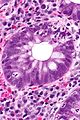
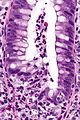
Difference between revisions of "Inflammatory bowel disease"
m (→Sign out) |
|||
| (72 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
*Biopsies for diagnosis should specify the (anatomical) site: | *Biopsies for diagnosis should specify the (anatomical) site: | ||
**Slight gradients exist in the large bowel that can be exploited for diagnostic purposes if the site information is known, for example: | **Slight gradients exist in the large bowel that can be exploited for diagnostic purposes if the site information is known, for example: | ||
***Paneth cell distal to the splenic flexure are abnormal. | ***[[Paneth cell]]s distal to the splenic flexure are abnormal. | ||
***Ulcerative colitis is often more severe distally - even in a pancolitis, as the disease starts in the rectum and progresses toward the cecum. | ***Ulcerative colitis is often more severe distally - even in a pancolitis, as the disease starts in the rectum and progresses toward the cecum. | ||
*Surveillance biopsies should specify the (anatomical) site - so, it possible to find any site of interest on a follow-up colonoscopy.<ref name=pmid16609751>{{Cite journal | last1 = Panaccione | first1 = R. | title = The approach to dysplasia surveillance in inflammatory bowel disease. | journal = Can J Gastroenterol | volume = 20 | issue = 4 | pages = 251-3 | month = Apr | year = 2006 | doi = | PMID = 16609751 | PMC = 2659899}}</ref> | *Surveillance biopsies should specify the (anatomical) site - so, it possible to find any site of interest on a follow-up colonoscopy.<ref name=pmid16609751>{{Cite journal | last1 = Panaccione | first1 = R. | title = The approach to dysplasia surveillance in inflammatory bowel disease. | journal = Can J Gastroenterol | volume = 20 | issue = 4 | pages = 251-3 | month = Apr | year = 2006 | doi = | PMID = 16609751 | PMC = 2659899}}</ref> | ||
=== | ===Biopsies all submitted in one bottle=== | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
COLON (SITE NOT FURTHER SPECIFIED), BIOPSIES: | COLON (SITE NOT FURTHER SPECIFIED), BIOPSIES: | ||
| Line 83: | Line 83: | ||
#*Atrophy = less glands ~ 3-4 glands/mm (normal = 7-8 glands/mm). | #*Atrophy = less glands ~ 3-4 glands/mm (normal = 7-8 glands/mm). | ||
#*Branching = common (normal = very rare branching). | #*Branching = common (normal = very rare branching). | ||
#*Distortion = bent glands, marked size variation (normal = "rack of test tubes"). | #*Distortion = bent glands, marked size variation<ref>URL: [http://www.histopath.com.au/assets/documents/Inflammatory%20bowel%20disease.pdf http://www.histopath.com.au/assets/documents/Inflammatory%20bowel%20disease.pdf]. Accessed on: 25 October 2013.</ref> (normal = "rack of test tubes"). | ||
#Distal Paneth cell metaplasia. | #Distal Paneth cell metaplasia. | ||
#*Paneth cells should ''not'' be in the left colon<ref name=pmid11851832>{{cite journal |author=Tanaka M, Saito H, Kusumi T, ''et al'' |title=Spatial distribution and histogenesis of colorectal Paneth cell metaplasia in idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease |journal=J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. |volume=16 |issue=12 |pages=1353–9 |year=2001 |month=December |pmid=11851832 |doi= |url=http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/resolve/openurl?genre=article&sid=nlm:pubmed&issn=0815-9319&date=2001&volume=16&issue=12&spage=1353}}</ref> - if you see 'em think of IBD and other long-standing injurious processes. | #*Paneth cells should ''not'' be in the left colon<ref name=pmid11851832>{{cite journal |author=Tanaka M, Saito H, Kusumi T, ''et al'' |title=Spatial distribution and histogenesis of colorectal Paneth cell metaplasia in idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease |journal=J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. |volume=16 |issue=12 |pages=1353–9 |year=2001 |month=December |pmid=11851832 |doi= |url=http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/resolve/openurl?genre=article&sid=nlm:pubmed&issn=0815-9319&date=2001&volume=16&issue=12&spage=1353}}</ref> - if you see 'em think of IBD and other long-standing injurious processes. | ||
#*Paneth cells have basal nuclei and coarse luminal granules.<ref name=Ref_H4P3_631>{{Ref H4P3|631}}</ref> | #*Paneth cells have basal nuclei and coarse luminal granules.<ref name=Ref_H4P3_631>{{Ref H4P3|631}}</ref> | ||
#**They should '''not''' be confused with endocrine cells -- these have apical nuclei and fine granules. | #**They should '''not''' be confused with endocrine cells -- these have apical nuclei and fine granules. | ||
#**They should '''not''' be confused with intraepithelial | #**They should '''not''' be confused with intraepithelial [[eosinophil]]s -- have smaller (~1/2) more intensely red granules. | ||
Notes: | Notes: | ||
# Microscopic features can be remembered by [[mnemonic]] ''CPP'': Crypts (abnormal), Plasmacytosis, Paneth cells where they don't belong. | # Microscopic features can be remembered by [[mnemonic]] ''CPP'': Crypts (abnormal), Plasmacytosis, Paneth cells where they don't belong. | ||
# If you see architectural distortion (e.g. crypt branching) in the left colon, look for Paneth cells. | # If you see architectural distortion (e.g. crypt branching) in the left colon, look for Paneth cells. | ||
# The hepatic flexure is considered the divider for normal paneth cells and abnormal paneth cells, i.e. paneth cells proximal to the hepatic flexure are normal; paneth cells distal to the hepatic flexure are abnormal.<ref>STC. 14 December 2009.</ref> | # The hepatic flexure is considered the divider for normal paneth cells and abnormal paneth cells, i.e. paneth cells proximal to the hepatic flexure are normal; paneth cells distal to the hepatic flexure are abnormal.<ref>STC. 14 December 2009.</ref> | ||
# Stretching of tissue may mimic atrophy; tip-off it is | # Stretching of tissue may mimic atrophy; tip-off it is artifact: thinning of mucosa.<ref name=Kirsch>Kirsch, R. 13 December 2010.</ref> | ||
Images | ====Images==== | ||
<gallery> | |||
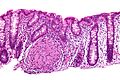
Image:Crohn%27s_disease_-_colon_-_high_mag.jpg | Crohn's disease - very well-formed granulomas in the [[colon]] - high mag. (WC) | |||
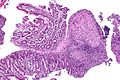
