|
|
| (144 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| '''Non-malignant skin disease''' is relatively common. The pathology may or may not be specific. Some diseases require clinical information to diagnose. | | '''Non-malignant skin disease''' is relatively common. The pathology may or may not be specific. Some diseases require clinical information to diagnose. |
|
| |
|
| An introduction to dermatopathology is in the ''[[dermatopathology]]'' article. [[Nevi]] (moles) and other melanocytic lesions are dealt with in the article ''[[melanocytic lesions]]''. Inflammatory skin conditions are dealt with in ''[[inflammatory skin disorders]]''. | | An introduction to dermatopathology is in the ''[[dermatopathology]]'' article. [[Nevi]] (moles) and other melanocytic lesions are dealt with in the article ''[[melanocytic lesions]]''. Inflammatory skin conditions are dealt with in ''[[inflammatory skin disorders]]''. |
| Line 5: |
Line 5: |
| =Other= | | =Other= |
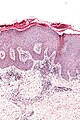
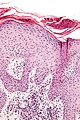
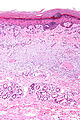
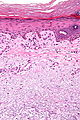
| ==Lichen simplex chronicus== | | ==Lichen simplex chronicus== |
| *Abbreviated ''LSC''.
| | {{Main|Lichen simplex chronicus}} |
| *[[AKA]] ''squamous cell hyperplasia''.<ref name=Ref_PBoD1011>{{Ref PBoD8|1011}}</ref>
| |
| | |
| ===General===
| |
| *May be considered a variant of ''spongiotic dermatitis''.<ref name=Ref_DCHH296>{{Ref DCHH|296}}</ref>; more specifically, some think it is an ''atopic dermatitis'' (which fits in the large ''[[spongiotic dermatitis]]'' category).<ref name=Ref_Derm26>{{Ref Derm|26}}</ref>
| |
| *It is lumped with the [[psoriasiform dermatitides]].
| |
| | |
| Etiology:<ref>URL: [http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1123423-overview http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1123423-overview]. Accessed on: 20 August 2010.</ref>
| |
| *Pruritus (itchness) -> mechanical trauma -> lichenification (thickened/leathery<ref>URL: [http://www.medterms.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=10131 http://www.medterms.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=10131]. Accessed on: 20 August 2010.</ref>.
| |
| | |
| ===Microscopic===
| |
| Features:<ref name=Ref_PBoD1065-6>{{Ref PBoD|1065-6}}</ref>
| |
| *Acanthosis (epithelial thickening) - irregular.
| |
| *Hyperkeratosis.
| |
| Other features:<ref>URL: [http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1123423-diagnosis http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1123423-diagnosis]. Accessed on: 20 August 2010.</ref>
| |
| *Spongiosis (epidermal intercellular edema -- cells appear to have a clear halo around 'em).
| |
| *Parakeratosis = retention of nuclei in the stratum corneum.
| |
| | |
| DDx:
| |
| *[[Prurigo nodularis]] - focal process (nodule or papule).
| |
| *Benign alveolar ridge keratosis ([[AKA]] oral lichen simplex chronicus<ref name=pmid18158926>{{Cite journal | last1 = Natarajan | first1 = E. | last2 = Woo | first2 = SB. | title = Benign alveolar ridge keratosis (oral lichen simplex chronicus): A distinct clinicopathologic entity. | journal = J Am Acad Dermatol | volume = 58 | issue = 1 | pages = 151-7 | month = Jan | year = 2008 | doi = 10.1016/j.jaad.2007.07.011 | PMID = 18158926 }}</ref>) - see [[oral pathology]].
| |
| | |
| Images:
| |
| *[http://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?title=File:Lichen_simplex_chronicus_-_low_mag.jpg LSC - low mag. (WC)].
| |
| *[http://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?title=File:Lichen_simplex_chronicus_-_high_mag.jpg LSC - high mag. (WC)].
| |
| | |
| ===Sign-out===
| |
| <pre>
| |
| SKIN, PUNCH BIOPSY:
| |
| - LICHEN SIMPLEX CHRONICUS.
| |
| - NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
| |
| </pre>
| |
| | |
| ====Oral====
| |
| <pre>
| |
| RETROMOLAR PAD, RIGHT, PUNCH BIOPSY:
| |
| - ORAL LICHEN SIMPLEX CHRONICUS.
| |
| - NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
| |
| </pre>
| |
| | |
| ====Micro====
| |
| The sections show a squamous mucosa with irregular psoriasiform change, parakeratosis, and focal hypergranulosis. There is no inflammation at the interface. Epidermal intercellular bridges are easily seen. There is no significant nuclear atypia. Mitoses are not evident.
| |
|
| |
|
| ==Prurigo nodularis== | | ==Prurigo nodularis== |
| Line 76: |
Line 35: |
| =Very common= | | =Very common= |
| ==Dermatomycosis== | | ==Dermatomycosis== |
| | :''Dermatophytosis'' redirects here. |
| ===General=== | | ===General=== |
| *[[microorganisms|Fungal infection]] of skin. | | *[[microorganisms|Fungal infection]] of skin. |
| Line 88: |
Line 48: |
| ***May be very fragmented in section ~ size of a neutrophil. | | ***May be very fragmented in section ~ size of a neutrophil. |
| *Perivascular inflammation, esp. neutrophils. | | *Perivascular inflammation, esp. neutrophils. |
| *Exocytosis - blood cell infiltrate the epidermis. | | *[[Exocytosis]] - blood cell infiltrate the epidermis. |
|
| |
|
| Images: | | ====Images==== |
| *[http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Dermatomycosis_-_intermed_mag.jpg Dermatomycosis - intermed. mag. (WC)].
| | <gallery> |
| *[http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Dermatomycosis_-_high_mag.jpg Dermatomycosis - high mag. (WC)].
| | Image:Dermatomycosis_-_intermed_mag.jpg | Dermatomycosis - intermed. mag. (WC) |
| *[http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Dermatomycosis_-_gms_-_low_mag.jpg Dermatomycosis - GMS - low mag. (WC)].
| | Image:Dermatomycosis_-_high_mag.jpg | Dermatomycosis - high mag. (WC) |
| *[http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Dermatomycosis_-_gms_-_high_mag.jpg Dermatomycosis - GMS stain - high mag. (WC)].
| | Image:Dermatomycosis_-_gms_-_low_mag.jpg | Dermatomycosis - GMS stain - low mag. (WC) |
| | Image:Dermatomycosis_-_gms_-_high_mag.jpg | Dermatomycosis - GMS stain - high mag. (WC) |
| | </gallery> |
| | www: |
| | *[http://missinglink.ucsf.edu/lm/DermatologyGlossary/img/Dermatology%20Glossary/Glossary%20Histo%20Images/tinea_pas.jpg Dermatophytosis (ucsf.edu)].<ref>URL: [http://missinglink.ucsf.edu/lm/DermatologyGlossary/tinea.html http://missinglink.ucsf.edu/lm/DermatologyGlossary/tinea.html]. Accessed on: 25 February 2013.</ref> |
|
| |
|
| ===Stains=== | | ===Stains=== |
| Line 113: |
Line 77: |
|
| |
|
| ==Cicatrix== | | ==Cicatrix== |
| *[[AKA]] ''scar'', ''dermal scar''.
| | {{Main|Dermal scar}} |
| ===General===
| |
| *Previous surgery, biopsy, trauma.
| |
| | |
| ===Microscopic===
| |
| Features:
| |
| *Loss of dermal papilla.
| |
| *Dense collagen - fibers run parallel to the dermal-epidermal (DE) junction<ref name=Ref_Derm499>{{Ref Derm|499}}</ref> - '''key feature'''.
| |
| *Loss of adnexal structures.
| |
| | |
| Other feature:
| |
| *Thin-walled blood vessels.
| |
| **Described as running perpendicular to the surface<ref name=Ref_Derm499>{{Ref Derm|499}}</ref> - this may not be apparent.
| |
| | |
| Note:
| |
| *There should not be any nuclear hyperchromasia or pleomorphism.<ref name=Ref_Derm479>{{Ref Derm|479}}</ref>
| |
| | |
| DDx:
| |
| *[[Malignant melanoma]], desmoplastic-neurotropic type - nuclear pleomorphism and/or hyperchromasia; may be focal.<ref name=Ref_Derm479>{{Ref Derm|479}}</ref>
| |
| *[[Dermatofibroma]].
| |
| *Desmoplastic [[Spitz nevus]].
| |
| *Sclerosing [[blue nevus]].
| |
| | |
| Image:
| |
| *[http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:ScarHistology.JPG Scar (WC)].
| |
| | |
| ===IHC===
| |
| *S100 focal/scattered +ve.
| |
| **Desmoplastic melanoma strong +ve.
| |
| *HMB-45 -ve.
| |
| **Sclerosing blue nevus +ve.
| |
| | |
| ===Sign out===
| |
| <pre>
| |
| SKIN, LOWER MID BACK, RE-EXCISION:
| |
| - DERMAL SCAR.
| |
| - SOLAR ELASTOSIS.
| |
| </pre>
| |
| | |
| ====Micro====
| |
| The sections show skin with a dermis with dense collagen fibres that run parallel to the skin surface without adnexal structures. The overlying dermal-epidermis interface lacks the typical undulation.
| |
|
| |
|
| ==Fibroepithelial polyp== | | ==Fibroepithelial polyp== |
| *[[AKA]] ''acrochordon'', ''skin tag''.
| | {{Main|Fibroepithelial polyp}} |
| ===General===
| |
| *Benign.
| |
| *Older people.
| |
| *May be associated with pregnancy, [[diabetes]], [[intestinal polyposis]].<ref name=Ref_PCPBoD8|596>{{Ref PCPBoD8|596}}</ref>
| |
| *Component of ''Birt–Hogg–Dubé syndrome'' - see: ''[[Kidney_tumours#Hereditary_renal_cell_carcinoma|Hereditary RCC]]''.
| |
| | |
| ===Gross===
| |
| *Raised skin-coloured lesion.
| |
| | |
| Image:
| |
| *[http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Skintagblemish.jpg Skin tag (WC)].
| |
| | |
| ===Microscopic===
| |
| Features:
| |
| *On a stalk / epithelium on three sides.
