Difference between revisions of "Fibrous pseudotumour of the paratesticular region"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (6 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Fibrous pseudotumour of the paratesticular region''' is a very rare tumour of the | {{ Infobox diagnosis | ||
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | |||
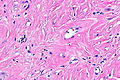
| Image = Paratesticular fibrous pseudotumour -- intermed mag.jpg | |||
| Width = | |||
| Caption = Paratesticular fibrous pseudotumour. [[H&E stain]]. | |||
| Synonyms = | |||
| Micro = [[spindle cells]] with moderate eosinophilic cytoplasm and indistinct cellular borders, no significant nuclear atypia | |||
| Subtypes = | |||
| LMDDx = [[leiomyoma]], [[fibroma]] of the tunics, [[fibromatosis]], [[solitary fibrous tumour]], [[inflammatory pseudotumour]] | |||
| Stains = | |||
| IHC = CD34 +ve/-ve, S-100 -ve, desmin -ve, [[keratins]] -ve | |||
| EM = | |||
| Molecular = | |||
| IF = | |||
| Gross = | |||
| Grossing = | |||
| Site = [[paratesticular region]] | |||
| Assdx = | |||
| Syndromes = | |||
| Clinicalhx = | |||
| Signs = | |||
| Symptoms = | |||
| Prevalence = very rare | |||
| Bloodwork = | |||
| Rads = | |||
| Endoscopy = | |||
| Prognosis = good | |||
| Other = | |||
| ClinDDx = other paratesticular lesions and testicular lesions | |||
| Tx = surgical excision to exclude serious pathology | |||
}} | |||
'''Fibrous pseudotumour of the paratesticular region''' is a very rare tumour of the [[paratesticular region]].<ref name=pmid24459661>{{Cite journal | last1 = Bharti | first1 = JN. | last2 = Dey | first2 = B. | last3 = Mittal | first3 = A. | last4 = Arora | first4 = P. | title = A case of fibrous pseudotumor of the paratesticular region. | journal = World J Mens Health | volume = 31 | issue = 3 | pages = 262-4 | month = Dec | year = 2013 | doi = 10.5534/wjmh.2013.31.3.262 | PMID = 24459661 }}</ref> | |||
==General== | ==General== | ||
*May be associated with the [[epididymis]] or tunica vaginalis of the [[testis]].<ref name=pmid24627288>{{Cite journal | last1 = Zhang | first1 = Z. | last2 = Yang | first2 = J. | last3 = Li | first3 = M. | last4 = Cai | first4 = W. | last5 = Liu | first5 = Q. | last6 = Wang | first6 = T. | last7 = Guo | first7 = X. | last8 = Wang | first8 = S. | last9 = Liu | first9 = J. | title = Paratesticular fibrous pseudotumor: a report of five cases and literature review. | journal = Front Med | volume = | issue = | pages = | month = Mar | year = 2014 | doi = 10.1007/s11684-014-0325-3 | PMID = 24627288 }}</ref> | *May be associated with the [[epididymis]] or tunica vaginalis of the [[testis]].<ref name=pmid24627288>{{Cite journal | last1 = Zhang | first1 = Z. | last2 = Yang | first2 = J. | last3 = Li | first3 = M. | last4 = Cai | first4 = W. | last5 = Liu | first5 = Q. | last6 = Wang | first6 = T. | last7 = Guo | first7 = X. | last8 = Wang | first8 = S. | last9 = Liu | first9 = J. | title = Paratesticular fibrous pseudotumor: a report of five cases and literature review. | journal = Front Med | volume = | issue = | pages = | month = Mar | year = 2014 | doi = 10.1007/s11684-014-0325-3 | PMID = 24627288 }}</ref> | ||
**Uncommonly associated with the epididymis (<10% of tumours<ref name=pmid11018636>{{Cite journal | last1 = Tobias-machado | first1 = M. | last2 = Corrêa Lopes Neto | first2 = A. | last3 = Heloisa Simardi | first3 = L. | last4 = Borrelli | first4 = M. | last5 = Wroclawski | first5 = ER. | title = Fibrous pseudotumor of tunica vaginalis and epididymis. | journal = Urology | volume = 56 | issue = 4 | pages = 670-2 | month = Oct | year = 2000 | doi = | PMID = 11018636 }}</ref>). | |||
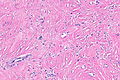
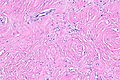
==Microscopic== | |||
Features:<ref name=pmid24627288/> | |||
