Difference between revisions of "ROS1-rearranged non-small cell lung carcinoma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
**Resection specimens: acinar pattern most common. | **Resection specimens: acinar pattern most common. | ||
==Images= | ===Images=== | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
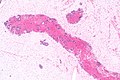
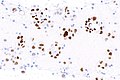
Image: Adenocarcinoma - ROS1 positive -- low mag.jpg | NSmCC - low mag. | Image: Adenocarcinoma - ROS1 positive -- low mag.jpg | NSmCC - low mag. | ||
| Line 24: | Line 23: | ||
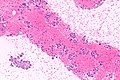
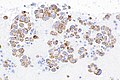
Image: Adenocarcinoma - ROS1 positive -- very high mag.jpg | NSmCC - very high mag. | Image: Adenocarcinoma - ROS1 positive -- very high mag.jpg | NSmCC - very high mag. | ||
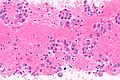
Image: Adenocarcinoma - ROS1 positive - TTF1 -- high mag.jpg | NSmCC - TTF-1 - high mag. | |||
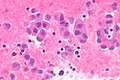
Image: Adenocarcinoma - ROS1 positive - napsin A -- high mag.jpg | NSmCC - napsin A - high mag. | |||
</gallery> | |||
==IHC== | |||
*ROS1 +ve. | |||
===Images=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
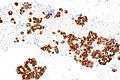
Image: Adenocarcinoma - ROS1 positive - ROS1 -- low mag.jpg | NSmCC - ROS1 - low mag. | Image: Adenocarcinoma - ROS1 positive - ROS1 -- low mag.jpg | NSmCC - ROS1 - low mag. | ||
Image: Adenocarcinoma - ROS1 positive - ROS1 -- intermed mag.jpg | NSmCC - ROS1 - intermed. mag. | Image: Adenocarcinoma - ROS1 positive - ROS1 -- intermed mag.jpg | NSmCC - ROS1 - intermed. mag. | ||
Image: Adenocarcinoma - ROS1 positive - ROS1 -- high mag.jpg | NSmCC - ROS1 -high mag. | Image: Adenocarcinoma - ROS1 positive - ROS1 -- high mag.jpg | NSmCC - ROS1 -high mag. | ||
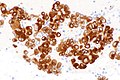
Image: Adenocarcinoma - ROS1 positive - ROS1 -- very high mag.jpg | NSmCC - ROS1 -very high mag. | Image: Adenocarcinoma - ROS1 positive - ROS1 -- very high mag.jpg | NSmCC - ROS1 -very high mag. | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Revision as of 02:30, 31 December 2019
ROS1-rearranged non-small cell lung carcinoma is a subtype of non-small cell lung carcinoma that can be treated with ALK inhibitors.[1]
General
- ROS1-rearrangements are seen in approximately 1-2% of non-small cell carcinoma.[2]
- Respond to target therapy, e.g. crizotinib.[3]
Microscopic
Features:
- Histology not definitive; however, predictive features are:[4]
- Cribriform structure.
- Psammoma bodies
Note:
- Most common pattern varies by specimen type:[4]
- Biopsy specimens: solid pattern most common.
- Resection specimens: acinar pattern most common.
Images
IHC
- ROS1 +ve.
Images
See also
References
- ↑ Shaw, AT.; Ou, SH.; Bang, YJ.; Camidge, DR.; Solomon, BJ.; Salgia, R.; Riely, GJ.; Varella-Garcia, M. et al. (Nov 2014). "Crizotinib in ROS1-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer.". N Engl J Med 371 (21): 1963-71. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1406766. PMID 25264305.
- ↑ "Targeted therapies for ROS1-rearranged non-small cell lung cancer". Drugs Today 55 (10): 641–652. October 2019. doi:10.1358/dot.2019.55.10.3030646. PMID 31720561.
- ↑ "Crizotinib in ROS1-rearranged advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC): updated results, including overall survival, from PROFILE 1001". Ann. Oncol. 30 (7): 1121–1126. July 2019. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdz131. PMC 6637370. PMID 30980071. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6637370/.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "A Prediction Model for ROS1-Rearranged Lung Adenocarcinomas based on Histologic Features". PLoS ONE 11 (9): e0161861. 2016. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0161861. PMC 5029801. PMID 27648828. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5029801/.