Image:Crohn%27s_disease_-_duodenum_-_intermed_mag.jpg | Crohn's disease - duodenum - intermed. mag. (WC) | |||
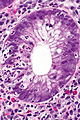
Image: Cryptitis_-_alt_--_very_high_mag.jpg | Cryptitis. (WC) | |||
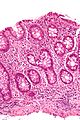
Image:Crypt_branching_high_mag.jpg | Crypt branching. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
===Grading=== | ===Grading=== | ||
| Line 116: | Line 117: | ||
| "A grading scheme"<ref name=Kirsch>Kirsch, R. 13 December 2010.</ref> | | "A grading scheme"<ref name=Kirsch>Kirsch, R. 13 December 2010.</ref> | ||
| - | | - | ||
| cryptitis | | [[cryptitis]] | ||
| | | [[crypt abscesses]] | ||
| erosions | | erosions | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 127: | Line 128: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
=====Images===== | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image: Cryptitis_--_very_high_mag.jpg | [[Cryptitis]]. (WC) | |||
Image: Crypt_abscess_--_very_high_mag.jpg | [[Crypt abscess]]. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
==Crohn's disease | ==Crohn's disease versus ulcerative colitis== | ||
*Some cases cannot be classified by the experts (see [[Inflammatory_bowel_disease#.22Indeterminate_colitis.22|"indeterminate colitis"]]). | *Some cases cannot be classified by the experts (see [[Inflammatory_bowel_disease#.22Indeterminate_colitis.22|"indeterminate colitis"]]). | ||
| Line 138: | Line 144: | ||
** UC may have 'ileal backwash' -- mild ileal inflammation due to backwash of inflammatory soup from colon. | ** UC may have 'ileal backwash' -- mild ileal inflammation due to backwash of inflammatory soup from colon. | ||
*"No granulomas". | *"No granulomas". | ||
**Superficial [[granulomas]] in the mucosa are non-specific, especially if they are beside an | **Superficial [[granulomas]] in the mucosa are non-specific, especially if they are beside an inflamed crypt, i.e. they may be present in UC.<ref name=pmid12147095>{{Cite journal | last1 = Shepherd | first1 = NA. | title = Granulomas in the diagnosis of intestinal Crohn's disease: a myth exploded? | journal = Histopathology | volume = 41 | issue = 2 | pages = 166-8 | month = Aug | year = 2002 | doi = | PMID = 12147095 }}</ref><ref name=pmid12121237>{{Cite journal | last1 = Mahadeva | first1 = U. | last2 = Martin | first2 = JP. | last3 = Patel | first3 = NK. | last4 = Price | first4 = AB. | title = Granulomatous ulcerative colitis: a re-appraisal of the mucosal granuloma in the distinction of Crohn's disease from ulcerative colitis. | journal = Histopathology | volume = 41 | issue = 1 | pages = 50-5 | month = Jul | year = 2002 | doi = | PMID = 12121237 }}</ref> | ||
***Deep granulomas are specific for Crohn's disease. | ***Deep granulomas are specific for Crohn's disease. | ||
| Line 172: | Line 178: | ||
**~ 10% of UC patients. | **~ 10% of UC patients. | ||
**~ 40% of UC + colectomy + [[pouchitis]]. | **~ 40% of UC + colectomy + [[pouchitis]]. | ||
Another study compares UC, CD and control individuals:<ref name=pmid20848539>{{Cite journal | last1 = Sonnenberg | first1 = A. | last2 = Melton | first2 = SD. | last3 = Genta | first3 = RM. | title = Frequent occurrence of gastritis and duodenitis in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. | journal = Inflamm Bowel Dis | volume = 17 | issue = 1 | pages = 39-44 | month = Jan | year = 2011 | doi = 10.1002/ibd.21356 | PMID = 20848539 }}</ref> | |||
*Gastritis: | |||
**UC: 19%. | |||
**CD: 33% | |||
**Controls: 13%. | |||
*Duodenitis: | |||
**UC: 3%. | |||
**CD: 26%. | |||
**Controls: 1%. | |||
Note: | |||
*Younger individuals (<18 years old) have significantly more gastritis and duodenitis.<ref name=pmid20848539/> | |||
====A tabular comparison==== | ====A tabular comparison==== | ||
| Line 210: | Line 229: | ||
|} | |} | ||
= | =Sign out= | ||
== | ===Quiescent inflammatory bowel disease=== | ||
*No accepted formal definition. | |||
* | |||
May be used when: | |||
#Non-specific "minimal abnormalities" are present. | |||
#There is a history of inflammatory bowel disease. | |||
"Minimal abnormalities" - features: | |||
*Apoptosis. | |||
*Macrophages in the lamina propria. | |||
*Lymphoid nodules. | |||
*"Abundant" plasma cells in the lamina propria. | |||
* | **''Abundant'' is subjective. | ||
* | |||
* | |||
* | |||
** | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
COLON, BIOPSIES: | |||
- | - QUIESCENT INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE. | ||
- NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA. | - NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA. | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
===Mild inflammation=== | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
SIGMOID COLON, BIOPSY: | SIGMOID COLON, BIOPSY: | ||
- MILD ACTIVE COLITIS, SEE COMMENT. | - MILD ACTIVE COLITIS WITH CHRONIC CHANGES, SEE COMMENT. | ||
- NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA. | - NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA. | ||
COMMENT: | COMMENT: | ||
No granulomata are identified. | No granulomata are identified. Mild architectural changes are present. | ||
The findings are compatible with inflammatory bowel disease or an infectious | |||
etiology. Clinical correlation is required. | |||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
===Mild-to-moderate inflammation=== | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
COLON, LEFT, BIOPSY: | |||
- MODERATE | - MILD-TO-MODERATE ACTIVE COLITIS WITH CHRONIC CHANGES. | ||
- NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA. | - NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA. | ||
COMMENT: | COMMENT: | ||
No definite granulomata are identified. | No definite granulomata are identified. Mild architectural changes are present. | ||
Cryptitis is seen in several crypts. Rare crypt abscesses are present. Lamina propria | |||
plasma cells are abundant throughout the biopsy. | |||
The findings are compatible with inflammatory bowel disease or an infectious | |||
The | etiology. Clinical correlation is required. | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
=== | ===Moderate inflammation=== | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
RECTUM, BIOPSY: | |||
- RECTAL MUCOSA WITH MODERATE ACTIVE INFLAMMATION AND CHRONIC CHANGES. | |||
- RECTAL MUCOSA | |||
- NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA. | - NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA. | ||
- SEE COMMENT. | |||
COMMENT: | COMMENT: | ||
No definite granulomata are identified. Architectural changes, including crypt drop out, | |||
identified. | are present. Lamina propria plasma cells are abundant throughout the biopsy and eosinophil | ||
numbers are mildly increased. Lymphoid aggregates with germinal centre formation are | |||
present. All fragments of tissue are affected. | |||
The findings are compatible with inflammatory bowel disease or an infectious | |||
etiology. Clinical correlation is required. | |||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
==== | =Specific diagnoses= | ||
==Ulcerative colitis== | |||
*Often abbreviated as ''UC''. | |||
{{Main|Ulcerative colitis}} | |||
==Crohn's disease== | ==Crohn's disease== | ||
* | *Abbreviated ''CD''. | ||
{{Main|Crohn's disease}} | |||
=="Indeterminate colitis"== | =="Indeterminate colitis"== | ||
| Line 519: | Line 311: | ||
#CUTE = Colitis of uncertain type or etiology. | #CUTE = Colitis of uncertain type or etiology. | ||
#*Should be reserved for resection specimens only. | #*Should be reserved for resection specimens only. | ||
==Dysplasia in inflammatory bowel disease== | ==Dysplasia in inflammatory bowel disease== | ||
| Line 526: | Line 316: | ||
Classified as per Riddell ''et al.'':<ref name=pmid6629368>{{Cite journal | last1 = Riddell | first1 = RH. | last2 = Goldman | first2 = H. | last3 = Ransohoff | first3 = DF. | last4 = Appelman | first4 = HD. | last5 = Fenoglio | first5 = CM. | last6 = Haggitt | first6 = RC. | last7 = Ahren | first7 = C. | last8 = Correa | first8 = P. | last9 = Hamilton | first9 = SR. | title = Dysplasia in inflammatory bowel disease: standardized classification with provisional clinical applications. | journal = Hum Pathol | volume = 14 | issue = 11 | pages = 931-68 | month = Nov | year = 1983 | doi = | PMID = 6629368 }}</ref><ref name=pmid11400142>{{Cite journal | last1 = Eaden | first1 = J. | last2 = Abrams | first2 = K. | last3 = McKay | first3 = H. | last4 = Denley | first4 = H. | last5 = Mayberry | first5 = J. | title = Inter-observer variation between general and specialist gastrointestinal pathologists when grading dysplasia in ulcerative colitis. | journal = J Pathol | volume = 194 | issue = 2 | pages = 152-7 | month = Jun | year = 2001 | doi = 10.1002/path.876 | PMID = 11400142 }}</ref><ref name=pmid11936264>{{Cite journal | last1 = Greenson | first1 = JK. | title = Dysplasia in inflammatory bowel disease. | journal = Semin Diagn Pathol | volume = 19 | issue = 1 | pages = 31-7 | month = Feb | year = 2002 | doi = | PMID = 11936264 }}</ref> | Classified as per Riddell ''et al.'':<ref name=pmid6629368>{{Cite journal | last1 = Riddell | first1 = RH. | last2 = Goldman | first2 = H. | last3 = Ransohoff | first3 = DF. | last4 = Appelman | first4 = HD. | last5 = Fenoglio | first5 = CM. | last6 = Haggitt | first6 = RC. | last7 = Ahren | first7 = C. | last8 = Correa | first8 = P. | last9 = Hamilton | first9 = SR. | title = Dysplasia in inflammatory bowel disease: standardized classification with provisional clinical applications. | journal = Hum Pathol | volume = 14 | issue = 11 | pages = 931-68 | month = Nov | year = 1983 | doi = | PMID = 6629368 }}</ref><ref name=pmid11400142>{{Cite journal | last1 = Eaden | first1 = J. | last2 = Abrams | first2 = K. | last3 = McKay | first3 = H. | last4 = Denley | first4 = H. | last5 = Mayberry | first5 = J. | title = Inter-observer variation between general and specialist gastrointestinal pathologists when grading dysplasia in ulcerative colitis. | journal = J Pathol | volume = 194 | issue = 2 | pages = 152-7 | month = Jun | year = 2001 | doi = 10.1002/path.876 | PMID = 11400142 }}</ref><ref name=pmid11936264>{{Cite journal | last1 = Greenson | first1 = JK. | title = Dysplasia in inflammatory bowel disease. | journal = Semin Diagn Pathol | volume = 19 | issue = 1 | pages = 31-7 | month = Feb | year = 2002 | doi = | PMID = 11936264 }}</ref> | ||
*Negative for dysplasia. | *Negative for dysplasia. | ||
*Indefinite for dysplasia. | *[[Indefinite for dysplasia]]. | ||
*Low grade dysplasia. | *Low grade dysplasia. | ||
*High grade dysplasia. | *High grade dysplasia. | ||
Notes: | Notes: | ||
*GI experts and generalists have similar rates agreement.<ref name=pmid11400142>{{Cite journal | last1 = Eaden | first1 = J. | last2 = Abrams | first2 = K. | last3 = McKay | first3 = H. | last4 = Denley | first4 = H. | last5 = Mayberry | first5 = J. | title = Inter-observer variation between general and specialist gastrointestinal pathologists when grading dysplasia in ulcerative colitis. | journal = J Pathol | volume = 194 | issue = 2 | pages = 152-7 | month = Jun | year = 2001 | doi = 10.1002/path.876 | PMID = 11400142 }}</ref> | *GI experts and generalists have similar rates of agreement.<ref name=pmid11400142>{{Cite journal | last1 = Eaden | first1 = J. | last2 = Abrams | first2 = K. | last3 = McKay | first3 = H. | last4 = Denley | first4 = H. | last5 = Mayberry | first5 = J. | title = Inter-observer variation between general and specialist gastrointestinal pathologists when grading dysplasia in ulcerative colitis. | journal = J Pathol | volume = 194 | issue = 2 | pages = 152-7 | month = Jun | year = 2001 | doi = 10.1002/path.876 | PMID = 11400142 }}</ref> | ||
===Microscopic=== | ===Microscopic=== | ||
| Line 541: | Line 331: | ||
==Dysplasia-associated lesion or mass== | ==Dysplasia-associated lesion or mass== | ||
*Abbreviated ''DALM''. | *Abbreviated ''DALM''. | ||
{{Main|Dysplasia-associated lesion or mass}} | |||
==Pouchitis== | ==Pouchitis== | ||
| Line 569: | Line 338: | ||
**Generally, pouches are ''not'' used in Crohn's disease. | **Generally, pouches are ''not'' used in Crohn's disease. | ||
*Chronic pouchitis seen in approximately 15% of patients.<ref name=pmid12617884 >{{Cite journal | last1 = Gionchetti | first1 = P. | last2 = Amadini | first2 = C. | last3 = Rizzello | first3 = F. | last4 = Venturi | first4 = A. | last5 = Poggioli | first5 = G. | last6 = Campieri | first6 = M. | title = Diagnosis and treatment of pouchitis. | journal = Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol | volume = 17 | issue = 1 | pages = 75-87 | month = Feb | year = 2003 | doi = | PMID = 12617884 }}</ref> | *Chronic pouchitis seen in approximately 15% of patients.<ref name=pmid12617884 >{{Cite journal | last1 = Gionchetti | first1 = P. | last2 = Amadini | first2 = C. | last3 = Rizzello | first3 = F. | last4 = Venturi | first4 = A. | last5 = Poggioli | first5 = G. | last6 = Campieri | first6 = M. | title = Diagnosis and treatment of pouchitis. | journal = Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol | volume = 17 | issue = 1 | pages = 75-87 | month = Feb | year = 2003 | doi = | PMID = 12617884 }}</ref> | ||
