Difference between revisions of "Salivary glands"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (→Microscopic) |
|||
| (197 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
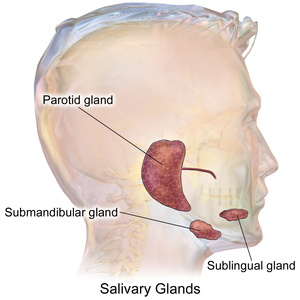
The '''salivary glands''' help digest food. ENT surgeons | [[Image:Blausen_0780_SalivaryGlands.png|thumb|300px|Schematic showing the major salivary glands. (WC)]] | ||
The '''salivary glands''' help digest food. ENT surgeons excise them if a malignancy is suspected. | |||
=Normal= | The [[cytopathology]] of the salivary glands is covered in the ''[[Head and neck cytopathology]]'' article. | ||
=Normal salivary glands= | |||
==Types of salivary glands== | ==Types of salivary glands== | ||
Types of glands:<ref>[http://www.lab.anhb.uwa.edu.au/mb140/CorePages/Oral/oral.htm#LABSALIVA http://www.lab.anhb.uwa.edu.au/mb140/CorePages/Oral/oral.htm#LABSALIVA]</ref> | Types of glands:<ref>[http://www.lab.anhb.uwa.edu.au/mb140/CorePages/Oral/oral.htm#LABSALIVA http://www.lab.anhb.uwa.edu.au/mb140/CorePages/Oral/oral.htm#LABSALIVA]</ref> | ||
| Line 16: | Line 19: | ||
#**Serous ~90% of gland. | #**Serous ~90% of gland. | ||
#**Mucinous ~10% of gland. | #**Mucinous ~10% of gland. | ||
#*Serous demilunes = mucinous gland with "cap" consisting of a serous glandular component. | |||
#**Demilune = crescent.<ref>URL: [http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/demilune http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/demilune]. Accessed on: 19 August 2011.</ref> | |||
#**Image: [http://pathology.mc.duke.edu/research/histo_course/demilunes.jpg Serous demilunes (duke.edu)].<ref>URL: [http://pathology.mc.duke.edu/research/pth225.html http://pathology.mc.duke.edu/research/pth225.html]. Accessed on: 19 August 2011.</ref> | |||
# Sublingual: | # Sublingual: | ||
#*Mucinous glands. | #*Mucinous glands. | ||
| Line 34: | Line 41: | ||
==Benign tumours== | ==Benign tumours== | ||
'''Tabular form - adapted from Thompson<ref>{{Ref HaNP|295-319}}</ref>''' | '''Tabular form - adapted from Thompson<ref>{{Ref HaNP|295-319}}</ref>''' | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable sortable" | ||
! Entity | |||
! Architecture | |||
! Morphology | |||
! Cell borders | |||
! Cytoplasm | |||
! Nucleus | |||
! DDx | |||
! Other | |||
! Image | |||
|- | |- | ||
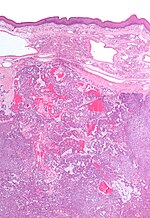
|Pleomorphic adenoma | |[[Pleomorphic adenoma]] | ||
| var. | | var. | ||
| '''mixed pop.'''; must include: (1) myoepithelium, (2) epithelium (ductal cells) | | '''mixed pop.'''; must include: (1) myoepithelium, (2) mesenchymal stroma, and (3) epithelium (ductal cells) ''or'' [[chondromyxoid stroma]] | ||
| var. | | var. | ||
| var. | | var. | ||
| (1) plasmacytoid | | (1) plasmacytoid | ||
| adenoid cystic | | [[adenoid cystic carcinoma]] | ||
| occ. encapsulated, <br>mixed pop. of glandular, <br>myoepithelial and mesenchymal cells | | occ. encapsulated, <br>mixed pop. of glandular, <br>myoepithelial and mesenchymal cells | ||
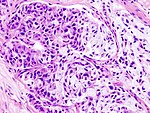
| [ | | [[Image:Pleomorphic_adenoma_(1)_parotid_gland.jpg | thumb | center |150px| PA. (WP)]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
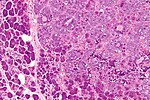
|Warthin tumour | |[[Warthin tumour]] | ||
| papillary, <br>'''bilayer''' | | papillary, <br>'''bilayer''' | ||
| cuboid (basal), columnar (apical) | | cuboid (basal), columnar (apical) | ||
| Line 61: | Line 68: | ||
| '''eosinophilic, abundant''' | | '''eosinophilic, abundant''' | ||
| unremarkable | | unremarkable | ||
| sebaceous lymphadenoma | | [[sebaceous lymphadenoma]] | ||
| AKA ''papillary cystadenoma lymphomatosum'' | | AKA ''papillary cystadenoma lymphomatosum'' | ||
