Difference between revisions of "Sertoli cell tumour"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
May be seen in several syndrome - esp. if there is calcification: | May be seen in several syndrome - esp. if there is calcification: | ||
*[[Carney complex]].<ref name=pmid21047926>{{Cite journal | last1 = Libé | first1 = R. | last2 = Horvath | first2 = A. | last3 = Vezzosi | first3 = D. | last4 = Fratticci | first4 = A. | last5 = Coste | first5 = J. | last6 = Perlemoine | first6 = K. | last7 = Ragazzon | first7 = B. | last8 = Guillaud-Bataille | first8 = M. | last9 = Groussin | first9 = L. | title = Frequent phosphodiesterase 11A gene (PDE11A) defects in patients with Carney complex (CNC) caused by PRKAR1A mutations: PDE11A may contribute to adrenal and testicular tumors in CNC as a modifier of the phenotype. | journal = J Clin Endocrinol Metab | volume = 96 | issue = 1 | pages = E208-14 | month = Jan | year = 2011 | doi = 10.1210/jc.2010-1704 | PMID = 21047926 }}</ref> | *[[Carney complex]].<ref name=pmid21047926>{{Cite journal | last1 = Libé | first1 = R. | last2 = Horvath | first2 = A. | last3 = Vezzosi | first3 = D. | last4 = Fratticci | first4 = A. | last5 = Coste | first5 = J. | last6 = Perlemoine | first6 = K. | last7 = Ragazzon | first7 = B. | last8 = Guillaud-Bataille | first8 = M. | last9 = Groussin | first9 = L. | title = Frequent phosphodiesterase 11A gene (PDE11A) defects in patients with Carney complex (CNC) caused by PRKAR1A mutations: PDE11A may contribute to adrenal and testicular tumors in CNC as a modifier of the phenotype. | journal = J Clin Endocrinol Metab | volume = 96 | issue = 1 | pages = E208-14 | month = Jan | year = 2011 | doi = 10.1210/jc.2010-1704 | PMID = 21047926 }}</ref> | ||
*[[Peutz-Jeghers syndrome]]. | *[[Peutz-Jeghers syndrome]].<ref name=pmid22732638>{{Cite journal | last1 = Gourgari | first1 = E. | last2 = Saloustros | first2 = E. | last3 = Stratakis | first3 = CA. | title = Large-cell calcifying Sertoli cell tumors of the testes in pediatrics. | journal = Curr Opin Pediatr | volume = 24 | issue = 4 | pages = 518-22 | month = Aug | year = 2012 | doi = 10.1097/MOP.0b013e328355a279 | PMID = 22732638 }}</ref> | ||
==Microscopic== | ==Microscopic== | ||
Revision as of 01:16, 26 December 2013
| Sertoli cell tumour | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
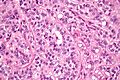
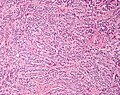
 Sertoli cell tumour. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | groups of cells in cords or trabeculae, cells have light staining bubbly cytoplasm +/- large cytoplasmic vacuoles, slightly irregular nucleoli, granular irregular appearing chromatin |
| LM DDx | granulosa cell tumour, epithelioid adenomatoid tumour, sertoli cell nodule |
| IHC | alpha-inhibin, calretinin |
| Site | testis, ovary |
|
| |
| Syndromes | Peutz-Jeghers syndrome, Carney complex |
|
| |
| Signs | testicular mass |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
Sertoli cell tumour is a sex cord-stromal tumour typically found in the testis.
General
- Arises from Sertoli cells (AKA nurse cells).
May be seen in several syndrome - esp. if there is calcification:
Microscopic
Features:
- Groups of cells in cords or trabeculae (beam-like arrangement).
- Cells have:
- Light staining bubbly cytoplasm +/- large cytoplasmic vacuoles.
- Slightly irregular nucleoli.
- Granular irregular appearing chromatin.
Negatives:
- Mitoses are rare.
- No significant nuclear atypia.
DDx:
- Granulosa cell tumour - may be very similar. Often has nuclear grooves.
- Epithelioid adenomatoid tumour.
- Sertoli cell nodule.
Images
www:
IHC
- Alpha-inhibin +ve. (???)
See also
References
- ↑ Libé, R.; Horvath, A.; Vezzosi, D.; Fratticci, A.; Coste, J.; Perlemoine, K.; Ragazzon, B.; Guillaud-Bataille, M. et al. (Jan 2011). "Frequent phosphodiesterase 11A gene (PDE11A) defects in patients with Carney complex (CNC) caused by PRKAR1A mutations: PDE11A may contribute to adrenal and testicular tumors in CNC as a modifier of the phenotype.". J Clin Endocrinol Metab 96 (1): E208-14. doi:10.1210/jc.2010-1704. PMID 21047926.
- ↑ Gourgari, E.; Saloustros, E.; Stratakis, CA. (Aug 2012). "Large-cell calcifying Sertoli cell tumors of the testes in pediatrics.". Curr Opin Pediatr 24 (4): 518-22. doi:10.1097/MOP.0b013e328355a279. PMID 22732638.