*May be assessed by fecal calprotectin.<ref name=pmid18301296>{{Cite journal | last1 = Johnson | first1 = MW. | last2 = Maestranzi | first2 = S. | last3 = Duffy | first3 = AM. | last4 = Dewar | first4 = DH. | last5 = Forbes | first5 = A. | last6 = Bjarnason | first6 = I. | last7 = Sherwood | first7 = RA. | last8 = Ciclitira | first8 = P. | last9 = Nicholls | first9 = JR. | title = Faecal calprotectin: a noninvasive diagnostic tool and marker of severity in pouchitis. | journal = Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol | volume = 20 | issue = 3 | pages = 174-9 | month = Mar | year = 2008 | doi = 10.1097/MEG.0b013e3282f1c9a7 | PMID = 18301296 }}</ref> | *May be assessed by [[fecal calprotectin]].<ref name=pmid18301296>{{Cite journal | last1 = Johnson | first1 = MW. | last2 = Maestranzi | first2 = S. | last3 = Duffy | first3 = AM. | last4 = Dewar | first4 = DH. | last5 = Forbes | first5 = A. | last6 = Bjarnason | first6 = I. | last7 = Sherwood | first7 = RA. | last8 = Ciclitira | first8 = P. | last9 = Nicholls | first9 = JR. | title = Faecal calprotectin: a noninvasive diagnostic tool and marker of severity in pouchitis. | journal = Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol | volume = 20 | issue = 3 | pages = 174-9 | month = Mar | year = 2008 | doi = 10.1097/MEG.0b013e3282f1c9a7 | PMID = 18301296 }}</ref> | ||
*Considered a clinico-pathologic diagnosis.<ref name=pmid20958905>{{Cite journal | last1 = Royston | first1 = DJ. | last2 = Warren | first2 = BF. | title = Are we reporting ileal pouch biopsies correctly? | journal = Colorectal Dis | volume = 13 | issue = 11 | pages = 1285-9 | month = Nov | year = 2011 | doi = 10.1111/j.1463-1318.2010.02452.x | PMID = 20958905 }}</ref><ref name=pmid12617884 >{{Cite journal | last1 = Gionchetti | first1 = P. | last2 = Amadini | first2 = C. | last3 = Rizzello | first3 = F. | last4 = Venturi | first4 = A. | last5 = Poggioli | first5 = G. | last6 = Campieri | first6 = M. | title = Diagnosis and treatment of pouchitis. | journal = Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol | volume = 17 | issue = 1 | pages = 75-87 | month = Feb | year = 2003 | doi = | PMID = 12617884 }}</ref> | *Considered a clinico-pathologic diagnosis.<ref name=pmid20958905>{{Cite journal | last1 = Royston | first1 = DJ. | last2 = Warren | first2 = BF. | title = Are we reporting ileal pouch biopsies correctly? | journal = Colorectal Dis | volume = 13 | issue = 11 | pages = 1285-9 | month = Nov | year = 2011 | doi = 10.1111/j.1463-1318.2010.02452.x | PMID = 20958905 }}</ref><ref name=pmid12617884 >{{Cite journal | last1 = Gionchetti | first1 = P. | last2 = Amadini | first2 = C. | last3 = Rizzello | first3 = F. | last4 = Venturi | first4 = A. | last5 = Poggioli | first5 = G. | last6 = Campieri | first6 = M. | title = Diagnosis and treatment of pouchitis. | journal = Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol | volume = 17 | issue = 1 | pages = 75-87 | month = Feb | year = 2003 | doi = | PMID = 12617884 }}</ref> | ||
===Microscopic=== | ===Microscopic=== | ||
Features:<ref name=pmid12794576>{{Cite journal | last1 = Shen | first1 = B. | last2 = Achkar | first2 = JP. | last3 = Connor | first3 = JT. | last4 = Ormsby | first4 = AH. | last5 = Remzi | first5 = FH. | last6 = Bevins | first6 = CL. | last7 = Brzezinski | first7 = A. | last8 = Bambrick | first8 = ML. | last9 = Fazio | first9 = VW. | title = Modified pouchitis disease activity index: a simplified approach to the diagnosis of pouchitis. | journal = Dis Colon Rectum | volume = 46 | issue = 6 | pages = 748-53 | month = Jun | year = 2003 | doi = 10.1097/01.DCR.0000070528.00563.D9 | PMID = 12794576 | URL = http://www.lri.ccf.org/pathobio/achkar/documents/Shen2003DisColonRectum.pdf }}</ref> | Features:<ref name=pmid12794576>{{Cite journal | last1 = Shen | first1 = B. | last2 = Achkar | first2 = JP. | last3 = Connor | first3 = JT. | last4 = Ormsby | first4 = AH. | last5 = Remzi | first5 = FH. | last6 = Bevins | first6 = CL. | last7 = Brzezinski | first7 = A. | last8 = Bambrick | first8 = ML. | last9 = Fazio | first9 = VW. | title = Modified pouchitis disease activity index: a simplified approach to the diagnosis of pouchitis. | journal = Dis Colon Rectum | volume = 46 | issue = 6 | pages = 748-53 | month = Jun | year = 2003 | doi = 10.1097/01.DCR.0000070528.00563.D9 | PMID = 12794576 | URL = http://www.lri.ccf.org/pathobio/achkar/documents/Shen2003DisColonRectum.pdf }}</ref> | ||
*[[Neutrophil]]s. | *[[Neutrophil]]s - intraepithelial ([[cryptitis]]). | ||
*+/-Crypt abscess - indicator of moderate or severe. | *+/-[[Crypt abscess]] (cluster of neutrophils in a gland) - indicator of moderate or severe. | ||
*Ulceration. | *Ulceration. | ||
Note: | |||
*Absence of Paneth cells and villi = colonic metaplasia,<ref name=pmid22892912/> associated with inflammation.<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Fruin | first1 = AB. | last2 = El-Zammer | first2 = O. | last3 = Stucchi | first3 = AF. | last4 = O'Brien | first4 = M. | last5 = Becker | first5 = JM. | title = Colonic metaplasia in the ileal pouch is associated with inflammation and is not the result of long-term adaptation. | journal = J Gastrointest Surg | volume = 7 | issue = 2 | pages = 246-53; discussion 253-4 | month = Feb | year = 2003 | doi = | PMID = 12600449 }}</ref> | |||
DDx: | |||
*[[Crohn's disease]] - [[pyloric gland metaplasia]] (PGM) suggestive but not diagnostic.<ref name=pmid23543088>{{Cite journal | last1 = Agarwal | first1 = S. | last2 = Stucchi | first2 = AF. | last3 = Dendrinos | first3 = K. | last4 = Cerda | first4 = S. | last5 = O'Brien | first5 = MJ. | last6 = Becker | first6 = JM. | last7 = Heeren | first7 = T. | last8 = Farraye | first8 = FA. | title = Is pyloric gland metaplasia in ileal pouch biopsies a marker for Crohn's disease? | journal = Dig Dis Sci | volume = 58 | issue = 10 | pages = 2918-25 | month = Oct | year = 2013 | doi = 10.1007/s10620-013-2655-4 | PMID = 23543088 }}</ref> | |||
