Difference between revisions of "Duodenum"
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
- SMALL BOWEL MUCOSA WITHIN NORMAL LIMITS. | - SMALL BOWEL MUCOSA WITHIN NORMAL LIMITS. | ||
- NEGATIVE FOR FINDINGS SUGGESTIVE OF CELIAC DISEASE. | - NEGATIVE FOR FINDINGS SUGGESTIVE OF CELIAC DISEASE. | ||
</pre> | |||
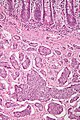
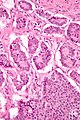
====Superficial Brunner's gland==== | |||
<pre> | |||
DUODENUM, BIOPSY: | |||
- SMALL BOWEL MUCOSA WITH BRUNNER'S GLANDS THAT ARE FOCALLY SUPERFICIAL. | |||
- NO FINDINGS SUGGESTIVE OF CELIAC DISEASE. | |||
- NEGATIVE FOR ACTIVE INFLAMMATION. | |||
- NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA. | |||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
Revision as of 12:58, 19 February 2014
The duodenum is the first part of the small bowel and receives food from the stomach. It is accessible by EGD (esophagogastroduodenoscopy) and frequently biopsied.
An introduction to gastrointestinal pathology is in the gastrointestinal pathology article.
The clinical history is often: r/o celiac or r/o giardia.
Getting started
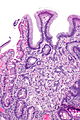
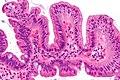
Normal duodenum
- Abbreviated ND.
General
- Very common.
Microscopic
- Three tall villi.
- Few intraepithelial lymphocytes; < 1 lymphocyte / 4 epithelial cells.
- No (pink) subepithelial collagen band.
- Predominant lamina propria cell: plasma cells.
- Lack of plasma cells suggests common variable immunodeficiency (CVID).[1]
- No organisms in lumen.
DDx:
- Intestinal metaplasia of the stomach - foveolar epithelium + other histologic components of the stomach.
- Chronic duodenitis - foveolar epithelium, Brunner's gland hyperplasia.
Sign out
DUODENUM, BIOPSY: - SMALL BOWEL MUCOSA AND BRUNNER'S GLANDS WITHIN NORMAL LIMITS.
DUODENUM, BIOPSY: - SMALL BOWEL MUCOSA WITHIN NORMAL LIMITS.
DUODENUM, BIOPSY: - SMALL BOWEL MUCOSA WITHIN NORMAL LIMITS. - NEGATIVE FOR FINDINGS SUGGESTIVE OF CELIAC DISEASE.
SMALL BOWEL (DUODENUM), BIOPSY: - SMALL BOWEL MUCOSA WITHIN NORMAL LIMITS. - NEGATIVE FOR FINDINGS SUGGESTIVE OF CELIAC DISEASE.
Superficial Brunner's gland
DUODENUM, BIOPSY: - SMALL BOWEL MUCOSA WITH BRUNNER'S GLANDS THAT ARE FOCALLY SUPERFICIAL. - NO FINDINGS SUGGESTIVE OF CELIAC DISEASE. - NEGATIVE FOR ACTIVE INFLAMMATION. - NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA.
Basic DDx
- Celiac sprue.
- Intraepithelial lymphocytes - key feature.
- Loss of villi.
- Giardia.
- Like celiac... but giardia organisms.
- Adenomas.
- Too much blue - similar to colonic adenomas.
- Cancer.
- Too much blue and epithelium in the wrong place.
More
- H. pylori only in areas of gastric metaplasia.[2]
Duodenal nodules DDX
| Duodenal nodule | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Benign (common) | Neoplastic | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Brunner's gland | Heterotopic gastric mucosa | Lymphoid nodule | Adenoma | NET | Paraganglioma | Prolapsed gastric polyp | Metastasis | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Infections of the duodenum[3]
Common:
Rare:
- Cryptosporidia.
- Microsporidia.
- Isospora belli.
- Cyclospora.
- MAC (Mycobacterium avium complex).
- CMV (cytomegalovirus).
- Cryptococcus neoformans.
Common stuffs
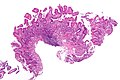
Gastric heterotopia of the duodenum
- AKA heterotopic gastric mucosa.
General
- Common ~15% of cases in one series.[4]
- Probably not related to Helicobacter pylori.[5]
Gross
- Typically nodules/polyps.[6]
Microscopic
Features:
- Foveolar epithelium.
