Difference between revisions of "Eosinophilic colitis"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m |
m (→Microscopic) |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ Infobox diagnosis | |||
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | |||
| Image = Eosinophilic_colitis_-_alt_--_high_mag.jpg | |||
| Width = | |||
| Caption = Eosinophilic colitis. [[H&E stain]]. | |||
| Synonyms = | |||
| Micro = abundant eosinophils - no agreed upon number - "most use 20/HPF", there is variation along the large bowel - normal in rectum <10/HPF, normal in cecum <30/HPF | |||
| Subtypes = | |||
| LMDDx = | |||
| Stains = | |||
| IHC = | |||
| EM = | |||
| Molecular = | |||
| IF = | |||
| Gross = | |||
| Grossing = | |||
| Site = [[colon]] | |||
| Assdx = | |||
| Syndromes = | |||
| Clinicalhx = | |||
| Signs = | |||
| Symptoms = | |||
| Prevalence = | |||
| Bloodwork = +/-eosinophilia | |||
| Rads = | |||
| Endoscopy = | |||
| Prognosis = | |||
| Other = | |||
| ClinDDx = | |||
| Tx = dependent on underlying cause | |||
}} | |||
'''Eosinophilic colitis''', abbreviated '''EC''', is an inflammatory process involving the [[colon]] ([[colitis]]) characterized by abundant [[eosinophil]]s. | '''Eosinophilic colitis''', abbreviated '''EC''', is an inflammatory process involving the [[colon]] ([[colitis]]) characterized by abundant [[eosinophil]]s. | ||
'''Eosinophilic proctitis''' redirects to this article, as the histology is quite similar. | |||
==General== | ==General== | ||
| Line 20: | Line 53: | ||
**"Most use 20/[[HPF]]" <ref name=pmid19554649>{{Cite journal | last1 = Okpara | first1 = N. | last2 = Aswad | first2 = B. | last3 = Baffy | first3 = G. | title = Eosinophilic colitis. | journal = World J Gastroenterol | volume = 15 | issue = 24 | pages = 2975-9 | month = Jun | year = 2009 | doi = | PMID = 19554649 | PMC = 2702104 }}</ref> - a definition that suffers from [[HPFitis]]. | **"Most use 20/[[HPF]]" <ref name=pmid19554649>{{Cite journal | last1 = Okpara | first1 = N. | last2 = Aswad | first2 = B. | last3 = Baffy | first3 = G. | title = Eosinophilic colitis. | journal = World J Gastroenterol | volume = 15 | issue = 24 | pages = 2975-9 | month = Jun | year = 2009 | doi = | PMID = 19554649 | PMC = 2702104 }}</ref> - a definition that suffers from [[HPFitis]]. | ||
***There is variation along the large bowel - normal in rectum <10/HPF, normal in cecum <30/HPF.<ref name=pmid19554649/> | ***There is variation along the large bowel - normal in rectum <10/HPF, normal in cecum <30/HPF.<ref name=pmid19554649/> | ||
*+/-Eosinophilic crytitis.<ref name=pmid24278727>{{Cite journal | last1 = Bates | first1 = AW. | title = Diagnosing eosinophilic colitis: histopathological pattern or nosological entity? | journal = Scientifica (Cairo) | volume = 2012 | issue = | pages = 682576 | month = | year = 2012 | doi = 10.6064/2012/682576 | PMID = 24278727 }}</ref> | |||
DDx:<ref name=pmid22012125/> | DDx:<ref name=pmid22012125/> | ||
| Line 30: | Line 64: | ||
*Autoimmune disease: | *Autoimmune disease: | ||
**[[Scleroderma]]. | **[[Scleroderma]]. | ||
**[[Churg-Strauss syndrome | **[[Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis]] (Churg-Strauss syndrome). | ||
**[[Celiac disease]]. | **[[Celiac disease]]. | ||
*[[Drug reaction]]s. | *[[Drug reaction]]s. | ||
===Images=== | |||
*[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2702104/figure/F1/ EC (nih.gov)].<ref name=pmid19554649>{{Cite journal | last1 = Okpara | first1 = N. | last2 = Aswad | first2 = B. | last3 = Baffy | first3 = G. | title = Eosinophilic colitis. | journal = World J Gastroenterol | volume = 15 | issue = 24 | pages = 2975-9 | month = Jun | year = 2009 | doi = | PMID = 19554649 | PMC = 2702104 }}</ref> | www: | ||
*[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2702104/figure/F1/ EC (nih.gov)].<ref name=pmid19554649>{{Cite journal | last1 = Okpara | first1 = N. | last2 = Aswad | first2 = B. | last3 = Baffy | first3 = G. | title = Eosinophilic colitis. | journal = World J Gastroenterol | volume = 15 | issue = 24 | pages = 2975-9 | month = Jun | year = 2009 | doi = | PMID = 19554649 | PMC = 2702104 }}</ref> | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image: Eosinophilic colitis -- intermed mag.jpg | EC - intermed. mag. (WC) | |||
Image: Eosinophilic colitis -- high mag.jpg | EC - high mag. (WC) | |||
Image: Eosinophilic colitis - alt -- high mag.jpg | EC - high mag. (WC) | |||
Image: Eosinophilic colitis -- very high mag.jpg | EC - very high mag. (WC) | |||
Image: Eosinophilic colitis - alt -- very high mag.jpg | EC - very high mag. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
==Sign out== | ==Sign out== | ||
Latest revision as of 21:47, 28 November 2016
Eosinophilic colitis, abbreviated EC, is an inflammatory process involving the colon (colitis) characterized by abundant eosinophils.
