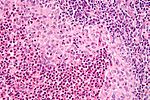
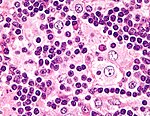
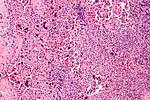
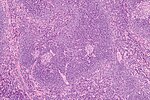
Difference between revisions of "Lymph node pathology"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (Castleman) |
(→Reactive follicular hyperplasia: split out) |
||
| (207 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
This article deals with '''lymph node pathology'''. An introduction to the lymph node is in the ''[[lymph nodes]]'' article. | This article deals with non-haematologic malignant, i.e. metastases, and non-malignant '''lymph node pathology'''. An introduction to the lymph node is in the ''[[lymph nodes]]'' article. | ||
==Kikuchi disease== | Haematologic malignancies (in lymph nodes) are dealt with in other articles - see ''[[haematopathology]]'' and ''[[lymphoma]]''. | ||
==Overview== | |||
Clinical: | |||
*Lymphadenopathy. | |||
Differential diagnosis:<ref>URL: [http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case289.html http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case289.html]. Accessed on: 14 January 2012.</ref> | |||
*Infectious - fungal, mycobacterial, viral, protozoal (Toxoplasma), bacterial (Chlamydia, Rickettsia, Bartonella)). | |||
*Neoplastic - lymphoma, carcinoma. | |||
*Endocrine - [[hyperthyroidism]]. | |||
*Trauma. | |||
*Autoimmune - [[SLE]], [[RA]], [[dermatomyositis]]. | |||
*Inflammatory - drugs (phenytoin). | |||
*Idiopathic - [[sarcoidosis]]. | |||
==Overview in a table== | |||
{| class="wikitable sortable" | |||
! Entity | |||
! Key feature | |||
! Other findings | |||
! IHC | |||
! DDx | |||
! Image | |||
|- | |||
| Non-specific reactive follicular hyperplasia (NSRFH) | |||
| large spaced cortical follicles | |||
| tingible body macrophages, normal dark/light GC pattern | |||
| BCL2 -ve | |||
| infection ([[Toxoplasmosis]], [[HIV]]/AIDS), [[Hodgkin's lymphoma]] | |||
| image ? | |||
|- | |||
| [[Lymph node metastasis]] | |||
| foreign cell population, usu. in subcapsular sinuses | |||
| +/-nuclear atypia, +/-malignant architecture | |||
| dependent on tumour type (see ''[[IHC]]'') | |||
| dependent on morphology, [[endometriosis]] (mimics adenocarcinoma), ectopic decidua (mimics [[SCC]]) | |||
| [[Image:Crc_met_to_node1.jpg|thumb|center|125px| CRC metastasis]] [[Image:Breast_carcinoma_in_a_lymph_node.jpg|thumb|center|125px | Breast metastasis]] | |||
|- | |||
| [[Progressive transformation of germinal centers]] | |||
| large (atypical) germinal centers | |||
| poorly demarcated germinal center (GC)/mantle zone interfaces, expanded mantle zone | |||
| IHC to r/o ''nodular lymphocyte predominant [[Hodgkin lymphoma]]'' (NLPHL) | |||
| NLPHL, follicular hyperplasia | |||
| [[Image:Progressive transformation_of_germinal_centres_-1-_very_low_mag.jpg|thumb|center|150px | PTGC - very low mag.]] | |||
|- | |||
| [[Toxoplasmosis]] | |||
| large follicles; epithelioid cells perifollicular & intrafollicular | |||
| reactive GCs, monocytoid cell clusters, epithelioid cells | |||
| IHC for toxoplasma | |||
| NSRFH, HIV/AIDS, [[Hodgkin's lymphoma]] | |||
