Mesothelial cytopathology
Mesothelial cytopathology is a large part of cytopathology. The article deals with cytopathology specimens from spaces lined with mesothelium, i.e. it deals with pericardial fluid, peritoneal fluid and pleural fluid.
An introduction to cytopathology is in the cytopathology article.
A general differential diagnosis of pleural effusion is given in the pleural effusion article.
Pleural fluid redirects to here.
Specimen types
- Wash, e.g. peritoneal wash: expect sheets of (benign squamous) cells.
- Spontaneous, e.g. pleural fluid: usually no large sheets.
Note: This distinction is important as wash specimens may have pseudopapillae.
Approach
Look for:
- Two cell populations.
- Large dark objects.
- Boerner's red flags.
Boerner's red flags:
- 3-D clusters.
- Doublet & triplets common.
- Quads-to-Quints - sweat breaks-out.
- Sextuplets... very nervous.
- "Busy" slide:
- Nuclear pleomorphism.
- Too many "intermediate cells".
- Mitoses - 1-2/slide is "many".
- Vacuolated cytoplasm.
- Small cells with high NC ratio.
Features of malignancy
Strongly suggestive of malignancy:
- 3-D clusters.
- Large clusters.
- Highly cellularity.
- Irregular nucleoli.
- Group pleomorphism.
May be suggestive:
- High NC ratio.
Differential diagnosis
- Adenocarcinoma not otherwise specified (NOS) - most common.
- Reactive mesothelium.
- Malignant mesothelioma.
- Serous carcinoma.
- Lymphoma.
Less common:
- Squamous carcinoma.
- Rheumatoid pleuritis.
- Systemic lupus erythematosus pleurisy.
- Endosalpingiosis.
- Endometriosis.
- Small cell carcinoma.
Peritoneal cavity specific
- Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) may be associated with ascites... but it is rarely positive for malignant cells.[1]
- HCC in ascites fluid is super rare -- I haven't seen a case.[2]
Normal mesothelium
Features:[3]
- "Window" or "space" between attached cells (due to microvilli).
- Cytoplasmic blebs.
- Bleb = "drop" of cytoplasm at cell periphery.
- +/-Multinucleated.
- Variable size (normal).
- Nucleoli (in reactive cells).
Note - abnormal features:
- Large clusters of cells, e.g. 150+ micrometres.
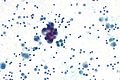
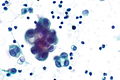
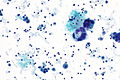
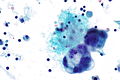
Images
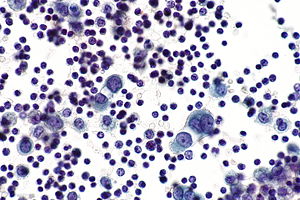
Reactive mesothelium
Sign out
Pleural Fluid, Right, Thoracentesis: - Negative for malignant cells. - Reactive mesothelial cells present in a background of abundant lymphocytes. Comment: Additional sampling should be considered within the clinical context.
Specific diagnoses - benign
Eosinophilic pleuritis
General
This has a large DDx:
- Trauma with air in the pleural cavity.
- Repeated tap in the context of pneumothorax.
- Pulmonary infarct.
- Pneumonia.
- Parasitic infections.
- Hodgkin lymphoma.
- Idiopathic - most common cause.
Cytology
Features:
- Eosinophils >10%.
Rheumatoid pleuritis
General
- History of rheumatoid arthritis.
- Cytologic appearance considered to be pathognomonic.[4]
Cytology
Features:[4]
- Large (single) multinucleated cells - classically spindled.
- May have epithelioid morphology.
- Necrotic debris - fluffy orange-to-blue crap.
Note:
- Necrotizing granulomatous inflammation.
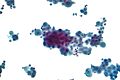
Systemic lupus erythematosus pleurisy
- AKA systemic lupus erythematosus pleuritis.
General
- Not common.
- Distinctive cytology.
Cytology
Features:
- Lupus erythematosus cells, usually abbreviated LE cells:[5]
Image:
Specific diagnoses - malignant
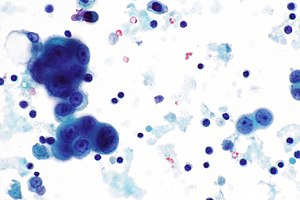
Malignant mesothelioma
General
- Can be challenging to diagnose.
- NC ratio may be normal in mesothelioma.
- Large NC ratios may be seen in reactive mesothelial cells.
- Focal hyperchromasia is seen in reactive mesothelial cells.
- Focal macronucleoli are seen in reactive mesothelial cells.
Cytopathology
Features:[7]
- Nuclear membrane irregularies (rare).
- Hyperchromasia - diffuse.
- 3-D clusters of cells (strongly suggestive).