- Gastric glands - body-type or antral-type.
DDx:
- Foveolar metaplasia (isolated) - see chronic duodenitis.
- Foveolar gastric-type dysplasia.[7]
Images
www:
Sign out
DUODENUM, BIOPSY: - SMALL BOWEL MUCOSA WITH GASTRIC (BODY-TYPE) HETEROTOPIA. - NEGATIVE FOR SIGNIFICANT PATHOLOGY.
Alternate
DUODENUM, BIOPSY: - SMALL BOWEL MUCOSA AND BRUNNER'S GLANDS WITHIN NORMAL LIMITS. - GASTRIC HETEROTOPIA, BODY-TYPE MUCOSA.
Celiac sprue
General
- Etiology: autoimmune.
Epidemiology
- Associated with:
- The skin condition dermatitis herpetiformis.[8]
- IgA deficiency - 10-15X more common in celiac disease vs. healthy controls.[9]
- Risk factor for gastrointestinal T cell lymphoma - known as: enteropathy-associated T cell lymphoma (EATL).
Clinical
Treatment:
- Gluten free diet.
- Mnemonic: BROW = barley, rye, oats, wheat.
Serologic testing:
- Anti-transglutaminase antibody.
- Alternative test: anti-endomysial antibody.
- IgA -- assoc. with celiac sprue.
Microscopic
Features:[10]
- Intraepithelial lymphocytes (IELs) - key feature.
- Loss of villi - important feature.
- Normal duodenal biopsy should have 3 good villi.
- Plasma cells - abundant (weak feature).
- Macrophages.
- Mitosis increased (in the crypts).
- +/-Collagen band (pink material in mucosa) - "Collagenous sprue"; must encompass ~25% of mucosa.
Image:
Notes:
- If you see acute inflammatory cells, i.e. neutrophils, consider Giardiasis and other infectious etiologies.
- Biopsy should consist of 2-3 sites. In children it is important to sample the duodenal cap, as it is the only affected site in ~10% of cases.
- Flat lesions without IELs are unlikely to be celiac sprue.
- Mucosa erosions are rare in celiac sprue; should prompt consideration of an alternate diagnosis (infection, medications, Crohn's disease).
Grading
Rarely done - see celiac sprue article.
Giardiasis
Acute duodenitis
- Abbreviated AD.
General
DDx:
- Infection.
- Helicobactor organisms in the stomach.
- Medications (NSAIDs).
- Crohn's disease (usually focal/patchy).
- Portal hypertension (portal hypertensive duodenopathy).[14]
- Celiac sprue.
Microscopic
Features:
- Intraepithelial lymphocytes.
- Neutrophils - "found without searching" - key feature.
- Eosinophils - "found without searching" - key feature.
- Plasma cells (increased).
Notes:
- One needs stomach concurrent biopsies to r/o Helicobactor.
- Erosions make celiac sprue much less likely.
- Presence of chronic inflammation useful for NSAIDs vs. Helicobacter organisms:
Sign out
DUODENUM, BIOPSY: - ACUTE DUODENITIS.
Acute on chronic duodenitis
DUODENUM, BIOPSY: - ACUTE ON CHRONIC DUODENITIS.
Micro
The sections show small bowel mucosa with intraepithelial neutrophils. The epithelium shows nuclear hyperchromasia, pseudostratification and nuclear enlargement; however, it matures toward the surface (reactive changes of the epithelium).
Brunner's glands are found focally in the lamina propria. Gastric foveolar-type epithelium is identified. Lamina propria plasma cells are abundant.
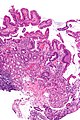
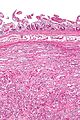
Chronic duodenitis
General
- This is not very well defined as plasma cells are present in a normal duodenum.
Gross
- Duodenal erythema.
Microscopic
Features:
- "Abundant" lamina propria plasma cells.
- Villous blunting.
- Brunner's gland hyperplasia.
DDx:
Sign out
DUODENUM, BIOPSY: - MODERATE NON-SPECIFIC CHRONIC DUODENTIS (SMALL BOWEL MUCOSA WITH VILLOUS BLUNTING, PROMINENT BRUNNER'S GLANDS, ABUNDANT LAMINA PROPRIA PLASMA CELLS AND OCCASIONAL INTRAEPITHELIAL LYMPHOCYTES, WITHOUT FOVEOLAR METAPLASIA). - NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA.