| [ | | [[Image:Papillary_cystadenoma_lymphomatosum2.jpg| thumb| center | 150px| PCL. (WP/Nephron)]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Basal cell adenoma | |[[Basal cell adenoma]] | ||
| var., '''islands surrounded'''<br>'''by hyaline bands''' | | var., '''islands surrounded'''<br>'''by hyaline bands''', lesion encapsulated | ||
| basaloid | | basaloid | ||
| subtle | | subtle | ||
| scant,<br>hyperchromatic | | scant,<br>hyperchromatic | ||
| granular | | granular | ||
| basal cell | | [[basal cell adenocarcinoma]] | ||
| - | | - | ||
| - | | - | ||
|- | |- | ||
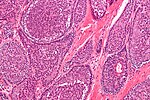
|Canalicular adenoma | |[[Canalicular adenoma]] | ||
| '''chains of cells''' | | '''chains of cells''' | ||
| cuboid or columnar | | cuboid or columnar | ||
| Line 81: | Line 88: | ||
| scant,<br>hyperchromatic | | scant,<br>hyperchromatic | ||
| granular | | granular | ||
| basal cell adenoma | | [[basal cell adenoma]] | ||
| exclusively oral cavity, 80% in upper lip; IHC: p63- | | exclusively oral cavity, 80% in upper lip; IHC: p63- | ||
| - | | [[Image:Canalicular_adenoma_--_high_mag.jpg | thumb | center |150px| CA. (WC)]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Sialoblastoma | |[[Sialoblastoma]] | ||
| var., '''islands surrounded'''<br>'''by loose fibrous stroma''' | | var., '''islands surrounded'''<br>'''by loose fibrous stroma''' | ||
| basaloid | | basaloid | ||
| Line 91: | Line 98: | ||
| scant, hyperch. | | scant, hyperch. | ||
| granular | | granular | ||
| basal cell | | [[basal cell adenocarcinoma]] | ||
| - | | - | ||
| - | | - | ||
| Line 99: | Line 106: | ||
==Malignant tumours== | ==Malignant tumours== | ||
'''Tabular form - adapted from Thompson<ref>{{Ref HaNP|325-357}}</ref>''' | '''Tabular form - adapted from Thompson<ref>{{Ref HaNP|325-357}}</ref>''' | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable sortable" | ||
! Entity | |||
! Architecture | |||
! Morphology | |||
! Cell borders | |||
! Cytoplasm | |||
! Nucleus | |||
! DDx | |||
! Other | |||
! Image | |||
|- | |- | ||
|Mucoepidermoid carcinoma | |[[Mucoepidermoid carcinoma]] | ||
| cystic & solid | | cystic & solid | ||
| epithelioid | | epithelioid | ||
| Line 117: | Line 125: | ||
| SCC (?) | | SCC (?) | ||
| IHC: p63+ | | IHC: p63+ | ||
| [[Image:Mucoepidermoid_carcinoma_%282%29_HE_stain.jpg |thumb| center| 150px | MEC. (WC)]] | |||
|- | |||
|[[Adenoid cystic carcinoma]] (AdCC) | |||
| pseudocysts,<br>'''[[cribriform]]''', solid,<br>hyaline stroma | |||
| epithelioid | |||
| subtle | |||
| '''scant''',<br>hyperchromatic | |||
| '''small'''<br>+/-"carrot-shaped" | |||
| [[pleomorphic adenoma]], [[PLGA]] | |||
| Stains: PAS+ (pseudocyst material), CD117+, cyclin D1+ | |||
| [[Image:Adenoid_cystic_carcinoma_-_high_mag.jpg|thumb|center|150px| AdCC. (WC/Nephron)]] | |||
|- | |- | ||
|Acinic cell | |[[Acinic cell carcinoma]] (AcCC) | ||
| sheets, acinar (islands) | | sheets, acinar (islands) | ||
| epithelioid | | epithelioid | ||
| clear | | clear | ||
| '''granular''' | | '''granular abundant''' | ||
| stippled, +/-occ. nucleoli | | '''stippled''', +/-occ. nucleoli | ||
| | | adenocarcinoma not otherwise specified, [[oncocytoma of salivary gland]] | ||
| Stains: PAS +ve, PAS-D +ve; [[IHC]]: S-100 -ve, p63 -ve | | Stains: PAS +ve, PAS-D +ve; [[IHC]]: S-100 -ve, p63 -ve | ||
| [[Image:Acinic_cell_carcinoma_-_high_mag.jpg | thumb| center|150px| AcCC. (WC/Nephron)]] | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | |[[Salivary duct carcinoma]] | ||
| glandular, [[cribriform]] | |||
| glandular, cribriform | |||
| columnar | | columnar | ||
| subtle/clear | | subtle/clear | ||
