Difference between revisions of "Kimura disease"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (→IHC) |
|||
| (12 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Kimura disease''' is a rare disease with abundant eosinophils. It may show-up in a [[lymph node]] specimen. | {{ Infobox diagnosis | ||
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | |||
| Image = Kimura_disease_-_very_high_mag.jpg | |||
| Width = | |||
| Caption = Kimura disease. [[H&E stain]]. | |||
| Micro = eosinophils and thick walled [[blood vessel]]s with [[hobnail]]ed endothelial cells | |||
| Subtypes = | |||
| LMDDx = [[angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia]], [[drug reaction]], infection (parasitic), [[lymphoma]], [[LCH]] | |||
| Stains = | |||
| IHC = | |||
| EM = | |||
| Molecular = | |||
| IF = | |||
| Gross = | |||
| Grossing = | |||
| Site = [[lymph node]], head and neck | |||
| Assdx = | |||
| Syndromes = | |||
| Clinicalhx = | |||
| Signs = | |||
| Symptoms = | |||
| Prevalence = extremely rare | |||
| Bloodwork = eosinophilia | |||
| Rads = | |||
| Endoscopy = | |||
| Prognosis = | |||
| Other = | |||
| ClinDDx = | |||
}} | |||
'''Kimura disease''' is a rare disease with abundant eosinophils. It may show-up in a [[lymph node]] specimen. It is similar to ''[[angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia]]''.<ref>URL: [http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1082603-overview http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1082603-overview]. Accessed on: 14 January 2012.</ref> | |||
==General== | ==General== | ||
| Line 18: | Line 47: | ||
Features:<ref name=Ref_ILNP190>{{Ref ILNP|190}}</ref> | Features:<ref name=Ref_ILNP190>{{Ref ILNP|190}}</ref> | ||
*Angiolymphoid proliferation. | *Angiolymphoid proliferation. | ||
**Thick walled blood vessels with (plump) hobnail endothelial cells.<ref>URL: [http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1098777-diagnosis http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1098777-diagnosis]. Accessed on: 8 August 2010.</ref> | **Thick walled blood vessels with (plump) [[hobnail]] endothelial cells.<ref>URL: [http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1098777-diagnosis http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1098777-diagnosis]. Accessed on: 8 August 2010.</ref> | ||
*Eosinophils - abundant - '''key feature'''. | *Eosinophils - abundant - '''key feature'''. | ||
| Line 24: | Line 53: | ||
*Drug reaction. | *Drug reaction. | ||
*Parasitic infection. | *Parasitic infection. | ||
*[[Angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia]]. | |||
Notes: | Notes: | ||
| Line 29: | Line 59: | ||
*Abundant eosinophils: consider [[Langerhans cell histiocytosis]]. | *Abundant eosinophils: consider [[Langerhans cell histiocytosis]]. | ||
Images | ===Images=== | ||
<gallery> | |||
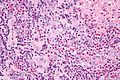
Image:Kimura_disease_-_very_high_mag.jpg | Kimura disease - very high mag. (WC) | |||
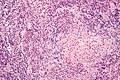
Image:Kimura_disease_-_high_mag.jpg | Kimura disease - high mag. (WC) | |||
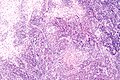
Image:Kimura_disease_-_intermed_mag.jpg | Kimura disease - intermed. mag. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
==IHC== | ==IHC== | ||
Latest revision as of 03:01, 31 October 2015
| Kimura disease | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
 Kimura disease. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | eosinophils and thick walled blood vessels with hobnailed endothelial cells |
| LM DDx | angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia, drug reaction, infection (parasitic), lymphoma, LCH |
| Site | lymph node, head and neck |
|
| |
| Prevalence | extremely rare |
| Blood work | eosinophilia |
Kimura disease is a rare disease with abundant eosinophils. It may show-up in a lymph node specimen. It is similar to angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia.[1]
General
- AKA eosinophilic lymphogranuloma, Kimura disease.
- Chronic inflammatory disorder - suspected to be infectious.
Clinical:
- Usually neck, periauricular.
- Peripheral blood eosinophilia.
- Increased blood IgE.
Epidemiology
- Males > females.
- Young.
- Asian.
Microscopic
Features:[2]
- Angiolymphoid proliferation.
- Eosinophils - abundant - key feature.
DDx:
- Drug reaction.
- Parasitic infection.
- Angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia.
Notes:
- In a lymph node... it may be signed-out as reactive lymphadenitis with follicular hyperplasia and prominent eosinophils, see comment.
- Abundant eosinophils: consider Langerhans cell histiocytosis.
Images
IHC
- Used to rule-out a clonal population, i.e. lymphoma.
See also
References
- ↑ URL: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1082603-overview. Accessed on: 14 January 2012.
- ↑ Ioachim, Harry L; Medeiros, L. Jeffrey (2008). Ioachim's Lymph Node Pathology (4th ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 190. ISBN 978-0781775960.
- ↑ URL: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1098777-diagnosis. Accessed on: 8 August 2010.