**PGM = glands with tall columnar cells with pale pink cytoplasm and a small basal nuclei - typically in the deep mucosa.<ref name=pmid23925821>{{Cite journal | last1 = Weber | first1 = CR. | last2 = Rubin | first2 = DT. | title = Chronic pouchitis versus recurrent Crohn's disease: a diagnostic challenge. | journal = Dig Dis Sci | volume = 58 | issue = 10 | pages = 2748-50 | month = Oct | year = 2013 | doi = 10.1007/s10620-013-2816-5 | PMID = 23925821 }}</ref> | |||
*Irritable pouch disease<ref name=pmid15073663>{{Cite journal | last1 = Beart | first1 = RW. | title = Is pouchitis a clinical, endoscopic, or histologic problem? | journal = Dis Colon Rectum | volume = 47 | issue = 6 | pages = 949; author reply 949-50 | month = Jun | year = 2004 | doi = 10.1007/s10350-004-0516-0 | PMID = 15073663 }}</ref><ref name=pmid18702649>{{Cite journal | last1 = Shen | first1 = B. | last2 = Liu | first2 = W. | last3 = Remzi | first3 = FH. | last4 = Shao | first4 = Z. | last5 = Lu | first5 = H. | last6 = DeLaMotte | first6 = C. | last7 = Hammel | first7 = J. | last8 = Queener | first8 = E. | last9 = Bambrick | first9 = ML. | title = Enterochromaffin cell hyperplasia in irritable pouch syndrome. | journal = Am J Gastroenterol | volume = 103 | issue = 9 | pages = 2293-300 | month = Sep | year = 2008 | doi = 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2008.01990.x | PMID = 18702649 }}</ref> - functional disease similar to [[irritable bowel syndrome]]. | |||
Images: | |||
*[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3400158/figure/f4-cln_67p705/ Pouchitis (nih.gov)].<ref name=pmid22892912>{{Cite journal | last1 = Arashiro | first1 = RT. | last2 = Teixeira | first2 = MG. | last3 = Rawet | first3 = V. | last4 = Quintanilha | first4 = AG. | last5 = Paula | first5 = HM. | last6 = Silva | first6 = AZ. | last7 = Nahas | first7 = SC. | last8 = Cecconello | first8 = I. | title = Histopathological evaluation and risk factors related to the development of pouchitis in patients with ileal pouches for ulcerative colitis. | journal = Clinics (Sao Paulo) | volume = 67 | issue = 7 | pages = 705-10 | month = Jul | year = 2012 | doi = | PMID = 22892912 | PMC = 3400158 | URL = http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3400158/}}</ref> | *[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3400158/figure/f4-cln_67p705/ Pouchitis (nih.gov)].<ref name=pmid22892912>{{Cite journal | last1 = Arashiro | first1 = RT. | last2 = Teixeira | first2 = MG. | last3 = Rawet | first3 = V. | last4 = Quintanilha | first4 = AG. | last5 = Paula | first5 = HM. | last6 = Silva | first6 = AZ. | last7 = Nahas | first7 = SC. | last8 = Cecconello | first8 = I. | title = Histopathological evaluation and risk factors related to the development of pouchitis in patients with ileal pouches for ulcerative colitis. | journal = Clinics (Sao Paulo) | volume = 67 | issue = 7 | pages = 705-10 | month = Jul | year = 2012 | doi = | PMID = 22892912 | PMC = 3400158 | URL = http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3400158/}}</ref> | ||
*[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3400158/figure/f3-cln_67p705/ Colonic metaplasia (nih.gov)].<ref name=pmid22892912/> | |||
====Scoring system==== | ====Scoring system==== | ||
| Line 594: | Line 372: | ||
**25-50%. | **25-50%. | ||
**>50. | **>50. | ||
===Sign out=== | |||
Note: | |||
*Dr. Robert Riddell is of the opinion: "Do '''not''' call any pouch inflammation as consistent with Crohn's disease." | |||
<pre> | |||
SMALL BOWEL POUCH, BIOPSY: | |||
- SMALL BOWEL MUCOSA WITH CHRONIC ACTIVE INFLAMMATION WITH ULCERATION, EARLY | |||
CRYPT ABSCESS FORMATION, CRYPTITIS, AND LOSS OF THE VILLOUS ARCHITECTURE. | |||
- NEGATIVE FOR GRANULOMAS AND NEGATIVE FOR PYLORIC GLAND METAPLASIA. | |||
- NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA. | |||
COMMENT: | |||
The findings are consistent with pouchitis. | |||
</pre> | |||
====Pyloric gland metaplasia present==== | |||
<pre> | |||
SMALL BOWEL POUCH, BIOPSY: | |||
- SMALL BOWEL MUCOSA WITH CHRONIC ACTIVE INFLAMMATION WITH ULCERATION, EARLY | |||
CRYPT ABSCESS FORMATION, CRYPTITIS, AND LOSS OF THE VILLOUS ARCHITECTURE. | |||
- PYLORIC GLAND METAPLASIA, FOCAL, SEE COMMENT. | |||
- NEGATIVE FOR GRANULOMAS. | |||
- NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA. | |||
COMMENT: | |||
The presence of pyloric gland metaplasia raises the possibility of Crohn's disease; | |||
however, in the context of previous biopsies with inflammation, the concurrent | |||
negative ileal biopsy and lack of granulomas, this individual is favoured to have | |||
pouchitis.</pre> | |||
=See also= | =See also= | ||
| Line 601: | Line 409: | ||
*[[Gastrointestinal pathology]]. | *[[Gastrointestinal pathology]]. | ||
*[[Intestinal polyps]]. | *[[Intestinal polyps]]. | ||
*[[Diverticular disease-associated colitis]]. | |||
*[[Pseudopyloric mucous glands]]. | |||
=References= | =References= | ||
Latest revision as of 17:09, 16 February 2019
Inflammatory bowel disease, abbreviated IBD, is the bread 'n butter of gastroenterology, and a significant number of gastrointestinal pathology specimens.
It exists in two main flavours:
- Crohn's disease (CD).
- Ulcerative colitis (UC).
Both are associated with an increased risk of colorectal carcinoma.[1]
Clinical
- It is important to differentiate UC and CD as the management is different.
- UC patients get pouches... CD patients do not.
- It is said that: There 's nothing like a pouch to bring out Crohn's disease.[2]
- People with long standing IBD have an increased risk for:
- Carcinoma - usually colorectal carcinoma.[3]
- Small increased risk for small bowel adenocarcinoma in Crohn's disease.[3]
- Lymphoma - in association with thiopurine use.[4]
- Carcinoma - usually colorectal carcinoma.[3]
Extra-intestinal manifestations of inflammatory bowel disease
Mnemonic (family-rated version) excellent cardiac surgery is pleasant and appreciated:
- Erythema nodosum.
- Clubbing.
- Sclerosing cholangitis.
- Iritis.
- Pyoderma gangrenosum.
- Aphthous ulcers.
- Arthritis.
Molecular
- NOD2[5] (AKA CARD15) variants are associated with stricturing CD, early need for surgery and recurrence.[6]
General clinical differential diagnosis
- Crohn's disease.
- Ulcerative colitis.
- Infective colitis/enteritis.