| Line 144: | Line 155: | ||
| metastatic breast carcinoma | | metastatic breast carcinoma | ||
| similar to ductal<br>breast carcinoma; male>female | | similar to ductal<br>breast carcinoma; male>female | ||
| [[Image:Salivary_duct_carcinoma_-a-_low_mag.jpg | thumb| center|150px | SDC. (WC/Nephron)]] | |||
|- | |- | ||
|Polymorphous low-grade adenocarcinoma | |[[Polymorphous adenocarcinoma]] (previously polymorphous low-grade adenocarcinoma) | ||
| variable, often small<br>nests, may be targetoid | | variable, often small<br>nests, may be targetoid | ||
| epithelioid | | epithelioid | ||
| Line 152: | Line 164: | ||
| ovoid & small with<br>small nucleoli | | ovoid & small with<br>small nucleoli | ||
| AdCC | | AdCC | ||
| minor salivary gland tumour,<br>often in palate,<br> cytologically monotonous; IHC: | | minor salivary gland tumour,<br>often in palate,<br> cytologically monotonous; IHC: [[S-100]]+, CK+, vim.+, GFAP+/-, BCL2+/- | ||
| [[Image:Polymorphous_low-grade_adenocarcinoma_-_very_low_mag.jpg|thumb|center|150px|PLGA. (WC/Nephron)]] | |||
|- | |- | ||
| [[Epithelial-myoepithelial carcinoma]] | |||
| '''nests (myoepithelial) with tubules (epithelial)''' | |||
| epithelioid | |||
| not distinct | |||
| eosinophilic cytoplasm; epithelial: scant; myoepithelial: moderate | |||
| focal clearing | |||
| [[AdCC]], [[pleomorphic adenoma]] | |||
| rare | |||
| [[Image:Epithelial-myoepithelial_carcinoma_-_high_mag.jpg |thumb|center|150px|EMCa. (WC/Nephron)]] | |||
|- | |||
| [[Basal cell adenocarcinoma]] | |||
| var., '''islands surrounded'''<br>'''by hyaline bands''', lesion '''not''' encapsulated | |||
| basaloid | |||
| subtle | |||
| scant,<br>hyperchromatic | |||
| granular | |||
| [[basal cell adenoma]] | |||
| rare, usu. parotid gland, may arise from a basal cell adenoma | |||
| [[Image:Basal_cell_adenocarcinoma_-_parotid_gland_-_high_mag.jpg|thumb|center|150px|BCA. (WC/Nephron)]] | |||
|} | |} | ||
==DDx== | ==DDx== | ||
Palate | ===Palate=== | ||
*Polymorphous | *[[Polymorphous adenocarcinoma]]. | ||
*Adenoid cystic carcinoma. | *[[Adenoid cystic carcinoma]]. | ||
*Pleomorphic adenoma. | *[[Pleomorphic adenoma]]. | ||
===Benign parotid tumours=== | |||
*Pleomorphic adenoma. | *[[Pleomorphic adenoma]]. | ||
*Warthin tumour. | *[[Warthin tumour]]. | ||
===Oncocytic tumours=== | |||
*Benign: | |||
**Oncocytoma. | |||
**[[Warthin tumour]]. | |||
*Malignant: | |||
**[[Mucoepidermoid carcinoma]], oncocytic variant. | |||
**[[Salivary duct carcinoma]]. | |||
**[[Carcinoma ex pleomorphic carcinoma]] with a salivary duct carcinoma component. | |||
**[[Apocrine carcinoma]]. | |||
**Oncocytic carcinoma. | |||
**[[Acinic cell carcinoma]], oncocytic variant. | |||
===Clear cell tumours=== | |||
*[[Mucoepidermoid carcinoma]], clear cell variant. | |||
*[[Acinic cell carcinoma]], clear cell variant. | |||
*[[Hyalinizing clear cell carcinoma]]. | |||
*[[Epithelial-myoepithelial carcinoma]]. | |||
*Metastatic [[clear cell carcinoma]]. | |||
**Metastatic [[clear cell renal cell carcinoma]]. | |||
===Basaloid neoplasms=== | |||
*[[Basal cell adenoma]]. | |||
*[[Basal cell adenocarcinoma]] | |||
*[[Pleomorphic adenoma]].<ref name=pmi12478487/> | |||
*[[Adenoid cystic carcinoma]].<ref name=pmi12478487/> | |||
*[[Small cell carcinoma]].<ref name=pmi12478487>{{Cite journal | last1 = Chhieng | first1 = DC. | last2 = Paulino | first2 = AF. | title = Basaloid tumors of the salivary glands. | journal = Ann Diagn Pathol | volume = 6 | issue = 6 | pages = 364-72 | month = Dec | year = 2002 | doi = 10.1053/adpa.2002.37013 | PMID = 12478487 }}</ref> | |||
==IHC overview== | ==IHC overview== | ||
General: | General: | ||