| [[Image:Toxoplasmosis_lymphadenopathy_-_low_mag.jpg|thumb|center|150px | TL - low mag.]] | |||
|- | |||
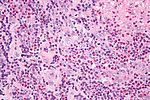
| [[Kikuchi disease]] (histiocystic necrotizing lymphadenitis) | |||
| No PMNs | |||
| histiocytes, [[necrosis]] | |||
| IHC for large cell lymphoma (CD30 + others) | |||
| [[SLE]] (has (blue) hematoxylin bodies in necrotic areas), large cell lymphomas | |||
| [[Image:Histiocytic_necrotizing_lymphadenitis_-_very_high_mag.jpg |thumb|center|150px| HNL - very high mag.]] | |||
|- | |||
| [[Cat-scratch disease]] | |||
| PMNs in necrotic area | |||
| "stellate" (or serpentine) shaped microabscesses, granulomas | |||
| B. henselae, [[Dieterle stain]] | |||
| [[HIV]]/AIDS, NSRFH | |||
| [[Image:Cat_scratch_disease_-_very_low_mag.jpg|thumb|center|150px|Cat scratch - very low mag.]] | |||
|- | |||
| [[Dermatopathic lymphadenopathy]] | |||
| melanin-laden histiocytes | |||
| [[histiocytosis]] | |||
| [[S-100]]+ve (interdigitating dendritic cells), CD1a+ve (Langerhans cells) | |||
| [[cutaneous T-cell lymphoma]] | |||
| [[Image:Dermatopathic_lymphadenopathy_-_intermed_mag.jpg |thumb|center|150px| DL - intermed. mag.]] | |||
|- | |||
| [[Kimura disease]] | |||
| eosinophils | |||
| angiolymphoid proliferation (thick-walled blood vessels with [[hobnail]] endothelial cells) | |||
| IHC ? | |||
| [[Langerhans cell histiocytosis]], drug reaction, [[angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia]] | |||
| [[Image:Kimura_disease_-_very_high_mag.jpg|thumb|center|150px|Kimura disease - very high mag.]] | |||
|- | |||
| [[Langerhans cell histiocytosis]] | |||
| abundant histiocytes with reniform nuclei | |||
| often prominent eosinophilia | |||
| [[S-100]]+, CD1a+ | |||
| [[Kimura disease]] (eosinophilia), [[Rosai-Dorfman disease]] | |||
| [[Image:Langerhans_cell_histiocytosis_-_very_high_mag.jpg|thumb|center|150px|LCH - very high mag.]] | |||
|- | |||
| [[Rosai-Dorfman disease]] | |||
| sinus histiocytosis | |||
| emperipolesis (intact cell within a macrophage) | |||
| [[S-100]]+, CD1a- | |||
| Langerhans cell histiocytosis | |||
| [[Image:Emperipolesis_-_very_high_mag.jpg |thumb|center|150px | RDD - very high mag.]] | |||
|- | |||
| [[Systemic lupus erythematosus]] lymphadenopathy | |||
| (blue) hematoxylin bodies | |||
| necrosis, no PMNs | |||
| IHC for large cell lymphoma (CD30 + others) | |||
| [[Kikuchi disease]], large cell [[lymphoma]]s | |||
| [[Image:Systemic_lupus_erythematosus_lymphadenopathy_-_high_mag.jpg|thumb|center|150px | SLEL - high mag.]] | |||
|- | |||
| [[Castleman disease]], hyaline vascular variant | |||
| thick mantle cell layer with laminar appearance ("onion skin" layering) | |||
| hyaline (pink crap), lollipops (large vessels into GC), no mitoses in GC | |||
| IHC - to r/o [[mantle cell lymphoma]] | |||
| mantle cell lymphoma, [[HIV]]/AIDS | |||
| [[Image:Castleman_disease_-_intermed_mag.jpg|thumb|center|150px | CD - intermed. mag.]] | |||
|- | |||
| Castleman disease, plasma cell variant | |||
| thick mantle cell layer | |||
| sinus perserved, interfollicular plasma cells, mitoses in GC | |||
