Difference between revisions of "Calcification"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(+image) |
|||
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
==Dystrophic calcification== | ==Dystrophic calcification== | ||
===General=== | |||
*Secondary to [[necrosis]] (coagulative, caseous, liquefactive).<ref name=Ref_PCPBoD8_20-21>{{Ref PCPBoD8|20-21}}</ref> | *Secondary to [[necrosis]] (coagulative, caseous, liquefactive).<ref name=Ref_PCPBoD8_20-21>{{Ref PCPBoD8|20-21}}</ref> | ||
| Line 12: | Line 13: | ||
*[[Atherosclerosis]]. | *[[Atherosclerosis]]. | ||
*[[Calcific aortic stenosis]].<ref name=pmid12779138>{{Cite journal | last1 = Novaro | first1 = GM. | last2 = Griffin | first2 = BP. | title = Calcific aortic stenosis: another face of atherosclerosis? | journal = Cleve Clin J Med | volume = 70 | issue = 5 | pages = 471-7 | month = May | year = 2003 | doi = | PMID = 12779138 | URL = http://www.ccjm.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=12779138 }}</ref> | *[[Calcific aortic stenosis]].<ref name=pmid12779138>{{Cite journal | last1 = Novaro | first1 = GM. | last2 = Griffin | first2 = BP. | title = Calcific aortic stenosis: another face of atherosclerosis? | journal = Cleve Clin J Med | volume = 70 | issue = 5 | pages = 471-7 | month = May | year = 2003 | doi = | PMID = 12779138 | URL = http://www.ccjm.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=12779138 }}</ref> | ||
*[[Calcinosis cutis]]. | |||
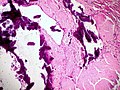
Image | ===Image=== | ||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Amyloidosis,_dystrophic_calcification,_H%26E.jpg | Dystrophic calcification. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
==Metastatic calcification== | |||
===General=== | |||
Causes of elevated calcium - mnemonic ''GRIMED'':<ref name=Ref_PCPBoD8_21>{{Ref PCPBoD8|21}}</ref><ref>{{Ref TN2006 |Emerg.}}</ref> | |||
*[[Granulomatous disease]], e.g. [[tuberculosis]], [[sarcoidosis]]. | |||
*Renal failure. | |||
*Immobility. | |||
*Malignancy, e.g. metastases to bone, [[multiple myeloma]]. | |||
*Endocrine disorders - especially those that elevate PTH. | |||
*Drugs. | |||
==See also== | |||
*[[Breast calcifications]]. | |||
*[[Psammoma bodies]]. | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Latest revision as of 16:16, 2 March 2016
Calcification is the formation of a calcium salt. It often happens in tissue.
Classification
It is typically classified as:[1]
- Dystrophic calcification.
- Metastatic calcification.
Dystrophic calcification
General
Examples - calcification in:
Image
Metastatic calcification
General
Causes of elevated calcium - mnemonic GRIMED:[3][4]
- Granulomatous disease, e.g. tuberculosis, sarcoidosis.
- Renal failure.
- Immobility.
- Malignancy, e.g. metastases to bone, multiple myeloma.
- Endocrine disorders - especially those that elevate PTH.
- Drugs.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Mitchell, Richard; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Abbas, Abul K.; Aster, Jon (2011). Pocket Companion to Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 20-21. ISBN 978-1416054542.
- ↑ Novaro, GM.; Griffin, BP. (May 2003). "Calcific aortic stenosis: another face of atherosclerosis?". Cleve Clin J Med 70 (5): 471-7. PMID 12779138.
- ↑ Mitchell, Richard; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Abbas, Abul K.; Aster, Jon (2011). Pocket Companion to Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 21. ISBN 978-1416054542.
- ↑ Shiau, Carolyn; Toren, Andrew (2006). Toronto Notes 2006: Comprehensive Medical Reference (Review for MCCQE 1 and USMLE Step 2) (22nd edition (2006) ed.). Toronto Notes for Medical Students, Inc.. pp. Emerg.. ISBN 978-0968592861.