Difference between revisions of "Autoimmune hepatitis"
(PBC -> change to newer term) |
|||
| (6 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
| Micro = interface hepatitis with plasma cells, +/- bile duct injury | | Micro = interface hepatitis with plasma cells, +/- bile duct injury | ||
| Subtypes = | | Subtypes = | ||
| LMDDx = [[viral hepatitis]], [[primary biliary | | LMDDx = [[viral hepatitis]], [[primary biliary cholangitis]], AIH-[[PBC]] overlap, [[PSC]]-AIH overlap, [[drug reaction]] | ||
| Stains = | | Stains = | ||
| IHC = | | IHC = | ||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
| Prognosis = poor without treatment | | Prognosis = poor without treatment | ||
| Other = | | Other = | ||
| ClinDDx = [[primary biliary | | ClinDDx = [[primary biliary cholangitis]], [[primary sclerosing cholangitis]] | ||
| Tx = corticosteroids, immunosuppression, liver transplant (end stage) | | Tx = corticosteroids, immunosuppression, liver transplant (end stage) | ||
}} | }} | ||
| Line 103: | Line 103: | ||
**Lots of plasma cells should prompt consideration of AIH. | **Lots of plasma cells should prompt consideration of AIH. | ||
*Atypical Autoimmune hepatitis may have zone III involvment (lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate)<ref name=pmid19452572>Non-classical phenotypes of autoimmune hepatitis and advances in diagnosis and treatment. Czaja AJ, Bayraktar Y. World J Gastroenterol. 2009 May 21;15(19):2314-28. Review. PMID 19452572.</ref> and a normal IgG.<ref>FW. 21 September 2009.</ref> | *Atypical Autoimmune hepatitis may have zone III involvment (lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate)<ref name=pmid19452572>Non-classical phenotypes of autoimmune hepatitis and advances in diagnosis and treatment. Czaja AJ, Bayraktar Y. World J Gastroenterol. 2009 May 21;15(19):2314-28. Review. PMID 19452572.</ref> and a normal IgG.<ref>FW. 21 September 2009.</ref> | ||
DDx: | |||
*[[Viral hepatitis]] - should have plasma cells. | |||
*[[Drug-induced liver injury]] - milder changes than AIH, portal [[neutrophil]]s and [[cholestasis]].<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Suzuki | first1 = A. | last2 = Brunt | first2 = EM. | last3 = Kleiner | first3 = DE. | last4 = Miquel | first4 = R. | last5 = Smyrk | first5 = TC. | last6 = Andrade | first6 = RJ. | last7 = Lucena | first7 = MI. | last8 = Castiella | first8 = A. | last9 = Lindor | first9 = K. | title = The use of liver biopsy evaluation in discrimination of idiopathic autoimmune hepatitis versus drug-induced liver injury. | journal = Hepatology | volume = 54 | issue = 3 | pages = 931-9 | month = Sep | year = 2011 | doi = 10.1002/hep.24481 | PMID = 21674554 }}</ref> | |||
*[[Primary biliary cholangitis]]. | |||
*AIH-PBC overlap. | |||
*PSC-AIH overlap. | |||
===Images=== | ===Images=== | ||
Table show [[AIH-nonCIR]] | |||
{| | |||
[[File:1 AIH 2 680x512px.tif|Expanded portal regions with dull edges suggestive of interface hepatitis (40X).]] | |||
[[File:2 AIH 2 680x512px.tif|PAS without diastase shows interface hepatitis (200X).]] | |||
[[File:3 AIH 2 680x512px.tif|Abundant plasma cells seen at higher power (400X).]] | |||
[[File:4 AIH 2 680x512px.tif|PAS with diastase shows intense inflammation of portal triad stroma, with some reduplication of ductal epithelium. The patient’s vial serology and anti-microbial antibody were negative. (200X).]] | |||
|} | |||
