Difference between revisions of "Small cell carcinoma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
*[[Chloroma]]. | *[[Chloroma]]. | ||
*[[Rhabdomyosarcoma]] - usu. [[CD56]] positive, may be keratin positive and positive for other [[neuroendocrine markers]].<ref name=pmid18487991>{{Cite journal | last1 = Bahrami | first1 = A. | last2 = Gown | first2 = AM. | last3 = Baird | first3 = GS. | last4 = Hicks | first4 = MJ. | last5 = Folpe | first5 = AL. | title = Aberrant expression of epithelial and neuroendocrine markers in alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma: a potentially serious diagnostic pitfall. | journal = Mod Pathol | volume = 21 | issue = 7 | pages = 795-806 | month = Jul | year = 2008 | doi = 10.1038/modpathol.2008.86 | PMID = 18487991 }}</ref> | *[[Rhabdomyosarcoma]] - usu. [[CD56]] positive, may be keratin positive and positive for other [[neuroendocrine markers]].<ref name=pmid18487991>{{Cite journal | last1 = Bahrami | first1 = A. | last2 = Gown | first2 = AM. | last3 = Baird | first3 = GS. | last4 = Hicks | first4 = MJ. | last5 = Folpe | first5 = AL. | title = Aberrant expression of epithelial and neuroendocrine markers in alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma: a potentially serious diagnostic pitfall. | journal = Mod Pathol | volume = 21 | issue = 7 | pages = 795-806 | month = Jul | year = 2008 | doi = 10.1038/modpathol.2008.86 | PMID = 18487991 }}</ref> | ||
*[[Atypical lung carcinoid tumour]] (lung only). | |||
*[[Typical lung carcinoid tumour]] (lung only). | |||
*Other [[small round cell tumours]]. | *Other [[small round cell tumours]]. | ||
| Line 48: | Line 50: | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
Image:Small_cell_lung_cancer_-_cytology.jpg | Small cell carcinoma - cytology - Field stain. (WC) | Image:Small_cell_lung_cancer_-_cytology.jpg | Small cell carcinoma - cytology - Field stain. (WC) | ||
Image: Lung small cell carcinoma - Diff-Quik -- high mag.jpg | SmCC - Diff-Quik - high mag. | Image: Lung small cell carcinoma - Diff-Quik -- high mag.jpg | SmCC - Diff-Quik - high mag. (WC) | ||
Image: Lung small cell carcinoma - Diff-Quik -- very high mag.jpg | SmCC - Diff-Quik - very high mag. | Image: Lung small cell carcinoma - Diff-Quik -- very high mag.jpg | SmCC - Diff-Quik - very high mag. (WC) | ||
Image: Lung small cell carcinoma - Diff-Quik -- extremely high mag.jpg | SmCC - Diff-Quik - extremely high mag. | Image: Lung small cell carcinoma - Diff-Quik -- extremely high mag.jpg | SmCC - Diff-Quik - extremely high mag. (WC) | ||
Image: Lung small cell carcinoma -- very high mag.jpg | SmCC - Pap stain - very high mag. | Image: Lung small cell carcinoma -- very high mag.jpg | SmCC - Pap stain - very high mag. (WC) | ||
Image: Lung small cell carcinoma -- extremely high mag.jpg | SmCC - Pap stain - extremely high mag. | Image: Lung small cell carcinoma -- extremely high mag.jpg | SmCC - Pap stain - extremely high mag. (WC) | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Latest revision as of 13:12, 26 April 2016

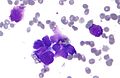
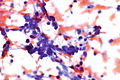
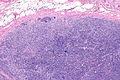
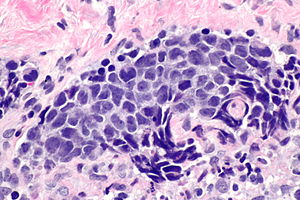
Micrograph showing a small cell carcinoma.
Small cell carcinoma is a type of carcinoma. It is mostly commonly from the lung; 95% of cases are from the lung.[1]
It may be abbreviated SCC, leading to confusion with squamous cell carcinoma.
Overview
Grouping
May be grouped as:[1]
- Pulmonary.
- Gastrointestinal.
- Genitourinary.
- Small cell carcinoma of the prostate gland - most common small cell carcinoma outside of the lung.[2]
- Small cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder.
- Ovarian small cell carcinoma of the hypercalcemic type.
- Head & neck.
- Breast.
- Other.
Sites other than lung
General
Classic tumour with paraneoplastic syndromes - may be associated with:[7]
- Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH).
- Clinical: hyponatremia.
- Paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration.
- Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome.