*Usually has limited value. | *Usually has limited value. <!--as per Ilan Weinreb--> | ||
Overview: | |||
*Luminal markers: CK7, CK19, CAM5.2 (LMWK). | *Luminal markers: [[CK7]], [[CK19]], CAM5.2 (LMWK). | ||
*Basal markers: p63, HMWK, CK14. | *Basal markers: p63, HMWK, CK14. | ||
*Myoepithelial markers: calponin, actin. | *Myoepithelial markers: calponin, actin. | ||
| Line 178: | Line 237: | ||
Notes: | Notes: | ||
*p63 and S-100 are sometimes call myoepithelial. | *p63 and S-100 are sometimes call myoepithelial. | ||
Specifics: | |||
*Calponin, S-100, Ki-67 may be useful as per Nagao ''et al.''<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Nagao | first1 = T. | last2 = Sato | first2 = E. | last3 = Inoue | first3 = R. | last4 = Oshiro | first4 = H. | last5 = H Takahashi | first5 = R. | last6 = Nagai | first6 = T. | last7 = Yoshida | first7 = M. | last8 = Suzuki | first8 = F. | last9 = Obikane | first9 = H. | title = Immunohistochemical analysis of salivary gland tumors: application for surgical pathology practice. | journal = Acta Histochem Cytochem | volume = 45 | issue = 5 | pages = 269-82 | month = Oct | year = 2012 | doi = 10.1267/ahc.12019 | PMID = 23209336 }}</ref> | |||
*Most salivary gland tumours are p40 positive and p63 positive; [[polymorphous adenocarcinoma]] is p63 positive and p40 negative.<ref name=pmid34518135>{{cite journal |authors=Sivakumar N, Narwal A, Pandiar D, Devi A, Anand R, Bansal D, Kamboj M |title=Diagnostic utility of p63/p40 in the histologic differentiation of salivary gland tumors: A systematic review |journal=Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol |volume=133 |issue=2 |pages=189–198 |date=February 2022 |pmid=34518135 |doi=10.1016/j.oooo.2021.07.010 |url=}}</ref> | |||
=Benign= | =Benign= | ||
| Line 185: | Line 248: | ||
*Ductal obstrution. | *Ductal obstrution. | ||
==Chronic | ==Chronic sialadenitis== | ||
== | {{Main|Chronic sialadenitis}} | ||
== | ==Salivary gland mucocele== | ||
{{Main|Salivary gland mucocele}} | |||
==Pleomorphic adenoma== | ==Pleomorphic adenoma== | ||
{{Main|Pleomorphic adenoma}} | |||
== | ==Myoepithelioma== | ||
{{Main|Myoepithelioma}} | |||
==Basal cell adenoma== | ==Basal cell adenoma== | ||
| Line 252: | Line 264: | ||
*~2% of salivary gland tumours. | *~2% of salivary gland tumours. | ||
*May be multifocal. | *May be multifocal. | ||
* | *Usually parotid gland, occasionally submandibular gland. | ||
*Female:male = ~2:1. | *Female:male = ~2:1. | ||
*May be seen in association with dermal | *May be seen in association with [[dermal cylindroma]]s in the context of a genetic mutation.<ref name=pmid12023583>{{Cite journal | last1 = Choi | first1 = HR. | last2 = Batsakis | first2 = JG. | last3 = Callender | first3 = DL. | last4 = Prieto | first4 = VG. | last5 = Luna | first5 = MA. | last6 = El-Naggar | first6 = AK. | title = Molecular analysis of chromosome 16q regions in dermal analogue tumors of salivary glands: a genetic link to dermal cylindroma? | journal = Am J Surg Pathol | volume = 26 | issue = 6 | pages = 778-83 | month = Jun | year = 2002 | doi = | PMID = 12023583 }}</ref> | ||
*Malignant transformation - rarely. | *Malignant transformation - rarely. | ||
===Microscopic=== | ===Microscopic=== | ||
Features: | Features: | ||
*Basophilic cells. | #Basal component. | ||
*Usu. nests | #*Basophilic cells - '''key feature'''. | ||
#*Usu. in nests. | |||
#**May be bilayered tubules ''or'' [[trabeculae]]. | |||
#*Large basophilic nucleus. | |||
#*Minimal-to-moderate eosinophilic cytoplasm. | |||
#Stromal cells. | |||
#*Plump spindle cells without significant nuclear atypia - '''distinguishing feature'''. | |||
#**Stromal cell nuclei width ~= diameter [[RBC]]. | |||