- Ischemic colitis/enteritis.
- Radiation colitis.
Others:
Specimens
- Biopsies for diagnosis.
- Surveillance biopsies - to rule-out dysplasia.
- Resections for disease that has failed medical management.
- Resections for dysplasia associated with inflammatory bowel disease.
Notes:
- Biopsies for diagnosis should specify the (anatomical) site:
- Slight gradients exist in the large bowel that can be exploited for diagnostic purposes if the site information is known, for example:
- Paneth cells distal to the splenic flexure are abnormal.
- Ulcerative colitis is often more severe distally - even in a pancolitis, as the disease starts in the rectum and progresses toward the cecum.
- Slight gradients exist in the large bowel that can be exploited for diagnostic purposes if the site information is known, for example:
- Surveillance biopsies should specify the (anatomical) site - so, it possible to find any site of interest on a follow-up colonoscopy.[7]
Biopsies all submitted in one bottle
COLON (SITE NOT FURTHER SPECIFIED), BIOPSIES: - MODERATE CHRONIC ACTIVE COLITIS. - NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA. - PLEASE SEE COMMENT. COMMENT: The sections show colorectal-type mucosa with focal cryptitis and rare neutrophilic crypt abscesses. Mild architectural changes, suggestive of a chronic colitis, are present. No granulomas are identified. Lymphoid aggregates with germinal centre formation are present in multiple fragments. The lamina propria has abundant plasma cells throughout the fragments; no fragments have apparent relative sparing. Paneth cells are present focally; however, the significance of the paneth cells cannot determined as the biopsy sites are not known. The findings are compatible with inflammatory bowel disease and chronic active infectious colitides. Clinical correlation is suggested.
Microscopic
Features helpful for the diagnosis of IBD - as based on a study:[8]
- Basal inflammation, i.e. crypt base, plasmacytosis with severe chronic inflammation.
- Crypt architectural abnormalities.
- Atrophy = less glands ~ 3-4 glands/mm (normal = 7-8 glands/mm).
- Branching = common (normal = very rare branching).
- Distortion = bent glands, marked size variation[11] (normal = "rack of test tubes").
- Distal Paneth cell metaplasia.
- Paneth cells should not be in the left colon[12] - if you see 'em think of IBD and other long-standing injurious processes.
- Paneth cells have basal nuclei and coarse luminal granules.[13]
- They should not be confused with endocrine cells -- these have apical nuclei and fine granules.
- They should not be confused with intraepithelial eosinophils -- have smaller (~1/2) more intensely red granules.
Notes:
- Microscopic features can be remembered by mnemonic CPP: Crypts (abnormal), Plasmacytosis, Paneth cells where they don't belong.
- If you see architectural distortion (e.g. crypt branching) in the left colon, look for Paneth cells.
- The hepatic flexure is considered the divider for normal paneth cells and abnormal paneth cells, i.e. paneth cells proximal to the hepatic flexure are normal; paneth cells distal to the hepatic flexure are abnormal.[14]
- Stretching of tissue may mimic atrophy; tip-off it is artifact: thinning of mucosa.[9]
Images
Crohn's disease - very well-formed granulomas in the colon - high mag. (WC)
Grading
Grading schemes for IBD in a table
| Nil | Mild | Moderate | Severe | |
| "A grading scheme"[9] | - | cryptitis | crypt abscesses | erosions |
| Gupta[15] | "0" (nil) | "1" (<50% of crypts have PMNs) |
"2" (>50% of crypts have PMNs) |
"3" (presence of ulcers or erosions) |
Images
Cryptitis. (WC)
Crypt abscess. (WC)
Crohn's disease versus ulcerative colitis
- Some cases cannot be classified by the experts (see "indeterminate colitis").
Robbins
UC features:[16]
- Mucosal involvement -- sometimes submucosa.
- No skip lesions.
- Colon/rectum only.
- UC may have 'ileal backwash' -- mild ileal inflammation due to backwash of inflammatory soup from colon.
- "No granulomas".
- Superficial granulomas in the mucosa are non-specific, especially if they are beside an inflamed crypt, i.e. they may be present in UC.[17][18]
- Deep granulomas are specific for Crohn's disease.
- Superficial granulomas in the mucosa are non-specific, especially if they are beside an inflamed crypt, i.e. they may be present in UC.[17][18]
Example of a superficial granuloma that is non-specific, i.e. this could be UC or CD:
Kirsch
Features of UC[9] - memory device DDDR:
- Diffuse inflammation.
- Diffuse arch. changes.
- Diffuse atrophy.
- Rectal involvement.
Words of caution
The following may be present in UC:[9]
- Cecal patch (cecal involvement without pancolitis).
- Patchy involvement
- Esp. in Tx'ed patients.
- Esp. in children.
- Ileitis - esp. in the context of severe pancolitis; known as backwash ileitis.
- Deep inflammation (in a fissure).
- Upper GI tract involvement -- see below.
Upper gastrointestinal tract involvement
- The old dogma was upper GI tract = Crohn's disease.
Characteristics of upper GI tract UC:[19]
- Most common:
- Focal gastritis.
- Mixed basal inflammation and superficial plasmacytosis in the stomach.
- Unique:
- Diffuse chronic duodenitis.
- ~ 10% of UC patients.
- ~ 40% of UC + colectomy + pouchitis.
Another study compares UC, CD and control individuals:[20]
- Gastritis:
- UC: 19%.
- CD: 33%
- Controls: 13%.
- Duodenitis:
- UC: 3%.
- CD: 26%.
- Controls: 1%.
Note:
- Younger individuals (<18 years old) have significantly more gastritis and duodenitis.[20]
A tabular comparison
Gross pathology:
| Feature | Crohn's disease | Ulcerative colitis |
| Lesion distribution | patchy | diffuse |
| Strictures | maybe | no |
| Perianal disease | yes/no | no |
| Rectal involvement | no | yes |
| Ileal involvement | yes, classic | usu. no; seen in pancolitis |
| Upper GI tract involvement | yes | yes (gaining acceptance) |
| Associated with PSC | not classically | yes |
Sign out
Quiescent inflammatory bowel disease
- No accepted formal definition.
May be used when:
- Non-specific "minimal abnormalities" are present.
- There is a history of inflammatory bowel disease.
"Minimal abnormalities" - features:
- Apoptosis.
- Macrophages in the lamina propria.
- Lymphoid nodules.
- "Abundant" plasma cells in the lamina propria.
- Abundant is subjective.
COLON, BIOPSIES: - QUIESCENT INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE. - NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA.
Mild inflammation
SIGMOID COLON, BIOPSY: - MILD ACTIVE COLITIS WITH CHRONIC CHANGES, SEE COMMENT. - NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA. COMMENT: No granulomata are identified. Mild architectural changes are present. The findings are compatible with inflammatory bowel disease or an infectious etiology. Clinical correlation is required.