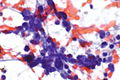
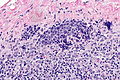
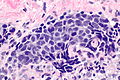
Microscopic
Features:
- Small cells -- typically 15-20 micrometers ~ 2x the size of RBC.
- Scant cytoplasm.
- Stippled chromatin +/- smudging of the chromatin.
- +/-Nuclear moulding.
DDx:
- Endometrial stromal condensation.
- Large cell lymphomas, e.g. DLBCL, ALCL.
- Chloroma.
- Rhabdomyosarcoma - usu. CD56 positive, may be keratin positive and positive for other neuroendocrine markers.[8]
- Atypical lung carcinoid tumour (lung only).
- Typical lung carcinoid tumour (lung only).
- Other small round cell tumours.
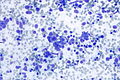
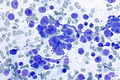
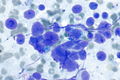
Images
Cytology
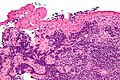
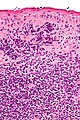
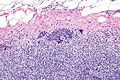
Metastatic
Small cell carcinoma in a lymph node
IHC
- Neuroendocrine markers +ve - confirm the diagnosis.
- IHC not particularity useful for determination of the primary site.[9] ‡
Note:
- ‡ A CT chest should be done to assess for a lung tumour; fortunately, lung small cell carcinoma and extrapulmonary small cell cancer are treated similarily.[10]
See also
- Lung tumours.
- Azzopardi phenomenon.
- Chloroma (AKA granulocytic sarcoma, myeloid sarcoma).
- Neuroendocrine tumours.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Grossman, RA.; Pedroso, FE.; Byrne, MM.; Koniaris, LG.; Misra, S. (May 2011). "Does surgery or radiation therapy impact survival for patients with extrapulmonary small cell cancers?". J Surg Oncol. doi:10.1002/jso.21976. PMID 21618245.
- ↑ Furtado, P.; Lima, MV.; Nogueira, C.; Franco, M.; Tavora, F. (2011). "Review of small cell carcinomas of the prostate.". Prostate Cancer 2011: 543272. doi:10.1155/2011/543272. PMID 22110988.
- ↑ Cesaretti, M.; Guarnieri, A.; Gaggelli, I.; Tirone, A.; Francioli, N.; Carli, AF.. "Small cell carcinoma of the breast. Report of a case.". Ann Ital Chir 82 (1): 61-4. PMID 21657157.
- ↑ Beach, DF.; Klump, WJ.; Haddad, G.; Reid, LM.; Schwarting, R.; Hageboutros, A. (Jun 2011). "Extrapulmonary small cell: a novel case of small cell carcinoma of the thyroid gland.". Med Oncol. doi:10.1007/s12032-011-9996-7. PMID 21644012.
- ↑ Morikawa, H.; Nakayama, Y.; Maeda, T.; Nadatani, Y.; Kobayashi, S.; Iwai, S.; Enomoto, M.; Tamori, A. et al. (Dec 2008). "A case of primary small cell carcinoma of the liver that was treated with chemotherapy.". Hepatol Int 2 (4): 500-4. doi:10.1007/s12072-008-9090-1. PMID 19669327.
- ↑ Choi, SJ.; Kim, JM.; Han, JY.; Ahn, SI.; Kim, JS.; Kim, L.; Park, IS.; Chu, YC. (Dec 2007). "Extrapulmonary small cell carcinoma of the liver: clinicopathological and immunohistochemical findings.". Yonsei Med J 48 (6): 1066-71. doi:10.3349/ymj.2007.48.6.1066. PMID 18159605.
- ↑ Sher, T.; Dy, GK.; Adjei, AA. (Mar 2008). "Small cell lung cancer.". Mayo Clin Proc 83 (3): 355-67. PMID 18316005.
- ↑ Bahrami, A.; Gown, AM.; Baird, GS.; Hicks, MJ.; Folpe, AL. (Jul 2008). "Aberrant expression of epithelial and neuroendocrine markers in alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma: a potentially serious diagnostic pitfall.". Mod Pathol 21 (7): 795-806. doi:10.1038/modpathol.2008.86. PMID 18487991.
- ↑ Lobins, R.; Floyd, J. (Feb 2007). "Small cell carcinoma of unknown primary.". Semin Oncol 34 (1): 39-42. doi:10.1053/j.seminoncol.2006.10.027. PMID 17270664.
- ↑ Brennan, SM.; Gregory, DL.; Stillie, A.; Herschtal, A.; Mac Manus, M.; Ball, DL. (Feb 2010). "Should extrapulmonary small cell cancer be managed like small cell lung cancer?". Cancer 116 (4): 888-95. doi:10.1002/cncr.24858. PMID 20052730.