
| Clin. DDx | nodule (lymph node, other tumours), hyperparathyroidism (parathyroid hyperplasia, parathyroid carcinoma), DDx of hypercalcemia |
| Treatment | surgical excision |
Parathyroid adenoma is a common benign pathology of the parathyroid gland.
General
- Clinical diagnosis - significant intraoperative drop of PTH after removal of suspected adenoma.[1]
- Most common cause of primary hyperparathyroidism.[2]
- May be associated with MEN 1 or MEN 2A.
MEN 1:
- Parathyroid adenoma.
- Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumour.
- Pituitary adenoma.
MEN 2A:
- Parathyroid adenoma.
- Medullary thyroid carcinoma.
- Pheochromocytoma.
Subtypes
Histologic subtyping:[3]
- Chief cell parathyroid adenoma.
- Common.
- Oxyphil parathyroid adenoma.
- Uncommon.[4]
- Mixed.
Gross
- One parathyroid gland is big... the others are small.
Note:
- There is a classification system by Perrier et al. that may be seen in radiology reports to describe the position of an adenoma.[5]
Weight
It is common practice to weight parathyroid tissue:
- Parathyroid adenoma are: 0.55 +/- 0.52 grams.[6]
- Normal parathyroids taken out with parathyroid adenomas are: 0.06 +/-0.03 grams.[6]
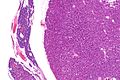
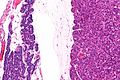
Microscopic
Features:
- Proliferation of parathyroid cells (chief cells, oxyphils or both) usually intermixed lacking adipose tissue.
- +/-Rim of normal parathyroid gland around the lesion[7] with adipose tissue.
Note:
- Generally, it is impossible to discern between parathyroid adenomas and parathyroid hyperplasias by histology alone.[7]
- One requires information on the size of the other glands to make the diagnosis.
- Ideally, histologic findings should be correlated with the PTH serology.
DDx:
- Parathyroid hyperplasia - differentiated by clinical history.
- Parathyroid carcinoma - destructive invasion of surrounding tissue or far away mets, increased proliferative activity.
- Lymph node.
- Hürthle cell adenoma - for oxyphil type (see below).
- Thyroid gland.
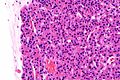
Chief cell parathyroid adenoma
Features:[2]
- Chief cells - key feature:
- Small central nucleus.
- Round with stippled chromatin - important.
- Moderate cytoplasm.
- Small central nucleus.
- +/-Scattered oxyphil cells:
- Large cells.
- Abundant cytoplasm.
- Architecture:
- Nests.
- Circular formations - often around capillaries (perivascular pseudorosettes).
Images
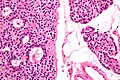
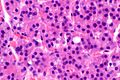
Oxyphil parathyroid adenoma
Features:[2]
- Oxyphil cells:
- Large cells.
- Abundant cytoplasm.
DDx:
- Hürthle cell adenoma of the thyroid gland.
Image
www
Sign out
Note:
- One should not say "negative for malignancy".
Parathyroid Gland (Submitted as "Right Superior Parathyroid Adenoma"), Excision: - Parathyroid adenoma with adjacent normal parathyroid tissue.
Chief cell type
Parathyroid Gland, Excision: - Chief cell parathyroid adenoma.
Parathyroid Gland, Excision: - Chief cell parathyroid adenoma with adjacent normal parathyroid tissue.
Oxyphil type
Right Superior Parathyroid, Excision: - Consistent with parathyroid adenoma (oxyphil type) with rim of normal appearing parathyroid tissue.
Tertiary hyperparathyroidism
A. Right Inferior Parathyroid, Excision: - Cellular parathyroid tissue with a rim of normal-appearing parathyroid tissue, compatible with parathyroid adenoma. B. Portion of Right Superior Parathyroid, Excision: - Cellular parathyroid compatible with adenoma or hyperplasia.
Unclear history
Submitted as "Right Inferior Parathyroid", Excision: - Hyperplastic appearing parathyroid tissue devoid of fat consisting of a mixture of chief cells and oncocytic cells, compatible with parathyroid adenoma in proper clinical context. - Unremarkable parathyroid tissue.
Block letters
PARATHYROID GLAND, EXCISION: - CHIEF CELL PARATHYROID ADENOMA.
Micro
The section shows an adenoma consisting predominantly of chief cells. A rim of normal parathyroid is seen adjacent to the adenoma. A small amount of unremarkable adipose tissue is present.
See also
References
- ↑ Özkul, MH.; Uyar, M.; Bayram, Ö.; Dikmen, B.. "Parathyroid scintigraphy and minimal invasive surgery in parathyroid adenomas.". Kulak Burun Bogaz Ihtis Derg 25 (4): 205-13. PMID 26211860.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Kumar, Vinay; Abbas, Abul K.; Fausto, Nelson; Aster, Jon (2009). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 1127. ISBN 978-1416031215.
- ↑ Moran, CA.; Suster, S. (Nov 2005). "Primary parathyroid tumors of the mediastinum: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study of 17 cases.". Am J Clin Pathol 124 (5): 749-54. doi:10.1309/WJEL-N05L-9A06-9DU0. PMID 16203274.
- ↑ Fleischer, J.; Becker, C.; Hamele-Bena, D.; Breen, TL.; Silverberg, SJ. (Dec 2004). "Oxyphil parathyroid adenoma: a malignant presentation of a benign disease.". J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89 (12): 5948-51. doi:10.1210/jc.2004-1597. PMID 15579742.
- ↑ Perrier, ND.; Edeiken, B.; Nunez, R.; Gayed, I.; Jimenez, C.; Busaidy, N.; Potylchansky, E.; Kee, S. et al. (Mar 2009). "A novel nomenclature to classify parathyroid adenomas.". World J Surg 33 (3): 412-6. doi:10.1007/s00268-008-9894-0. PMID 19148701.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Yao, K.; Singer, FR.; Roth, SI.; Sassoon, A.; Ye, C.; Giuliano, AE. (Jul 2004). "Weight of normal parathyroid glands in patients with parathyroid adenomas.". J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89 (7): 3208-13. doi:10.1210/jc.2003-031184. PMID 15240594.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Taxy, J.; Husain, A; Montag, A. (2009). Biopsy Interpretation: The Frozen Section (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 191. ISBN 978-0781767798.
- ↑ URL: http://library.med.utah.edu/WebPath/EXAM/IMGQUIZ/enfrm.html. Accessed on: 6 December 2010.