Mild-to-moderate inflammation
COLON, LEFT, BIOPSY: - MILD-TO-MODERATE ACTIVE COLITIS WITH CHRONIC CHANGES. - NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA. COMMENT: No definite granulomata are identified. Mild architectural changes are present. Cryptitis is seen in several crypts. Rare crypt abscesses are present. Lamina propria plasma cells are abundant throughout the biopsy. The findings are compatible with inflammatory bowel disease or an infectious etiology. Clinical correlation is required.
Moderate inflammation
RECTUM, BIOPSY: - RECTAL MUCOSA WITH MODERATE ACTIVE INFLAMMATION AND CHRONIC CHANGES. - NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA. - SEE COMMENT. COMMENT: No definite granulomata are identified. Architectural changes, including crypt drop out, are present. Lamina propria plasma cells are abundant throughout the biopsy and eosinophil numbers are mildly increased. Lymphoid aggregates with germinal centre formation are present. All fragments of tissue are affected. The findings are compatible with inflammatory bowel disease or an infectious etiology. Clinical correlation is required.
Specific diagnoses
Ulcerative colitis
- Often abbreviated as UC.
Crohn's disease
- Abbreviated CD.
"Indeterminate colitis"
- "Indeterminate colitis" is a confusing term and should be avoided.[21]
Suggested terminology
- IBDU = IBD unclassified.
- CUTE = Colitis of uncertain type or etiology.
- Should be reserved for resection specimens only.
Dysplasia in inflammatory bowel disease
General
Classified as per Riddell et al.:[22][23][24]
- Negative for dysplasia.
- Indefinite for dysplasia.
- Low grade dysplasia.
- High grade dysplasia.
Notes:
- GI experts and generalists have similar rates of agreement.[23]
Microscopic
Features:[25]
- Nuclear changes at the surface - key feature.
- Nuclear hyperchromasia.
- Nuclear enlargement - ellipsoid or spherical.
Dysplasia-associated lesion or mass
- Abbreviated DALM.
Pouchitis
General
- Inflammation of an ileal pouch; pouches are a treatment for ulcerative colitis.
- Generally, pouches are not used in Crohn's disease.
- Chronic pouchitis seen in approximately 15% of patients.[26]
- May be assessed by fecal calprotectin.[27]
- Considered a clinico-pathologic diagnosis.[28][26]
Microscopic
Features:[29]
- Neutrophils - intraepithelial (cryptitis).
- +/-Crypt abscess (cluster of neutrophils in a gland) - indicator of moderate or severe.
- Ulceration.
Note:
DDx:
- Crohn's disease - pyloric gland metaplasia (PGM) suggestive but not diagnostic.[32]
- PGM = glands with tall columnar cells with pale pink cytoplasm and a small basal nuclei - typically in the deep mucosa.[33]
- Irritable pouch disease[34][35] - functional disease similar to irritable bowel syndrome.
Images:
Scoring system
Pouchitis disease activity index (PDAI) - based on clinical and pathologic factors:
- Active pouchitis >= 7.
- Remission < 7.
The histologic component of the PDAI:[29]
- Neutrophils.
- Mild.
- Moderate - crypt abscesses.
- Severe - crypt abscesses.
- Ulceration per LPF (mean).
- <25%.
- 25-50%.
- >50.
Sign out
Note:
- Dr. Robert Riddell is of the opinion: "Do not call any pouch inflammation as consistent with Crohn's disease."
SMALL BOWEL POUCH, BIOPSY: - SMALL BOWEL MUCOSA WITH CHRONIC ACTIVE INFLAMMATION WITH ULCERATION, EARLY CRYPT ABSCESS FORMATION, CRYPTITIS, AND LOSS OF THE VILLOUS ARCHITECTURE. - NEGATIVE FOR GRANULOMAS AND NEGATIVE FOR PYLORIC GLAND METAPLASIA. - NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA. COMMENT: The findings are consistent with pouchitis.
Pyloric gland metaplasia present
SMALL BOWEL POUCH, BIOPSY: - SMALL BOWEL MUCOSA WITH CHRONIC ACTIVE INFLAMMATION WITH ULCERATION, EARLY CRYPT ABSCESS FORMATION, CRYPTITIS, AND LOSS OF THE VILLOUS ARCHITECTURE. - PYLORIC GLAND METAPLASIA, FOCAL, SEE COMMENT. - NEGATIVE FOR GRANULOMAS. - NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA. COMMENT: The presence of pyloric gland metaplasia raises the possibility of Crohn's disease; however, in the context of previous biopsies with inflammation, the concurrent negative ileal biopsy and lack of granulomas, this individual is favoured to have pouchitis.
See also
- Colon.
- Colorectal tumours.
- Common variable immunodeficiency.
- Gastrointestinal pathology.
- Intestinal polyps.
- Diverticular disease-associated colitis.
- Pseudopyloric mucous glands.
References
- ↑ Schmidt C, Bielecki C, Felber J, Stallmach A (June 2010). "Surveillance strategies in inflammatory bowel disease". Minerva Gastroenterol Dietol 56 (2): 189–201. PMID 20485256.
- ↑ URL: http://www.gihealthfoundation.org/library/ppts/postcolectomypatient.pdf. 3 March 2011.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Claessen, MM.; Siersema, PD.; Vleggaar, FP. (Apr 2011). "IBD-related carcinoma.". Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 25 Suppl 1: S27-38. doi:10.1016/S1521-6918(11)70007-5. PMID 21640928.
- ↑ Vos, AC.; Bakkal, N.; Minnee, RC.; Casparie, MK.; de Jong, DJ.; Dijkstra, G.; Stokkers, P.; van Bodegraven, AA. et al. (Sep 2011). "Risk of malignant lymphoma in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases: A Dutch nationwide study.". Inflamm Bowel Dis 17 (9): 1837-1845. doi:10.1002/ibd.21582. PMID 21830262.
- ↑ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 605956
- ↑ Alvarez-Lobos M, Arostegui JI, Sans M, et al. (November 2005). "Crohn's disease patients carrying Nod2/CARD15 gene variants have an increased and early need for first surgery due to stricturing disease and higher rate of surgical recurrence". Ann. Surg. 242 (5): 693–700. PMC 1409853. PMID 16244543. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1409853/.
- ↑ Panaccione, R. (Apr 2006). "The approach to dysplasia surveillance in inflammatory bowel disease.". Can J Gastroenterol 20 (4): 251-3. PMC 2659899. PMID 16609751. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2659899/.
- ↑ Tanaka M, Riddell RH, Saito H, Soma Y, Hidaka H, Kudo H (January 1999). "Morphologic criteria applicable to biopsy specimens for effective distinction of inflammatory bowel disease from other forms of colitis and of Crohn's disease from ulcerative colitis". Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 34 (1): 55–67. PMID 10048734.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 9.5 Kirsch, R. 13 December 2010.
- ↑ "Pathology of ulcerative colitis". http://www.histopathology-india.net/UlCol.htm. Retrieved 17 January 2011.
- ↑ URL: http://www.histopath.com.au/assets/documents/Inflammatory%20bowel%20disease.pdf. Accessed on: 25 October 2013.
