End-stage kidney
(Redirected from ESRD)
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| End-stage kidney | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
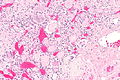
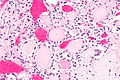
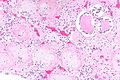
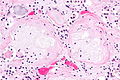
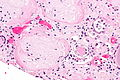
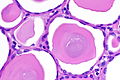
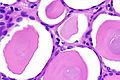
 End-stage kidney with thyroidization. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
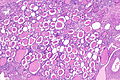
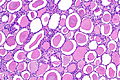
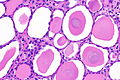
| LM | global sclerosis of the glomeruli, interstitial fibrosis, +/-thyroidization (colloid-like hyaline cast formation that impart an appearance that mimics the thyroid gland) |
| Gross | small kidneys, thinned renal cortex, +/-dilated renal calyces, +/-cysts |
| Site | kidney - see medical kidney diseases |
|
| |
| Associated Dx | chronic pyelonephritis, acquired cystic disease-associated renal cell carcinoma, papillary renal cell carcinoma, acquired renal cystic disease |
| Clinical history | +/-diabetes mellitus (most common) |
End-stage kidney, abbreviated ESK, is a non-functional (chronically damaged) kidney.
End-stage renal disease (abbreviated ESRD) and end-stage kidney disease (abbreviated ESKD) redirect here.
General
- Many end-stage renal disease (ESRD) kidneys have a similar appearance.
- Notable exception: polycystic kidney diseases have distinctive appearance, e.g. ADPKD.
Gross
- Small kidneys.
- Thinned renal cortex.
- +/-Dilated renal calyces.
- +/-Cysts.
Note:
- Normal (adult) kidneys are ~11 cm from pole-to-pole.[1]
Microscopic
Features:
- Global sclerosis of the glomeruli.
- Interstitial fibrosis.
- +/-Thyroidization - colloid-like hyaline cast formation that impart an appearance that mimics the thyroid gland:[2]
- Typical of chronic pyelonephritis and obstructive nephropathy.
- +/-Interstitial nephritis.
- +/-Pyelonephritis.
Note:
- The end-stage kidney, much like the end-stage liver, often does not have apparent disease specific findings.
DDx:
- Diabetic nephropathy - most common cause of ESRD in North America, may have vague nodularity.
- Chronic pyelonephritis - commonly associated with ESRD.
- Renal papillary adenoma - common incidental finding.
- Acquired cystic disease of the kidney - seen in ESRD, may be an concurrent pathology.
- Other causes of end-stage renal disease.
Images
www:
Case 1
Case 2
Sign out
Right Kidney, Nephrectomy:
- End-stage kidney with predominantly obsolete glomeruli, thyroidization and
chronic interstitial inflammation.
- Minimal chronic inflammation of renal pelvis and ureter.
- NEGATIVE for malignancy.
Block letters
KIDNEY, LEFT, NEPHRECTOMY: - END-STAGE KIDNEY WITH MULTIPLE ABSCESSES ASSOCIATED WITH GIANT CELLS AND HISTIOCYTIC RESPONSE. - CHRONIC PYELONEPHRITIS AND INTERSTITIAL NEPHRITIS. - ATHEROSCLEROSIS, MILD-TO-MODERATE. - NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
See also
References
- ↑ Glodny, B.; Unterholzner, V.; Taferner, B.; Hofmann, KJ.; Rehder, P.; Strasak, A.; Petersen, J. (2009). "Normal kidney size and its influencing factors - a 64-slice MDCT study of 1.040 asymptomatic patients.". BMC Urol 9: 19. doi:10.1186/1471-2490-9-19. PMID 20030823.
- ↑ Ito, S.; Kobayashi, A.; Tsuchiya, T.; Moriyama, Y.; Kikuchi, M.; Deguchi, T.; Yamaguchi, Y. (Aug 2009). "Thyroidization in renal allografts.". Clin Transplant 23 Suppl 20: 6-9. doi:10.1111/j.1399-0012.2009.01001.x. PMID 19594588.