Peptic duodenitis
General
- A somewhat controversial type of chronic duodenitis.
- Considered to be a consequence of peptic ulcer disease (Helicobacter gastritis).
- One of the key components of the diagnosis is foveolar metaplasia and it is disputed that this is really due to Helicobacter.
- Genta et al. consider gastric foveolar metaplasia a congenital lesion.[5]
Microscopic
Features:[17]
- Gastric foveolar metaplasia - key feature.
- Brunner's gland hyperplasia.
- +/-Inflammation - neutrophils.[citation needed]
- Ulceration.[citation needed]
DDx:
- Chronic duodenitis not otherwise specified - no foveolar metaplasia, abundant plasma cells.
- Acute duodenitis.
- Brunner's gland hyperplasia.
- Gastric heterotopia of the duodenum.
Images
Stains
Foveolar metaplasia:
- PAS stain +ve.[17]
- Mucicarmine stain +ve.
Sign out
Foveolar metaplasia only
DUODENUM, BIOPSY: - SMALL BOWEL MUCOSA WITH FOCAL GASTRIC FOVEOLAR METAPLASIA. - BRUNNER'S GLANDS NOT IDENTIFIED. - VILLI AND INTRAEPITHELIAL LYMPHOCYTES WITHIN NORMAL LIMITS (NEGATIVE FOR CELIAC DISEASE). - NEGATIVE FOR ACUTE DUODENITIS. - NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA.
DUODENUM, BIOPSY: - SMALL BOWEL MUCOSA WITH FOCAL GASTRIC FOVEOLAR METAPLASIA. - BRUNNER'S GLANDS NOT IDENTIFIED. - NEGATIVE FOR ACUTE DUODENITIS. - NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA.
Chronic duodenitis
DUODENUM, BIOPSY: - SMALL BOWEL MUCOSA WITH BRUNNER'S GLAND IN THE LAMINA PROPRIA AND GASTRIC FOVEOLAR METAPLASIA -- CONSISTENT WITH CHRONIC DUODENITIS. - NEGATIVE FOR ACUTE DUODENITIS. - NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
DUODENUM, BIOPSY: - SMALL BOWEL MUCOSA WITH PROMINENT BRUNNER'S GLANDS AND FOCAL GASTRIC FOVEOLAR METAPLASIA. - NEGATIVE FOR ACUTE INFLAMMATION. - NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA.
Micro
The sections show small bowel mucosa and a small amount of submucosa. Brunner's glands are abundant and found focally in the lamina propria. Gastric foveolar-type epithelium is identified. Intraepithelial neutrophils are not identified.
The epithelium matures appropriately. There is no increase in intraepithelial lymphocytes.
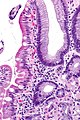
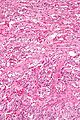
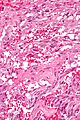
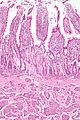
Brunner's gland hyperplasia
- Brunner's gland hamartoma redirects here.
General
- Benign.
- Usually asymptomatic.[19]
Note:
- The AFIP uses the term Brunner's gland hamartoma for lesions > 5 mm.[20]
- Multiple lesions less than 5 mm are hyperplasia.
Gross
- Nodularity of the duodenum.
Microscopic
Features:
- Prominent Brunner's gland.
- Tubular structures - formed by cells abundant cytoplasm that is clear with eosinophilic "cobwebs" and a round, small basal nucleus without a nucleolus.
- Brunner's glands close to the surface epithelium - key feature.[21]
- +/-Pancreatic acini and ducts.[20]
DDx:
- Foveolar metaplasia (isolated) - see peptic duodenitis.
- Peptic duodenitis.
Image:
Sign out
DUODENUM, BIOPSY: - CONSISTENT WITH BRUNNER'S GLAND HYPERPLASIA. - SMALL BOWEL MUCOSA WITHOUT SIGNIFICANT PATHOLOGY.
DUODENUM, BIOPSY: - SMALL BOWEL MUCOSA WITHOUT SIGNIFICANT PATHOLOGY. - PROMINENT BRUNNER'S GLANDS WITH EXTENSION INTO THE LAMINA PROPRIA.
Superficial Brunner's glands
DUODENUM, BIOPSY: - SMALL BOWEL MUCOSA WITH BRUNNER'S GLANDS THAT ARE FOCALLY SUPERFICIAL. - NO FINDINGS SUGGESTIVE OF CELIAC DISEASE. - NEGATIVE FOR ACTIVE INFLAMMATION. - NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA.
