Programmed death-ligand 1
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
The printable version is no longer supported and may have rendering errors. Please update your browser bookmarks and please use the default browser print function instead.

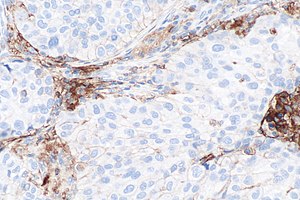
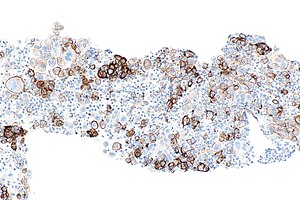
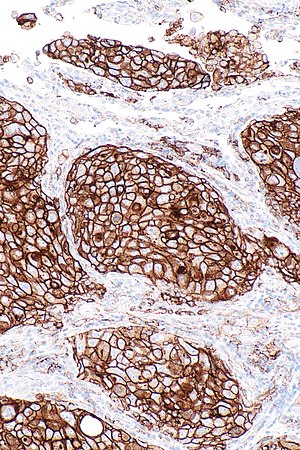
Micrograph showing a PD-L1 positive non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC). PD-L1 immunostain (22C3). (WC)
Programmed death-ligand 1, commonly abbreviated PD-L1, is a protein with an important role in immune system regulation and cancer.
Normally, PD-L1 on cells binds with programmed cell death 1 on the T lymphocytes.[1]
PD-L1 is also known as CD274.[2]
General
- In theory, positive PD-L1 immunostaining predicts response to anti-PD-L1 drugs.[3]
- Carcinoma cell is considered "PD-L1 positive" if the cell membrane is partially or completely stained.[4]
- It is, however, more complex than that. Some tumour types are invariably positive, e.g. classical Hodgkin lymphoma, so testing is unhelpful. In contrast, tumors such as malignant melanoma respond regardless of PD-L1 immunoexpression.
- The plethora of companion diagnostics developed for each PD-1/ PD-L1 inhibitor has created challenges, as these assays include different IHC antibody clones, staining protocols and platforms, scoring systems, and cutoffs for defining positivity.
- Nivolumab - 28-8 (Dako)
- Pembrolizumab - 22C3 (Dako)
- Aterolizumab - SP142 (Ventana)
- Durvalumab - SP263 (Ventana)
- Avelumab - 73-10 (Dako)
Background
Cytotoxic T cell function is regulated by receptor pairs found on the tumour and lymphocyte:[1]
| Function | Tumour cell | T cell |
|---|---|---|
| Antigen presentation | MHC | TCR |
| Signal inhibition | PD-1 | PD-L1 (CD274), PD-L2 (CD273) |
Prognosis
- Good prognosis - in high-grade ovarian serous carcinoma, associated with tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes.[5]
Drugs - Immune checkpoint inhibitors
- PD-1 inhibitors:
- Nivolumab (Opdivo, Bristol-Myers Squibb).
- Pembrolizumab (Keytruda, Merck).
- PD-L1 inhibitors:
- Atezolizumab (Tecentriq, Roche).[3]
- Durvalumab (Imfinzi, AstraZeneca).
- Avelumab (Bavencio, Merck/Pfizer).
Anti-PD-L1 drugs - use
PD-L1 antibodies are being used to treat:[6]
- Malignant melanoma.
- Non-small cell lung cancer.
- Associated with response predicted by tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes and PD-L1 IHC positivity of the tumour cells.[3]
- Renal cell carcinoma.
- Urothelial carcinoma.
- Merkel cell carcinoma
- Acute myeloid leukemia
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Ribas, A. (Jun 2012). "Tumor immunotherapy directed at PD-1.". N Engl J Med 366 (26): 2517-9. doi:10.1056/NEJMe1205943. PMID 22658126.
- ↑ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 605402
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Fehrenbacher, L.; Spira, A.; Ballinger, M.; Kowanetz, M.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Mazieres, J.; Park, K.; Smith, D. et al. (Mar 2016). "Atezolizumab versus docetaxel for patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (POPLAR): a multicentre, open-label, phase 2 randomised controlled trial.". Lancet. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(16)00587-0. PMID 26970723.
- ↑ Scheel, AH.; Dietel, M.; Heukamp, LC.; Jöhrens, K.; Kirchner, T.; Reu, S.; Rüschoff, J.; Schildhaus, HU. et al. (Oct 2016). "Harmonized PD-L1 immunohistochemistry for pulmonary squamous-cell and adenocarcinomas.". Mod Pathol 29 (10): 1165-72. doi:10.1038/modpathol.2016.117. PMID 27389313.
- ↑ Webb, JR.; Milne, K.; Kroeger, DR.; Nelson, BH. (May 2016). "PD-L1 expression is associated with tumor-infiltrating T cells and favorable prognosis in high-grade serous ovarian cancer.". Gynecol Oncol 141 (2): 293-302. doi:10.1016/j.ygyno.2016.03.008. PMID 26972336.
- ↑ Gandini, S.; Massi, D.; Mandalà, M. (Apr 2016). "PD-L1 expression in cancer patients receiving anti PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies: A systematic review and meta-analysis.". Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 100: 88-98. doi:10.1016/j.critrevonc.2016.02.001. PMID 26895815.