#*Dense hyaline stroma. | |||
#Tubular component. | |||
#*Within basal component, may be minimal. | |||
#Lesion is encapsulated - '''key feature'''. | |||
Notes: | Notes: | ||
*No chondromyxoid stroma. | *No chondromyxoid stroma. | ||
**Chondromyxoid stroma present -> pleomorphic adenoma. | **Chondromyxoid stroma present -> [[pleomorphic adenoma]]. | ||
*Neoplastic cells | *Neoplastic cells embedded in stroma ("stromal invasion") = basal cell adenocarcinoma. | ||
**Basal cell adenocarcinoma may be cytologically indistinguishable from basal cell adenoma, i.e. "bad" architecture makes it a basal cell adenocarcinoma. | **Basal cell adenocarcinoma may be cytologically indistinguishable from basal cell adenoma, i.e. "bad" architecture makes it a basal cell adenocarcinoma. | ||
DDx: | |||
*[[Adenoid cystic carcinoma]] - not encapsulated. | |||
*[[Basal cell adenocarcinoma]] - not encapsulated. | |||
*[[Canalicular adenoma]] - different site; canalicular adenoma is the in oral cavity, usually upper lip. | |||
Images: | |||
*[http://moon.ouhsc.edu/kfung/jty1/Com/ComImage/Com304-3-LM1.gif BCA (ouhsc.edu)].<ref>URL: [http://moon.ouhsc.edu/kfung/jty1/Com/Com304-3-Diss.htm http://moon.ouhsc.edu/kfung/jty1/Com/Com304-3-Diss.htm]. Accessed on: 25 October 2011.</ref> | |||
*[http://www.webpathology.com/image.asp?n=1&Case=115 BCA (webpathology.com)]. | |||
*[http://www.webpathology.com/image.asp?n=4&Case=115 BCA (webpathology.com)]. | |||
*[http://www.flickr.com/photos/euthman/5691555734/in/set-72057594114099781/ BCA (flickr.com/euthman)]. | |||
===IHC=== | ===IHC=== | ||
*Luminal stains +ve: CK7 +ve, CAM5.2 +ve. | *Luminal stains +ve: CK7 +ve, CAM5.2 +ve. | ||
*p63 +ve -- basal component. | |||
*[[S-100]] +ve -- spindle cells in the stroma. | |||
==Canalicular adenoma== | ==Canalicular adenoma== | ||
{{Main|Canalicular adenoma}} | |||
== | ==Warthin tumour== | ||
{{Main|Warthin tumour}} | |||
== | |||
==Sebaceous adenoma== | ==Sebaceous adenoma== | ||
{{Main|Sebaceous adenoma}} | |||
*Benign counterpart of ''[[sebaceous carcinoma]]''. | |||
*Benign counterpart of ''sebaceous carcinoma''. | |||
== | ==Sebaceous lymphadenoma== | ||
{{Main|Sebaceous lymphadenoma}} | |||
== | ==Oncocytoma of the salivary gland== | ||
*[[AKA]] ''salivary gland oncocytoma''. | |||
{{Main|Oncocytoma of the salivary gland}} | |||
=Malignant= | =Malignant= | ||
| Line 364: | Line 329: | ||
==Mucoepidermoid carcinoma== | ==Mucoepidermoid carcinoma== | ||
{{Main|Mucoepidermoid carcinoma}} | |||
== | ==Acinic cell carcinoma== | ||
{{Main|Acinic cell carcinoma}} | |||
== | |||
==Adenoid cystic carcinoma== | ==Adenoid cystic carcinoma== | ||
{{Main|Adenoid cystic carcinoma}} | |||
Note: The [[breast]] tumour is dealt with in ''[[adenoid cystic carcinoma of the breast]]''. | |||
==Salivary duct carcinoma== | ==Salivary duct carcinoma== | ||
{{Main|Salivary duct carcinoma}} | |||
=== | ==Intraductal carcinoma of the salivary gland== | ||
{{Main|Intraductal carcinoma of the salivary gland}} | |||
==Polymorphous adenocarcinoma== | |||
*Abbreviated ''PAC''. | |||
*Previously known as ''polymorphous low-grade adenocarcinoma'', abbreviated ''PLGA''. | |||
{{Main|Polymorphous adenocarcinoma}} | |||
==Polymorphous | |||
*Abbreviated '' | |||
* | |||
==Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma== | ==Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma== | ||
*Abbreviated ''Ca ex PA''. | *Abbreviated ''Ca ex PA''. | ||
{{Main|Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma}} | |||
=== | ==Epithelial-myoepithelial carcinoma== | ||
{{Main|Epithelial-myoepithelial carcinoma}} | |||
==Basal cell adenocarcinoma== | |||
{{Main|Basal cell adenocarcinoma}} | |||