| Eosinophilic colitis | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
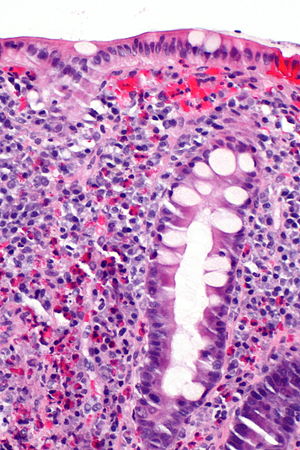 Eosinophilic colitis. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | abundant eosinophils - no agreed upon number - "most use 20/HPF", there is variation along the large bowel - normal in rectum <10/HPF, normal in cecum <30/HPF |
| Site | colon |
|
| |
| Blood work | +/-eosinophilia |
| Treatment | dependent on underlying cause |
Eosinophilic proctitis redirects to this article, as the histology is quite similar.
General
- Rare.
- May be a component of eosinophilic gastroenteritis.[1]
Clinical features:[1]
- Abdominal pain
- Diarrhea +/-blood.
- +/-Weight loss.
Gross
Features - endoscopic:[1]
- Edema.
- Granular appearance.
Microscopic
Features:[1]
- Abundant eosinophils - no agreed upon number.
- +/-Eosinophilic crytitis.[3]
DDx:[1]
- Inflammatory bowel disease:
- Infection:
- Autoimmune disease:
- Scleroderma.
- Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Churg-Strauss syndrome).
- Celiac disease.
- Drug reactions.
Images
www:
Sign out
DESCENDING COLON, BIOPSY: - COLONIC MUCOSA WITH MILD EOSINOPHILIA, SEE COMMENT. - NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA. COMMENT: Focally, there are up to 40 eosinophils / 0.2376 mm*mm (approx. field area at 400X). This is a non-specific finding. No eosinophilic crypt abscesses are seen. No (neutrophilic) cryptitis is present. Clinical correlation is suggested.
DESCENDING COLON, BIOPSY: - COLONIC MUCOSA WITH MILD EOSINOPHILIA, SEE COMMENT. - NEGATIVE FOR ACTIVE COLITIS. - NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA. COMMENT: There are up to 40 eosinophils / 0.2376 mm*mm (field area at 400X). This is a non-specific finding. The differential diagnosis includes inflammatory bowel disease, infection (especially helminths), a drug reaction, and autoimmune disorders (e.g. Churg-Strauss syndrome, celiac disease, scleroderma). Clinical correlation is required.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Alfadda, AA.; Storr, MA.; Shaffer, EA. (2011). "Eosinophilic colitis: an update on pathophysiology and treatment.". Br Med Bull 100: 59-72. doi:10.1093/bmb/ldr045. PMC 3165205. PMID 22012125. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3165205/.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Okpara, N.; Aswad, B.; Baffy, G. (Jun 2009). "Eosinophilic colitis.". World J Gastroenterol 15 (24): 2975-9. PMC 2702104. PMID 19554649. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2702104/.
- ↑ Bates, AW. (2012). "Diagnosing eosinophilic colitis: histopathological pattern or nosological entity?". Scientifica (Cairo) 2012: 682576. doi:10.6064/2012/682576. PMID 24278727.