| [[HHV-8]] | |||
| HIV/AIDS | |||
| image ? | |||
|- | |||
| [[Intranodal palisaded myofibroblastoma]] | |||
| spindle cells with nuclear palisading | |||
| [[RBC extravasation]], fibrillary bodies with a central vessel "amianthoid fibers" | |||
| SMA+, cyclin D1+ | |||
| [[schwannoma]] | |||
| [[Image:Intranodal_palisaded_myofibroblastoma_-_very_high_mag.jpg|thumb|center|150px|IPM - very high mag.]] | |||
|- | |||
<!-- | entity | |||
| key feature | |||
| other features | |||
| IHC | |||
| DDx | |||
| image --> | |||
|} | |||
===Follicular lymphoma vs. reactive follicular hyperplasia=== | |||
Factors to consider:<ref>DB. 4 August 2010.</ref> | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
! | |||
! Reactive follicular <br>hyperplasia | |||
! Follicular lymphoma | |||
|- | |||
| Follicle location | |||
| cortex | |||
| cortex and medulla | |||
|- | |||
| Germinal center edge | |||
| sharp/well-demarcated | |||
| poorly demarcated | |||
|- | |||
| Germinal center density | |||
| well spaced, sinuses open | |||
| crowded, sinuses effaced/<br>compressed to nothingness | |||
|- | |||
| Tingible body <br>macrophages | |||
| common | |||
| uncommon | |||
|- | |||
| Germinal center<br>light/dark pattern | |||
| normal | |||
| abnormal | |||
|} | |||
==Lymph node metastasis== | |||
{{Main|Lymph node metastasis}} | |||
==Kaposi sarcoma== | |||
{{Main|Kaposi sarcoma}} | |||
*One of the few non-lymphoid primary lymph node tumours.<ref name=pmid1918406>{{Cite journal | last1 = Bigotti | first1 = G. | last2 = Coli | first2 = A. | last3 = Mottolese | first3 = M. | last4 = Di Filippo | first4 = F. | title = Selective location of palisaded myofibroblastoma with amianthoid fibres. | journal = J Clin Pathol | volume = 44 | issue = 9 | pages = 761-4 | month = Sep | year = 1991 | doi = | PMID = 1918406 | PMC = 496726 }}</ref> | |||
==Melanocytic nevi== | |||
{{Main|Melanocytic lesions}} | |||
:See: ''[[Dermatopathic lymphadenopathy]]''. | |||
*Benign melanocytic nevi can be found in lymph nodes.<ref name=pmid1918406>{{Cite journal | last1 = Bigotti | first1 = G. | last2 = Coli | first2 = A. | last3 = Mottolese | first3 = M. | last4 = Di Filippo | first4 = F. | title = Selective location of palisaded myofibroblastoma with amianthoid fibres. | journal = J Clin Pathol | volume = 44 | issue = 9 | pages = 761-4 | month = Sep | year = 1991 | doi = | PMID = 1918406 | PMC = 496726 }}</ref> | |||
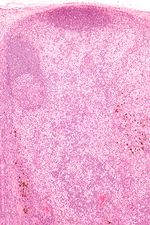
==Progressive transformation of germinal centers== | |||
{{Main|Progressive transformation of germinal centers}} | |||
*Abbreviated as ''PTGC''. | |||
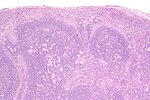
==Reactive follicular hyperplasia== | |||
{{Main|Reactive follicular hyperplasia}} | |||
==Diffuse paracortical hyperplasia== | |||
===General=== | ===General=== | ||
* | *Benign. | ||
===Microscopic=== | |||
* | Features:<ref name=Ref_ILNP179>{{Ref_ILNP|179}}</ref> | ||
* | *Interfollicular areas enlarged - '''key feature'''. | ||
* | **T cell population increased. | ||
**Plasma cells. | |||
**Macrophages. | |||
**Large Reed-Sternberg-like cells. | |||
==Sinus histiocytosis== | |||