==Sebaceous carcinoma== | |||
{{Main|Sebaceous carcinoma}} | |||
It is similar to the tumour found in the skin. | |||
== | ==Hyalinizing clear cell carcinoma== | ||
{{Main|Hyalinizing clear cell carcinoma}} | |||
=See also= | =See also= | ||
| Line 655: | Line 371: | ||
*[[Breast]]. | *[[Breast]]. | ||
*[[Head and neck cytopathology]]. | *[[Head and neck cytopathology]]. | ||
*[[Lacrimal gland]]. | |||
=References= | =References= | ||
| Line 660: | Line 377: | ||
[[Category:Head and neck pathology]] | [[Category:Head and neck pathology]] | ||
[[Category:Salivary gland|Salivary gland]] | |||
Latest revision as of 20:36, 2 June 2024
The salivary glands help digest food. ENT surgeons excise them if a malignancy is suspected.
The cytopathology of the salivary glands is covered in the Head and neck cytopathology article.
Normal salivary glands
Types of salivary glands
Types of glands:[1]
- Serrous - eosinophilic cytoplasmic granules, acinar arrangement - vaguely resembles the acinar morphology of the pancreas.
- Mucinous - light eosinophilic staining.
Identifying the glands
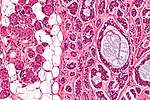
The three main glands:
- Parotid:
- Serous glands - lower viscosity, acini (lobules).[2]
- Most tumours in this gland are benign.
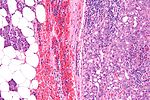
- Submandibular:
- Serous and mucinous glands.
- Serous ~90% of gland.
- Mucinous ~10% of gland.
- Serous demilunes = mucinous gland with "cap" consisting of a serous glandular component.
- Demilune = crescent.[3]
- Image: Serous demilunes (duke.edu).[4]
- Serous and mucinous glands.
- Sublingual:
- Mucinous glands.
Other:
- Adipose tissue is found between the glands.
- It increases with age.
Images:
Memory devices:
- The parotid gland vaguely resembles the pancreas.
- Submandibular = glands are mixed.
Overview
Benign tumours
Tabular form - adapted from Thompson[5]
| Entity | Architecture | Morphology | Cell borders | Cytoplasm | Nucleus | DDx | Other | Image |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pleomorphic adenoma | var. | mixed pop.; must include: (1) myoepithelium, (2) mesenchymal stroma, and (3) epithelium (ductal cells) or chondromyxoid stroma | var. | var. | (1) plasmacytoid | adenoid cystic carcinoma | occ. encapsulated, mixed pop. of glandular, myoepithelial and mesenchymal cells |
|
| Warthin tumour | papillary, bilayer |
cuboid (basal), columnar (apical) | clearly seen | eosinophilic, abundant | unremarkable | sebaceous lymphadenoma | AKA papillary cystadenoma lymphomatosum | |
| Basal cell adenoma | var., islands surrounded by hyaline bands, lesion encapsulated |
basaloid | subtle | scant, hyperchromatic |
granular | basal cell adenocarcinoma | - | - |
| Canalicular adenoma | chains of cells | cuboid or columnar | subtle | scant, hyperchromatic |
granular | basal cell adenoma | exclusively oral cavity, 80% in upper lip; IHC: p63- | |
| Sialoblastoma | var., islands surrounded by loose fibrous stroma |
basaloid | subtle | scant, hyperch. | granular | basal cell adenocarcinoma | - | - |
Malignant tumours
Tabular form - adapted from Thompson[6]
| Entity | Architecture | Morphology | Cell borders | Cytoplasm | Nucleus | DDx | Other | Image |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mucoepidermoid carcinoma | cystic & solid | epithelioid | distinct | fuffy, clear, abundant |
nuclei sm. | SCC (?) | IHC: p63+ | |
| Adenoid cystic carcinoma (AdCC) | pseudocysts, cribriform, solid, hyaline stroma |
epithelioid | subtle | scant, hyperchromatic |
small +/-"carrot-shaped" |
pleomorphic adenoma, PLGA | Stains: PAS+ (pseudocyst material), CD117+, cyclin D1+ | |