Autoimmune hepatitis. Expanded portal regions with dull edges suggestive of interface hepatitis (UL 40X). PAS without diastase shows interface hepatitis (UR 200X). Abundant plasma cells seen at higher power (LL 400X). PAS with diastase shows intense inflammation of portal triad stroma, with some reduplication of ductal epithelium. The patient’s vial serology and anti-microbial antibody were negative. (LR 200X). | |||
Table show [[AIH-CIR]] | |||
{| | |||
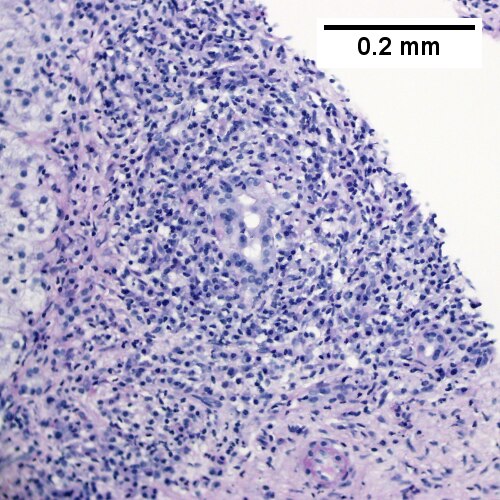
[[File:CIrrhosis Mult Cause - 1 - 400X 1369x1024px shot 04.tif|Trichrome shows blue fibrosis about hepatocyte nodules]] | |||
[[File:CIrrhosis Mult Cause - 1 - 400X 1369x1024px shot 01.tif|Inflammation includes occasional plasma cells (yellow arrowhead)]] | |||
[[File:CIrrhosis Mult Cause - 1 - 400X 1369x1024px shot 02.tif|Ballooning degeneration is present]] | |||
[[File:CIrrhosis Mult Cause - 1 - 400X 1369x1024px shot 03.tif|PAS without diastase shows piecemeal necrosis (not very good on wedge biopsies in my experience)]] | |||
|} | |||
Chronic hepatitis with changes of autoimmune hepatitis and with cirrhosis and steatosis. Trichrome shows blue fibrosis about hepatocyte nodules with steatosis (UL, 40X). Inflammation includes occasional plasma cells (UR, 400X, yellow arrowhead at plasma cell), consistent with history of autoimmune hepatitis. Ballooning degeneration is present (LL, 400X). PAS without diastase shows piecemeal necrosis, (LR, 400X). The patient had also had diabetes. | |||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
Image:Autoimmune_hepatitis_-_low_mag.jpg | AIH - low mag. (WC) | Image:Autoimmune_hepatitis_-_low_mag.jpg | AIH - low mag. (WC) | ||
| Line 128: | Line 158: | ||
serology is suggested, if not done. | serology is suggested, if not done. | ||
The histology is not suggestive of primary biliary | The histology is not suggestive of primary biliary cholangitis. | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
Latest revision as of 21:01, 30 September 2021
| Autoimmune hepatitis | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
 Autoimmune hepatitis. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | interface hepatitis with plasma cells, +/- bile duct injury |
| LM DDx | viral hepatitis, primary biliary cholangitis, AIH-PBC overlap, PSC-AIH overlap, drug reaction |
| Site | liver |
|
| |
| Clinical history | usu. women - young or middle-aged |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
| Blood work | ANA +ve, IgG elevated, LKM-1 +ve, SMA +ve, HBV -ve, HCV -ve, HIV -ve |
| Prognosis | poor without treatment |
| Clin. DDx | primary biliary cholangitis, primary sclerosing cholangitis |
| Treatment | corticosteroids, immunosuppression, liver transplant (end stage) |
Autoimmune hepatitis, abbreviated AIH, in an uncommon medical liver disease that occurs in adults and children.
General
- Several criteria exist to diagnose and histology (alone) is not sufficient.
- Classically, young and middle aged women.[1]
- May occur in men.
- Often a fluctuating course.
- Untreated AIH has a poor outcome.[1]
- Leads to cirrhosis and liver failure.
Diagnosis
Simplifed diagnostic criteria (2008):[2]
- Antibody titer.
- Elevated IgG.
- Liver pathology.
- Exclusion of viral hepatitis.
Details (scoring):[2]
| Finding | Score |
| ANA or SMA 1:40 | 1 point |
| ANA or SMA 1:80 | 2 points |
| LKM-1 1:40 | 2 points |
| IgG upper normal | 1 point |
| IgG 1.1x upper limit | 2 points |
| Histology compatible | 1 point |
| Typical AIH histo. | 2 points |
| No viral hepatitis | 2 points |
Interpretation: Definite >= 7 points. Probable = 6 points.
Notes:
- Autoantibodies may be seen in HCV.[2]
- A normal IgG is very unusual in AIH - but may be seen in atypical variants with zone III involvment.
Abbreviations:
- ANA = anti-nuclear antibody.
