Difference between revisions of "Sertoli cell tumour"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→IHC) |
(→IHC) |
||
| Line 69: | Line 69: | ||
*Alpha-inhibin +ve (~95% of cases<ref name=pmid17721194/>). | *Alpha-inhibin +ve (~95% of cases<ref name=pmid17721194/>). | ||
*Calretiin +ve (~55% of cases<ref name=pmid17721194/>). | *Calretiin +ve (~55% of cases<ref name=pmid17721194/>). | ||
*Beta-catenin (nuclear | *Beta-catenin +ve (nuclear).<ref>{{cite journal |authors=Zhang C, Ulbright TM |title=Nuclear Localization of β-Catenin in Sertoli Cell Tumors and Other Sex Cord-Stromal Tumors of the Testis: An Immunohistochemical Study of 87 Cases |journal=Am J Surg Pathol |volume=39 |issue=10 |pages=1390–4 |date=October 2015 |pmid=26034868 |doi=10.1097/PAS.0000000000000455 |url=}}</ref> | ||
**Negative beta-catenin should make one consider other diagnoses.{{fact}} | |||
**May be negative in malignant sertoli cell tumours. | |||
Others: | Others: | ||
Revision as of 10:51, 13 September 2023
| Sertoli cell tumour | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
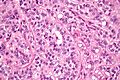
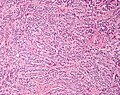
 Sertoli cell tumour. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | groups of cells in cords or trabeculae, cells have light staining bubbly cytoplasm +/- large cytoplasmic vacuoles, slightly irregular nucleoli, granular irregular appearing chromatin |
| LM DDx | granulosa cell tumour, epithelioid adenomatoid tumour, sertoli cell nodule, Sertoli-Leydig tumour |
| IHC | alpha-inhibin, calretinin |
| Site | testis, ovary |
|
| |
| Syndromes | Peutz-Jeghers syndrome, Carney complex |
|
| |
| Signs | testicular mass |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
Sertoli cell tumour is a sex cord-stromal tumour typically found in the testis. It is occasionally seen in women.
General
May be seen in several syndrome - esp. if there is calcification:
Microscopic
Features:
- Groups of cells in cords or trabeculae (beam-like arrangement).
- Cells have:
- Light staining bubbly cytoplasm +/- large cytoplasmic vacuoles.
- Slightly irregular nucleoli.
- Granular irregular appearing chromatin.
Negatives:
- Mitoses are rare.
- No significant nuclear atypia.
DDx:
- Granulosa cell tumour - may be very similar. Often has nuclear grooves.
- Epithelioid adenomatoid tumour.
- Sertoli cell nodule.
- Sertoli-Leydig tumour - esp. in ovary.
Images
www:
IHC
- Alpha-inhibin +ve (~95% of cases[4]).
- Calretiin +ve (~55% of cases[4]).
- Beta-catenin +ve (nuclear).[5]
- Negative beta-catenin should make one consider other diagnoses.[citation needed]
- May be negative in malignant sertoli cell tumours.
Others:
- WT-1 +ve.[4]
See also
References
- ↑ Zizi-Sermpetzoglou, A.; Petrakopoulou, N.; Tepelenis, N.; Savvaidou, V.; Manoloudaki, K.; Katsoulis, M. (2010). "Pure Sertoli cell tumor. a case report and review of the literature.". Eur J Gynaecol Oncol 31 (1): 117-9. PMID 20349797.
- ↑ Libé, R.; Horvath, A.; Vezzosi, D.; Fratticci, A.; Coste, J.; Perlemoine, K.; Ragazzon, B.; Guillaud-Bataille, M. et al. (Jan 2011). "Frequent phosphodiesterase 11A gene (PDE11A) defects in patients with Carney complex (CNC) caused by PRKAR1A mutations: PDE11A may contribute to adrenal and testicular tumors in CNC as a modifier of the phenotype.". J Clin Endocrinol Metab 96 (1): E208-14. doi:10.1210/jc.2010-1704. PMID 21047926.
- ↑ Gourgari, E.; Saloustros, E.; Stratakis, CA. (Aug 2012). "Large-cell calcifying Sertoli cell tumors of the testes in pediatrics.". Curr Opin Pediatr 24 (4): 518-22. doi:10.1097/MOP.0b013e328355a279. PMID 22732638.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Zhao, C.; Bratthauer, GL.; Barner, R.; Vang, R. (Sep 2007). "Diagnostic utility of WT1 immunostaining in ovarian sertoli cell tumor.". Am J Surg Pathol 31 (9): 1378-86. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e3180339961. PMID 17721194.
- ↑ Zhang C, Ulbright TM (October 2015). "Nuclear Localization of β-Catenin in Sertoli Cell Tumors and Other Sex Cord-Stromal Tumors of the Testis: An Immunohistochemical Study of 87 Cases". Am J Surg Pathol 39 (10): 1390–4. doi:10.1097/PAS.0000000000000455. PMID 26034868.