| Acinic cell carcinoma (AcCC) | sheets, acinar (islands) | epithelioid | clear | granular abundant | stippled, +/-occ. nucleoli | adenocarcinoma not otherwise specified, oncocytoma of salivary gland | Stains: PAS +ve, PAS-D +ve; IHC: S-100 -ve, p63 -ve | |
| Salivary duct carcinoma | glandular, cribriform | columnar | subtle/clear | hyperchromatic | columnar | metastatic breast carcinoma | similar to ductal breast carcinoma; male>female |
|
| Polymorphous adenocarcinoma (previously polymorphous low-grade adenocarcinoma) | variable, often small nests, may be targetoid |
epithelioid | indistinct | eosinophilic | ovoid & small with small nucleoli |
AdCC | minor salivary gland tumour, often in palate, cytologically monotonous; IHC: S-100+, CK+, vim.+, GFAP+/-, BCL2+/- |
|
| Epithelial-myoepithelial carcinoma | nests (myoepithelial) with tubules (epithelial) | epithelioid | not distinct | eosinophilic cytoplasm; epithelial: scant; myoepithelial: moderate | focal clearing | AdCC, pleomorphic adenoma | rare | |
| Basal cell adenocarcinoma | var., islands surrounded by hyaline bands, lesion not encapsulated |
basaloid | subtle | scant, hyperchromatic |
granular | basal cell adenoma | rare, usu. parotid gland, may arise from a basal cell adenoma |
DDx
Palate
Benign parotid tumours
Oncocytic tumours
- Benign:
- Oncocytoma.
- Warthin tumour.
- Malignant:
- Mucoepidermoid carcinoma, oncocytic variant.
- Salivary duct carcinoma.
- Carcinoma ex pleomorphic carcinoma with a salivary duct carcinoma component.
- Apocrine carcinoma.
- Oncocytic carcinoma.
- Acinic cell carcinoma, oncocytic variant.
Clear cell tumours
- Mucoepidermoid carcinoma, clear cell variant.
- Acinic cell carcinoma, clear cell variant.
- Hyalinizing clear cell carcinoma.
- Epithelial-myoepithelial carcinoma.
- Metastatic clear cell carcinoma.
- Metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma.
Basaloid neoplasms
- Basal cell adenoma.
- Basal cell adenocarcinoma
- Pleomorphic adenoma.[7]
- Adenoid cystic carcinoma.[7]
- Small cell carcinoma.[7]
IHC overview
General:
- Usually has limited value.
Overview:
- Luminal markers: CK7, CK19, CAM5.2 (LMWK).
- Basal markers: p63, HMWK, CK14.
- Myoepithelial markers: calponin, actin.
- Uncommitted: S-100.
Notes:
- p63 and S-100 are sometimes call myoepithelial.
Specifics:
- Calponin, S-100, Ki-67 may be useful as per Nagao et al.[8]
- Most salivary gland tumours are p40 positive and p63 positive; polymorphous adenocarcinoma is p63 positive and p40 negative.[9]
Benign
General DDx:
- Inflammation.
- Neoplasm.
- Ductal obstrution.
Chronic sialadenitis
Main article: Chronic sialadenitis
Salivary gland mucocele
Main article: Salivary gland mucocele
Pleomorphic adenoma
Main article: Pleomorphic adenoma
Myoepithelioma
Main article: Myoepithelioma
Basal cell adenoma
General
- ~2% of salivary gland tumours.
- May be multifocal.
- Usually parotid gland, occasionally submandibular gland.
- Female:male = ~2:1.
- May be seen in association with dermal cylindromas in the context of a genetic mutation.[10]
- Malignant transformation - rarely.
Microscopic
Features:
- Basal component.
- Basophilic cells - key feature.
- Usu. in nests.
- May be bilayered tubules or trabeculae.
- Large basophilic nucleus.
- Minimal-to-moderate eosinophilic cytoplasm.
- Stromal cells.
- Plump spindle cells without significant nuclear atypia - distinguishing feature.
- Stromal cell nuclei width ~= diameter RBC.
- Dense hyaline stroma.
- Plump spindle cells without significant nuclear atypia - distinguishing feature.
- Tubular component.
- Within basal component, may be minimal.
- Lesion is encapsulated - key feature.
Notes:
- No chondromyxoid stroma.
- Chondromyxoid stroma present -> pleomorphic adenoma.