| |
| *Benign epidermis.
| |
| | |
| DDx:
| |
| *Pedunculated [[seborrheic keratosis]] - typically have epidermal hyperplasia, hyperkeratosis, horn cysts.<ref name=Ref_Derm342>{{Ref Derm|342}}</ref>
| |
| | |
| Image:
| |
| *[http://dermatlas.med.jhmi.edu/derm/IndexDisplay.cfm?ImageID=1767547949 Fibroepithelial polyp (dermatlas.med.jhmi.edu)].<ref>URL: [http://dermatlas.med.jhmi.edu/derm/result.cfm?Diagnosis=1196583692 http://dermatlas.med.jhmi.edu/derm/result.cfm?Diagnosis=1196583692]. Accessed on: 1 September 2011.</ref>
| |
| | |
| ===Sign out===
| |
| <pre>
| |
| SKIN ("SKIN TAG"), THIGH, EXCISION:
| |
| - FIBROEPITHELIAL POLYP.
| |
| </pre>
| |
| | |
| ====Micro====
| |
| The sections show a fragment of skin with epithelium on three sides. The epithelium matures and is not hypertrophic. Orthokeratosis is present. The core of the lesion has fibrofatty tissue. There is no inflammation.
| |
|
| |
|
| ==Actinic keratosis== | | ==Actinic keratosis== |
| :''Bowenoid actinic keratosis'' redirects to here.
| | {{Main|Actinic keratosis}} |
| *Abbreviated ''AK''.
| |
| *[[AKA]] ''solar keratosis''.<ref name=pmid18393780>{{Cite journal | last1 = Weinberg | first1 = JM. | title = Topical therapy for actinic keratoses: current and evolving therapies. | journal = Rev Recent Clin Trials | volume = 1 | issue = 1 | pages = 53-60 | month = Jan | year = 2006 | doi = | PMID = 18393780 }}</ref><ref name=pmid18067626>{{Cite journal | last1 = Roewert-Huber | first1 = J. | last2 = Stockfleth | first2 = E. | last3 = Kerl | first3 = H. | title = Pathology and pathobiology of actinic (solar) keratosis - an update. | journal = Br J Dermatol | volume = 157 Suppl 2 | issue = | pages = 18-20 | month = Dec | year = 2007 | doi = 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2007.08267.x | PMID = 18067626 }}</ref>
| |
| | |
| ===General===
| |
| *Considered a precursor of [[squamous cell carcinoma of the skin]].<ref name=pmid18067626>{{Cite journal | last1 = Roewert-Huber | first1 = J. | last2 = Stockfleth | first2 = E. | last3 = Kerl | first3 = H. | title = Pathology and pathobiology of actinic (solar) keratosis - an update. | journal = Br J Dermatol | volume = 157 Suppl 2 | issue = | pages = 18-20 | month = Dec | year = 2007 | doi = 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2007.08267.x | PMID = 18067626 }}</ref>
| |
| | |
| Risk factors:<ref name=Ref_PBoD8_1180>{{Ref PBoD8|1180}}</ref>
| |
| *Sun exposure.
| |
| *Immune suppression (e.g. organ transplant recipients).
| |
| | |
| ===Gross===
| |
| Features:
| |
| *Yellow-brown scaly, patches.
| |
| *Sandpaper sensation - on touching.
| |
| *May be pigmented.<ref>URL: [http://www.dermoscopy-ids.org/index.php/newest-case/79-lentigo-maligna-vs-pigmented-actinic-keratosis http://www.dermoscopy-ids.org/index.php/newest-case/79-lentigo-maligna-vs-pigmented-actinic-keratosis]. Accessed on: 23 August 2012.</ref>
| |
| | |
| ===Microscopic===
| |
| Features:<ref>URL: [http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1099775-workup#a0723 http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1099775-workup#a0723]. Accessed on: 1 September 2011.</ref>
| |
| *Epidermal nuclear atypia:
| |
| **Variation is size, shape and staining - must involve basilar layer.
| |
| ***Nuclear enlargement - '''key feature'''.
| |
| ***Hyperchromasia.
| |
| *Abnormal epidermal architecture:
| |
| **Palisading.{{Fact}}
| |
| *+/-Parakeratosis - may alternate with orthokeratosis, esp. early lesions.<ref name=Ref_Derm353>{{Ref Derm|353}}</ref>
| |
| *+/-Irregular acanthosis.
| |
| | |
| Note:
| |
| *May be full thickness - known as ''bowenoid actinic keratosis''.<ref name=pmid19515076>{{Cite journal | last1 = Bagazgoitia | first1 = L. | last2 = Cuevas | first2 = J. | last3 = Juarranz | first3 = A. | title = Expression of p53 and p16 in actinic keratosis, bowenoid actinic keratosis and Bowen's disease. | journal = J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol | volume = 24 | issue = 2 | pages = 228-30 | month = Feb | year = 2010 | doi = 10.1111/j.1468-3083.2009.03337.x | PMID = 19515076 }}</ref>
| |
| | |
| DDx:
| |
| *[[Actinic cheilitis]] - the same lesion on the lip.<ref name=pmid3305604>{{Cite journal | last1 = Picascia | first1 = DD. | last2 = Robinson | first2 = JK. | title = Actinic cheilitis: a review of the etiology, differential diagnosis, and treatment. | journal = J Am Acad Dermatol | volume = 17 | issue = 2 Pt 1 | pages = 255-64 | month = Aug | year = 1987 | doi = | PMID = 3305604 }}</ref>
| |
| *[[Bowen's disease]] - full thickness involvement - with involvement of adnexal epithelium and follicular epithelium.<ref name=pmid19515076/>
| |
| *[[Paget disease of the breast]].
| |
| *[[Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin]].
| |
| *[[Lentigo maligna]] (melanoma in situ on sun damaged skin) - esp. for ''pigmented AK''.<ref name=Ref_Derm353>{{Ref Derm|353}}</ref>
| |
| *[[Seborrheic keratosis]] - should not have basilar nuclear atypia.
| |
| | |
| Images:
| |
| *[http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Actinic_Keratosis,_H%26E.jpg Actinic keratosis (WC)].
| |
| *[http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:SkinTumors-P5280065.JPG Actinic keratosis (WC)].
| |
| *[http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:SkinTumors-P5280055.JPG Actinic keartosis (WC)].
| |
| *[http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Bowenoid_actinic_keratosis_-_high_mag.jpg Bowenoid actinic keratosis - high mag. (WC)].
| |
| *[http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Bowenoid_actinic_keratosis_-_very_high_mag.jpg Bowenoid actinic keratosis - very high mag. (WC)].
| |
| ====Histologic subtypes of actinic keratosis====
| |
| Like most common things, there are several variants:<ref name=Ref_Derm353>{{Ref Derm|353}}</ref>
| |
| *Hypertrophic actinic keratosis.
| |
| **Increased thickness of: (1) epidermis and, (2) stratum corneum.<ref name=Ref_Derm352>{{Ref Derm|352}}</ref>
| |
| *Acantholytic actinic keratosis.
| |
| *Proliferative actinic keratosis - downward finger-like projections of the epidermis.
| |
| *Pigmented actinic keratosis.
| |
| **DDx: [[lentigo maligna]].
| |
| *Lichenoid actinic keratosis.
| |
| | |
| ===Sign out===
| |
| <pre>
| |
| SKIN LESION, RIGHT THIGH, BIOPSY:
| |
| - HYPERTROPHIC ACTINIC KERATOSIS.
| |
| - SOLAR ELASTOSIS.
| |
| - NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
| |
| </pre>
| |
| | |
| ====Bowenoid====
| |
| <pre>
| |
| SKIN LESION, RIGHT DISTAL FOREARM, BIOPSY:
| |
| - BOWENOID ACTINIC KERATOSIS, COMPLETELY EXCISED IN PLANE OF SECTION.
| |
| - EXTENSIVE SOLAR ELASTOSIS.
| |
| - NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
| |
| </pre>
| |
| | |
| ====Micro====
| |
| =====General=====
| |
| The sections show skin with basilar epidermal nuclear enlargement and hyperchromasia with irregular nuclear palisading. Hyperkeratosis and parakeratosis is present. A granular layer is present. The dermal-epidermal interface is sharply-demarcated. There is focal inflammation at the interface. Extensive solar elastosis is present.
| |
| | |
| There is no clefting of the lesion from the surrounding stroma. The surrounding stroma does not have a myxoid quality.
| |
| | |
| =====Bowenoid=====
| |
| The sections show skin with epidermal nuclear enlargement and hyperchromasia with irregular nuclear palisading. The lesion involves the full thickness of the epidermis; however, it spares adnexal and follicular epithelium. Proliferative activity is present. Hyperkeratosis and parakeratosis is present. A granular layer is present. The dermal-epidermal interface is sharply-demarcated. There is focal inflammation at the interface. Extensive solar elastosis is present.
| |
| | |
| There is no clefting of the lesion from the surrounding stroma. Intercellular bridges are identified.
| |
|
| |
|
| ==Actinic cheilitis== | | ==Actinic cheilitis== |
| Line 290: |
Line 103: |
|
| |
|
| ==Seborrheic keratosis== | | ==Seborrheic keratosis== |
| *Abbreviated ''SK''.
| | {{Main|Seborrheic keratosis}} |
| ===General===
| |
| *Benign.
| |
| *Most common tumour in older people.<ref name=emed_sk2>URL: [http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1059477-overview#a0199 http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1059477-overview#a0199]. Accessed on: 26 August 2011.</ref>
| |
| *"Large number" of SKs = paraneoplastic syndrome (''Leser–Trélat sign'').<ref name=Ref_PCPBoD8_595>{{Ref PCPBoD8|595}}</ref>
| |
| | |
| Epidemiology:
| |
| *Old people.
| |
| *Usually in sun exposed area.<ref name=emed_sk1>URL: [http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1059477-overview http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1059477-overview]. Accessed on: 26 August 2011.</ref>
| |
| | |
| ===Gross===
| |
| *"Stuck-on" appearance - raised lesion.
| |
| | |
| Image(s):
| |
| *[http://www.dermatlas.org/derm/IndexDisplay.cfm?ImageID=91774460 SK - gross image (dermatlas.org)].
