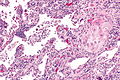
Difference between revisions of "Squamous cell carcinoma of the lung"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 73: | Line 73: | ||
There is no consensus on how grading of lung SCC should be done; however, a three tiered system is suggested in the CAP protocol,<ref name=cap_protocol_v3400>URL: [http://www.cap.org/ShowProperty?nodePath=/UCMCon/Contribution%20Folders/WebContent/pdf/cp-lung-16protocol-3400.pdf http://www.cap.org/ShowProperty?nodePath=/UCMCon/Contribution%20Folders/WebContent/pdf/cp-lung-16protocol-3400.pdf]. Version: 3.4.0.0. Accessed on: 23 March 2016.</ref> and some older data is suggestive that such a system for lung SCC can be predictive.<ref name=pmid7092385>{{Cite journal | last1 = Chung | first1 = CK. | last2 = Zaino | first2 = R. | last3 = Stryker | first3 = JA. | last4 = O'Neill | first4 = M. | last5 = DeMuth | first5 = WE. | title = Carcinoma of the lung: evaluation of histological grade and factors influencing prognosis. | journal = Ann Thorac Surg | volume = 33 | issue = 6 | pages = 599-604 | month = Jun | year = 1982 | doi = | PMID = 7092385 }}</ref> | There is no consensus on how grading of lung SCC should be done; however, a three tiered system is suggested in the CAP protocol,<ref name=cap_protocol_v3400>URL: [http://www.cap.org/ShowProperty?nodePath=/UCMCon/Contribution%20Folders/WebContent/pdf/cp-lung-16protocol-3400.pdf http://www.cap.org/ShowProperty?nodePath=/UCMCon/Contribution%20Folders/WebContent/pdf/cp-lung-16protocol-3400.pdf]. Version: 3.4.0.0. Accessed on: 23 March 2016.</ref> and some older data is suggestive that such a system for lung SCC can be predictive.<ref name=pmid7092385>{{Cite journal | last1 = Chung | first1 = CK. | last2 = Zaino | first2 = R. | last3 = Stryker | first3 = JA. | last4 = O'Neill | first4 = M. | last5 = DeMuth | first5 = WE. | title = Carcinoma of the lung: evaluation of histological grade and factors influencing prognosis. | journal = Ann Thorac Surg | volume = 33 | issue = 6 | pages = 599-604 | month = Jun | year = 1982 | doi = | PMID = 7092385 }}</ref> | ||
The grading system loosely defined by the CAP protocol (version 3.4.0.0):<ref name=cap_protocol_v3400/> | |||
*Grade 1 (well differentiated) - extensive keratinization. | *Grade 1 (well differentiated) - extensive keratinization. | ||
*Grade 2 (moderately differentiated) - some keratinization. | *Grade 2 (moderately differentiated) - some keratinization. | ||
Revision as of 16:39, 23 March 2016
| Squamous cell carcinoma of the lung | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
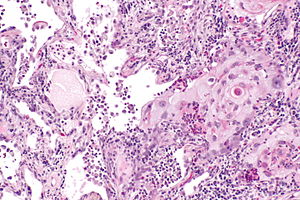 Squamous cell carcinoma of the lung. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| Synonyms | squamous carcinoma of the lung |
| LM DDx | lung adenocarcinoma, non-small cell lung carcinoma, metastatic squamous cell carcinoma, others |
| IHC | p40 +ve, p63 +ve, TTF-1 -ve, CK7 -ve |
| Staging | lung cancer staging |
| Site | lung - see lung tumours |
|
| |
| Clinical history | smoking |
| Symptoms | +/-hemoptysis |
| Prevalence | common |
| Blood work | serum calcium elevated |
| Radiology | typically a mass assoc. with a large airway, +/-spiculated, +/-cavitation |
| Prognosis | usually poor |
| Clin. DDx | other lung tumours - esp. small cell carcinoma of the lung |
| Treatment | surgical resection if possible |
Squamous cell carcinoma of the lung, also lung squamous cell carcinoma, is a common malignant lung tumour that is associated with smoking.
It is also known as squamous carcinoma of the lung and lung squamous carcinoma.
Squamous cell carcinoma can be abbreviated SCC; however, this can be confusing as small cell carcinoma is sometimes abbreviated as such.
General
- Strong association with smoking.
- May be treated with surgery.
Clinical:
- May be associated with elevated serum calcium.[1]
- +/-Hemoptysis.
Gross
- Lung mass - usually centrally located, i.e. associated with a large airway.