- Clusters of cells with "knobby" border; border is hobnail-like.
- Large clusters of cells; >10 cells in a cluster (rare in benign).
- Large NC ratio (common - not specific).
- Gigantic cells; cells 2X+ neighbouring mesothelial cell (uncommon - but strong).
- Nucleoli:
- Macronucleoli - must be widespread (not common - strong).
- Multiple nucleoli.
- Irregular nucleoli (strong).
Notes:
- Single cells/small clusters - suggestive of mesothelioma vs. serous carcinoma. (???)
Mesothelioma versus reactive mesothelium:[7]
| Characteristic | Reactive mesothelial cells | Mesothelioma |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Flat sheets | 3-D groups |
| Group size | Small, <10 cells | Large, >10 cells |
| Nuclear atypia - see Note 1. | +/-Hyperchromasia, +/-focal atypia | +/-Widespread atypia |
| Large cells | +/-Yes | No |
| Nucleoli | Common - small, focal large | +/-Large widespread, +/-multiple |
Note 1:
- Best assessed on single cells.
Images
www:
IHC
Adenocarcinoma
Cytology
Adenocarcinoma in fluid - features:[8]
- Classically large morules (clusters of cells that are heaped/are "3-dimensional"), known as cannonballs, with "community borders".
- "Community border" = smooth, low surface area border; should be differentiated from a "knobby" border seen in mesothelioma.
- Intracytoplasmic "lumens"/inclusions (think lobular carcinoma).
DDx of cannonballs:[8]
- Breast.
- Ovary.
- Lung.
- GI.
Images
Colorectal adenocarcinoma
- May be abbreviated CRA.
General
- Cytology may be distinctive.
Cytology
Features:
- Cannonballs (non-specific).
- Suggestive of CRA:[8]
- Pseudostratified cells.
- Columnar cells.
Note:
- See adenocarcinoma section above for other types of adenocarcinoma.
Serous carcinoma
General
- S. Boerner believes one can and ought to separate adenocarcinoma from serous carcinoma.
Microscopic
Features:
- Large nucleoli.[9]
- Cilia.[10]
- Abnormal architecture:[11]
- Large clusters of cells / micropapillae (?).
- Nuclear overlap.
- +/-True papillae.[12]
Note 1 - classic features of serous (see gynecologic pathology article):
- Columnar cells.
- Cilia.
- Papillae.
- Psammoma bodies.
DDx of serous carcinoma (found in ascites fluid):
- Cervix.
- Endometrium.
- Intravacuolar neutrophils are erroneously believed to be indicative of this.[12]
- Uterine tube.
- Ovary.
- Primary peritoneal.
Images
www:
IHC
- WT-1 +ve.
- CA-125 +ve.
- D2-40 +ve.
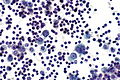
Lymphoma
General
- Can only be reasonably certain for large cell lymphomas, e.g. DLBCL.
- The diagnosis of small cell lymphomas relies on architecture and immunostains.
Cytology
Features:
- Dyscohesive cells ~2x a resting lymphocyte - usually with scant blue cytoplasm.
DDx:
Images
See also
References
- ↑ Lefkowitch, Jay H. (2006). Anatomic Pathology Board Review (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 679. ISBN 978-1416025887.
- ↑ SB. 8 January 2010.
- ↑ Lefkowitch, Jay H. (2006). Anatomic Pathology Board Review (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 674. ISBN 978-1416025887.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Naylor, B.. "The pathognomonic cytologic picture of rheumatoid pleuritis. The 1989 Maurice Goldblatt Cytology award lecture.". Acta Cytol 34 (4): 465-73. PMID 2197838.
- ↑ URL:http://www.tabers.com/tabersonline/ub/view/Tabers/143167/34/L_E__cell. Accessed on: 12 April 2012.
- ↑ URL: http://library.med.utah.edu/WebPath/IMMHTML/IMM008.html. Accessed on: 12 April 2012.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Tadrous, Paul.J. Diagnostic Criteria Handbook in Histopathology: A Surgical Pathology Vade Mecum (1st ed.). Wiley. pp. 359-60. ISBN 978-0470519035.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Lefkowitch, Jay H. (2006). Anatomic Pathology Board Review (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 675. ISBN 978-1416025887.
- ↑ Kuebler, DL.; Nikrui, N.; Bell, DA.. "Cytologic features of endometrial papillary serous carcinoma.". Acta Cytol 33 (1): 120-6. PMID 2916358.
- ↑ http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/journal/112702002/abstract?CRETRY=1&SRETRY=0
- ↑ Weir, MM.; Bell, DA. (Oct 2001). "Cytologic identification of serous neoplasms in peritoneal fluids.". Cancer 93 (5): 309-18. PMID 11668465.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Boerner, S. 12 January 2010.