Alveolar soft part sarcoma
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Alveolar soft part sarcoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
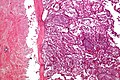
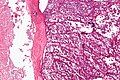
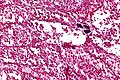
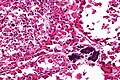
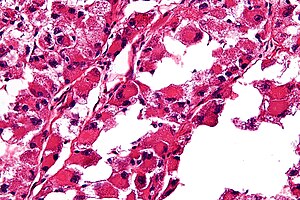 ASPS. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
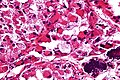
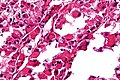
| LM | large cells (~30-50 μm) with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm and an eccentric nucleus +/-nucleolus, arranged in nests/separated by thin septa - vaguely resembles alveoli (at low power) |
| LM DDx | paraganglioma, clear cell renal cell carcinoma, alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma |
| Stains | PAS +ve (cytoplasm) |
| IHC | TFE3 +ve (suggestive of translocation) |
| EM | intracytoplasmic crystal lattice with ~5 nm fibres spaced 10 nm apart |
| Molecular | t(X;17) |
| Site | soft tissue - usu. head and neck |
|
| |
| Clinical history | usu. slow growing mass |
| Prevalence | rare |
| Prognosis | ultimately poor |
Alveolar soft part sarcoma, abbreviated ASPS, is a rare malignant soft tissue lesion typically seen in younger individuals.
General
- Adolescents/young adults.
- Children -- classically location: orbit and base of tongue.[1]
- Typical indolent initially - ultimately a poor prognosis.[2]
Microscopic
Features:[3]
- Arranged in nests/separated by thin septa; vaguely resembles alveoli (at low power).
- Large cells (~30-50 μm) with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm.
- May be focally cleared.
- An eccentric nucleus.
- +/-Nucleolus, prominent.
- +/-Multi-nucleation (common).
DDx:
- Paraganglioma.
- Clear cell renal cell carcinoma - areas with cytoplasmic clearing.
- Rhabdomyosarcoma, alveolar - usu. does not have sheets of rhabdoid cells, no cross striations.
Images
www:
Stains
- PAS +ve (cytoplasmic) - considered the most useful.[4]
- PASD +ve (cytoplasmic).
IHC
- TFE3 +ve -- suggestive of characteristic translocation.
- Desmin ~ 50% of cases.[2]
Others:[2]
- EMA -ve.
- Cytokeratins -ve.
- HMB45 -ve.
- Melan‐A -ve.
- Chromogranin A -ve.
- Synaptophysin -ve.
Molecular
- t(X;17)(p11.2;q25).[5]
Note:
- Same translocation may be seen in renal tumour with Xp11.2 translocation.
EM
- Distinctive membrane-bound intracytoplasmic crystal lattice with ~5 nm fibres spaced 10 nm apart.[2]
Image:
See also
References
- ↑ Anbarasi, K.; Sathasivasubramanian, S.; Kuruvilla, S.. "Alveolar soft-part sarcoma of tongue.". Indian J Pathol Microbiol 54 (3): 581-3. doi:10.4103/0377-4929.85099. PMID 21934227.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 Folpe, AL.; Deyrup, AT. (Nov 2006). "Alveolar soft-part sarcoma: a review and update.". J Clin Pathol 59 (11): 1127-32. doi:10.1136/jcp.2005.031120. PMC 1860509. PMID 17071801. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1860509/.
- ↑ Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 627. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ Zarrin-Khameh, N.; Kaye, KS. (Mar 2007). "Alveolar soft part sarcoma.". Arch Pathol Lab Med 131 (3): 488-91. doi:10.1043/1543-2165(2007)131[488:ASPS]2.0.CO;2. PMID 17516754.
- ↑ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 606243