- ↑ Tanaka M, Saito H, Kusumi T, et al (December 2001). "Spatial distribution and histogenesis of colorectal Paneth cell metaplasia in idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease". J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 16 (12): 1353–9. PMID 11851832. http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/resolve/openurl?genre=article&sid=nlm:pubmed&issn=0815-9319&date=2001&volume=16&issue=12&spage=1353.
- ↑ Mills, Stacey E. (2006). Histology for Pathologists (3rd ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 631. ISBN 9780781762410.
- ↑ STC. 14 December 2009.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 Gupta RB, Harpaz N, Itzkowitz S, et al. (October 2007). "Histologic inflammation is a risk factor for progression to colorectal neoplasia in ulcerative colitis: a cohort study". Gastroenterology 133 (4): 1099–105; quiz 1340–1. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2007.08.001. PMC 2175077. PMID 17919486. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2175077/.
- ↑ Cotran, Ramzi S.; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Nelso Fausto; Robbins, Stanley L.; Abbas, Abul K. (2005). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (7th ed.). St. Louis, Mo: Elsevier Saunders. pp. 850. ISBN 0-7216-0187-1.
- ↑ Shepherd, NA. (Aug 2002). "Granulomas in the diagnosis of intestinal Crohn's disease: a myth exploded?". Histopathology 41 (2): 166-8. PMID 12147095.
- ↑ Mahadeva, U.; Martin, JP.; Patel, NK.; Price, AB. (Jul 2002). "Granulomatous ulcerative colitis: a re-appraisal of the mucosal granuloma in the distinction of Crohn's disease from ulcerative colitis.". Histopathology 41 (1): 50-5. PMID 12121237.
- ↑ Lin J, McKenna BJ, Appelman HD (November 2010). "Morphologic findings in upper gastrointestinal biopsies of patients with ulcerative colitis: a controlled study". Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 34 (11): 1672–7. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e3181f3de93. PMID 20962621.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 Sonnenberg, A.; Melton, SD.; Genta, RM. (Jan 2011). "Frequent occurrence of gastritis and duodenitis in patients with inflammatory bowel disease.". Inflamm Bowel Dis 17 (1): 39-44. doi:10.1002/ibd.21356. PMID 20848539.
- ↑ Geboes K, Colombel JF, Greenstein A, et al. (June 2008). "Indeterminate colitis: a review of the concept--what's in a name?". Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 14 (6): 850–7. doi:10.1002/ibd.20361. PMID 18213696.
- ↑ Riddell, RH.; Goldman, H.; Ransohoff, DF.; Appelman, HD.; Fenoglio, CM.; Haggitt, RC.; Ahren, C.; Correa, P. et al. (Nov 1983). "Dysplasia in inflammatory bowel disease: standardized classification with provisional clinical applications.". Hum Pathol 14 (11): 931-68. PMID 6629368.
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 Eaden, J.; Abrams, K.; McKay, H.; Denley, H.; Mayberry, J. (Jun 2001). "Inter-observer variation between general and specialist gastrointestinal pathologists when grading dysplasia in ulcerative colitis.". J Pathol 194 (2): 152-7. doi:10.1002/path.876. PMID 11400142.
- ↑ Greenson, JK. (Feb 2002). "Dysplasia in inflammatory bowel disease.". Semin Diagn Pathol 19 (1): 31-7. PMID 11936264.
- ↑ URL: http://surgpathcriteria.stanford.edu/gi/ulcerative-colitis/printable.html. Accessed on: 12 March 2013.
- ↑ 26.0 26.1 Gionchetti, P.; Amadini, C.; Rizzello, F.; Venturi, A.; Poggioli, G.; Campieri, M. (Feb 2003). "Diagnosis and treatment of pouchitis.". Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 17 (1): 75-87. PMID 12617884.
- ↑ Johnson, MW.; Maestranzi, S.; Duffy, AM.; Dewar, DH.; Forbes, A.; Bjarnason, I.; Sherwood, RA.; Ciclitira, P. et al. (Mar 2008). "Faecal calprotectin: a noninvasive diagnostic tool and marker of severity in pouchitis.". Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 20 (3): 174-9. doi:10.1097/MEG.0b013e3282f1c9a7. PMID 18301296.
- ↑ Royston, DJ.; Warren, BF. (Nov 2011). "Are we reporting ileal pouch biopsies correctly?". Colorectal Dis 13 (11): 1285-9. doi:10.1111/j.1463-1318.2010.02452.x. PMID 20958905.
- ↑ 29.0 29.1 Shen, B.; Achkar, JP.; Connor, JT.; Ormsby, AH.; Remzi, FH.; Bevins, CL.; Brzezinski, A.; Bambrick, ML. et al. (Jun 2003). "Modified pouchitis disease activity index: a simplified approach to the diagnosis of pouchitis.". Dis Colon Rectum 46 (6): 748-53. doi:10.1097/01.DCR.0000070528.00563.D9. PMID 12794576.
- ↑ 30.0 30.1 30.2 Arashiro, RT.; Teixeira, MG.; Rawet, V.; Quintanilha, AG.; Paula, HM.; Silva, AZ.; Nahas, SC.; Cecconello, I. (Jul 2012). "Histopathological evaluation and risk factors related to the development of pouchitis in patients with ileal pouches for ulcerative colitis.". Clinics (Sao Paulo) 67 (7): 705-10. PMC 3400158. PMID 22892912. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3400158/.
- ↑ Fruin, AB.; El-Zammer, O.; Stucchi, AF.; O'Brien, M.; Becker, JM. (Feb 2003). "Colonic metaplasia in the ileal pouch is associated with inflammation and is not the result of long-term adaptation.". J Gastrointest Surg 7 (2): 246-53; discussion 253-4. PMID 12600449.
- ↑ Agarwal, S.; Stucchi, AF.; Dendrinos, K.; Cerda, S.; O'Brien, MJ.; Becker, JM.; Heeren, T.; Farraye, FA. (Oct 2013). "Is pyloric gland metaplasia in ileal pouch biopsies a marker for Crohn's disease?". Dig Dis Sci 58 (10): 2918-25. doi:10.1007/s10620-013-2655-4. PMID 23543088.
- ↑ Weber, CR.; Rubin, DT. (Oct 2013). "Chronic pouchitis versus recurrent Crohn's disease: a diagnostic challenge.". Dig Dis Sci 58 (10): 2748-50. doi:10.1007/s10620-013-2816-5. PMID 23925821.
- ↑ Beart, RW. (Jun 2004). "Is pouchitis a clinical, endoscopic, or histologic problem?". Dis Colon Rectum 47 (6): 949; author reply 949-50. doi:10.1007/s10350-004-0516-0. PMID 15073663.
- ↑ Shen, B.; Liu, W.; Remzi, FH.; Shao, Z.; Lu, H.; DeLaMotte, C.; Hammel, J.; Queener, E. et al. (Sep 2008). "Enterochromaffin cell hyperplasia in irritable pouch syndrome.". Am J Gastroenterol 103 (9): 2293-300. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.2008.01990.x. PMID 18702649.