Invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast is the most common form of invasive breast cancer. It arises from ductal carcinoma in situ.
| Invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
 | |
|
| |
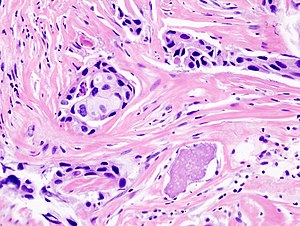
| LM | Invasive ductal carcinoma. H&E stain. |
| LM DDx | DCIS, invasive lobular carcinoma |
| EM | usu. ER and PR +ve, usu. HER2 -ve, mammoglobin +ve, CK7 +ve, CK20 -ve |
| Site | breast |
|
| |
| Signs | +/-palpable breast mass |
| Prevalence | common |
| Prognosis | dependent on stage and grade, good to poor |
| Clin. DDx | other breast tumours |
It is also known as NST (No Specific Type). Generically, it may be referred to as invasive mammary carcinoma.
General
- Most common type of invasive breast cancer.
Gross
- White, firm stellate lesion.
Microscopic
Features:
- Atypical cells:
- Usually >2x RBC diameter.
- Nucleoli common.
- Forming ducts or sheets.
- +/-Mitoses.
- +/-Necrosis.
- Evidence of invasion:
- Atypical nucleus adjacent to adipocyte - diagnostic.
- "Infiltrative" pattern:
- Small glands of variable size within desmoplastic stroma.
- Glands lined by a single layer of cells.
DDx:
IHC
Myoepithelial markers - diagnostic for invasion:
- SMMS -ve.
- p63 -ve.
Prognostic markers - may be useful for metastates:
- ER +ve (diffuse).
- PR +ve (diffuse).
- HER2 -ve.
Invasive lobular carcinoma versus invasive ductal carcinoma:[1]
- E-cadherin -ve (includes incomplete membrane staining).
See also
References
- ↑ de Deus Moura, R.; Wludarski, SC.; Carvalho, FM.; Bacchi, CE. (Jan 2013). "Immunohistochemistry applied to the differential diagnosis between ductal and lobular carcinoma of the breast.". Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 21 (1): 1-12. doi:10.1097/PAI.0b013e318255bafa. PMID 22595945.