:Should '''not''' be confused with ''[[sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy]]'', also known as Rosai-Dorfman disease. | |||
{{Main|Sinus histiocytosis}} | |||
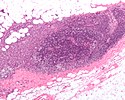
==Kikuchi disease== | |||
*[[AKA]] ''histiocytic necrotising lymphadenitis'' (HNL).<ref name="pmid15570824">{{cite journal |author=Kaushik V, Malik TH, Bishop PW, Jones PH |title=Histiocytic necrotising lymphadenitis (Kikuchi's disease): a rare cause of cervical lymphadenopathy |journal=Surgeon |volume=2 |issue=3 |pages=179–82 |year=2004 |month=June |pmid=15570824 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | |||
*[[AKA]] ''Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease''. | |||
{{Main|Kikuchi disease}} | |||
==Systemic lupus erythematosus lymphadenopathy== | |||
{{Main|Systemic lupus erythematosus lymphadenopathy}} | |||
==Castleman disease== | |||
* | *[[AKA]] ''angiofollicular lymph node hyperplasia'', ''giant lymph node hyperplasia''.<ref>URL: [http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/castleman-disease/DS01000 http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/castleman-disease/DS01000]. Accessed on: 17 June 2010.</ref> | ||
* | *Abbreviated '''CD'''. | ||
{{Main|Castleman disease}} | |||
== | ==Cat-scratch disease== | ||
*[[AKA]] ''cat scratch fever''. | |||
{{Main|Cat scratch disease}} | |||
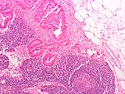
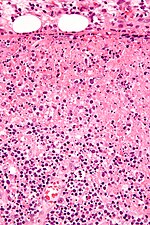
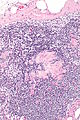
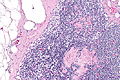
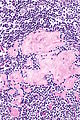
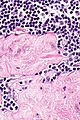
==Toxoplasma lymphadenitis== | |||
* | {{Main|Toxoplasma}} | ||
===General=== | |||
*Caused by protozoan ''Toxoplasma gondii''. | |||
===Microscopic=== | |||
Features:<ref name=Ref_ILNP113>{{Ref ILNP|113}}</ref> | |||
** | *Reactive germinal centers (pale areas - larger than usual). | ||
**Abundant | **Often poorly demarcated - due to loose epithelioid cell clusters at germinal center edge - '''key feature'''. | ||
** | *Epithelioid cells - perifollicular & intrafollicular. | ||
**Loose aggregates of histiocytes (do not form round granulomas): | |||
***Abundant pale cytoplasm. | |||
***Nucleoli. | |||
*Monocytoid cells (monocyte-like cells) - in cortex & paracortex. | |||
**Large cells in islands/sheets '''key feature''' with: | |||
***Abundant pale cytoplasm - '''important'''. | |||
***Well-defined cell border - '''important'''. | |||
***Singular nucleus. | |||
**Cell clusters usually have interspersed neutrophils. | |||
Images: | Images: | ||
*[http:// | *[http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Toxoplasmosis_lymphadenopathy_-_low_mag.jpg Toxoplasmosis - low mag. (WC)]. | ||
*[http:// | *[http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Toxoplasmosis_lymphadenopathy_-_high_mag.jpg Toxoplasmosis - high mag. (WC)]. | ||
Notes: | |||
*Monocytoid cells CD68 -ve. | |||
===IHC=== | ===IHC=== | ||
* | *IHC for toxoplasmosis. | ||
==Dermatopathic lymphadenopathy== | |||
{{Main|Dermatopathic lymphadenopathy}} | |||