- SMA = smooth muscle antibody.
- LKM-1 = liver kidney microsomal type 1 antibody.
Treatment
Microscopic
Classification:[2]
- Typical:
- Interface hepatitis (zone 1).
- Lymphoplasmacytic infiltration of portal tracts / lobule.
- Periportal plasma cells - key feature.[4]
- Lymphoplasmacytic infiltration of portal tracts / lobule.
- Emperipolesis - one cell penetrates into another one (uncommon finding).
- Hepatic rosette - inflammatory cells around reactive hepatocytes.[5]
- Interface hepatitis (zone 1).
- Compatible:
- Chronic hepatitis - lymphocytic dominant.
- Atypical:
- Signs of an other disease.
Notes:
- PAS stain may be useful - find plasma cells.[6]
- Lots of plasma cells should prompt consideration of AIH.
- Atypical Autoimmune hepatitis may have zone III involvment (lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate)[3] and a normal IgG.[7]
DDx:
- Viral hepatitis - should have plasma cells.
- Drug-induced liver injury - milder changes than AIH, portal neutrophils and cholestasis.[8]
- Primary biliary cholangitis.
- AIH-PBC overlap.
- PSC-AIH overlap.
Images
Table show AIH-nonCIR

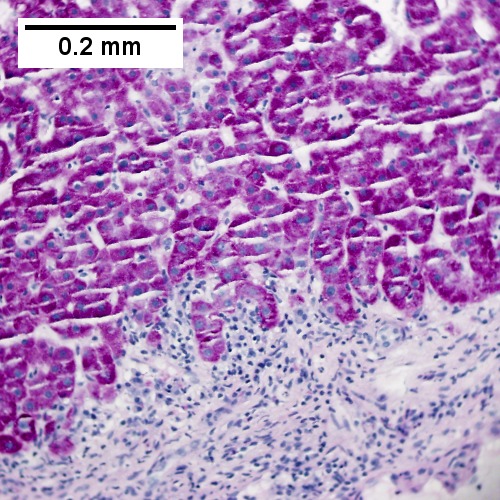

Autoimmune hepatitis. Expanded portal regions with dull edges suggestive of interface hepatitis (UL 40X). PAS without diastase shows interface hepatitis (UR 200X). Abundant plasma cells seen at higher power (LL 400X). PAS with diastase shows intense inflammation of portal triad stroma, with some reduplication of ductal epithelium. The patient’s vial serology and anti-microbial antibody were negative. (LR 200X).
Table show AIH-CIR
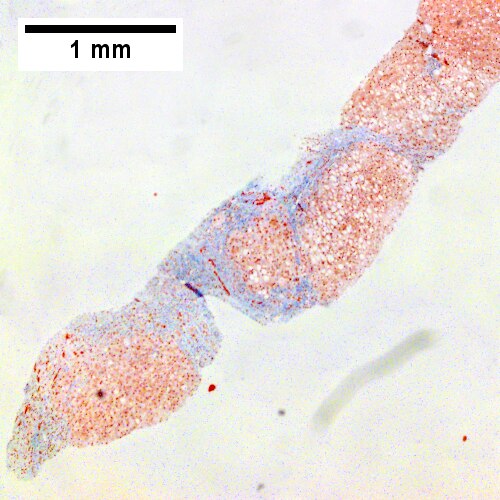
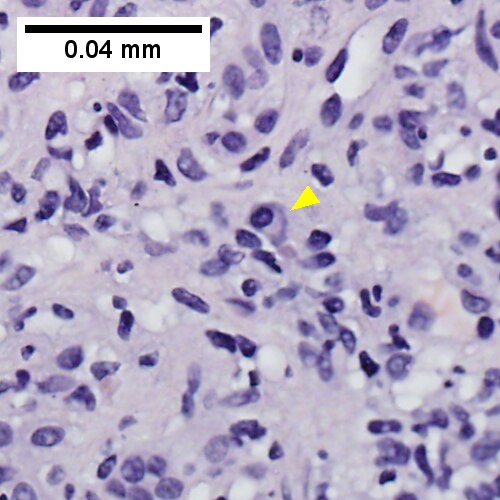
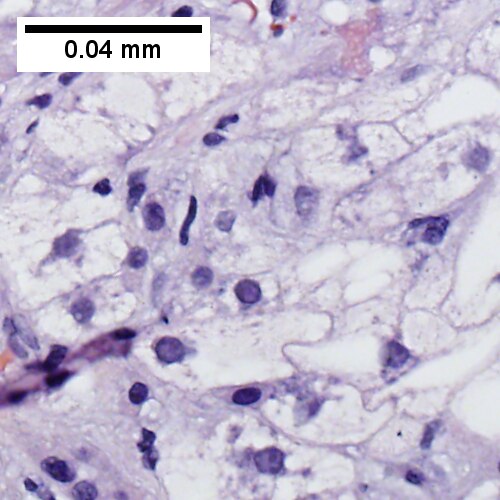

Chronic hepatitis with changes of autoimmune hepatitis and with cirrhosis and steatosis. Trichrome shows blue fibrosis about hepatocyte nodules with steatosis (UL, 40X). Inflammation includes occasional plasma cells (UR, 400X, yellow arrowhead at plasma cell), consistent with history of autoimmune hepatitis. Ballooning degeneration is present (LL, 400X). PAS without diastase shows piecemeal necrosis, (LR, 400X). The patient had also had diabetes.