| |
| | |
| ===Microscopic===
| |
| Features:<ref name=Ref_PCPBoD8_595>{{Ref PCPBoD8|595}}</ref>
| |
| *Raised above skin surface.
| |
| *Border sharply demarcated.
| |
| *Hyperkeratosis - stratum corneum extra thick.
| |
| **May be minimal.
| |
| *Horn cysts - intraepidermal collections of keratin - '''key feature'''.
| |
| **Actually invaginations - '''not''' true cysts; thus, they may more accurately be called ''pseudohorn cysts''.<ref>URL: [http://www.healthcare.uiowa.edu/dermatology/dpt/HornCyst.htm http://www.healthcare.uiowa.edu/dermatology/dpt/HornCyst.htm]. Accessed on: 13 September 2012.</ref>
| |
| *Clusters of cells with brown granular material in the superficial dermis/dermoepidermal junction - pigmented melanocytes.
| |
| | |
| DDx:<ref name=Ref_Derm338-9>{{Ref Derm|338-9}}</ref>
| |
| *[[Actinic keratosis]] - especially, irritated SKs; have nuclear atypia and parakeratosis.
| |
| *[[Verruca vulgaris]] - SK may have papillomatous projections.
| |
| *[[Basal cell carcinoma]], fibroepitheliomatous pattern - esp. reticulated SK.
| |
| *[[Melanocytic nevus]].
| |
| *[[Condyloma acuminatum]] - may have horn cysts, more probable than SK in the genital area.
| |
| | |
| Images:
| |
| *[http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Seborrheic_keratosis_(1).jpg Seborrheic keratosis - low mag. (WC)].
| |
| *[http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Seborrheic_keratosis_%282%29.jpg Seborrheic keratosis - high mag. (WC)].
| |
| *[http://www.dermatlas.org/derm/IndexDisplay.cfm?ImageID=-1985374774 Seborrheic keratosis - high mag. (dermatlas.org)].
| |
| *[http://www.dermatlas.org/derm/IndexDisplay.cfm?ImageID=-1880960893 Seborrheic keratosis - low mag. (dermatlas.org)].
| |
| | |
| ====Histologic subtypes====
| |
| Like very common lesion, there are subtypes:<ref name=Ref_Derm338-9>{{Ref Derm|338-9}}</ref>
| |
| *Acanthotic seborrheic keratosis - thickened ''stratum spinosum''; thick epidermis.
| |
| *Reticulated seborrheic keratosis - vaguely resembles [[fibroepithelioma of Pinkus]] (BCC, fibroepitheliomatous pattern).
| |
| *Irritated seborrheic keratosis - spongiosis (epidermal intercellular edema) and inflammation.
| |
| *Digitated seborrheic keratosis - papillomatous projections.
| |
| | |
| ===Sign out===
| |
| <pre>
| |
| SKIN, MID BACK, SHAVE BIOPSY:
| |
| - SEBORRHEIC KERATOSIS.
| |
| </pre>
| |
| | |
| ====Micro====
| |
| The sections show skin with acanthosis, pseudohorn cysts, parakeratosis, hyperkeratosis and focal basal epidermal pigmentation. There is no basal nuclear atypia, no mitoses and no melanocytic nests. There is minimal dermal inflammation. There is no solar elastosis.
| |
| | |
| =====Without horn pseudocysts=====
| |
| The sections show skin with acanthosis, a thin layer of compact keratin and focal basal epidermal pigmentation. Dilated blood vessels surrounded by collagen are seen in the superficial dermis. No pseudohorn cysts are identified. A granular layer is present.
| |
| | |
| There is no basal nuclear atypia. There is no mitotic activity and no melanocytic nests. There is no solar elastosis. No koilocytes are apparent.
| |
|
| |
|
| ==Pilomatricoma== | | ==Pilomatricoma== |
| *[[AKA]] ''calcifying epithelioma of Malherbe''<ref>{{Ref Derm|387}}</ref>, [[AKA]] ''pilomatrixoma''.
| | {{Main|Pilomatricoma}} |
| ===General===
| |
| *Benign skin tumour.
| |
| *Most common solid skin tumour of children.<ref name=emed1058965>URL: [http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1058965-overview http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1058965-overview]. Accessed on: 10 September 2011.</ref>
| |
| *CTNNB1 gene mutation important in pathogenesis.<ref name=Ref_PCPBoD8_597>{{Ref PCPBoD8|597}}</ref>
| |
| | |
| Clinical:
| |
| *Hard nodule - calcification.
| |
| *+/-Painful.
| |
| | |
| Treatment:
| |
| *Surgical excision.<ref name=emed1058965>[http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1058965-overview http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1058965-overview]</ref>
| |
| | |
| ===Microscopic===
| |
| Features:<ref name=emed1058965dx>URL: [http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1058965-diagnosis http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1058965-diagnosis]. Accessed on: 10 September 2011.</ref>
| |
| *Nodular circumscribed lower dermis/subcutaneous adipose lesion; thus, usu. surrounded by connective tissue.
| |
| **Sharpy demarcated island of cells.
| |
| **Calcification in 75%.
| |
| *Cells:<ref>[http://www.bccancer.bc.ca/HPI/CE/cytotechnology/cytosleuthquiz/nongyne/ngcase02d.htm http://www.bccancer.bc.ca/HPI/CE/cytotechnology/cytosleuthquiz/nongyne/ngcase02d.htm]</ref>
| |
| **Basaloid epithelial cells - have prominent nucleoli.
| |
| **Anucleate squamous cells ("ghost cells").
| |
| **Giant cell foreign body type [[granulomas]] (form in reaction to keratin).
| |
| | |
| Notes:
| |
| *Keratin a prominent feature on cytology - lots of orange stuff.
| |
| *May ossify.
| |
| | |
| Images:
| |
| *[http://www.bccancer.bc.ca/HPI/CE/cytotechnology/cytosleuthquiz/nongyne/ngcase02.htm Pilomatrixoma - cytology (bccancer.bc.ca)].
| |
| *[http://www.dermrounds.com/photo/1980062:Photo:431 Pilomatrixoma - histology (dermrounds.com)].
| |
| *[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Pilomatrixoma_-_high_mag.jpg Pilomatrixoma - high mag. (WC)].
| |
| *[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Pilomatrixoma_-_intermed_mag.jpg Pilomatrixoma - intermed. mag. (WC)].
| |
| | |
| DDx:
| |
| *[[Epidermal inclusion cyst]].
| |
| *Pilomatrix carcinoma - invasive border, cytologic atypia, necrosis.<ref>{{Ref Derm|389}}</ref>
| |
| *[[Squamous cell carcinoma]].
| |
| *[[Basal cell carcinoma]].
| |
| | |
| ===Sign out===
| |
| <pre>
| |
| SKIN LESION, RIGHT ARM, EXCISION:
| |
| - PILOMATRICOMA.
| |
| </pre>
| |
|
| |
|
| ==Dermatofibroma== | | ==Dermatofibroma== |
| *Abbreviated ''DF''.
| | {{Main|Dermatofibroma}} |
| ===General===
| |
| *AKA ''fibrous histiocytoma''.
| |
| *Reactive process -- it is ''not'' a neoplasm.
| |
| *Usually associated with previous trauma.
| |
| **In women... usually legs.
| |
| | |
| ===Microscopic===
| |
| Features:<ref name=Ref_WMSP492>{{Ref WMSP|492}}</ref>
| |
| *Prominent fibrous bundles, especially at the edge of the lesion.
| |
| **Surrounded by spindle cells (fibroblasts).
| |
| ***Usually thought of as fibroblasts surrounded by fibrous material ("collagen-trapping").
| |
| *Lack of adnexal structures, i.e. no sweat glands, no hair.
| |
| *+/-Epidermal changes - known as "dirty fingers":<ref>BD. 13 April 2011.</ref>
| |
| **Acanthosis (thickened epithelial layer - specifically thickened ''stratum spinosum'').
| |
| **Basal keratinocyte hyperpigmentation.
| |
| | |
| DDx:
| |
| *[[Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans]] (DFSP) - usu. deeper, classically has adnexal structures and fat within lesion.
| |
| *[[Neurofibroma]].
| |
| *[[Blue nevus]].
| |
| *[[Melanoma]], esp. desmoplastic neurotropic-type.
| |
| *[[Fibromatosis]].
| |
| | |
| Images:
| |
| *[http://missinglink.ucsf.edu/lm/DermatologyGlossary/dermatofibroma.html Dermatofibroma (ucsf.edu)].
| |
| *[http://www.pacificderm.org/newsflashcpcapril04.html DF - several images (pacificderm.org)].
| |
| *[http://biocare.net/products/antibodies/f/357/ DF stained with factor XIIIa (biocare.net)].
| |
| | |
| ====Subtypes====
| |
| Like all common things... there are subtypes:<ref>{{Ref Sternberg5|51}}</ref>
| |
| *Cellular.
| |
| *Deep penetrating.
| |
| *Lipidized - with foamy macrophages, hemorrhage and Touton-like giant cells.
| |
| *Epithelioid cell histiocytoma.
| |
| *Fibrotic.
| |
| *Aneurysmal - large blood filled + features of ''lipidized''.
| |
| *Granular cell dermatofibroma.
| |
| *Dermatofibroma with monster cells.
| |
| =====Cellular dermatofibroma=====
| |
| Features:
| |
| *High cell density in the dermis - "blue" at low power.
| |
| *Collagen bundles - '''key feature'''.
| |
| | |
| Images:
| |
| *[http://www.surgicalpathologyatlas.com/glfusion/mediagallery/media.php?f=0&sort=0&s=20080802171836877 Cellular dermatofibroma (surgicalpathologyatlas.com)].