==Kimura lymphadenopathy== | |||
{{Main|Kimura disease}} | |||
== | ==Rosai-Dorfman disease== | ||
*Abbreviated ''RDD''. | |||
*[[AKA]] ''sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy'', abbreviated ''SHML''. | |||
{{Main|Rosai-Dorfman disease}} | |||
==Langerhans cell histiocytosis== | |||
{{Main|Langerhans cell histiocytosis}} | |||
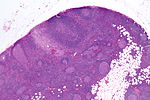
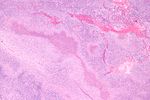
==Lymph node hyalinization== | |||
*[[AKA]] ''hyalinized lymph node''. | |||
===General=== | ===General=== | ||
*Benign. | *Benign. | ||
*Associated with aging.<ref name=pmid12973685>{{Cite journal | last1 = Taniguchi | first1 = I. | last2 = Murakami | first2 = G. | last3 = Sato | first3 = A. | last4 = Fujiwara | first4 = D. | last5 = Ichikawa | first5 = H. | last6 = Yajima | first6 = T. | last7 = Kohama | first7 = G. | title = Lymph node hyalinization in elderly Japanese. | journal = Histol Histopathol | volume = 18 | issue = 4 | pages = 1169-80 | month = Oct | year = 2003 | doi = | PMID = 12973685 }}</ref> | |||
===Microscopic=== | ===Microscopic=== | ||
Features:<ref> | Features: | ||
*Hyaline material (acellular pink stuff on H&E) within a [[lymph node]]. | |||
* | Subdivided into:<ref name=pmid12973685/> | ||
*Mediastinal-type. | |||
**Usually in medullary sinus. | |||
**Onion peel-like appearance. | |||
*Pelvic-type hyalinization. | |||
**Discrete round, eosinophilic, glassy appearance at low power, whirled/fibrous at high power. | |||
**+/-Calcification. | |||
DDx: | |||
*[[Amyloidosis]] - cotton candy-like appearance, usu. no calcifications. | |||
====Images==== | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image: Hyalinized lymph node -- intermed mag.jpg | Hyalinized LN - intermed. mag. | |||
Image: Hyalinized lymph node - alt -- intermed mag.jpg | Hyalinized LN - intermed. mag. | |||
Image: Hyalinized lymph node -- high mag.jpg | Hyalinized LN - high mag. | |||
Image: Hyalinized lymph node -- very high mag.jpg | Hyalinized LN - very high mag. | |||
</gallery> | |||
www: | |||
*[http://www.flickriver.com/photos/euthman/sets/72157594513987154/ Lymph node with amyloidosis - several images (flickriver.com)]. | |||
===Sign out=== | |||
*Not reported. | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| Line 63: | Line 296: | ||
[[Category:Haematopathology]] | [[Category:Haematopathology]] | ||
[[Category:Lymph node pathology|Lymph node pathology]] | |||
Latest revision as of 15:16, 16 February 2021
This article deals with non-haematologic malignant, i.e. metastases, and non-malignant lymph node pathology. An introduction to the lymph node is in the lymph nodes article.
Haematologic malignancies (in lymph nodes) are dealt with in other articles - see haematopathology and lymphoma.
Overview
Clinical:
- Lymphadenopathy.
Differential diagnosis:[1]
- Infectious - fungal, mycobacterial, viral, protozoal (Toxoplasma), bacterial (Chlamydia, Rickettsia, Bartonella)).
- Neoplastic - lymphoma, carcinoma.
- Endocrine - hyperthyroidism.
- Trauma.
- Autoimmune - SLE, RA, dermatomyositis.
- Inflammatory - drugs (phenytoin).
- Idiopathic - sarcoidosis.
