Spironolactone bodies
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
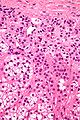
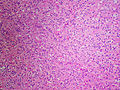
Spironolactone bodies are seen in the cortex of the adrenal gland in the context of long-term spironolcatone use.
General
Etiology:
- Long-term use of spironolactone.
Note:
- Aldosterone antagonist.
- Commonly used anti-hypertensive medication.[1]
- May be used to treat hypertension due to primary hyperaldosteronism related to adrenal pathology (nodular cortical hyperplasia or adenoma).
- Other uses include treatment of adult acne harnessing an antiandrogenic activity.
Microscopic
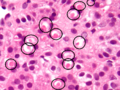
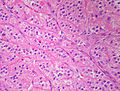
Features:[2]
- Location: zona glomerulosa (where aldosterone is produced).
- Appearance: eosinophilic spherical laminated whorls.
Images
See also
References
- ↑ Patel, KA.; Calomeni, EP.; Nadasdy, T.; Zynger, DL. (Aug 2014). "Adrenal gland inclusions in patients treated with aldosterone antagonists (Spironolactone/Eplerenone): incidence, morphology, and ultrastructural findings.". Diagn Pathol 9 (1): 147. doi:10.1186/1746-1596-9-147. PMID 25108298.
- ↑ Kovacs K, Horvath E, Singer W (December 1973). "Fine structure and morphogenesis of spironolactone bodies in the zona glomerulosa of the human adrenal cortex". J. Clin. Pathol. 26 (12): 949-57. PMC 477936. PMID 4131694. http://jcp.bmj.com/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=4131694.