Difference between revisions of "Hemangioma"
Jensflorian (talk | contribs) (→General: CNS) |
|||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
| Site = [[soft tissue]], [[skin]], [[liver hemangioma|liver]] (dealt with in separate article), others | | Site = [[soft tissue]], [[skin]], [[liver hemangioma|liver]] (dealt with in separate article), others | ||
| Assdx = [[Castleman disease]] - for glomeruloid hemangioma | | Assdx = [[Castleman disease]] - for glomeruloid hemangioma | ||
| Syndromes = [[POEMS syndrome]] - for glomeruloid hemangioma | | Syndromes = [[POEMS syndrome]] - for glomeruloid hemangioma, [[Maffucci's syndrome]] | ||
| Clinicalhx = | | Clinicalhx = | ||
| Signs = | | Signs = | ||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
'''Hemangioma''' is a very common benign [[vascular tumour]]. | '''Hemangioma''' is a very common benign [[vascular tumour]]. | ||
''Hemangiomas of the [[liver]]'' are dealt with in the article ''[[liver hemangioma]]''. | ''Hemangiomas of the [[liver]]'' are dealt with in the article ''[[liver hemangioma]]''. | ||
''Anastomosing hemangioma'' is dealt with in the article ''[[anastomosing hemangioma]]''. | |||
==General== | ==General== | ||
| Line 66: | Line 68: | ||
*Cavernous. | *Cavernous. | ||
*Capillary. | *Capillary. | ||
====Syndromic associations==== | |||
*[[Maffucci's syndrome]].<ref name=pmid6584817>{{cite journal |authors=Laskaris G, Skouteris C |title=Maffucci's syndrome. Report of a case with oral hemangiomas |journal=Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol |volume=57 |issue=3 |pages=263–6 |date=March 1984 |pmid=6584817 |doi=10.1016/0030-4220(84)90181-6 |url=}}</ref> | |||
*[[POEMS syndrome]]. | |||
==Microscopic== | ==Microscopic== | ||
| Line 118: | Line 124: | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
*[[Vascular tumours]]. | *[[Vascular tumours]]. | ||
*[[Pneumocytoma]] - previously known as ''sclerosing hemangioma''. | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Latest revision as of 21:13, 16 May 2022
| Hemangioma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
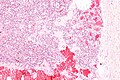
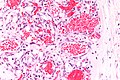
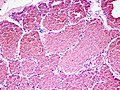
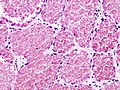
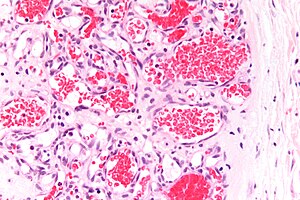 Capillary hemangioma. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | channels lined by benign endothelium containing RBCs |
| Subtypes | soft tissue (capillary, cavernous, arteriovenous, venous, intramuscular, synovial), childhood (tufted, microvenular hemangioma, glomeruloid hemangioma, epithelioid hemangioma (see angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia), targetoid hemosideric hemangioma, infantile hemangioma) |
| LM DDx | lymphangioma, angiokeratoma, lobular capillary hemangioma (pyogenic granuloma). |
| IHC | CD31 +ve, D2-40 -ve, GLUT-1 +ve -- juvenile hemangioma |
| Site | soft tissue, skin, liver (dealt with in separate article), others |
|
| |
| Associated Dx | Castleman disease - for glomeruloid hemangioma |
| Syndromes | POEMS syndrome - for glomeruloid hemangioma, Maffucci's syndrome |
|
| |
| Prevalence | common vascular lesion |
| Prognosis | benign |
| Hemangioma | |
|---|---|
| External resources | |
| EHVSC | 10172 |
Hemangioma is a very common benign vascular tumour.
Hemangiomas of the liver are dealt with in the article liver hemangioma.
Anastomosing hemangioma is dealt with in the article anastomosing hemangioma.
