Serous carcinoma of the ovary
Serous carcinoma of the ovary, also ovarian serous carcinoma, is relatively common malignant ovarian tumour.
| Serous carcinoma of the ovary | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
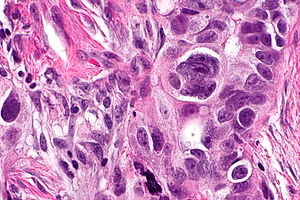 Serous carcinoma. H&E stain. | |
| LM DDx | serous carcinoma from other sites, clear cell carcinoma of the ovary, poorly differentiated endometrioid carcinoma of the ovary, ovarian serous borderline tumour for low-grade tumours |
| IHC | WT-1 +ve, CK7 +ve, ER +ve, HNF-1beta -ve |
| Molecular | +/-BRCA1 mutation, +/-BRCA2 mutation |
| Gross | solid and cystic, serous fluid |
| Site | ovary - see ovarian tumours |
|
| |
| Signs | adnexal mass |
| Blood work | CA-125 elevated |
| Radiology | complex mass with solid and cystic area, often large |
| Prognosis | poor for high-grade |
| Treatment | surgery, chemotherapy |
General
- Most common malignant ovarian tumour in the eldery.
- Poor prognosis.
- May be associated with a BRCA1 gene or BRCA2 gene mutation.[1]
- Approximately 20% of high-grade serous carcinoma are associated with BRCA1 or BRCA2.[2]
Precursors lesions:
- Serous borderline tumours for low-grade serious carcinoma.
- Serous tubal intraepithelial carcinoma (STIC)[3] for high-grade serous carcinoma.
Gross
- Ovarian mass.
- Typically solid with multiple cystic areas.
- Often >10 cm.
Note:
- Lesions <10 cm and unilocular are usually benign.[4]
Microscopic
Features:
- Nuclear pleomorphism:
- Variation in size - often marked.
- Variation in staining.
- Variation in shape.
- +/-Macronucleolus - key feature.
- Eccentric nucleus.
- Architecture:
- Solid.
- Papillary - classic.
- Glandular - uncommon.
- +/-Psammoma bodies - uncommon.
- +/-Necrosis - often extensive.
DDx:
- Clear cell carcinoma of the ovary - less nuclear size variation.
- Endometrioid carcinoma of the ovary - usu. lower grade.
- Primary peritoneal serous carcinoma - bulk of tumour in peritoneum, small ovarian tumour.
- Other non-ovarian serous carcinomas - see serous carcinoma.
- Ovarian serous borderline tumour - mild to moderate nuclear atypia, no invasion, few mitoses.
Grading
Serous carcinoma is subdivided into:[5][6]
| Grade | Nuclear atypia (most important) | Mitotic rate |
|---|---|---|
| Low-grade (Type I) | mild/moderate atypia: round/oval nuclei, evenly distributed chromatin, +/-conspicuous nucleoli |
<=12 mitoses/10 HPFs † |
| High-grade (Type II) | severe atypia: >=3:1 size variation, irregular chromatin, +/-macronucleoli |
>12 mitoses/10 HPFs † |
Notes:
- † Definition suffers from HPFitis.
- In fairness, the paper[6] notes that the Olympus BH2 microscope was used. The 40x objective on this microscope has a field diameter of 0.5 mm, according to a manual found online.[7] Assuming this is so, the field area is 0.19635 mm2. Thus, in standard units, the cut-point would be 6.1115 mitoses/1 mm2 and the sample area 1.9635 mm2.
- Tumours very rarely transform from low-grade to high-grade.[8]
Images
www:
IHC
Others:
- HNF-1beta -ve.[12][13]
- Usually +ve in clear cell carcinoma of the ovary.
- PAX2 +ve.
- Usually -ve in malignant mesothelioma.[14]
Sign out
A. RIGHT OVARY, BIOPSY: - SEROUS CARCINOMA, HIGH-GRADE. - PSAMMOMATOUS CALCIFICATIONS. B. OMENTUM, BIOPSY: - SEROUS CARCINOMA, HIGH-GRADE. - PSAMMOMATOUS CALCIFICATIONS. COMMENT: The morphology is compatible with a serous carcinoma (prominent nucleoli, large nuclear size variation, psammomatous calcifications). The immunostaining is that of a serous carcinoma: POSITIVE: CK7, ER, PR (focal), CA-125, WT-1. NEGATIVE: CK20, p53. The ovary has multiple small tumour nodules. The status of the opposite ovary is unknown. The bulk of the tumour in the specimen provided is in the omentum. Clinical and radiologic correlation is suggested for the determination of the primary site of this serous carcinoma. High-grade serous carcinoma of ovary/fallopain tube/periteonum is associated with BRCA1/2 mutation in approximately 20% of patients. Referral to genetic counselling is recommended.
