Difference between revisions of "Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumour"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(tweak) |
(→IHC) |
||
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
| Micro = inflammation ([[plasma cells]] - predominant, lymphocytes, eosinophils), [[spindle cells]] without atypia +/-fascicular architecture, +/-mitoses (none atypical), +/-[[necrosis]], +/-hemorrhage, +/-calcification | | Micro = inflammation ([[plasma cells]] - predominant, lymphocytes, eosinophils), [[spindle cells]] without atypia +/-fascicular architecture, +/-mitoses (none atypical), +/-[[necrosis]], +/-hemorrhage, +/-calcification | ||
| Subtypes = | | Subtypes = | ||
| LMDDx = [[calcifying fibrous pseudotumour]], [[inflammatory fibroid tumour]], [[nodular fasciitis]], [[gastrointestinal stromal tumour]] | | LMDDx = [[calcifying fibrous pseudotumour]], [[inflammatory fibroid tumour]], [[nodular fasciitis]], [[gastrointestinal stromal tumour]], [[epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma]] | ||
| Stains = | | Stains = | ||
| IHC = | | IHC = | ||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
*Mostly benign. | *Mostly benign. | ||
*Children & young adults. | *Children & young adults. | ||
May be treated with: | |||
*[[ALK inhibitors]].<ref name=pmid30790150>{{Cite journal | last1 = Honda | first1 = K. | last2 = Kadowaki | first2 = S. | last3 = Kato | first3 = K. | last4 = Hanai | first4 = N. | last5 = Hasegawa | first5 = Y. | last6 = Yatabe | first6 = Y. | last7 = Muro | first7 = K. | title = Durable response to the ALK inhibitor alectinib in inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of the head and neck with a novel SQSTM1-ALK fusion: a case report. | journal = Invest New Drugs | volume = | issue = | pages = | month = Feb | year = 2019 | doi = 10.1007/s10637-019-00742-2 | PMID = 30790150 }}</ref> | |||
*Drugs that act on ROS1 rearrangements, e.g. [[crizotinib]].<ref name=pmid30642440>{{Cite journal | last1 = Mai | first1 = S. | last2 = Xiong | first2 = G. | last3 = Diao | first3 = D. | last4 = Wang | first4 = W. | last5 = Zhou | first5 = Y. | last6 = Cai | first6 = R. | title = Case report: Crizotinib is effective in a patient with ROS1-rearranged pulmonary inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor. | journal = Lung Cancer | volume = 128 | issue = | pages = 101-104 | month = Feb | year = 2019 | doi = 10.1016/j.lungcan.2018.12.016 | PMID = 30642440 }}</ref> | |||
==Gross== | ==Gross== | ||
| Line 61: | Line 65: | ||
*[[Gastrointestinal stromal tumour]].<ref name=pmid24938355>{{Cite journal | last1 = Kataoka | first1 = TR. | last2 = Yamashita | first2 = N. | last3 = Furuhata | first3 = A. | last4 = Hirata | first4 = M. | last5 = Ishida | first5 = T. | last6 = Nakamura | first6 = I. | last7 = Hirota | first7 = S. | last8 = Haga | first8 = H. | last9 = Katsuyama | first9 = E. | title = An inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor exhibiting immunoreactivity to KIT: a case report focusing on a diagnostic pitfall. | journal = World J Surg Oncol | volume = 12 | issue = | pages = 186 | month = | year = 2014 | doi = 10.1186/1477-7819-12-186 | PMID = 24938355 }}</ref> | *[[Gastrointestinal stromal tumour]].<ref name=pmid24938355>{{Cite journal | last1 = Kataoka | first1 = TR. | last2 = Yamashita | first2 = N. | last3 = Furuhata | first3 = A. | last4 = Hirata | first4 = M. | last5 = Ishida | first5 = T. | last6 = Nakamura | first6 = I. | last7 = Hirota | first7 = S. | last8 = Haga | first8 = H. | last9 = Katsuyama | first9 = E. | title = An inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor exhibiting immunoreactivity to KIT: a case report focusing on a diagnostic pitfall. | journal = World J Surg Oncol | volume = 12 | issue = | pages = 186 | month = | year = 2014 | doi = 10.1186/1477-7819-12-186 | PMID = 24938355 }}</ref> | ||
*[[IgG4-related systemic disease]].<ref name=pmid21297584/> | *[[IgG4-related systemic disease]].<ref name=pmid21297584/> | ||
*[[Epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma]]. | |||
Notes: | Notes: | ||
| Line 78: | Line 83: | ||
*CD117 -ve. | *CD117 -ve. | ||
**Case report of CD117 +ve.<ref name=pmid24938355/> | **Case report of CD117 +ve.<ref name=pmid24938355/> | ||
*CD30 -ve. | |||
Variable staining with: | Variable staining with: | ||
| Line 87: | Line 93: | ||
==Molecular== | ==Molecular== | ||
*ALK rearrangements.<ref name=pmid21297584/> | *ALK rearrangements.<ref name=pmid21297584/> | ||
*ROS1 rearrangements.<ref name=pmid30642440>{{Cite journal | last1 = Mai | first1 = S. | last2 = Xiong | first2 = G. | last3 = Diao | first3 = D. | last4 = Wang | first4 = W. | last5 = Zhou | first5 = Y. | last6 = Cai | first6 = R. | title = Case report: Crizotinib is effective in a patient with ROS1-rearranged pulmonary inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor. | journal = Lung Cancer | volume = 128 | issue = | pages = 101-104 | month = Feb | year = 2019 | doi = 10.1016/j.lungcan.2018.12.016 | PMID = 30642440 }}</ref> | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
Latest revision as of 00:28, 26 March 2024
Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumour, abbreviated IMT, is an uncommon soft tissue lesion.
| Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumour | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
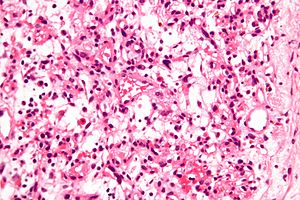 Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumour. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | inflammation (plasma cells - predominant, lymphocytes, eosinophils), spindle cells without atypia +/-fascicular architecture, +/-mitoses (none atypical), +/-necrosis, +/-hemorrhage, +/-calcification |
| LM DDx | calcifying fibrous pseudotumour, inflammatory fibroid tumour, nodular fasciitis, gastrointestinal stromal tumour, epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma |
| Site | soft tissue - see fibroblastic/myofibroblastic tumours |
|
| |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
| Prognosis | benign |
| Clin. DDx | other soft tissue lesions |
It is also known as inflammatory pseudotumour, and inflammatory fibrosarcoma[1] and plasma cell granuloma.[2][3]
General
- Mostly benign.
- Children & young adults.
May be treated with:
- ALK inhibitors.[4]
- Drugs that act on ROS1 rearrangements, e.g. crizotinib.[5]
Gross
- Classically located in mesentery of ileocolic region or small bowel.[1]
- May be seen in the urinary bladder.[6]
Microscopic
Features:[1]
- Inflammation:
- Plasma cells - predominant - key feature.[7]
- Lymphocytes.
- Eosinophils.
- Spindle cells without atypia.
- +/-Fascicular architecture.
- Mitoses -- though none atypical.
- +/-Necrosis.
- +/-Hemorrhage.
- Calcifications.
DDx:
- Calcifying fibrous pseudotumour (has psammomatous calcifications).
- Inflammatory fibroid tumour.
- Nodular fasciitis.
- Gastrointestinal stromal tumour.[8]
- IgG4-related systemic disease.[7]
- Epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma.
Notes:
- Some consider this a wastebasket diagnosis... for benign appearing spindle cell lesions.[9]
Images
IHC
Features - dependent on site:
Variable staining with:
Negative:[10]
- S100, CD117, CD68.
Molecular
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 610. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ URL: http://www.uptodate.com/contents/inflammatory-myofibroblastic-tumor-plasma-cell-granuloma-of-the-lung. Accessed on: 27 November 2011.
- ↑ Manohar, B.; Bhuvaneshwari, S. (Jan 2011). "Plasma cell granuloma of gingiva.". J Indian Soc Periodontol 15 (1): 64-6. doi:10.4103/0972-124X.82275. PMID 21772725.
- ↑ Honda, K.; Kadowaki, S.; Kato, K.; Hanai, N.; Hasegawa, Y.; Yatabe, Y.; Muro, K. (Feb 2019). "Durable response to the ALK inhibitor alectinib in inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of the head and neck with a novel SQSTM1-ALK fusion: a case report.". Invest New Drugs. doi:10.1007/s10637-019-00742-2. PMID 30790150.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Mai, S.; Xiong, G.; Diao, D.; Wang, W.; Zhou, Y.; Cai, R. (Feb 2019). "Case report: Crizotinib is effective in a patient with ROS1-rearranged pulmonary inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor.". Lung Cancer 128: 101-104. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2018.12.016. PMID 30642440.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Tsuzuki, T.; Magi-Galluzzi, C.; Epstein, JI. (Dec 2004). "ALK-1 expression in inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of the urinary bladder.". Am J Surg Pathol 28 (12): 1609-14. PMID 15577680.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Saab, ST.; Hornick, JL.; Fletcher, CD.; Olson, SJ.; Coffin, CM. (Apr 2011). "IgG4 plasma cells in inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor: inflammatory marker or pathogenic link?". Mod Pathol 24 (4): 606-12. doi:10.1038/modpathol.2010.226. PMID 21297584.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Kataoka, TR.; Yamashita, N.; Furuhata, A.; Hirata, M.; Ishida, T.; Nakamura, I.; Hirota, S.; Haga, H. et al. (2014). "An inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor exhibiting immunoreactivity to KIT: a case report focusing on a diagnostic pitfall.". World J Surg Oncol 12: 186. doi:10.1186/1477-7819-12-186. PMID 24938355.
- ↑ URL: http://www.pathconsultddx.com/pathCon/diagnosis?pii=S1559-8675%2806%2970283-2. Accessed on: 10 May 2011.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 Shi, H.; Li, Y.; Wei, L.; Sun, L. (Apr 2010). "Primary colorectal inflammatory myofibroblastic tumour: a clinicopathological and immunohistochemical study of seven cases.". Pathology 42 (3): 235-41. doi:10.3109/00313021003631312. PMID 20350216.
- ↑ Miyamoto, H.; Montgomery, EA.; Epstein, JI. (Apr 2010). "Paratesticular fibrous pseudotumor: a morphologic and immunohistochemical study of 13 cases.". Am J Surg Pathol 34 (4): 569-74. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e3181d438cb. PMID 20216379.