General
Hemangiomas to remember - if you're only going remember a few:
- Glomeruloid, infantile, cavernous, capillary, arteriovenous, venous and intramuscular.
- ICD-O: 9120/0.
Childhood
Common childhood hemangiomas:[1]
- Tufted - small clusters of blood vessels.
- Microvenular hemangioma.
- Glomeruloid hemangioma - associated with POEMS syndrome, Castleman disease.[2][3]
- Epithelioid hemangioma - see angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia.
- Targetoid hemosideric hemangioma.
- Infantile hemangioma (AKA juvenile hemangioma[4]) - these tumours are GLUT-1 +ve. They tumours grow and then spontaneously regress.[5]
Soft tissue
Several types are seen in soft tissue:[6]
- Capillary.
- Cavernous.
- Arteriovenous.
- Venous.
- Intramuscular.
- Synovial.
CNS
Usually from bone, rarely dural and parenchymal hemangiomas.
- Cavernous.
- Capillary.
Syndromic associations
Microscopic
Features:
- Channels lined by benign endothelium containing RBCs.
DDx:
- Lymphangioma.
- Angiokeratoma.
- Lobular capillary hemangioma (pyogenic granuloma).
Images
www:
IHC
- CD31 +ve.
- D2-40 -ve.[8]
Juvenile hemangioma:[4]
- GLUT-1 +ve.
Sign out
Subcutaneous Neck Lesion, Left, Excision: - Cavernous hemangioma. - NEGATIVE for malignancy.
Block letters
SUBCUTANEOUS NECK LESION, LEFT, EXCISION: - CAVERNOUS HEMANGIOMA. - NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
LESION, LEFT SIDE OF FACE, EXCISION: - CAPILLARY HEMANGIOMA. - NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
Micro - skin
The sections show hair-bearing skin with abundant small superficial vascular channels containing red blood cells. The endothelial cells of the vascular channels do not have atypia. No mitotic activity is appreciated. The overlying epidermis is unremarkable. Extensive solar elastosis is present. No nevus is identified.
See also
- Vascular tumours.
- Pneumocytoma - previously known as sclerosing hemangioma.
References
- ↑ Prieto VG, Shea CR (July 1999). "Selected cutaneous vascular neoplasms. A review". Dermatol Clin 17 (3): 507–20, viii. PMID 10410855.
- ↑ Uthup S, Balachandran K, Ammal VA, et al. (August 2006). "Renal involvement in multicentric Castleman disease with glomeruloid hemangioma of skin and plasmacytoma". Am. J. Kidney Dis. 48 (2): e17–24. doi:10.1053/j.ajkd.2006.04.089. PMID 16860182.
- ↑ Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 618. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 North, PE.; Waner, M.; Mizeracki, A.; Mihm, MC. (Jan 2000). "GLUT1: a newly discovered immunohistochemical marker for juvenile hemangiomas.". Hum Pathol 31 (1): 11-22. PMID 10665907.
- ↑ Dadras, SS.; North, PE.; Bertoncini, J.; Mihm, MC.; Detmar, M. (Sep 2004). "Infantile hemangiomas are arrested in an early developmental vascular differentiation state.". Mod Pathol 17 (9): 1068-79. doi:10.1038/modpathol.3800153. PMID 15143338.
- ↑ Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 602. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ Laskaris G, Skouteris C (March 1984). "Maffucci's syndrome. Report of a case with oral hemangiomas". Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 57 (3): 263–6. doi:10.1016/0030-4220(84)90181-6. PMID 6584817.
- ↑ Kahn, HJ.; Bailey, D.; Marks, A. (Apr 2002). "Monoclonal antibody D2-40, a new marker of lymphatic endothelium, reacts with Kaposi's sarcoma and a subset of angiosarcomas.". Mod Pathol 15 (4): 434-40. doi:10.1038/modpathol.3880543. PMID 11950918.