Micro
The sections show small bowel mucosa and a small amount of submucosa. Brunner's glands are abundant and found focally in the lamina propria.
The epithelium matures appropriately. There is no increase in intraepithelial lymphocytes. No foveolar metaplasia of the epithelium is identified.
Weird stuff
Disaccharidases deficiency
General
- Common among asians.
- Includes: lactase, sucrase, and maltase.
- Lactase changes seen with mild histomorphologic changes.[22]
- Maltase and sucrase only affected in moderate and severe lesions.
Microscopic
Features:[22]
- Decreased villous-crypt ratio (mild to severe).
- +/-Inflammation (only in moderate and severe).
DDx:
- Celiac disease.[23]
Notes:
- May have normal histomorphology.[22]
Whipple disease
Microvillous inclusion disease
This rare disease presents very shortly after birth.
Tufting enteropathy
- AKA intestinal epithelial dysplasia.
General
- Genetic disease[24] - related to abnormal enterocytes (development and/or differentiation).
- Gene implicated: EPCAM.[25]
Microscopic
Features:[26]
- Villous atrophy
- Mononuclear cell infiltration of the lamina propria
- Abnormal surface enterocytes:
- Focal crowding -- resembling tufts.
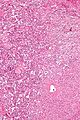
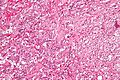
Gangliocytic paraganglioma
- Abbreviated GP.
General
- Extremely rare.[27]
- May be associated with neurofibromatosis type 1.[28]
- Classified a neuroendocrine tumour.[29]
- Usually has a mix of the features seen in: neuroendocrine tumours, paragangliomas and ganglioneuromas.
Clinical - presentation:[30]
- GI bleed ~ 45% of cases.
- Abdominal pain ~ 43% of cases.
- Anemia ~ 15% of cases.
Gross
- Classically in the duodenum ~90% of cases.[30]
Microscopic
Features - three components:[31][32]
- Ganglion cells = large cells with:
- Round large nucleus.
- Prominent nucleolus.
- Moderate or abundant cytoplasm.
- Epithelioid cells (neuroendocrine component):
- Arranged in nests or cords.
- Stippled chromatin.
- Spindle cells (schwannian component):
- Moderate or abundant cytoplasm.
- Nucleus spindle-shaped or ellipsoid.
DDx:[31]
- Poorly differentiated carcinoma.
- Neuroendocrine tumour.
- Paraganglioma.
Images
www:
- Epithelioid cells of a GP (wjso.com).
- Ganglion cell in a GP (wjso.com).
- Ganglion cells in a GP (pubcan.org).[33]
- GP (surgicalpathologyatlas.com).
IHC
- Synaptophysin +ve.
- CD56 +ve.
- Chromogranin A +ve.
- HU +ve in ganglion-like cells.
- S100 +ve in spindle cells & sustentacular cells.
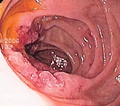
Pseudomelanosis duodeni
General
- Rare.
- Consists of iron and lipofuscin.[34]
Associations:[35]
- Hypertension ~90% of cases.
- Iron supplementation ~75% of cases.
- End-stage renal disease ~60% of cases.
Note:
- The associations are different than for melanosis coli.
Gross/endoscopic
- Dark spots ~35% of cases.[35]
Microscopic
Features:
- Dark pigment in the lamina propria macrophages.
Images:
Stains
- Prussian blue +ve ~80% of cases.[35]
Tumours
Lymphoma
- Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma.
- Enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma (EATL) - due to celiac sprue.
- MALT lymphoma - common GI tract lymphoma.
- Mantle cell lymphoma.
- Diffuse large B cell lymphoma.
Note:
- Hodgkin's lymphoma does not arise in the GI tract.
Adenocarcinoma of the duodenum
General
- Duodenum - most common site in small bowel.
- Ampulla of Vater most common site in the duodenum - see ampullary carcinoma.
Risk factors:
Gross
- Mass ulcerating or exophytic.
Image:
Microscopic
Features:
- Similar to large bowel adenocarcinomas - see colorectal tumours article.
DDx:
IHC
- SMAD4 -ve/+ve.[36]
Duodenal neuroendocrine tumour
General
- Like neuroendocrine tumours elsewhere.