| |
| *[http://www.dermpedia.org/node/2292 Cellular dermatofibroma (dermpedia.org)].<ref>URL: [http://www.dermpedia.org/case/cellular-dermatofibroma-mimicking-dermatofibrosarcoma-protuberans# http://www.dermpedia.org/case/cellular-dermatofibroma-mimicking-dermatofibrosarcoma-protuberans#]. Accessed on: 4 February 2012.</ref>
| |
| | |
| ===IHC===
| |
| Features:<ref name=pmid7694515>{{cite journal |author=Abenoza P, Lillemoe T |title=CD34 and factor XIIIa in the differential diagnosis of dermatofibroma and dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans |journal=Am J Dermatopathol |volume=15 |issue=5 |pages=429–34 |year=1993 |month=October |pmid=7694515 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name=pmid9129699>{{cite journal |author=Goldblum JR, Tuthill RJ |title=CD34 and factor-XIIIa immunoreactivity in dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans and dermatofibroma |journal=Am J Dermatopathol |volume=19 |issue=2 |pages=147–53 |year=1997 |month=April |pmid=9129699 |doi= |url=}}</ref>
| |
| *Factor XIIIa +ve.
| |
| **Usually negative in [[DFSP]].
| |
| *CD34 -ve.
| |
| **Usually positive in DFSP.
| |
| *D2-40 +ve.<ref name=pmid20062007>{{cite journal |author=Bandarchi B, Ma L, Marginean C, Hafezi S, Zubovits J, Rasty G |title=D2-40, a novel immunohistochemical marker in differentiating dermatofibroma from dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans |journal=Mod. Pathol. |volume=23 |issue=3 |pages=434–8 |year=2010 |month=March |pmid=20062007 |doi=10.1038/modpathol.2009.176 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| **Usually negative in DFSP.
| |
|
| |
|
| ==Ezcema== | | ==Ezcema== |
| Line 500: |
Line 157: |
|
| |
|
| DDx - acneiform disorder:<ref name=Ref_Derm77>{{Ref Derm|77}}</ref> | | DDx - acneiform disorder:<ref name=Ref_Derm77>{{Ref Derm|77}}</ref> |
| *Rosacea. | | *[[Rosacea]]. |
| *Infective folliculitis. | | *Infective folliculitis. |
| *Perioral dermatitis. | | *Perioral dermatitis. |
| Line 509: |
Line 166: |
|
| |
|
| ==Solar elastosis== | | ==Solar elastosis== |
| *[[AKA]] ''actinic elastosis''. | | *[[AKA]] ''actinic elastosis''.<ref>URL: [http://www.dermnetnz.org/dermal-infiltrative/solar-elastosis.html http://www.dermnetnz.org/dermal-infiltrative/solar-elastosis.html]. Accessed on: 27 March 2013.</ref> |
| ===General=== | | ===General=== |
| *Very common. | | *Very common. |
| Line 527: |
Line 184: |
|
| |
|
| Note: | | Note: |
| *It doesn't really look like anything else.
| | *The DDx above is things associated with sun damaged skin. |
| **The DDx above is things to think about that are associated with sun damaged skin.
| | *Dermal mucin (as my be seen in [[lupus erythematosus]]) is a possible mimic - but it isn't spaghetti-like and the "background" (an [[interface dermatitis]]) is different. |
|
| |
|
| Images: | | ====Images==== |
| *[[WC]]:
| | <gallery> |
| **[http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Solar_elastosis_-_intermed_mag.jpg Solar elastosis - intermed. mag. (WC)].
| | Image:Solar_elastosis_-_intermed_mag.jpg | Solar elastosis - intermed. mag. (WC) |
| **[http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Solar_elastosis_-_high_mag.jpg Solar elastosis - high mag. (WC)].
| | Image:Solar_elastosis_-_high_mag.jpg | Solar elastosis - high mag. (WC) |
| *www:
| | </gallery> |
| **[http://dermpathexpert.com/id88.html Solar elastosis - several images (dermpathexpert.com)].
| | www: |
| | *[http://dermpathexpert.com/id88.html Solar elastosis - several images (dermpathexpert.com)]. |
|
| |
|
| ===Sign out=== | | ===Sign out=== |
| Line 544: |
Line 202: |
| </pre> | | </pre> |
|
| |
|
| =Very common - viral= | | =====Prominent blood vessels===== |
| ==Verruca vulgaris== | | <pre> |
| *[[AKA]] common wart.
| | SKIN LESION, LEFT CHEEK, BIOPSY: |
| ===General=== | | - SKIN WITH SOLAR ELASTOSIS AND PROMINENT SMALL BLOOD VESSELS. |
| *Etiology - [[HPV]].
| | </pre> |
| *Very common.
| |
| | |
| Notes:
| |
| *Related to [[condyloma acuminatum]].
| |
| | |
| ===Microscopic===
| |
| Features:<ref>URL: [http://missinglink.ucsf.edu/lm/DermatologyGlossary/verruca_vulgaris.html http://missinglink.ucsf.edu/lm/DermatologyGlossary/verruca_vulgaris.html]. Accessed on: 14 July 2010.</ref>
| |
| *Hyperkeratosis (more keratin - thick stratum corneum) - in "columns"; keratin in separate towers - ''not'' a flat thick sheet.
| |
| *Hypergranulosis (thicker stratum granulosum).
| |
| *Acanthosis (thickening of the stratum spinosum).
| |
| **+/-Rete ridge lengthening (~7-10x normal) and thickening - ''papillomatous hyperplasia''.
| |
| *Large blood vessels at the dermal-epidermal junction - between the rete ridges.
| |
| *+/-Viral changes - perinuclear halo, nucleus small and hyperchromatic<ref name=Ref_Derm106-7>{{Ref Derm|106-7}}</ref> - '''important''' when present.
| |
| **+/-Binucleation.
| |
| | |
| Memory device: there is more of everything - more s. corneum, s. granulosum, s. spinosum, longer rete ridges, more (larger) blood vessels.
| |
| | |
| DDx:
| |
| *[[Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin|Squamous cell carcinoma]] - nuclear atypia full thickness and often more pronounced.
| |
| *Hypertrophic [[actinic keratosis]] - often accompanied by solar elastosis.
| |
| **Actinic keratosis with superimposed [[lichen simplex chronicus]].<ref name=Ref_Derm353>{{Ref Derm|353}}</ref>
| |
| *[[Seborrheic keratosis]] - may have focal clear cell changes.
| |
|
| |
|
| Images:
| |
| *[http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Verruca_vulgaris_-_very_low_mag.jpg Verruca vulgaris - very low mag. (WC)].
| |
| *[http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Verruca_vulgaris_-_intermed_mag.jpg Verruca vulgaris - intermed mag. (WC)].
| |
|
| |
| ===Sign out===
| |
| <pre> | | <pre> |
| SKIN LESION, RIGHT LOWER LEG, SHAVE BIOPSY:
| | SUPERIOR SHOULDER, LEFT, PUNCH BIOPSY: |
| - VERRUCA VULGARIS. | | - BENIGN SKIN WITH MODERATE SOLAR ELASTOSIS, PROMINENT SMALL BLOOD VESSELS AND |
| | SCATTERED PERIVASCULAR LYMPHOCYTES AND PLASMA CELLS. |
| | - NEGATIVE FOR BASAL CELL CARCINOMA. |
| | - NEGATIVE FOR ACTINIC KERATOSIS. |
| </pre> | | </pre> |
|
| |
|
| ====Micro==== | | ====Micro==== |
| The sections show skin with elongated rete ridges, acanthosis, hypergranulosis, hyperkeratosis in vertical columns, focal parakeratosis, dilated blood vessels at the dermal-epidermal junction and koilocytic change. Mild basilar nuclear atypia is present. | | The sections show hair bearing skin with solar elastosis and numerous small dilated blood vessels. The dermis is mildly fibrotic. Compact keratin is present. |
| | |
| | The epidermis matures to the surface. A granular layer is present. There is no basal |
| | epidermal atypia. No melanocytic nests are identified. There is no palisading of the basal |
| | cells. Rare scattered lymphocytes are in the dermis. |
| | |
| | =Very common - viral= |
| | ==Verruca vulgaris== |
| | {{Main|Verruca vulgaris}} |
|
| |
|
| ==Verruca plana== | | ==Verruca plana== |
| Line 596: |
Line 238: |
| *Viral keratohyaline. | | *Viral keratohyaline. |
| *Koilocytes. | | *Koilocytes. |
| *Acanthosis - yet flat surface and base. | | *[[Acanthosis]] - yet flat surface and base. |
|
| |
|
| Notes: | | Notes: |
| *It differs from verruca vulgaris... (1) orthokeratosis, (2) flat surface and base. | | *It differs from [[verruca vulgaris]]... (1) orthokeratosis, (2) flat surface and base. |
|
| |
|
| =Less common= | | =Less common= |
| Line 619: |
Line 261: |
| **Lymphocytes - usu. predominant. | | **Lymphocytes - usu. predominant. |
| *+/-Chronic changes: | | *+/-Chronic changes: |
| **Acanthosis. | | **[[Acanthosis]]. |
| **Hyperkeratosis. | | **Hyperkeratosis. |
| **Hypergranulosis. | | **Hypergranulosis. |
| Line 640: |
Line 282: |
|
| |
|
| ==Clear cell acanthoma== | | ==Clear cell acanthoma== |
| ===General===
| | {{Main|Clear cell acanthoma}} |
| *Benign.
| |
| *Elderly.
| |
| *Classically on the leg.<ref name=pmid18583817>{{Cite journal | last1 = Akin | first1 = FY. | last2 = Ertam | first2 = I. | last3 = Ceylan | first3 = C. | last4 = Kazandi | first4 = A. | last5 = Ozdemir | first5 = F. | title = Clear cell acanthoma: new observations on dermatoscopy. | journal = Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol | volume = 74 | issue = 3 | pages = 285-7 | month = | year = | doi = | PMID = 18583817 | URL = http://www.ijdvl.com/text.asp?2008/74/3/285/41396 }}</ref>
| |
| *Rare.
| |
| *Clinically not distinct.
| |
| **Suspected clinically in only ~3% of cases.<ref name=pmid20931670>{{Cite journal | last1 = Morrison | first1 = LK. | last2 = Duffey | first2 = M. | last3 = Janik | first3 = M. | last4 = Shamma | first4 = HN. | title = Clear cell acanthoma: a rare clinical diagnosis prior to biopsy. | journal = Int J Dermatol | volume = 49 | issue = 9 | pages = 1008-11 | month = Sep | year = 2010 | doi = | PMID = 20931670 }}</ref>
| |
| | |
| ===Microscopic===
| |
| Features:<ref>URL: [http://www.drmihm.com/cases/case.cfm?CaseID=45 http://www.drmihm.com/cases/case.cfm?CaseID=45]. Accessed on: 7 February 2012.</ref>
| |
| *Psoriasiform pattern - epidermal thickening (acanthosis).
