Small cell carcinoma of the lung
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
'Small cell carcinoma of the lung, also small cell lung carcinoma (abbreviated SCLC)[1] is an aggressive malignant tumour of the lung. It is strongly associated with smoking.
General
- Strong association with smoking.
- Typically treated with chemotherapy.
- Poor prognosis.
On a spectrum of lesions (benign to malignant):[1]
- Tumourlet.
- Carcinoid.
- Atypical carcinoid.
- Small cell carinoma/large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma.
Precursor lesion - uncommonly seen:
- Pulmonary neuroendocrine cell hyperplasia.[1]
Gross
- Central location (close to large airways) - typical.
- Necrosis.
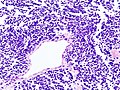
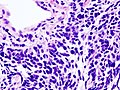
Microscopic
Features:
- Stippled chromatin.
- High NC ratio, scant basophilic cytoplasm.
- Typically small cells ~2x RBC diameter.
- +/-Nuclear moulding.
- Necrosis.
- Mitoses.
Notes:
- There should be no nucleolus.
DDx:
- Metastatic small cell carcinoma.
- Lymphoma.
- Atypical carcinoid.
- Other small round blue cell tumours.
- Large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma (LCNEC).
Images
IHC
- Synaptophysin +ve.
- May be very weak.
- TTF-1 +ve (15 of 16 cases).[2]
Sign out
LOWER LOBE OF LUNG, LEFT, CORE BIOPSY: - SMALL CELL CARCINOMA.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Travis, WD. (Oct 2010). "Advances in neuroendocrine lung tumors.". Ann Oncol 21 Suppl 7: vii65-71. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdq380. PMID 20943645.
- ↑ Wu, M.; Szporn, AH.; Zhang, D.; Wasserman, P.; Gan, L.; Miller, L.; Burstein, DE. (Oct 2005). "Cytology applications of p63 and TTF-1 immunostaining in differential diagnosis of lung cancers.". Diagn Cytopathol 33 (4): 223-7. doi:10.1002/dc.20337. PMID 16138374.