Difference between revisions of "Hypertrophic decidual vasculopathy"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ Infobox diagnosis | |||
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | |||
| Image = Hypertrophic decidual vasculopathy intermed mag.jpg | |||
| Width = | |||
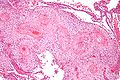
| Caption = Hypertrophic decidual vasculopathy. [[H&E stain]]. | |||
| Synonyms = decidual vasculopathy | |||
| Micro = Mild or moderate: perivascular inflammatory cells, +/-vascular thrombosis, smooth muscle hypertrophy, endothelial hyperplasia; severe: atherosis of maternal blood vessels, foamy macrophages within vascular wall, fibrinoid [[necrosis]] of vessel wall | |||
| Subtypes = | |||
| LMDDx = | |||
| Stains = | |||
| IHC = | |||
| EM = | |||
| Molecular = | |||
| IF = | |||
| Gross = | |||
| Grossing = | |||
| Staging = | |||
| Site = [[placenta]] | |||
| Assdx = [[intrauterine growth restriction]] | |||
| Syndromes = | |||
| Clinicalhx = | |||
| Signs = [[hypertension]] | |||
| Symptoms = | |||
| Prevalence = uncommon | |||
| Bloodwork = | |||
| Rads = | |||
| Endoscopy = | |||
| Prognosis = | |||
| Other = | |||
| ClinDDx = gestational hypertension, [[HELLP syndrome]] | |||
| Tx = dependent on severity | |||
}} | |||
'''Hypertrophic decidual vasculopathy''', also known as '''decidual vasculopathy''', is a pathology of the placenta seen in the context of (gestational) [[hypertension]]. | '''Hypertrophic decidual vasculopathy''', also known as '''decidual vasculopathy''', is a pathology of the placenta seen in the context of (gestational) [[hypertension]]. | ||
Revision as of 14:03, 27 November 2015
| Hypertrophic decidual vasculopathy | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
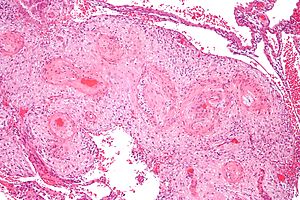 Hypertrophic decidual vasculopathy. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| Synonyms | decidual vasculopathy |
|
| |
| LM | Mild or moderate: perivascular inflammatory cells, +/-vascular thrombosis, smooth muscle hypertrophy, endothelial hyperplasia; severe: atherosis of maternal blood vessels, foamy macrophages within vascular wall, fibrinoid necrosis of vessel wall |
| Site | placenta |
|
| |
| Associated Dx | intrauterine growth restriction |
| Signs | hypertension |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
| Clin. DDx | gestational hypertension, HELLP syndrome |
| Treatment | dependent on severity |
Hypertrophic decidual vasculopathy, also known as decidual vasculopathy, is a pathology of the placenta seen in the context of (gestational) hypertension.
General
- A change seen in hypertension.
- Seen in intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR).
Microscopic
Features:[1]
- Mild or moderate:
- Perivascular inflammatory cells.
- +/-Vascular thrombosis.
- Smooth muscle hypertrophy.
- Endothelial hyperplasia.
- Above two lead to narrowing of the decidual spiral arteries[2] -- key feature.
- Severe:[1]
- Atherosis of maternal blood vessels.
- Foamy macrophages within vascular wall.
- Fibrinoid necrosis of vessel wall (amorphous eosinophilic material vessel wall).
- Atherosis of maternal blood vessels.
- Suggestive:[3]
- Decidual vasculitis - lymphocyte predominant without plasma cells.
Note:
- Smooth muscle hypertrophy can also be understood as lack of physiological conversion of spiral arteries of the uterus.[4]
Images
www:
Sign out
PLACENTA, UMBILICAL CORD AND FETAL MEMBRANES, CESAREAN SECTION: - DECIDUAL VASCULOPATHY. - PLACENTA SMALL FOR GESTATIONAL AGE (222 GRAMS). - PLACENTAL DISC WITH EARLY THIRD TRIMESTER VILLI WITH: -- MULTIPLE PLACENTAL INFARCTS. -- PERIVILLOUS FIBRIN DEPOSITION. - THREE VESSEL UMBILICAL CORD WITHIN NORMAL LIMITS. - FETAL MEMBRANES WITHIN NORMAL LIMITS. COMMENT: The 10th percentile placental mass (pre-fixation) for 32 weeks and 6 days is approximately 247 grams.
Suggestive of decidual vasculopathy
PLACENTA, UMBILICAL CORD AND FETAL MEMBRANES, CESAREAN SECTION: - CHANGES SUGGESTIVE OF DECIDUAL VASCULOPATHY (DECIDUAL VASCULITIS). - PLACENTAL DISC WITH EARLY THIRD TRIMESTER VILLI AND A PLACENTAL INFARCT (2.5 CM IN MAXIMAL DIMENSION). - THREE VESSEL UMBILICAL CORD WITHIN NORMAL LIMITS. - FETAL MEMBRANES WITHIN NORMAL LIMITS.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Roberts, DJ.; Post, MD. (Dec 2008). "The placenta in pre-eclampsia and intrauterine growth restriction.". J Clin Pathol 61 (12): 1254-60. doi:10.1136/jcp.2008.055236. PMID 18641412.
- ↑ AFIP - Placental Pathology. P.122. ISBN: 1-881041-89-1. 2004.
- ↑ Baergen, Rebecca N. (2011). Manual of Pathology of the Human Placenta (2nd ed.). Springer. pp. 339. ISBN 978-1441974938.
- ↑ Naicker, T.; Khedun, SM.; Moodley, J.; Pijnenborg, R. (Aug 2003). "Quantitative analysis of trophoblast invasion in preeclampsia.". Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 82 (8): 722-9. PMID 12848643.
- ↑ URL: http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case75.html. Accessed on: 2 January 2012.