| |
| *Keratinocytes:
| |
| **Pale or light pink cytoplasm (when compared to surrounding non-lesional keratinocytes).
| |
| **Separated from one another (spongiosis).
| |
| *+/-Stratum corneum [[neutrophil]]s.
| |
| | |
| DDx:
| |
| *[[Psoriasis vulgaris]].
| |
| | |
| Images:
| |
| *[http://www.drmihm.com/cases/casefigure.cfm?figID=906&CaseID=45 CCA (drmihm.com)].
| |
| *[http://www.dermatlas.com/derm/IndexDisplay.cfm?ImageID=-327718365 CCA - low mag. (dermatlas.com)].
| |
| *[http://www.dermatlas.com/derm/IndexDisplay.cfm?ImageID=546460717 CCA - high mag. (dermatlas.com)].
| |
|
| |
|
| ==Chondrodermatitis nodularis chronica helicis== | | ==Chondrodermatitis nodularis chronica helicis== |
| *[[AKA]] ''chondrodermatitis nodularis helicis''. | | *[[AKA]] ''chondrodermatitis nodularis helicis''. |
| *Abbreviated ''CNCH''. | | *Abbreviated ''CNCH''. |
| ===General===
| | *[[AKA]] ''Winkler disease''.<ref>URL: [http://www.head-face-med.com/content/4/1/2 http://www.head-face-med.com/content/4/1/2]. Accessed on: 16 January 2014.</ref> |
| *Tender/painful - '''key clinical feature'''. | | {{Main|Chondrodermatitis nodularis chronica helicis}} |
| *Typically right [[ear]] - people more often sleep on this one.<ref name=pmid17879469>{{Cite journal | last1 = Devani | first1 = A. | last2 = Barankin | first2 = B. | title = Dermacase. Chondrodermatitis nodularis chronica helicis. | journal = Can Fam Physician | volume = 53 | issue = 5 | pages = 821, 837 | month = May | year = 2007 | doi = | PMID = 17879469 }}</ref>
| |
| *Usually >40 years old.
| |
| | |
| Etiology:
| |
| *Trauma/mechanical.
| |
| | |
| ===Gross===
| |
| *[[Papule]] on ear.
| |
| *+/-Erythematous.
| |
| *+/-Crust.
| |
| | |
| Clinical DDx:<ref name=pmid17879469/>
| |
| *[[BCC]].
| |
| *[[SCC]].
| |
| | |
| Images:
| |
| *[http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Chondrodermatitis.jpg CNCH (WC)].
| |
| *[http://www.dermnetnz.org/lesions/chondrodermatitis.html CNCH (dermnetnz.org)].
| |
| | |
| ===Microscopic===
| |
| Features:<ref name=pmid17879469/>
| |
| *Dermal inflammation.
| |
| *Epithelial hyperlasia.
| |
| *Fibrosis.
| |
| *Cartilaginous pathology:
| |
| **Perichondrial inflammation - '''key feature'''.
| |
| **Perichondrial disruption.
| |
| **+/-Necrosis.
| |
| **+/-Hemorrhage.
| |
| | |
| Images:
| |
| *[http://www.dermpedia.org/case/chondrodermatitis-nodularis-chronica-helicis CNCH (dermpedia.org)].
| |
| *[http://www.surgicalpathologyatlas.com/glfusion/mediagallery/media.php?s=20080802171837514 CNCH (surgicalpathologyatlas.com)].
| |
| *[http://dermatlas.med.jhmi.edu/derm/indexDisplay.cfm?ImageID=2140701395 CNCH (dermatlas.med.jhmi.edu)].
| |
| | |
| ===Sign out===
| |
| ====Superficial biopsy====
| |
| <pre>
| |
| SKIN LESION, LEFT ANTIHELIX OF EAR, BIOPSY:
| |
| - SUPERFICIAL SKIN WITH ACANTHOSIS, HYPERKERATOSIS, MODERATE SOLAR ELASTOSIS,
| |
| HYPERGRANULOSIS AND A MILD LYMPHOCYTIC PERIVASCULAR INFILTRATE.
| |
| - NO CARTILAGE IS IDENTIFIED.
| |
| - NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA AND MALIGNANCY.
| |
| | |
| COMMENT:
| |
| The findings are non-specific. Chondrodermatitis cannot be excluded.
| |
| </pre>
| |
|
| |
|
| ==Cutaneous calcinosis== | | ==Cutaneous calcinosis== |
| *[[AKA]] ''calcinosis cutis''. | | *[[AKA]] ''calcinosis cutis''. |
| ===General===
| | {{Main|Cutaneous calcinosis}} |
| *Benign in itself; underlying cause may not be benign.
| |
| *May be a [[scrotum|scrotal]] lesion - known as ''scrotal calcinosis''.<ref name=pmid20178701>{{Cite journal | last1 = Dubey | first1 = S. | last2 = Sharma | first2 = R. | last3 = Maheshwari | first3 = V. | title = Scrotal calcinosis: idiopathic or dystrophic? | journal = Dermatol Online J | volume = 16 | issue = 2 | pages = 5 | month = | year = 2010 | doi = | PMID = 20178701 }}</ref>
| |
| | |
| Subtypes:<ref name=emed>URL: [http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1103137-overview http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1103137-overview]. Accessed on: 21 September 2011.</ref>
| |
| #Dystrophic - due to death of cells; may be related to a tumour.
| |
| #Metastatic - due to chronic renal failure; hyperkalemia; paraneoplastic phenomenon.
| |
| #Iatrogenic - post surgical.
| |
| #Idiopathic.
| |
| | |
| ===Microscopic===
| |
| Features:
| |
| *Dermal calcification:
| |
| **Acellular purple blobs on [[H&E]].
| |
| ***+/-Artefactual tearing of surrounding tissue due to processing (cutting).
| |
| ***+/-Small artefactual lines ~1-2 micrometers due to processing (cutting).
| |
| **Usu. well-circumscribed.
| |
| | |
| Images:
| |
| *[http://nelspruit-histopath.blogspot.com/2010/12/skin-calcinosis-cutis.html Calcinosis cutis (blogspot.com)].
| |
|
| |
|
| ==Dilated pore of Winer== | | ==Dilated pore of Winer== |
| ===General=== | | ===General=== |
| *Benign. | | *Benign. |
| *Looks like zit. | | *Looks like a zit. |
|
| |
|
| ===Microscopic=== | | ===Microscopic=== |
| Features:<ref name=Ref_WMSP486>{{Ref WMSP|486}}</ref> | | Features:<ref name=Ref_WMSP486>{{Ref WMSP|486}}</ref> |
| *Dilated hair follicle with keratin. | | *Dilated hair follicle with keratin. |
| *Acanthosis. | | *[[Acanthosis]]. |
| *Budding of epidermis (into dermis). | | *Budding of epidermis (into dermis). |
|
| |
| ==Lichenoid keratosis==
| |
| *[[AKA]] ''lichen planus-like keratosis''.
| |
| *[[AKA]] ''lichenoid keratosis''.
| |
|
| |
| ===General===
| |
| *Caucasians - middle age or older.
| |
| *May be a variant of [[seborrheic keratosis]] (with marked inflammation).<ref name=Ref_Derm346>{{Ref Derm|346}}</ref>
| |
|
| |
| Clinical DDx:<ref name=Ref_Derm346>{{Ref Derm|346}}</ref>
| |
| *[[Basal cell carcinoma]], [[squamous cell carcinoma of the skin]], melanocytic neoplasm.
| |
|
| |
| ===Microscopic===
| |
| Features:<ref name=Ref_Derm347>{{Ref Derm|347}}</ref>
| |
| *Hyperkeratosis.
| |
| *Parakeratosis.
| |
| *Band of inflammatory cells at DE junction (lichenoid inflammation).
| |
| *Dead keratinocytes (Civatte bodies).
| |
| *Dermal melanophages.
| |
|
| |
|
| DDx: | | DDx: |
| *[[Lichen planus]] - need clinical correlation (mucosal lesions). | | *[[Pilar sheath acanthoma]]. |
| *[[Drug reaction]].
| |
| *[[Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma]].
| |
| *Regressed melanocytic lesion, esp. [[malignant melanoma]].
| |
| *Lichenoid [[actinic keratosis]] - has atypical hyperchromatic basal cells - esp. at edge of lesion, usu. in the context of [[solar elastosis]].
| |
|
| |
|
| Images:
| | Image: |
| *[http://www.dermpathexpert.com/id57.html Lichenoid keratosis (dermpathexpert.com)]. | | *[http://dermpathexpert.com/id90.html Dilated pore of Winer (dermpathexpert.com)]. |
|
| |
|
| ===Sign out=== | | ==Lichenoid keratosis== |
| <pre>
| | *[[AKA]] ''lichen planus-like keratosis''. |
| SKIN LESION, MID-MIDDLE BACK, PUNCH BIOPSY:
| | {{Main|Lichenoid keratosis}} |
| - LICHENOID KERATOSIS. | |
| </pre>
| |
|
| |
|
| ==Granuloma annulare== | | ==Granuloma annulare== |
| ===General===
| | {{Main|Granuloma annulare}} |
| *Benign and self-limited condition.
| |
| *Etiology unknown - may be assoc. with trauma.<ref name=Ref_Derm51>{{Ref Derm|51}}</ref>
| |
| | |
| ===Gross===
| |
| *Typically extremities - usu. arms and hands.<ref name=Ref_Derm51>{{Ref Derm|51}}</ref>
| |
| | |
| ===Microscopic===
| |
| Features:<ref name=Ref_WMSP478>{{Ref WMSP|478}}</ref>
| |
| *Dermal palisading [[granuloma]] - typically superficial-to-mid dermis - surrounds:
| |
| **Necrotic collagen - '''key feature'''.
| |
| ***Nuclei "missing" - have undergone karyolysis.
