Difference between revisions of "Acquired cystic disease-associated renal cell carcinoma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(chg pic) |
|||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
==Microscopic== | ==Microscopic== | ||
Features: | Features: | ||
* | *Fused tubular structures/cribriforming/sieve-like architecture.<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Srigley | first1 = JR. | last2 = Delahunt | first2 = B. | last3 = Eble | first3 = JN. | last4 = Egevad | first4 = L. | last5 = Epstein | first5 = JI. | last6 = Grignon | first6 = D. | last7 = Hes | first7 = O. | last8 = Moch | first8 = H. | last9 = Montironi | first9 = R. | title = The International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) Vancouver Classification of Renal Neoplasia. | journal = Am J Surg Pathol | volume = 37 | issue = 10 | pages = 1469-89 | month = Oct | year = 2013 | doi = 10.1097/PAS.0b013e318299f2d1 | PMID = 24025519 }} | ||
</ref> | </ref> | ||
**[[ | **Focal papillary architecture - common.<ref name=pmid16434887>{{Cite journal | last1 = Tickoo | first1 = SK. | last2 = dePeralta-Venturina | first2 = MN. | last3 = Harik | first3 = LR. | last4 = Worcester | first4 = HD. | last5 = Salama | first5 = ME. | last6 = Young | first6 = AN. | last7 = Moch | first7 = H. | last8 = Amin | first8 = MB. | title = Spectrum of epithelial neoplasms in end-stage renal disease: an experience from 66 tumor-bearing kidneys with emphasis on histologic patterns distinct from those in sporadic adult renal neoplasia. | journal = Am J Surg Pathol | volume = 30 | issue = 2 | pages = 141-53 | month = Feb | year = 2006 | doi = | PMID = 16434887 }}</ref> | ||
**Tumour cells have prominent nucleoli ([[ISUP nucleolar grade]] 3) and eosinophilic cytoplasm. | |||
*Oxylate crystals - '''important'''. | *Oxylate crystals - '''important'''. | ||
**Look somewhat like cholesterol clefts. | **Look somewhat like cholesterol clefts. | ||
**Seen easily in [[polarized light]]. | **Seen easily in [[polarized light]]. | ||
*[[Acquired cystic disease]] in background - required. | |||
**Changes of [[end-stage kidney]] (obsolete glomeruli, thyroidization, interstitial fibrosis). | |||
DDx: | DDx: | ||
Revision as of 03:41, 27 April 2016
| Acquired cystic disease-associated renal cell carcinoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
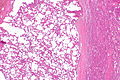
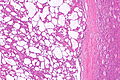
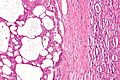
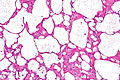
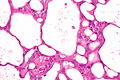
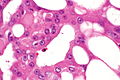
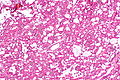
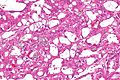
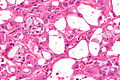
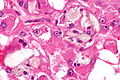
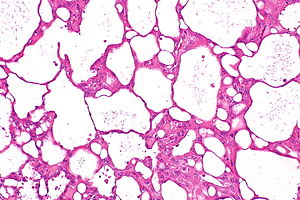 Acquired cystic disease-associated renal cell carcinoma. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | sieve-like architecture (tubular structures/cribriforming), oxylate crystals - seen best in polarized light |
| LM DDx | acquired cystic renal disease, papillary renal cell carcinoma, hereditary leiomyomatosis renal cell carcinoma syndrome associated renal cell carcinoma |
| IHC | AMACR +ve, CD10 +ve, pankeratin +ve, CK7 +ve (heterogeneous), EMA -ve |
| Gross | kidney with cystic changes, thinned cortex |
| Grossing notes | total nephrectomy for tumour grossing, partial nephrectomy grossing |
| Staging | kidney cancer staging |
| Site | kidney - see kidney tumours |
|
| |
| Associated Dx | end-stage renal disease |
| Prevalence | rare |
Acquired cystic disease-associated renal cell carcinoma, abbreviated ACD-RCC, is a rare kidney cancer that arises in the context of chronic renal failure.
General
- Arise in the context of long-standing end-stage renal disease (ESRD).[1]
Gross
- Cysts.
Microscopic
Features:
- Fused tubular structures/cribriforming/sieve-like architecture.[2]
- Focal papillary architecture - common.[3]
- Tumour cells have prominent nucleoli (ISUP nucleolar grade 3) and eosinophilic cytoplasm.
- Oxylate crystals - important.
- Look somewhat like cholesterol clefts.
- Seen easily in polarized light.
- Acquired cystic disease in background - required.
- Changes of end-stage kidney (obsolete glomeruli, thyroidization, interstitial fibrosis).
DDx:
- Acquired cystic renal disease.
- Papillary renal cell carcinoma.
- Hereditary leiomyomatosis renal cell carcinoma syndrome associated renal cell carcinoma.
Images
Case
www
IHC
Features:[1]
- AMACR +ve.
- CD10 +ve.
- Pankeratin +ve.
- CK7 +ve (heterogeneous).
Others:[1]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Ahn, S.; Kwon, GY.; Cho, YM.; Jun, SY.; Choi, C.; Kim, HJ.; Park, YW.; Park, WS. et al. (Mar 2013). "Acquired cystic disease-associated renal cell carcinoma: further characterization of the morphologic and immunopathologic features.". Med Mol Morphol. doi:10.1007/s00795-013-0028-x. PMID 23471757.
- ↑ Srigley, JR.; Delahunt, B.; Eble, JN.; Egevad, L.; Epstein, JI.; Grignon, D.; Hes, O.; Moch, H. et al. (Oct 2013). "The International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) Vancouver Classification of Renal Neoplasia.". Am J Surg Pathol 37 (10): 1469-89. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e318299f2d1. PMID 24025519.
- ↑ Tickoo, SK.; dePeralta-Venturina, MN.; Harik, LR.; Worcester, HD.; Salama, ME.; Young, AN.; Moch, H.; Amin, MB. (Feb 2006). "Spectrum of epithelial neoplasms in end-stage renal disease: an experience from 66 tumor-bearing kidneys with emphasis on histologic patterns distinct from those in sporadic adult renal neoplasia.". Am J Surg Pathol 30 (2): 141-53. PMID 16434887.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 URL: https://www.auanet.org/education/modules/pathology/kidney-carcinomas/acquired-cystic.cfm. Accessed on: 13 May 2015.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 Amin, Mahul B.; Eble, John; Grignon, David; Srigley, John. (2013). Urological Pathology (1st ed.). Wolters Kluwer. pp. 113. ISBN 978-0781782814.