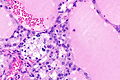
Unclassified renal cell carcinoma
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Unclassified renal cell carcinoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
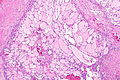
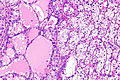
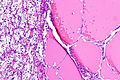
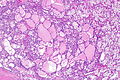
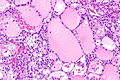
 Unclassified renal cell carcinoma with thyroid-like and clear cell-like areas. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | One of the following: (1) a combination of other RCC histologic types, (2) "non-identifiable" pattern/unrecognizable cell type (3) pure sarcomatoid RCC without an identifiable (epithelioid) RCC subtype |
| LM DDx | clear cell renal cell carcinoma, collecting duct carcinoma, undifferentiated carcinoma extending into kidney, kidney metastasis, retroperitoneal sarcoma, newly described renal tumour or emerging entity - see Vancouver classification, collision tumour |
| Gross | kidney mass |
| Grossing notes | partial nephrectomy grossing, total nephrectomy for tumour grossing |
| Staging | kidney cancer staging |
| Site | kidney - see kidney tumours |
|
| |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
| Prognosis | poor |
| Clin. DDx | other renal tumours |
| Treatment | excision if feasible |
Unclassified renal cell carcinoma, abbreviated URCC, is a malignant epithelial tumour arising from the kidney parenchyma, i.e. a renal cell carcinoma, that cannot be further classified.
General
- Uncommon.
- A WHO classification diagnosis of exclusion.
- Worse prognosis than clear cell renal cell carcinoma.[1]
- High variation in the prevalence (when comparing institutions); this suggests a lack of uniformity in the diagnosis of this subtype.[1]
Gross
- Mass lesion arising from the kidney - solid and/or cystic.
- Confined to kidney or predominantly within the kidney.
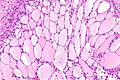
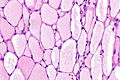
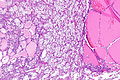
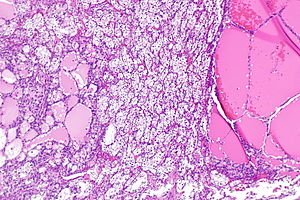
Microscopic
Features:
- Malignant tumour that is one of the following:[2][3]
- A combination of other RCC histologic types (~35% of cases of URCC).
- Has a "non-identifiable" pattern/unrecognizable cell type (~60% of cases of URCC).
- Pure sarcomatoid RCC without an identifiable (epithelioid) RCC subtype (~5% of cases of URCC).[3]
DDx:
- Clear cell renal cell carcinoma.
- Collecting duct carcinoma.
- Undifferentiated carcinoma.
- Kidney metastasis - typically metastatic carcinoma.
- Retroperitoneal sarcoma, e.g. pleomorphic undifferentiated sarcoma.
- Newly described renal tumour or emerging entity - see Vancouver classification.
- Collision tumour, e.g. urothelial carcinoma and identifiable renal cell carcinoma.
Images
Case
IHC
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Karakiewicz, PI.; Hutterer, GC.; Trinh, QD.; Pantuck, AJ.; Klatte, T.; Lam, JS.; Guille, F.; de La Taille, A. et al. (Oct 2007). "Unclassified renal cell carcinoma: an analysis of 85 cases.". BJU Int 100 (4): 802-8. doi:10.1111/j.1464-410X.2007.07148.x. PMID 17822461.
- ↑ Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 293. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Lopez-Beltran, A.; Kirkali, Z.; Montironi, R.; Blanca, A.; Algaba, F.; Scarpelli, M.; Yorukoglu, K.; Hartmann, A. et al. (Sep 2012). "Unclassified renal cell carcinoma: a report of 56 cases.". BJU Int 110 (6): 786-93. doi:10.1111/j.1464-410X.2012.10934.x. PMID 22404824.
- ↑ Carvalho, JC.; Thomas, DG.; McHugh, JB.; Shah, RB.; Kunju, LP. (Mar 2012). "p63, CK7, PAX8 and INI-1: an optimal immunohistochemical panel to distinguish poorly differentiated urothelial cell carcinoma from high-grade tumours of the renal collecting system.". Histopathology 60 (4): 597-608. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2559.2011.04093.x. PMID 22260386.