| |
| **Mucin - important.
| |
| ***Loose/pale, paucicellular, eosinophilic.
| |
| *Chronic inflammatory cells.
| |
| | |
| Notes:
| |
| #There may be multiple small foci with intervening normal dermis.<ref name=Ref_Derm51>{{Ref Derm|51}}</ref>
| |
| #Granuloma annulare can be subclassified into ''subcutaneous'' and ''interstitial''.
| |
| #Histomorphologically similar to ''[[Rheumatoid nodule]].
| |
| #[[Neutrophil]]s may be seen.<ref name=pmid17544961>{{Cite journal | last1 = Requena | first1 = L. | last2 = Fernández-Figueras | first2 = MT. | title = Subcutaneous granuloma annulare. | journal = Semin Cutan Med Surg | volume = 26 | issue = 2 | pages = 96-9 | month = Jun | year = 2007 | doi = 10.1016/j.sder.2007.02.006 | PMID = 17544961 }}</ref>
| |
| | |
| DDx:
| |
| *[[Necrobiosis lipoidica]] - little mucin, no normal dermis between foci,<ref name=Ref_Derm51>{{Ref Derm|51}}</ref> plasma cells - common,<ref name=dermnetnz_nl>URL: [http://dermnetnz.org/pathology/necrobiosis-lipoidica-path.html http://dermnetnz.org/pathology/necrobiosis-lipoidica-path.html]. Accessed on: 24 January 2012.</ref> may involve the fat - tend to be deeper.
| |
| *[[Rheumatoid nodule]] - has fibrin in the core of the granuloma (instead of mucin), multinucleated macrophages more common.<ref name=Ref_Derm52-3>{{Ref Derm|52-3}}</ref>
| |
| *[[Epithelioid sarcoma]] - esp. if the lesion appears to be mid-to-deep dermis.
| |
| | |
| Images:
| |
| *WC:
| |
| **[http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Granuloma_annulare_-_add_-_intermed_mag.jpg Granuloma annulare - intermed. mag. (WC)].
| |
| **[http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Granuloma_annulare_-_high_mag.jpg Granuloma annulare - high mag. (WC)].
| |
| **[http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Granuloma_annulare_-_add_-_high_mag.jpg Granuloma annular - palisaded granuloma - high mag. (WC)].
| |
| *www:
| |
| **[http://www.dermaamin.com/site/histopathology-of-the-skin/61-i/1813-interstitial-granuloma-annulare-.html Granuloma annulare (dermaamin.com)].
| |
| | |
| ===Stains===
| |
| *[[Alcian blue stain|Alcian blue]] (pH 2.5) +ve (for mucin).<ref name=pmid20523767/><ref name=Ref_Derm51>{{Ref Derm|51}}</ref>
| |
| | |
| Image:
| |
| *[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2861218/figure/F7/ Granuloma annulare (nih.gov)].<ref name=pmid20523767>{{Cite journal | last1 = Yun | first1 = JH. | last2 = Lee | first2 = JY. | last3 = Kim | first3 = MK. | last4 = Seo | first4 = YJ. | last5 = Kim | first5 = MH. | last6 = Cho | first6 = KH. | last7 = Kim | first7 = MB. | last8 = Lee | first8 = WS. | last9 = Lee | first9 = KH. | title = Clinical and pathological features of generalized granuloma annulare with their correlation: a retrospective multicenter study in Korea. | journal = Ann Dermatol | volume = 21 | issue = 2 | pages = 113-9 | month = May | year = 2009 | doi = 10.5021/ad.2009.21.2.113 | PMID = 20523767 | PMC = 2861218 }}</ref>
| |
|
| |
|
| ==Necrobiosis lipoidica== | | ==Necrobiosis lipoidica== |
| ===General===
| | {{Main|Necrobiosis lipoidica}} |
| Associated with:
| |
| *[[Diabetes mellitus]] - known as ''necrobiosis lipoidica diabeticorum''.
| |
| *[[Rheumatoid arthritis]].
| |
| | |
| ===Microscopic===
| |
| Features:<ref name=Ref_Derm51>{{Ref Derm|51}}</ref>
| |
| *Dermal palisading [[granuloma]] around:
| |
| **Necrotic collagen - '''key feature'''.
| |
| ***Nuclei "missing" - have undergone karyolysis.
| |
| *Little mucin, no normal dermis between foci.
| |
| *Plasma cells - common.<ref name=dermnetnz_nl>URL: [http://dermnetnz.org/pathology/necrobiosis-lipoidica-path.html http://dermnetnz.org/pathology/necrobiosis-lipoidica-path.html]. Accessed on: 24 January 2012.</ref>
| |
| *May involve adipose tissue.
| |
| | |
| DDx:
| |
| *[[Granuloma annulare|Granuloma a'''nn'''ulare]] - '''m'''ore '''m'''ucin, normal dermis between foci,<ref name=Ref_Derm51>{{Ref Derm|51}}</ref> plasma cells uncommon,<ref name=dermnetnz_nl/> no fat involvement - usu. more superficial.
| |
| *[[Rheumatoid nodule]].
| |
| | |
| Images:
| |
| *[http://dermatology.cdlib.org/103/NYU/case_presentations/042004n10.html Necrobiosis lipoidica (dermatology.cdlib.org)].
| |
| *[http://www.drmihm.com/cases/case.cfm?CaseID=53 Necrobiosis lipoidica (drmihm.com)].
| |
| *[http://dermnetnz.org/pathology/necrobiosis-lipoidica-path.html Necrobiosis lipoidica (dermnetnz.org)].
| |
|
| |
|
| ==Keloid== | | ==Keloid== |
| *''Hypertrophic scar'' redirects to this section.
| | {{Main|Keloid}} |
| ===General===
| |
| *Sites of previous trauma/surgery, esp. in dark skinned individuals.<ref name=Ref_WMSP492>{{Ref WMSP|492}}</ref>
| |
| | |
| ===Microscopic===
| |
| Features:<ref name=Ref_WMSP492>{{Ref WMSP|492}}</ref>
| |
| *Thick collagen bundles - surrounded by paler staining fibroblasts - '''key feature'''.
| |
| *Lesion replaces adnexal structures, e.g. hair, sweat glands.
| |
| | |
| DDx:
| |
| *Hypertrophic scar.
| |
| | |
| NB:
| |
| *'''Reported as "keloidal-type collagen"'''; the clinician decides between ''hypertrophic scar'' and ''keloid''.
| |
| | |
| Images:
| |
| *[[WC]]:
| |
| **[http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Keloid_-_add_-_low_mag.jpg Keloid - low mag. (WC)].
| |
| **[http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Keloid_-_add_-_intermed_mag.jpg Keloid - intermed. mag. (WC)].
| |
| **[http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Keloid_-_high_mag.jpg Keloid - high mag. (WC)].
| |
| *www:
| |
| **[http://missinglink.ucsf.edu/lm/DermatologyGlossary/keloids.html Keloid (ucsf.edu)].
| |
|
| |
|
| ==Angiofibroma== | | ==Angiofibroma== |
| :See also: ''[[nasopharyngeal angiofibroma]]''. | | :See also: ''[[nasopharyngeal angiofibroma]]''. |
| :Should '''not''' be confused with ''[[angiokeratoma]]''. | | :Should '''not''' be confused with ''[[angiokeratoma]]''. |
| :''Fibrous papule'' redirects here.
| | {{Main|Angiofibroma}} |
| | |
| | ==Benign fibrous papule== |
| | *[[AKA]] ''fibrous papule''. |
| | |
| ===General=== | | ===General=== |
| *May be seen in the context of [[tuberous sclerosis]] - especially "butterfly area of the face".<ref name=Ref_WMSP492>{{Ref WMSP|492}}</ref> | | *An ''[[angiofibroma]]'' on the face that is solitary.<ref name=Ref_Derm505>{{Ref Derm|505}}</ref><ref name=pmid18032900>{{Cite journal | last1 = Jacyk | first1 = WK. | last2 = Rütten | first2 = A. | last3 = Requena | first3 = L. | title = Fibrous papule of the face with granular cells. | journal = Dermatology | volume = 216 | issue = 1 | pages = 56-9 | month = | year = 2008 | doi = 10.1159/000109359 | PMID = 18032900 }}</ref> |
| *Solitary lesions in adults are known as ''fibrous papules'' and classically arise on the nose.<ref name=Ref_Derm505>{{Ref Derm|505}}</ref>
| |
|
| |
|
| Clinical:
| | ===Gross=== |
| *Firm, dome-shaped, flesh coloured. | | *Solitary lesion of the face - '''important'''.<ref name=Ref_Derm505>{{Ref Derm|505}}</ref> |
| | **Usually on the nose.<ref name=pmid18032900/> |
|
| |
|
| ===Microscopic=== | | ===Microscopic=== |
| Line 893: |
Line 345: |
| **Enlarged fibroblasts. | | **Enlarged fibroblasts. |
| *Dilated small vessels. | | *Dilated small vessels. |
| | *+/-Multinucleated stromal cells.<ref name=pmid543528>{{Cite journal | last1 = Ragaz | first1 = A. | last2 = Berezowsky | first2 = V. | title = Fibrous papule of the face. A study of five cases by electron microscopy. | journal = Am J Dermatopathol | volume = 1 | issue = 4 | pages = 353-6 | month = | year = 1979 | doi = | PMID = 543528 }}</ref> |
| | *+/-Stellate cells.<ref name=pmid543528/> |
|
| |
|
| Image:
| | DDx: |
| *[http://www.drdittmar.lu/images/sce/angiofibroma-s.jpg Angiofibroma (drdittmar.lu)].<ref>URL: [http://www.drdittmar.lu/Services.aspx http://www.drdittmar.lu/Services.aspx]. Accessed on: 1 September 2011.</ref> | | *[[Angiofibroma]] - not solitary or not on the nose. |
|
| |
|
| ==Molluscum contagiosum== | | Note: |
| ===General=== | | *Several variants exist.<ref name=pmid18032900>{{Cite journal | last1 = Jacyk | first1 = WK. | last2 = Rütten | first2 = A. | last3 = Requena | first3 = L. | title = Fibrous papule of the face with granular cells. | journal = Dermatology | volume = 216 | issue = 1 | pages = 56-9 | month = | year = 2008 | doi = 10.1159/000109359 | PMID = 18032900 }}</ref> |
| *Etiology: caused by ''molluscum contagiosum virus''.