Overview in a table
| Entity | Key feature | Other findings | IHC | DDx | Image |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-specific reactive follicular hyperplasia (NSRFH) | large spaced cortical follicles | tingible body macrophages, normal dark/light GC pattern | BCL2 -ve | infection (Toxoplasmosis, HIV/AIDS), Hodgkin's lymphoma | image ? |
| Lymph node metastasis | foreign cell population, usu. in subcapsular sinuses | +/-nuclear atypia, +/-malignant architecture | dependent on tumour type (see IHC) | dependent on morphology, endometriosis (mimics adenocarcinoma), ectopic decidua (mimics SCC) | |
| Progressive transformation of germinal centers | large (atypical) germinal centers | poorly demarcated germinal center (GC)/mantle zone interfaces, expanded mantle zone | IHC to r/o nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma (NLPHL) | NLPHL, follicular hyperplasia | |
| Toxoplasmosis | large follicles; epithelioid cells perifollicular & intrafollicular | reactive GCs, monocytoid cell clusters, epithelioid cells | IHC for toxoplasma | NSRFH, HIV/AIDS, Hodgkin's lymphoma | |
| Kikuchi disease (histiocystic necrotizing lymphadenitis) | No PMNs | histiocytes, necrosis | IHC for large cell lymphoma (CD30 + others) | SLE (has (blue) hematoxylin bodies in necrotic areas), large cell lymphomas | |
| Cat-scratch disease | PMNs in necrotic area | "stellate" (or serpentine) shaped microabscesses, granulomas | B. henselae, Dieterle stain | HIV/AIDS, NSRFH | |
| Dermatopathic lymphadenopathy | melanin-laden histiocytes | histiocytosis | S-100+ve (interdigitating dendritic cells), CD1a+ve (Langerhans cells) | cutaneous T-cell lymphoma | |
| Kimura disease | eosinophils | angiolymphoid proliferation (thick-walled blood vessels with hobnail endothelial cells) | IHC ? | Langerhans cell histiocytosis, drug reaction, angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia | |
| Langerhans cell histiocytosis | abundant histiocytes with reniform nuclei | often prominent eosinophilia | S-100+, CD1a+ | Kimura disease (eosinophilia), Rosai-Dorfman disease | |
| Rosai-Dorfman disease | sinus histiocytosis | emperipolesis (intact cell within a macrophage) | S-100+, CD1a- | Langerhans cell histiocytosis | |
| Systemic lupus erythematosus lymphadenopathy | (blue) hematoxylin bodies | necrosis, no PMNs | IHC for large cell lymphoma (CD30 + others) | Kikuchi disease, large cell lymphomas | |
| Castleman disease, hyaline vascular variant | thick mantle cell layer with laminar appearance ("onion skin" layering) | hyaline (pink crap), lollipops (large vessels into GC), no mitoses in GC | IHC - to r/o mantle cell lymphoma | mantle cell lymphoma, HIV/AIDS | |
| Castleman disease, plasma cell variant | thick mantle cell layer | sinus perserved, interfollicular plasma cells, mitoses in GC | HHV-8 | HIV/AIDS | image ? |
| Intranodal palisaded myofibroblastoma | spindle cells with nuclear palisading | RBC extravasation, fibrillary bodies with a central vessel "amianthoid fibers" | SMA+, cyclin D1+ | schwannoma |
Follicular lymphoma vs. reactive follicular hyperplasia
Factors to consider:[2]
| Reactive follicular hyperplasia |
Follicular lymphoma | |
|---|---|---|
| Follicle location | cortex | cortex and medulla |
| Germinal center edge | sharp/well-demarcated | poorly demarcated |
| Germinal center density | well spaced, sinuses open | crowded, sinuses effaced/ compressed to nothingness |
| Tingible body macrophages |
common | uncommon |
| Germinal center light/dark pattern |
normal | abnormal |
Lymph node metastasis
Main article: Lymph node metastasis
Kaposi sarcoma
Main article: Kaposi sarcoma
- One of the few non-lymphoid primary lymph node tumours.[3]
Melanocytic nevi
Main article: Melanocytic lesions
- Benign melanocytic nevi can be found in lymph nodes.[3]
Progressive transformation of germinal centers
Main article: Progressive transformation of germinal centers
- Abbreviated as PTGC.
Reactive follicular hyperplasia
Main article: Reactive follicular hyperplasia
Diffuse paracortical hyperplasia
General
- Benign.
Microscopic
Features:[4]
- Interfollicular areas enlarged - key feature.
- T cell population increased.
- Plasma cells.
- Macrophages.