www:
Emperipolesis:
Sign out
LIVER, RIGHT LOBE, CORE BIOPSY: - LIVER WITH INTERFACE HEPATITIS (GRADE 2/4) WITH PLASMA CELLS. - MODERATE FIBROSIS (STAGE 2/4). COMMENT: The histologic findings are compatible with autoimmune hepatitis. Serologic findings (ANA positive, IgG positive, viral serology negative) are noted. Correlation with LKM-1 serology is suggested, if not done. The histology is not suggestive of primary biliary cholangitis.
Micro
The sections show two cores of liver with an interface hepatitis with plasma cells. Numerous eosinophils are seen focally in the portal tract. The number of ducts is focally increased in several portal tracts and associated with neutrophils (ductular reaction). Size of biopsy: adequate. Fragmentation: absent. Fibrosis: Stage 2/4. Fibrous septa: present. Septa with curved contours: present, focally only. Large droplet steatosis (% of hepatocytes): minimal <5%. Ballooning of hepatocytes: absent. Mallory-Denk bodies: absent. Portal inflammation: present (1/4). Interface activity: mild (1/4). Lobular necroinflammation: not identified. Ducts: numbers within normal limits. Duct injury: present. Ductular reaction: present. Cholestasis: not apparent. Terminal hepatic venules: present. Iron stain: absent. Ground glass cells with routine stains: absent.
See also
References
- ↑ Jump up to: 1.0 1.1 1.2 Francque, S.; Vonghia, L.; Ramon, A.; Michielsen, P. (2012). "Epidemiology and treatment of autoimmune hepatitis.". Hepat Med 4: 1-10. doi:10.2147/HMER.S16321. PMID 24367228.
- ↑ Jump up to: 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Scoring systems for the diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis: past, present, and future. Wiegard C, Schramm C, Lohse AW. Semin Liver Dis. 2009 Aug;29(3):254-61. Epub 2009 Aug 12. PMID 19675998
- ↑ Jump up to: 3.0 3.1 Non-classical phenotypes of autoimmune hepatitis and advances in diagnosis and treatment. Czaja AJ, Bayraktar Y. World J Gastroenterol. 2009 May 21;15(19):2314-28. Review. PMID 19452572.
- ↑ Mitchell, Richard; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Abbas, Abul K.; Aster, Jon (2011). Pocket Companion to Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 448. ISBN 978-1416054542.
- ↑ Jump up to: 5.0 5.1 Malik, TA.; Saeed, S. (May 2010). "Autoimmune hepatitis: a review.". J Pak Med Assoc 60 (5): 381-7. PMID 20527613. http://www.jpma.org.pk/full_article_text.php?article_id=2051.
- ↑ URL: http://iv.iiarjournals.org/content/19/6/1097.abstract. Accessed on: 9 December 2010.
- ↑ FW. 21 September 2009.
- ↑ Suzuki, A.; Brunt, EM.; Kleiner, DE.; Miquel, R.; Smyrk, TC.; Andrade, RJ.; Lucena, MI.; Castiella, A. et al. (Sep 2011). "The use of liver biopsy evaluation in discrimination of idiopathic autoimmune hepatitis versus drug-induced liver injury.". Hepatology 54 (3): 931-9. doi:10.1002/hep.24481. PMID 21674554.