*Spindle cells with: | |||
**Moderate eosinophilic cytoplasm. | |||
**Indistinct cellular borders. | |||
DDx:<ref name=pmid24627288/> | |||
*[[Leiomyoma]]. | |||
*[[Fibroma]] of the tunics. | |||
*[[Fibromatosis]]. | |||
*[[Solitary fibrous tumour]]. | |||
*[[Inflammatory pseudotumour]]. | |||
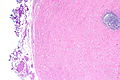
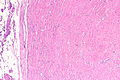
===Images=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
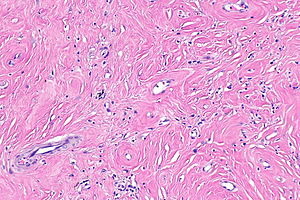
Image: Paratesticular fibrous pseudotumour -- very low mag.jpg | PFP - very low mag. | |||
Image: Paratesticular fibrous pseudotumour -- low mag.jpg | PFP - low mag. | |||
Image: Paratesticular fibrous pseudotumour -- intermed mag.jpg | PFP - intermed. mag. | |||
Image: Paratesticular fibrous pseudotumour - alt -- intermed mag.jpg | PFP - intermed. mag. | |||
Image: Paratesticular fibrous pseudotumour -- high mag.jpg | PFP - high mag. | |||
</gallery> | |||
==IHC== | |||
Features:<ref name=pmid9060599>{{Cite journal | last1 = Jones | first1 = MA. | last2 = Young | first2 = RH. | last3 = Scully | first3 = RE. | title = Benign fibromatous tumors of the testis and paratesticular region: a report of 9 cases with a proposed classification of fibromatous tumors and tumor-like lesions. | journal = Am J Surg Pathol | volume = 21 | issue = 3 | pages = 296-305 | month = Mar | year = 1997 | doi = | PMID = 9060599 }}</ref> | |||
*CD34 +ve/-ve. | |||
*S-100 -ve. | |||
*Desmin -ve. | |||
*Keratin -ve. | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
Latest revision as of 03:10, 2 August 2016
| Fibrous pseudotumour of the paratesticular region | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
 Paratesticular fibrous pseudotumour. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | spindle cells with moderate eosinophilic cytoplasm and indistinct cellular borders, no significant nuclear atypia |
| LM DDx | leiomyoma, fibroma of the tunics, fibromatosis, solitary fibrous tumour, inflammatory pseudotumour |
| IHC | CD34 +ve/-ve, S-100 -ve, desmin -ve, keratins -ve |
| Site | paratesticular region |
|
| |
| Prevalence | very rare |
| Prognosis | good |
| Clin. DDx | other paratesticular lesions and testicular lesions |
| Treatment | surgical excision to exclude serious pathology |
Fibrous pseudotumour of the paratesticular region is a very rare tumour of the paratesticular region.[1]
General
- May be associated with the epididymis or tunica vaginalis of the testis.[2]
- Uncommonly associated with the epididymis (<10% of tumours[3]).
Microscopic
Features:[2]
- Spindle cells with:
- Moderate eosinophilic cytoplasm.
- Indistinct cellular borders.
DDx:[2]
- Leiomyoma.
- Fibroma of the tunics.
- Fibromatosis.
- Solitary fibrous tumour.
- Inflammatory pseudotumour.
Images
IHC
Features:[4]
- CD34 +ve/-ve.
- S-100 -ve.
- Desmin -ve.
- Keratin -ve.
See also
References
- ↑ Bharti, JN.; Dey, B.; Mittal, A.; Arora, P. (Dec 2013). "A case of fibrous pseudotumor of the paratesticular region.". World J Mens Health 31 (3): 262-4. doi:10.5534/wjmh.2013.31.3.262. PMID 24459661.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Zhang, Z.; Yang, J.; Li, M.; Cai, W.; Liu, Q.; Wang, T.; Guo, X.; Wang, S. et al. (Mar 2014). "Paratesticular fibrous pseudotumor: a report of five cases and literature review.". Front Med. doi:10.1007/s11684-014-0325-3. PMID 24627288.
- ↑ Tobias-machado, M.; Corrêa Lopes Neto, A.; Heloisa Simardi, L.; Borrelli, M.; Wroclawski, ER. (Oct 2000). "Fibrous pseudotumor of tunica vaginalis and epididymis.". Urology 56 (4): 670-2. PMID 11018636.
- ↑ Jones, MA.; Young, RH.; Scully, RE. (Mar 1997). "Benign fibromatous tumors of the testis and paratesticular region: a report of 9 cases with a proposed classification of fibromatous tumors and tumor-like lesions.". Am J Surg Pathol 21 (3): 296-305. PMID 9060599.