| |
|
| |
|
| ===Microscopic=== | | ===Images=== |
| Features:
| | *[http://www.dermaamin.com/site/histopathology-of-the-skin/58-f/1739-fibrous-papule-angiofibroma-.html Fibrous papule (dermaamin.com)]. |
| *A suprabasilar epidermal lesion consisting of "molluscum bodies", i.e. ''molluscum bodies'' are found above the stratum basale.<ref>[http://www.missionforvisionusa.org/anatomy/2006/08/what-is-molluscum-contagiosum.html http://www.missionforvisionusa.org/anatomy/2006/08/what-is-molluscum-contagiosum.html]</ref> | |
| *Molluscum bodies - '''key feature''':
| |
| **Large cells with abundant granular eosinophilic cytoplasm.
| |
| **Small peripheral nucleus.
| |
|
| |
|
| Notes:
| | ===Sign out=== |
| *Molluscum bodies very vaguely resemble ''[[signet ring cell]]s'' -- but:
| | <pre> |
| **Cytoplasm eosinophilic and granular.
| | SKIN LESION, CHIN, BIOPSY: |
| **Nucleus usually smaller than in signet ring cell.
| | - BENIGN FIBROUS PAPULE. |
| **''Molluscum bodies'' are only the epidermis - an uncommon place to find SRCs without finding them elsewhere.
| | </pre> |
| *The granular eosinophilic cytoplasm represents accumulated virons.
| |
|
| |
|
| DDx:
| | ==Molluscum contagiosum== |
| *Nothing really - it is very distinctive.
| | {{Main|Molluscum contagiosum}} |
| | |
| Image(s):
| |
| *[http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Molluscum_contagiosum_high_mag.jpg Molluscum contagiosum - high mag. (WC)].
| |
| *[http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Molluscum_contagiosum_low_mag.jpg Molluscum contagiosum - low magnification (WC)].
| |
|
| |
|
| ==Superficial dermal infiltrates== | | ==Superficial dermal infiltrates== |
| Line 953: |
Line 397: |
|
| |
|
| ==Mastocytosis== | | ==Mastocytosis== |
| ===General===
| | {{Main|Mastocytosis}} |
| *Abundance of [[mast cell]]s.
| |
| | |
| Classification:<ref name=pmid21083038>{{Cite journal | last1 = Arock | first1 = M. | last2 = Valent | first2 = P. | title = Pathogenesis, classification and treatment of mastocytosis: state of the art in 2010 and future perspectives. | journal = Expert Rev Hematol | volume = 3 | issue = 4 | pages = 497-516 | month = Aug | year = 2010 | doi = 10.1586/ehm.10.42 | PMID = 21083038 }}</ref>
| |
| #Cutaneous (only) - usually children.
| |
| #*Urticaria pigmentosa.
| |
| #*Others.
| |
| #Systemic - usually adults.
| |
| #*Indolent subvariant.
| |
| #*Aggressive subvariant.
| |
| #*Leukemic subvariant.
| |
| | |
| ===Microscopic===
| |
| Features:<ref name=Ref_PBoD8|1185>{{Ref PBoD8|1185}}</ref>
| |
| *Cells in the superficial/mid dermis that are:
| |
| **Lymphocyte-like with more cytoplasm that is granular.
| |
| ***Cells may have spindled or stellate morphology.
| |
| ***Tend to be more abundant around vessels.
| |
| *+/-Eosinophils (common).
| |
| *+/-Edema - often prominent; gives cells a white halo.
| |
| | |
| Notes:
| |
| *Lymphocyte vs. mast cell:
| |
| **Lymphocytes = round; mast cells = ovoid.
| |
| | |
| Images:
| |
| *www:
| |
| **[http://www.jameswpattersonmd.com/case_studies/index.cfm?CFID=387434 Mastocytosis - low res. (jameswpattersonmd.com)].
| |
| **[http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case366.html Mastocytosis - bone marrow - several images (upmc.edu)].
| |
| *[[WC]]:
| |
| **[http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Mastocytosis_-_high_mag.jpg Mastocytosis - high mag. (WC)].
| |
| **[http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Mastocytosis_-_cropped_-_very_high_mag.jpg Mastocytosis - very high mag. (WC)].
| |
| **[http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case409.html Systemic mastocytosis - several images (upmc.edu)].
| |
| | |
| ===Stains===
| |
| *[[Toluidine blue stain|Toluidine blue]] -- highlights the granules.
| |
| | |
| ===IHC===
| |
| *CD117 +ve.
| |
| *Tryptase +ve.<ref name=pmid21866466>{{Cite journal | last1 = Rudzki | first1 = Z. | last2 = Sotlar | first2 = K. | last3 = Kudela | first3 = A. | last4 = Starzak-Gwóźdź | first4 = J. | last5 = Horny | first5 = HP. | title = Systemic mastocytosis (SM) and associated malignant bone marrow histiocytosis - a hitherto undescribed form of SM-AHNMD. | journal = Pol J Pathol | volume = 62 | issue = 2 | pages = 101-4 | month = | year = 2011 | doi = | PMID = 21866466 }}
| |
| </ref>
| |
|
| |
|
| ==Ichthyosis== | | ==Ichthyosis== |
| Line 1,011: |
Line 415: |
|
| |
|
| ==Palmar fibromatosis== | | ==Palmar fibromatosis== |
| {{Main|Fibromatosis}}
| |
| *[[AKA]] ''Dupuytren's contracture''. | | *[[AKA]] ''Dupuytren's contracture''. |
| *[[AKA]] ''Dupuytren disease''. | | *[[AKA]] ''Dupuytren disease''. |
| ===General===
| | {{Main|Palmar fibromatosis}} |
| Clinical:<ref>URL: [http://www.humpath.com/palmar-fibromatosis http://www.humpath.com/palmar-fibromatosis]. Accessed on: 6 January 2011.</ref>
| |
| *Usually older - 60s or 70s (years old).
| |
| *Male > female.
| |
| *Associated with:
| |
| **Alcohol abuse.
| |
| *May be familial.
| |
| | |
| ===Gross===
| |
| *Ring finger - classic location.{{fact}}
| |
| *Nodular.
| |
| *Poorly demarcated.
| |
| | |
| Image:
| |
| *[http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Morbus_dupuytren_fcm.jpg Palmar fibromatosis (WC)].
| |
| | |
| ===Microscopic===
| |
| Features:<ref>URL: [http://surgpathcriteria.stanford.edu/softfib/plantar_fibromatosis/printable.html http://surgpathcriteria.stanford.edu/softfib/plantar_fibromatosis/printable.html]. Accessed on: 6 January 2011.</ref><ref name=standford_pf_ddx>URL: [http://surgpathcriteria.stanford.edu/softfib/palmar_fibromatosis/differentialdiagnosis.html http://surgpathcriteria.stanford.edu/softfib/palmar_fibromatosis/differentialdiagnosis.html]. Accessed on: 9 November 2012.</ref>
| |
| *Poorly demarcated, usu. multiple lesions/multiple nodules.
| |
| *Composed of bland spindle cells in dense collagen.
| |
| **Pale grey cytoplasm (moderate quantity).
| |
| **Pale ovoid nuclei with small round nucleoli.
| |
| *Giant cells - rare.
| |
| | |
| Note:
| |
| *No nuclear atypia.
| |
| *Mitotic figures - rarely present, none atypical.
| |
| *May see Pacinian corpuscle.
| |
| | |
| DDx:<ref name=standford_pf_ddx>URL: [http://surgpathcriteria.stanford.edu/softfib/palmar_fibromatosis/differentialdiagnosis.html http://surgpathcriteria.stanford.edu/softfib/palmar_fibromatosis/differentialdiagnosis.html]. Accessed on: 9 November 2012.</ref>
| |
| *[[Calcifying aponeurotic fibroma]] - calcification, chondroid differentiation, usu. < 20 years old.
| |
| *Extra-abdominal desmoid [[fibromatosis]] - extremely rare on hands and feet, muscle infiltrative.
| |
| *Inclusion body [[fibromatosis]].
| |
| *[[Fibrosarcoma]] - atypia, necrosis, herring-bone pattern.
| |
| *[[Synovial sarcoma]] - one mass.
| |
| *[[Epithelioid sarcoma]] - necrosis, atypia.
| |
| *[[metastasis|Metastatic]] metaplastic carcinoma, e.g. [[metaplastic breast carcinoma]] - extremely uncommon.
| |
| | |
| Images:
| |
| *[http://www.biomedsearch.com/attachments/display/00/16/69/68/16696857/1479-5876-4-21-2.jpg Palmer fibromatosis (biomedsearch.com)].<ref name=pmid16696857>{{cite journal |author=Wang L, Zhu H |title=Clonal analysis of palmar fibromatosis: a study whether palmar fibromatosis is a real tumor |journal=J Transl Med |volume=4 |issue= |pages=21 |year=2006 |pmid=16696857 |pmc=1488873 |doi=10.1186/1479-5876-4-21 |url=http://www.biomedsearch.com/nih/Clonal-analysis-palmar-fibromatosis-study/16696857.html}}</ref>
| |
| *[http://alf3.urz.unibas.ch/pathopic/e/getpic-fra.cfm?id=8235 Palmar fibromatosis (unibas.ch)].
| |
| *[http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:WVSOM_Pacinian_Corpuscle.JPG Pacinian corpuscle (WC)].
| |
| | |
| ===IHC===
| |
| *Beta-catenin +ve (cytoplasmic & nuclear).<ref name=pmid18958538>{{Cite journal | last1 = Degreef | first1 = I. | last2 = De Smet | first2 = L. | last3 = Sciot | first3 = R. | last4 = Cassiman | first4 = JJ. | last5 = Tejpar | first5 = S. | title = Beta-catenin overexpression in Dupuytren's disease is unrelated to disease recurrence. | journal = Clin Orthop Relat Res | volume = 467 | issue = 3 | pages = 838-45 | month = Mar | year = 2009 | doi = 10.1007/s11999-008-0590-z | PMID = 18958538 }}</ref>
| |
| | |
| ===Sign out===
| |
| <pre>
| |
| PALMAR FASCIA, LEFT, FASCIECTOMY:
| |
| - PALMAR FIBROMATOSIS.