- Use of the term carcinoid is discouraged.[37][38][39]
Associations:
Microscopic
Features:[40]
- Usu. nests of cells - may be:
- Trabecular.
- Glandular - common in stomatostatin producing tumours.
- Stippled chromatin - (AKA salt-and-pepper chromatin, coarse chromatin).
- Classically subepithelial/mural.
- +/-Psammoma bodies - suggestive of somatostatinoma and NF1.[41]
DDx:
Images
Ampullary tumours
General
- Individuals with high-grade dysplasia (on biopsy) are usually treated with a pancreaticoduodenectomy (Whipple procedure), as local resections have a very high recurrence rate.[42]
Microscopic
Features:
- See ampullary tumours.
DDx:
- Intraductal papillary mucinous tumour (IPMT) - a pancreatic tumour, see pancreas article.
- Invasive ductal carcinoma of the pancreas.
Sign out
- Ampullary carcinoma - has separate staging.
Traditional adenoma
- Duodenal adenoma redirects here.
General
- Strong association of familial adenomatous polyposis.
- In one series of 208 adenomas, almost 70% were from FAP patients.[43]
- Commonly found in association foveolar metaplasia - especially in sporadic cases ~60% of cases.
- In FAP ~30% of cases have foveolar metaplasia.[43]
Sign out
POLYP, DUODENUM, EXCISION: - TUBULAR ADENOMA. -- NEGATIVE FOR HIGH-GRADE DYSPLASIA.
See also
References
- ↑ Agarwal S, Smereka P, Harpaz N, Cunningham-Rundles C, Mayer L (July 2010). "Characterization of immunologic defects in patients with common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) with intestinal disease". Inflamm Bowel Dis. doi:10.1002/ibd.21376. PMID 20629103.
- ↑ El-Zimaity. 18 October 2010.
- ↑ Serra S, Jani PA (November 2006). "An approach to duodenal biopsies". J. Clin. Pathol. 59 (11): 1133–50. doi:10.1136/jcp.2005.031260. PMC 1860495. PMID 16679353. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1860495/?tool=pubmed.
- ↑ Jump up to: 4.0 4.1 Terada, T. (2012). "Pathologic observations of the duodenum in 615 consecutive duodenal specimens: I. benign lesions.". Int J Clin Exp Pathol 5 (1): 46-51. PMID 22295146.
- ↑ Jump up to: 5.0 5.1 Genta, RM.; Kinsey, RS.; Singhal, A.; Suterwala, S. (Nov 2010). "Gastric foveolar metaplasia and gastric heterotopia in the duodenum: no evidence of an etiologic role for Helicobacter pylori.". Hum Pathol 41 (11): 1593-600. doi:10.1016/j.humpath.2010.04.010. PMID 20656325.
- ↑ Shousha, S.; Spiller, RC.; Parkins, RA. (Jan 1983). "The endoscopically abnormal duodenum in patients with dyspepsia: biopsy findings in 60 cases.". Histopathology 7 (1): 23-34. PMID 6840712.
- ↑ Park, do Y.; Srivastava, A.; Kim, GH.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Deshpande, V.; Zukerberg, LR.; Song, GA.; Lauwers, GY. (Apr 2008). "Adenomatous and foveolar gastric dysplasia: distinct patterns of mucin expression and background intestinal metaplasia.". Am J Surg Pathol 32 (4): 524-33. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e31815b890e. PMID 18300795.
- ↑ TN 2007 D22
- ↑ Kumar, V.; Jarzabek-Chorzelska, M.; Sulej, J.; Karnewska, K.; Farrell, T.; Jablonska, S. (Nov 2002). "Celiac disease and immunoglobulin a deficiency: how effective are the serological methods of diagnosis?". Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 9 (6): 1295-300. PMID 12414763.
- ↑ Cotran, Ramzi S.; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Nelso Fausto; Robbins, Stanley L.; Abbas, Abul K. (2005). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (7th ed.). St. Louis, Mo: Elsevier Saunders. pp. 843. ISBN 0-7216-0187-1.
- ↑ Biagi F, Luinetti O, Campanella J, et al. (August 2004). "Intraepithelial lymphocytes in the villous tip: do they indicate potential coeliac disease?". J. Clin. Pathol. 57 (8): 835–9. doi:10.1136/jcp.2003.013607. PMC 1770380. PMID 15280404. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1770380/.