- Large Reed-Sternberg-like cells.
Sinus histiocytosis
- Should not be confused with sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy, also known as Rosai-Dorfman disease.
Main article: Sinus histiocytosis
Kikuchi disease
Main article: Kikuchi disease
Systemic lupus erythematosus lymphadenopathy
Main article: Systemic lupus erythematosus lymphadenopathy
Castleman disease
Main article: Castleman disease
Cat-scratch disease
- AKA cat scratch fever.
Main article: Cat scratch disease
Toxoplasma lymphadenitis
Main article: Toxoplasma
General
- Caused by protozoan Toxoplasma gondii.
Microscopic
Features:[7]
- Reactive germinal centers (pale areas - larger than usual).
- Often poorly demarcated - due to loose epithelioid cell clusters at germinal center edge - key feature.
- Epithelioid cells - perifollicular & intrafollicular.
- Loose aggregates of histiocytes (do not form round granulomas):
- Abundant pale cytoplasm.
- Nucleoli.
- Loose aggregates of histiocytes (do not form round granulomas):
- Monocytoid cells (monocyte-like cells) - in cortex & paracortex.
- Large cells in islands/sheets key feature with:
- Abundant pale cytoplasm - important.
- Well-defined cell border - important.
- Singular nucleus.
- Cell clusters usually have interspersed neutrophils.
- Large cells in islands/sheets key feature with:
Images:
Notes:
- Monocytoid cells CD68 -ve.
IHC
- IHC for toxoplasmosis.
Dermatopathic lymphadenopathy
Main article: Dermatopathic lymphadenopathy
Kimura lymphadenopathy
Main article: Kimura disease
Rosai-Dorfman disease
- Abbreviated RDD.
- AKA sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy, abbreviated SHML.
Main article: Rosai-Dorfman disease
Langerhans cell histiocytosis
Main article: Langerhans cell histiocytosis
Lymph node hyalinization
- AKA hyalinized lymph node.
General
- Benign.
- Associated with aging.[8]
Microscopic
Features:
- Hyaline material (acellular pink stuff on H&E) within a lymph node.
Subdivided into:[8]
- Mediastinal-type.
- Usually in medullary sinus.
- Onion peel-like appearance.
- Pelvic-type hyalinization.
- Discrete round, eosinophilic, glassy appearance at low power, whirled/fibrous at high power.
- +/-Calcification.
DDx:
- Amyloidosis - cotton candy-like appearance, usu. no calcifications.
Images
www:
Sign out
- Not reported.
See also
References
- ↑ URL: http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case289.html. Accessed on: 14 January 2012.
- ↑ DB. 4 August 2010.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Bigotti, G.; Coli, A.; Mottolese, M.; Di Filippo, F. (Sep 1991). "Selective location of palisaded myofibroblastoma with amianthoid fibres.". J Clin Pathol 44 (9): 761-4. PMC 496726. PMID 1918406. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC496726/.
- ↑ Ioachim, Harry L; Medeiros, L. Jeffrey (2008). Ioachim's Lymph Node Pathology (4th ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 179. ISBN 978-0781775960.
- ↑ Kaushik V, Malik TH, Bishop PW, Jones PH (June 2004). "Histiocytic necrotising lymphadenitis (Kikuchi's disease): a rare cause of cervical lymphadenopathy". Surgeon 2 (3): 179–82. PMID 15570824.
- ↑ URL: http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/castleman-disease/DS01000. Accessed on: 17 June 2010.
- ↑ Ioachim, Harry L; Medeiros, L. Jeffrey (2008). Ioachim's Lymph Node Pathology (4th ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 113. ISBN 978-0781775960.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Taniguchi, I.; Murakami, G.; Sato, A.; Fujiwara, D.; Ichikawa, H.; Yajima, T.; Kohama, G. (Oct 2003). "Lymph node hyalinization in elderly Japanese.". Histol Histopathol 18 (4): 1169-80. PMID 12973685.