| |
| </pre>
| |
| | |
| ====Micro====
| |
| The sections show multiple poorly-demarcated nodules composed of bland spindle cells with moderate pale grey cytoplasm and pale ellipsoid nuclei with small round nucleoli. The poorly-demarcated nodules are completely surrounded by dense collagen. Calcification is not present. There is no nuclear atypia or necrosis. Mitotic activity is not identified.
| |
|
| |
|
| ==Angiomyoma== | | ==Angiomyoma== |
| Line 1,086: |
Line 436: |
|
| |
|
| ==Angiokeratoma== | | ==Angiokeratoma== |
| ===General===
| | {{Main|Angiokeratoma}} |
| *Rare.
| |
| *May be seen in the context of [[Fabry disease]].<ref name=pmid16403380/>
| |
| | |
| Notes:
| |
| *Shouldn't be confused with ''[[angiofibroma]]'' which is associated [[tuberous sclerosis]].
| |
| | |
| ===Microscopic===
| |
| Features:<ref name=pmid16403380>{{Cite journal | last1 = Karen | first1 = JK. | last2 = Hale | first2 = EK. | last3 = Ma | first3 = L. | title = Angiokeratoma corporis diffusum (Fabry disease). | journal = Dermatol Online J | volume = 11 | issue = 4 | pages = 8 | month = | year = 2005 | doi = | PMID = 16403380 }}</ref>
| |
| *Ectatic superficial dermal vessels.
| |
| *Overlying hyperkeratosis (thick stratum corneum).
| |
| | |
| Others features:{{fact}}
| |
| *Irregular acanthosis.
| |
| *Longer rete ridges.
| |
| | |
| DDx:
| |
| *[[Venous lake]].
| |
| | |
| Images:
| |
| *[[WC]]:
| |
| **[http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Angiokeratoma_-_low_mag.jpg Angiokeratoma - low mag. (WC)].
| |
| **[http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Angiokeratoma_-_intermed_mag.jpg Angiokeratoma - intermed. mag. (WC)].
| |
| *www:
| |
| **[http://www.pathologyoutlines.com/images/skintumorangiokerat1.jpg Angiokeratoma (pathologyoutlines.com)].
| |
|
| |
|
| ==Inverted follicular keratosis== | | ==Inverted follicular keratosis== |
| Line 1,138: |
Line 464: |
| *[http://www.flickr.com/photos/euthman/3059309003/ Inverted follicular keratosis - low mag. (flickr.com)]. | | *[http://www.flickr.com/photos/euthman/3059309003/ Inverted follicular keratosis - low mag. (flickr.com)]. |
| *[http://www.flickr.com/photos/euthman/3060145702/ Inverted follicular keratosis - high mag. (flickr.com)]. | | *[http://www.flickr.com/photos/euthman/3060145702/ Inverted follicular keratosis - high mag. (flickr.com)]. |
| | *[http://mckeedermpath.com/SPOT%20DIAGNOSIS%20CASE%20474.html Inverted follicular keratosis - several images (mckeedermpath.com)]. |
|
| |
|
| ===Sign out=== | | ===Sign out=== |
| Line 1,144: |
Line 471: |
| - INVERTED FOLLICULAR KERATOSIS. | | - INVERTED FOLLICULAR KERATOSIS. |
| </pre> | | </pre> |
| | |
| | ====Micro==== |
| | The sections show skin with acanthosis, pseudohorn cysts, and focal basal epidermal pigmentation. There is no basal nuclear atypia, no mitoses and there are no melanocytic nests. There is minimal dermal inflammation. There is no apparent solar elastosis. |
|
| |
|
| ==Focal cutaneous mucinosis== | | ==Focal cutaneous mucinosis== |
| Line 1,173: |
Line 503: |
| :'''''Not''' to be confused with [[nodular fasciitis]]''. | | :'''''Not''' to be confused with [[nodular fasciitis]]''. |
| *[[AKA]] ''flesh-eating disease''. | | *[[AKA]] ''flesh-eating disease''. |
| ===General===
| | {{Main|Necrotizing fasciitis}} |
| *High mortality.
| |
| *May be diagnosed at [[frozen section]].<ref name=pmid9386043>{{Cite journal | last1 = Majeski | first1 = J. | last2 = Majeski | first2 = E. | title = Necrotizing fasciitis: improved survival with early recognition by tissue biopsy and aggressive surgical treatment. | journal = South Med J | volume = 90 | issue = 11 | pages = 1065-8 | month = Nov | year = 1997 | doi = | PMID = 9386043 }}</ref>
| |
| *Classically associated with ''Group A streptococcus''.
| |
| | |
| Treatment:
| |
| *Operative debridement.
| |
| | |
| ===Microscopic===
| |
| Features:
| |
| *Necrosis of fascia - '''key feature'''.<ref name=pmid15735411>{{Cite journal | last1 = Wong | first1 = CH. | last2 = Wang | first2 = YS. | title = The diagnosis of necrotizing fasciitis. | journal = Curr Opin Infect Dis | volume = 18 | issue = 2 | pages = 101-6 | month = Apr | year = 2005 | doi = | PMID = 15735411 | URL = http://www.sepeap.org/archivos/pdf/9859.pdf }}</ref>
| |
| **[[PMN]]s and necrotic debris (amorphous grey or pink material).
| |
| | |
| Note:
| |
| *Fat lobules between septae may be normal.
| |
| | |
| DDx:
| |
| *[[Cellulitis]].
| |
| | |
| Images:
| |
| *[http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Necrotizing_fasciitis_-_intermed_mag.jpg Necrotizing fasciitis - intermed. mag. (WC)].
| |
| *[http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Necrotizing_fasciitis_-_high_mag.jpg Necrotizing fasciitis - high mag. (WC)].
| |
|
| |
|
| ==Porokeratosis== | | ==Porokeratosis== |
| ===General===
| | {{Main|Porokeratosis}} |
| *Genetic.
| |
| *Several subtypes.
| |
| | |
| Notes:
| |
| *Not the same as ''punctate porokeratotic keratoderma''.<ref name=pmid20137755>{{Cite journal | last1 = Alikhan | first1 = A. | last2 = Burns | first2 = T. | last3 = Zargari | first3 = O. | title = Punctate porokeratotic keratoderma. | journal = Dermatol Online J | volume = 16 | issue = 1 | pages = 13 | month = | year = 2010 | doi = | PMID = 20137755 | URL = http://dermatology.cdlib.org/1601/case_presentations/ppk/alikhan.html }}</ref>
| |
| | |
| ===Microscopic===
| |
| Features:
| |
| *Cornoid lamella (pathognomonic) - '''key feature''':
| |
| **Compact keratosis over a hair follicle.
| |
| *+/-Rete ridge loss.
| |
| | |
| Images:
| |
| *[[WC]]:
| |
| **[http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Porokeratosis_-_intermed_mag.jpg Porokeratosis - intermed. mag. (WC)].
| |
| **[http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Porokeratosis_-_very_high_mag.jpg Porokeratosis - very high mag. (WC)].
| |
|
| |
|
| ==Nevus sebaceous== | | ==Nevus sebaceous== |
| *[[AKA]] ''nevus sebaceous of Jadassohn''. | | *[[AKA]] ''nevus sebaceous of Jadassohn''. |
| ===General===
| | {{Main|Nevus sebaceous}} |
| *Congenital.
| |
| *Face or scalp.
| |
| | |
| ===Microscopic===
| |
| Features:
| |
| *Abundant sebaceous glands.
| |
|
| |
|
| ==Nevus lipomatosus superficialis== | | ==Nevus lipomatosus superficialis== |
| *Abbreviated ''NLS''. | | *Abbreviated ''NLS''. |
| ===General===
| | *[[AKA]] ''nevus lipomatosus cutaneous superficialis'', abbreviated ''NLCS''. |
| *Rare. | | *[[AKA]] ''nevus lipomatosus''.<ref name=pmid15677959>{{Cite journal | last1 = Kaw | first1 = P. | last2 = Carlson | first2 = A. | last3 = Meyer | first3 = DR. | title = Nevus lipomatosus (pedunculated lipofibroma) of the eyelid. | journal = Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg | volume = 21 | issue = 1 | pages = 74-6 | month = Jan | year = 2005 | doi = | PMID = 15677959 }}</ref> |
| *Congenital. | | {{Main|Nevus lipomatosus superficialis}} |
| *Usually lower trunk or gluteal region.<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Jones | first1 = EW. | last2 = Marks | first2 = R. | last3 = Pongsehirun | first3 = D. | title = Naevus superficialis lipomatosus. A clinicopathological report of twenty cases. | journal = Br J Dermatol | volume = 93 | issue = 2 | pages = 121-33 | month = Aug | year = 1975 | doi = | PMID = 1235780 }}</ref>
| |
| | |
| ===Microscopic===
| |
| Features:<ref name=pmid19495497>{{Cite journal | last1 = Yap | first1 = FB. | title = Nevus lipomatosus superficialis. | journal = Singapore Med J | volume = 50 | issue = 5 | pages = e161-2 | month = May | year = 2009 | doi = | PMID = 19495497 | URL = http://smj.sma.org.sg/5005/5005cr3.pdf }}</ref>
| |
| *Benign adipose tissue in the superficial dermis.
| |
| | |
| DDx:
| |
| *[[Lipoma]].
| |
| | |
| Image:
| |
| *[http://www.dermaamin.com/site/images/histo-pic/n/nevus-lipomatosus-superficialis/nevus-lipomatosus-superficialis1.jpg NLS (dermamin.com)].<ref>URL: [http://www.dermaamin.com/site/histopathology-of-the-skin/66-n/1971-nevus-lipomatosus-superficialis----.html http://www.dermaamin.com/site/histopathology-of-the-skin/66-n/1971-nevus-lipomatosus-superficialis----.html]. Accessed on: 7 March 2012.</ref>
| |
|
| |
|
| =Bullous disease= | | =Bullous disease= |