- Neoplastic cells embedded in stroma ("stromal invasion") = basal cell adenocarcinoma.
- Basal cell adenocarcinoma may be cytologically indistinguishable from basal cell adenoma, i.e. "bad" architecture makes it a basal cell adenocarcinoma.
DDx:
- Adenoid cystic carcinoma - not encapsulated.
- Basal cell adenocarcinoma - not encapsulated.
- Canalicular adenoma - different site; canalicular adenoma is the in oral cavity, usually upper lip.
Images:
IHC
- Luminal stains +ve: CK7 +ve, CAM5.2 +ve.
- p63 +ve -- basal component.
- S-100 +ve -- spindle cells in the stroma.
Canalicular adenoma
Main article: Canalicular adenoma
Warthin tumour
Main article: Warthin tumour
Sebaceous adenoma
Main article: Sebaceous adenoma
- Benign counterpart of sebaceous carcinoma.
Sebaceous lymphadenoma
Main article: Sebaceous lymphadenoma
Oncocytoma of the salivary gland
- AKA salivary gland oncocytoma.
Main article: Oncocytoma of the salivary gland
Malignant
One approach:
- Differentiate -- luminal vs. myoepithelial vs. basal (mucoepideroid).
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
Main article: Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
Acinic cell carcinoma
Main article: Acinic cell carcinoma
Adenoid cystic carcinoma
Main article: Adenoid cystic carcinoma
Note: The breast tumour is dealt with in adenoid cystic carcinoma of the breast.
Salivary duct carcinoma
Main article: Salivary duct carcinoma
Intraductal carcinoma of the salivary gland
Main article: Intraductal carcinoma of the salivary gland
Polymorphous adenocarcinoma
- Abbreviated PAC.
- Previously known as polymorphous low-grade adenocarcinoma, abbreviated PLGA.
Main article: Polymorphous adenocarcinoma
Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma
- Abbreviated Ca ex PA.
Main article: Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma
Epithelial-myoepithelial carcinoma
Main article: Epithelial-myoepithelial carcinoma
Basal cell adenocarcinoma
Main article: Basal cell adenocarcinoma
Sebaceous carcinoma
Main article: Sebaceous carcinoma
It is similar to the tumour found in the skin.
Hyalinizing clear cell carcinoma
Main article: Hyalinizing clear cell carcinoma
See also
References
- ↑ http://www.lab.anhb.uwa.edu.au/mb140/CorePages/Oral/oral.htm#LABSALIVA
- ↑ http://www.lab.anhb.uwa.edu.au/mb140/CorePages/Epithelia/Epithel.htm
- ↑ URL: http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/demilune. Accessed on: 19 August 2011.
- ↑ URL: http://pathology.mc.duke.edu/research/pth225.html. Accessed on: 19 August 2011.
- ↑ Thompson, Lester D. R. (2006). Head and Neck Pathology: A Volume in Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 295-319. ISBN 978-0443069604.
- ↑ Thompson, Lester D. R. (2006). Head and Neck Pathology: A Volume in Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 325-357. ISBN 978-0443069604.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Chhieng, DC.; Paulino, AF. (Dec 2002). "Basaloid tumors of the salivary glands.". Ann Diagn Pathol 6 (6): 364-72. doi:10.1053/adpa.2002.37013. PMID 12478487.
- ↑ Nagao, T.; Sato, E.; Inoue, R.; Oshiro, H.; H Takahashi, R.; Nagai, T.; Yoshida, M.; Suzuki, F. et al. (Oct 2012). "Immunohistochemical analysis of salivary gland tumors: application for surgical pathology practice.". Acta Histochem Cytochem 45 (5): 269-82. doi:10.1267/ahc.12019. PMID 23209336.
- ↑ Sivakumar N, Narwal A, Pandiar D, Devi A, Anand R, Bansal D, Kamboj M (February 2022). "Diagnostic utility of p63/p40 in the histologic differentiation of salivary gland tumors: A systematic review". Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol 133 (2): 189–198. doi:10.1016/j.oooo.2021.07.010. PMID 34518135.
- ↑ Choi, HR.; Batsakis, JG.; Callender, DL.; Prieto, VG.; Luna, MA.; El-Naggar, AK. (Jun 2002). "Molecular analysis of chromosome 16q regions in dermal analogue tumors of salivary glands: a genetic link to dermal cylindroma?". Am J Surg Pathol 26 (6): 778-83. PMID 12023583.
- ↑ URL: http://moon.ouhsc.edu/kfung/jty1/Com/Com304-3-Diss.htm. Accessed on: 25 October 2011.