See also
References
- ↑ Demsky, R.; McCuaig, J.; Maganti, M.; Murphy, KJ.; Rosen, B.; Armel, SR. (Aug 2013). "Keeping it simple: genetics referrals for all invasive serous ovarian cancers.". Gynecol Oncol 130 (2): 329-33. doi:10.1016/j.ygyno.2013.05.003. PMID 23707676.
- ↑ Schrader, KA.; Hurlburt, J.; Kalloger, SE.; Hansford, S.; Young, S.; Huntsman, DG.; Gilks, CB.; McAlpine, JN. (Aug 2012). "Germline BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations in ovarian cancer: utility of a histology-based referral strategy.". Obstet Gynecol 120 (2 Pt 1): 235-40. doi:10.1097/AOG.0b013e31825f3576. PMID 22776961.
- ↑ Vang, R.; Shih, IeM.; Kurman, RJ. (Jan 2013). "Fallopian tube precursors of ovarian low- and high-grade serous neoplasms.". Histopathology 62 (1): 44-58. doi:10.1111/his.12046. PMID 23240669.
- ↑ Bailey, CL.; Ueland, FR.; Land, GL.; DePriest, PD.; Gallion, HH.; Kryscio, RJ.; van Nagell, JR. (Apr 1998). "The malignant potential of small cystic ovarian tumors in women over 50 years of age.". Gynecol Oncol 69 (1): 3-7. doi:10.1006/gyno.1998.4965. PMID 9570990.
- ↑ Vang, R.; Shih, IeM.; Kurman, RJ. (Sep 2009). "Ovarian low-grade and high-grade serous carcinoma: pathogenesis, clinicopathologic and molecular biologic features, and diagnostic problems.". Adv Anat Pathol 16 (5): 267-82. doi:10.1097/PAP.0b013e3181b4fffa. PMID 19700937.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Malpica, A.; Deavers, MT.; Lu, K.; Bodurka, DC.; Atkinson, EN.; Gershenson, DM.; Silva, EG. (Apr 2004). "Grading ovarian serous carcinoma using a two-tier system.". Am J Surg Pathol 28 (4): 496-504. PMID 15087669.
- ↑ URL: [www.alanwood.net/downloads/olympus-bh-2-bht-manual.pdf www.alanwood.net/downloads/olympus-bh-2-bht-manual.pdf]. Accessed on: 1 January 2014.
- ↑ Garg, K.; Park, KJ.; Soslow, RA. (Sep 2012). "Low-grade serous neoplasms of the ovary with transformation to high-grade carcinomas: a report of 3 cases.". Int J Gynecol Pathol 31 (5): 423-8. doi:10.1097/PGP.0b013e31824ae6f2. PMID 22833081.
- ↑ Ayhan, A.; Kurman, RJ.; Yemelyanova, A.; Vang, R.; Logani, S.; Seidman, JD.; Shih, IeM. (Aug 2009). "Defining the cut point between low-grade and high-grade ovarian serous carcinomas: a clinicopathologic and molecular genetic analysis.". Am J Surg Pathol 33 (8): 1220-4. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e3181a24354. PMC 2716424. PMID 19461510. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2716424/.
- ↑ Köbel, M.; Kalloger, SE.; Carrick, J.; Huntsman, D.; Asad, H.; Oliva, E.; Ewanowich, CA.; Soslow, RA. et al. (Jan 2009). "A limited panel of immunomarkers can reliably distinguish between clear cell and high-grade serous carcinoma of the ovary.". Am J Surg Pathol 33 (1): 14-21. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e3181788546. PMID 18830127.
- ↑ DeLair, D.; Oliva, E.; Köbel, M.; Macias, A.; Gilks, CB.; Soslow, RA. (Jan 2011). "Morphologic spectrum of immunohistochemically characterized clear cell carcinoma of the ovary: a study of 155 cases.". Am J Surg Pathol 35 (1): 36-44. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e3181ff400e. PMID 21164285.
- ↑ Tsuchiya, A.; Sakamoto, M.; Yasuda, J.; Chuma, M.; Ohta, T.; Ohki, M.; Yasugi, T.; Taketani, Y. et al. (Dec 2003). "Expression profiling in ovarian clear cell carcinoma: identification of hepatocyte nuclear factor-1 beta as a molecular marker and a possible molecular target for therapy of ovarian clear cell carcinoma.". Am J Pathol 163 (6): 2503-12. PMID 14633622. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1892387/?tool=pubmed.
- ↑ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 189907
- ↑ Gao, FF.; Krasinskas, AM.; Chivukula, M. (May 2012). "Is PAX2 a reliable marker in differentiating diffuse malignant mesotheliomas of peritoneum from serous carcinomas of müllerian origin?". Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 20 (3): 272-6. doi:10.1097/PAI.0b013e3182366531. PMID 22498671.