Difference between revisions of "Juvenile polyp"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(+cat.) |
(split-out) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Juvenile polyp''', abbreviated '''JP''', is a type of [[hamartoma|hamartomatous]][[Gastrointestinal tract polyps|gastrointestinal polyp]]. | |||
In adults, it is known as a '''retention polyp'''. | |||
==General== | |||
May be part of a syndrome: | |||
*[[Juvenile polyposis syndrome]] (JPS) - see JPS article for criteria. | |||
*[[Cronkhite-Canada syndrome]]. | |||
*[[Cowden syndrome]]. | |||
==Gross== | |||
*Mushroom-like shape. | |||
==Microscopic== | |||
Features:<ref name=Ref_PBoD859>{{Ref PBoD|859}}</ref><ref name=pmid12692201>{{Cite journal | last1 = Bronner | first1 = MP. | title = Gastrointestinal inherited polyposis syndromes. | journal = Mod Pathol | volume = 16 | issue = 4 | pages = 359-65 | month = Apr | year = 2003 | doi = 10.1097/01.MP.0000062992.54036.E4 | PMID = 12692201 | url = http://www.nature.com/modpathol/journal/v16/n4/full/3880773a.html }}</ref> | |||
*Eroded, smooth or lobulated surface. | |||
*Pedunculated. | |||
*Increased lamina propria (LP) +/- edema. | |||
*Cystically dilated gland. | |||
*Often inflammed. | |||
Mnemonic ''DIES'' = dilated glands, increased LP & inflammation of the LP, eroded/smooth surface, stalk. | |||
Notes: | |||
*May have nuclear changes like those seen in adenomatous polyps. | |||
DDx: | |||
*[[Inflammatory polyp]]. | |||
*[[Hyperplastic polyp of the stomach]] - less lamina propria, foveolar hyperplasia (long tortuous glands). | |||
*[[Cronkhite-Canada syndrome]] - have changes in the surrounding mucosa, clinical findings (nail atrophy, skin pigment, alopecia). | |||
===Images=== | |||
www: | |||
*[http://www.nature.com/modpathol/journal/v16/n4/fig_tab/3880773f4.html Juvenile polyp (nature.com)]. | |||
<gallery> | |||
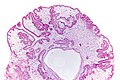
Image:Gastric_juvenile_polyp_-_very_low_mag.jpg | Juvenile polyp of the stomach - very low mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
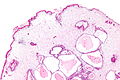
Image:Gastric_juvenile_polyp_-_2_-_very_low_mag.jpg | Juvenile polyp of the stomach - very low mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
</gallery> | |||
==IHC== | |||
*Usually none. | |||
Notes: | |||
*IHC can be used if it is suspected to have dysplasia (p53, Ki-67). | |||
**p53 mutations in dysplastic epithelium -- negative stain (normal). | |||
==Sign out== | |||
<pre> | |||
RECTOSIGMOID POLYP, BIOPSY: | |||
- RETENTION POLYP. | |||
</pre> | |||
==See also== | |||
*[[Gastrointestinal tract polyps]]. | |||
==References== | |||
{{Reflist|2}} | |||
[[Category:Diagnosis]] | [[Category:Diagnosis]] | ||
[[Category:Gastrointestinal pathology]] | |||
Revision as of 01:45, 7 November 2013
Juvenile polyp, abbreviated JP, is a type of hamartomatousgastrointestinal polyp.
In adults, it is known as a retention polyp.
General
May be part of a syndrome:
- Juvenile polyposis syndrome (JPS) - see JPS article for criteria.
- Cronkhite-Canada syndrome.
- Cowden syndrome.
Gross
- Mushroom-like shape.
Microscopic
- Eroded, smooth or lobulated surface.
- Pedunculated.
- Increased lamina propria (LP) +/- edema.
- Cystically dilated gland.
- Often inflammed.
Mnemonic DIES = dilated glands, increased LP & inflammation of the LP, eroded/smooth surface, stalk.
Notes:
- May have nuclear changes like those seen in adenomatous polyps.
DDx:
- Inflammatory polyp.
- Hyperplastic polyp of the stomach - less lamina propria, foveolar hyperplasia (long tortuous glands).
- Cronkhite-Canada syndrome - have changes in the surrounding mucosa, clinical findings (nail atrophy, skin pigment, alopecia).
Images
www:
IHC
- Usually none.
Notes:
- IHC can be used if it is suspected to have dysplasia (p53, Ki-67).
- p53 mutations in dysplastic epithelium -- negative stain (normal).
Sign out
RECTOSIGMOID POLYP, BIOPSY: - RETENTION POLYP.
See also
References
- ↑ Cotran, Ramzi S.; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Nelso Fausto; Robbins, Stanley L.; Abbas, Abul K. (2005). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (7th ed.). St. Louis, Mo: Elsevier Saunders. pp. 859. ISBN 0-7216-0187-1.
- ↑ Bronner, MP. (Apr 2003). "Gastrointestinal inherited polyposis syndromes.". Mod Pathol 16 (4): 359-65. doi:10.1097/01.MP.0000062992.54036.E4. PMID 12692201. http://www.nature.com/modpathol/journal/v16/n4/full/3880773a.html.