Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis
(Redirected from XGP)
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
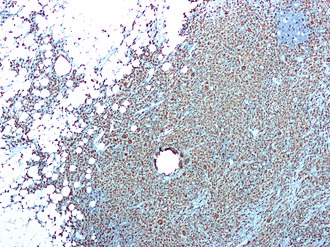 Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis. CD68 immunostain. | |
|
| |
| LM | abundant (foamy) macrophages (associated with the collecting system - medulla, not cortex), +/-giant cells, +/-cholesterol clefts, +/-interstitial lymphocytes and plasma cells, +/-interstitial fibrosis, +/-calcifications |
| LM DDx | malakoplakia, RCC - especially PRCC, granulomatous disease, chronic pyelonephritis, interstitial nephritis, occasionally renal cell carcinoma |
| Stains | PAS-D -ve |
| IHC | CD68 +ve, CD10 -ve, pankeratin -ve |
| Site | kidney - see kidney tumours |
|
| |
| Associated Dx | diabetes mellitus, history of UTI, nephrolithiasis, GU obstruction (various causes) |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
| Radiology | dilated upper GU system |
| Clin. DDx | renal cell carcinoma, pyelonephritis |
| Treatment | antibiotics, occasionally nephrectomy |
Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis, abbreviated XGP, is an inflammatory process of the kidney that can mimic renal cell carcinoma.
General
- May mimic renal cell carcinoma - especially radiologically.
- Usually lower pole.[citation needed]
- Associated with:
- Diabetes mellitus.
- History of urinary tract infection.[1]
- Nephrolithiasis.
- GU obstruction.[2]
- Occasionally an indication for nephrectomy.[1][2]
- Most common organism (in the context of nephrectomy specimens) - Proteus mirabilis.[2]
Microscopic
Features:
- Abundant (foamy) macrophages.
- Associated with the collecting system - medulla, not cortex.
- +/-Giant cells.
- +/-Interstitial lymphocytes and plasma cells.
- +/-Interstitial fibrosis.
- +/-Cholesterol clefts (common).
- +/-Calcifications - dystrophic.
DDx:
- Malakoplakia.
- Basophilic inclusions -- inside or outside of macrophages - often size of RBC or larger (Michaelis-Gutmann bodies).
- Renal cell carcinoma - especially papillary RCC (as this has foamy macrophages).
- Granulomatous disease.
- Chronic pyelonephritis.
- Interstitial nephritis.
- Renal cell carcinoma - foamy macrophages may be abundant.[3]
Images
www:
Stains
- PAS-D -ve.
- Done to look for malakoplakia.
IHC
- CD68 +ve.
- RCC markers (CD10, RCC) all negative.
Sign out
RIGHT KIDNEY, NEPHRECTOMY: - XANTHOGRANULOMATOUS PYELONEPHRITIS. - CHRONIC INTERSTITIAL NEPHRITIS. - INCREASED NUMBERS OF TOTALLY SCLEROSED GLOMERULI AND GLOMERULI WITH FOCAL SCLEROSIS. - MARKED INTERSTITIAL FIBROSIS. - NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY. COMMENT: Immunostaining demonstrates abundant CD68 positive cells (macrophages). A CD10 immunostain is non-concerning (it highlights glomeruli). A pankeratin immunostain is non-concerning (it highlights benign renal tubules).
Compatible XGP
"KIDNEY" LESION, LEFT, BIOPSY: - FIBROMUSCULAR TISSUE WITH A MIXED INFLAMMATORY INFILTRATE. - CELLULAR DEBRIS WITH SURROUNDING LOOSELY AGGREGATED HISTIOCYTES. - NO RENAL PARENCHYMA IDENTIFIED. - NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY. COMMENT: A SMA immunostain highlights the muscle component, and a CD68 immunostain marks abundant histiocytes. No epithelial component is identified with a pankeratin immunostain.
Micro
The sections show degenerative renal parenchyma with surrounding histiocytes, other inflammatory cells, fibrosis and cholesterol clefts.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Afgan F, Mumtaz S, Ather MH (2007). "Preoperative diagnosis of xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis". Urol J 4 (3): 169–73. PMID 17987581.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Al-Ghazo MA, Ghalayini IF, Matalka II, Al-Kaisi NS, Khader YS (October 2006). "Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis: Analysis of 18 cases". Asian J Surg 29 (4): 257–61. PMID 17098659.
- ↑ Iskandar, SS.; Prahlow, JA.; White, WL. (Jun 1993). "Lipid-laden foamy macrophages in renal cell carcinoma. Potential frozen section diagnostic pitfall.". Pathol Res Pract 189 (5): 549-52. doi:10.1016/S0344-0338(11)80364-X. PMID 8378177.
- ↑ Li, L.; Parwani, AV. (May 2011). "Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis.". Arch Pathol Lab Med 135 (5): 671-4. doi:10.1043/2009-0769-RSR.1. PMID 21526966.