- ↑ Oberhuber G, Granditsch G, Vogelsang H (October 1999). "The histopathology of coeliac disease: time for a standardized report scheme for pathologists". Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 11 (10): 1185–94. PMID 10524652.
- ↑ Corazza GR, Villanacci V, Zambelli C, et al. (July 2007). "Comparison of the interobserver reproducibility with different histologic criteria used in celiac disease". Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 5 (7): 838–43. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2007.03.019. PMID 17544877.
- ↑ Shudo, R.; Yazaki, Y.; Sakurai, S.; Uenishi, H.; Yamada, H.; Sugawara, K. (Apr 2002). "Duodenal erosions, a common and distinctive feature of portal hypertensive duodenopathy.". Am J Gastroenterol 97 (4): 867-73. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.2002.05602.x. PMID 12003421.
- ↑ Taha AS, Dahill S, Nakshabendi I, Lee FD, Sturrock RD, Russell RI (September 1993). "Duodenal histology, ulceration, and Helicobacter pylori in the presence or absence of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs". Gut 34 (9): 1162–6. PMC 1375446. PMID 8406146. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1375446/.
- ↑ Hashash JG, Atweh LA, Saliba T, et al. (November 2007). "Acute NSAID-related transmural duodenitis and extensive duodenal ulceration". Clin Ther 29 (11): 2448–52. doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2007.11.012. PMID 18158085.
- ↑ Jump up to: 17.0 17.1 Iacobuzio-Donahue, Christine A.; Montgomery, Elizabeth A. (2005). Gastrointestinal and Liver Pathology: A Volume in the Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 145. ISBN 978-0443066573.
- ↑ Tan, YM.; Wong, WK. (2002). "Giant Brunneroma as an unusual cause of upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage: report of a case.". Surg Today 32 (10): 910-2. doi:10.1007/s005950200179. PMID 12376792.
- ↑ Jump up to: 19.0 19.1 Lee, WC.; Yang, HW.; Lee, YJ.; Jung, SH.; Choi, GY.; Go, H.; Kim, A.; Cha, SW. (Jun 2008). "Brunner's gland hyperplasia: treatment of severe diffuse nodular hyperplasia mimicking a malignancy on pancreatic-duodenal area.". J Korean Med Sci 23 (3): 540-3. doi:10.3346/jkms.2008.23.3.540. PMID 18583897.
- ↑ Jump up to: 20.0 20.1 20.2 Patel, ND.; Levy, AD.; Mehrotra, AK.; Sobin, LH. (Sep 2006). "Brunner's gland hyperplasia and hamartoma: imaging features with clinicopathologic correlation.". AJR Am J Roentgenol 187 (3): 715-22. doi:10.2214/AJR.05.0564. PMID 16928936.
- ↑ Franzin, G.; Musola, R.; Ghidini, O.; Manfrini, C.; Fratton, A. (Dec 1985). "Nodular hyperplasia of Brunner's glands.". Gastrointest Endosc 31 (6): 374-8. PMID 4076734.
- ↑ Jump up to: 22.0 22.1 22.2 Langman JM, Rowland R (July 1990). "Activity of duodenal disaccharidases in relation to normal and abnormal mucosal morphology". J. Clin. Pathol. 43 (7): 537–40. PMC 502575. PMID 2116456. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC502575/.
- ↑ Murray IA, Smith JA, Coupland K, Ansell ID, Long RG (February 2001). "Intestinal disaccharidase deficiency without villous atrophy may represent early celiac disease". Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 36 (2): 163–8. PMID 11252408.
- ↑ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 613217
- ↑ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 185535
- ↑ Goulet O, Salomon J, Ruemmele F, de Serres NP, Brousse N (2007). "Intestinal epithelial dysplasia (tufting enteropathy)". Orphanet J Rare Dis 2: 20. doi:10.1186/1750-1172-2-20. PMC 1878471. PMID 17448233. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1878471/.
- ↑ Wu, GC.; Wang, KL.; Zhang, ZT. (Jan 2012). "Gangliocytic paraganglioma of the duodenum: a case report.". Chin Med J (Engl) 125 (2): 388-9. PMID 22340577.
- ↑ Castoldi, L.; De Rai, P.; Marini, A.; Ferrero, S.; De Luca, V.; Tiberio, G. (2001). "Neurofibromatosis-1 and Ampullary Gangliocytic Paraganglioma Causing Biliary and Pancreatic Obstruction.". Int J Gastrointest Cancer 29 (2): 93-98. PMID 12754392.