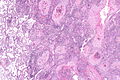
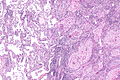
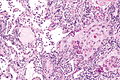
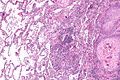
Image
Microscopic
Features:
- Central nucleus.
- Dense appearing cytoplasm, usu. eosinophilic.
- +/-Small nucleolus.
- Intracellular bridges - classic.
Note:
- Lymphovascular invasion (LVI) is relatively common in small tumours. In one series of NSLC tumours less than 2 cm the prevalence of LVI was 16%.[2]
- Unlike in lung adenocarcinoma, LVI in lung SCC does not seem to increase the risk of distant metastases and death.[3]
DDx:
- Metastatic squamous cell carcinoma.
- Adenocarcinoma of the lung.
- Non-small cell lung carcinoma - diagnosis should be avoided if possible.
- Small cell carcinoma of the lung - for basaloid squamous cell carcinoma.
Grading
There is no consensus on how grading of lung SCC should be done; however, a three tiered system is suggested in the CAP protocol,[4] and some older data is suggestive that such a system for lung SCC can be predictive.[5]
The grading system loosely defined by the CAP protocol (version 3.4.0.0):[4]
- Grade 1 (well differentiated) - extensive keratinization.
- Grade 2 (moderately differentiated) - some keratinization.
- Grade 3 (poorly differentiated) - no/little keratinization.
Images
Cytology
IHC
- p40 +ve.[6]
- p63 +ve -- less specific.
- Calponin -ve.
- CK5/6 +ve.
Others:[7]
- CK7 -ve.
- CK20 -ve.
- TTF-1 -ve.
- Positive in adenocarcinoma of the lung.
SCC versus adenocarcinoma:
- p40 +ve.
- CK5/6 +ve.
- TTF-1 -ve.
- Napsin -ve.
Sign out
LUNG, RIGHT UPPER LOBE, BIOPSY: - INVASIVE SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA. COMMENT: The tumour stains as follows: POSITIVE: p40, CK5/6. NEGATIVE: TTF-1, napsin.
Resection
LUNG, RIGHT UPPER LOBE, LOBECTOMY: - SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA, MODERATELY DIFFERENTIATED, pT2b, pN0. -- MARGINS NEGATIVE. -- PLEASE SEE TUMOUR SUMMARY.
See also
References
- ↑ Campbell, JH.; Ralston, S.; Boyle, IT.; Banham, SW. (May 1991). "Symptomatic hypercalcaemia in lung cancer.". Respir Med 85 (3): 223-7. PMID 1831917.
- ↑ Tao H, Hayashi T, Sano F, et al. (November 2013). "Prognostic impact of lymphovascular invasion compared with that of visceral pleural invasion in patients with pN0 non-small-cell lung cancer and a tumor diameter of 2 cm or smaller". J. Surg. Res. 185 (1): 250–4. doi:10.1016/j.jss.2013.05.104. PMID 23830361.
- ↑ Higgins KA, Chino JP, Ready N, et al. (July 2012). "Lymphovascular invasion in non-small-cell lung cancer: implications for staging and adjuvant therapy". J Thorac Oncol 7 (7): 1141–7. doi:10.1097/JTO.0b013e3182519a42. PMID 22617241.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 URL: http://www.cap.org/ShowProperty?nodePath=/UCMCon/Contribution%20Folders/WebContent/pdf/cp-lung-16protocol-3400.pdf. Version: 3.4.0.0. Accessed on: 23 March 2016.
- ↑ Chung, CK.; Zaino, R.; Stryker, JA.; O'Neill, M.; DeMuth, WE. (Jun 1982). "Carcinoma of the lung: evaluation of histological grade and factors influencing prognosis.". Ann Thorac Surg 33 (6): 599-604. PMID 7092385.
- ↑ Bishop, JA.; Teruya-Feldstein, J.; Westra, WH.; Pelosi, G.; Travis, WD.; Rekhtman, N. (Mar 2012). "p40 (ΔNp63) is superior to p63 for the diagnosis of pulmonary squamous cell carcinoma.". Mod Pathol 25 (3): 405-15. doi:10.1038/modpathol.2011.173. PMID 22056955.
- ↑ Montezuma, D.; Azevedo, R.; Lopes, P.; Vieira, R.; Cunha, AL.; Henrique, R. (Dec 2013). "A panel of four immunohistochemical markers (CK7, CK20, TTF-1, and p63) allows accurate diagnosis of primary and metastatic lung carcinoma on biopsy specimens.". Virchows Arch 463 (6): 749-54. doi:10.1007/s00428-013-1488-z. PMID 24126803.