- ↑ URL: http://www.cap.org/apps/docs/committees/cancer/cancer_protocols/2011/SmallbowelNET_11protocol.pdf. Accessed on: 29 March 2012.
- ↑ Jump up to: 30.0 30.1 Okubo, Y.; Wakayama, M.; Nemoto, T.; Kitahara, K.; Nakayama, H.; Shibuya, K.; Yokose, T.; Yamada, M. et al. (2011). "Literature survey on epidemiology and pathology of gangliocytic paraganglioma.". BMC Cancer 11: 187. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-11-187. PMID 21599949.
- ↑ Jump up to: 31.0 31.1 Wong, A.; Miller, AR.; Metter, J.; Thomas, CR. (Mar 2005). "Locally advanced duodenal gangliocytic paraganglioma treated with adjuvant radiation therapy: case report and review of the literature.". World J Surg Oncol 3 (1): 15. doi:10.1186/1477-7819-3-15. PMID 15740625.
- ↑ URL: http://surgpathcriteria.stanford.edu/gitumors/gangliocytic-paraganglioma/printable.html. Accessed on: 31 May 2012.
- ↑ URL: http://www.pubcan.org/printicdotopo.php?id=5028. Accessed on: 15 April 2012.
- ↑ Lin, HJ.; Tsay, SH.; Chiang, H.; Tsai, YT.; Lee, SD.; Yeh, YS.; Lo, GH. (Apr 1988). "Pseudomelanosis duodeni. Case report and review of literature.". J Clin Gastroenterol 10 (2): 155-9. PMID 2458404.
- ↑ Jump up to: 35.0 35.1 35.2 Giusto, D.; Jakate, S. (Feb 2008). "Pseudomelanosis duodeni: associated with multiple clinical conditions and unpredictable iron stainability - a case series.". Endoscopy 40 (2): 165-7. doi:10.1055/s-2007-995472. PMID 18253910.
- ↑ Bläker, H.; Aulmann, S.; Helmchen, B.; Otto, HF.; Rieker, RJ.; Penzel, R. (2004). "Loss of SMAD4 function in small intestinal adenocarcinomas: comparison of genetic and immunohistochemical findings.". Pathol Res Pract 200 (1): 1-7. PMID 15157044.
- ↑ Chetty, R. (Apr 2008). "Requiem for the term 'carcinoid tumour' in the gastrointestinal tract?". Can J Gastroenterol 22 (4): 357-8. PMID 18414708.
- ↑ Klöppel, G.; Perren, A.; Heitz, PU. (Apr 2004). "The gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine cell system and its tumors: the WHO classification.". Ann N Y Acad Sci 1014: 13-27. PMID 15153416.
- ↑ Klöppel G (July 2003). "[Neuroendocrine tumors of the gastrointestinal tract]" (in German). Pathologe 24 (4): 287–96. doi:10.1007/s00292-003-0636-7. PMID 14513276.
- ↑ URL: http://www.cap.org/apps/docs/committees/cancer/cancer_protocols/2011/SmallbowelNET_11protocol.pdf. Accessed on: 29 March 2012.
- ↑ Kim, JA.; Choi, WH.; Kim, CN.; Moon, YS.; Chang, SH.; Lee, HR. (Mar 2011). "Duodenal somatostatinoma: a case report and review.". Korean J Intern Med 26 (1): 103-7. doi:10.3904/kjim.2011.26.1.103. PMID 21437171.
- ↑ Meneghetti, AT.; Safadi, B.; Stewart, L.; Way, LW. (Dec 2005). "Local resection of ampullary tumors.". J Gastrointest Surg 9 (9): 1300-6. doi:10.1016/j.gassur.2005.08.031. PMID 16332486.
- ↑ Jump up to: 43.0 43.1 Rubio, CA. (Jun 2007). "Gastric duodenal metaplasia in duodenal adenomas.". J Clin Pathol 60 (6): 661-3. doi:10.1136/jcp.2006.039388. PMC 1955048. PMID 16837629. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1955048/.
External links
Review article(s)
- Serra S, Jani PA (November 2006). "An approach to duodenal biopsies". J. Clin. Pathol. 59 (11): 1133–50. doi:10.1136/jcp.2005.031260. PMC 1860495. PMID 16679353. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1860495/?tool=pubmed.