Acute synovitis
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Acute synovitis | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
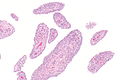
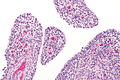
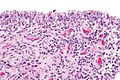
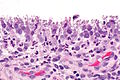
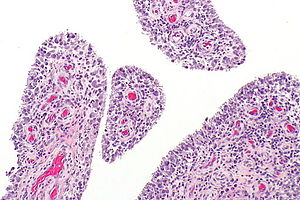 Acute synovitis. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | synovium with neutrophils |
| LM DDx | infectious synovitis |
| Site | joints |
|
| |
| Clinical history | +/-procedure |
| Signs | swelling, erythema, warm joint |
| Symptoms | +/-pain |
| Other | joint culture |
Acute synovitis is an inflammatory process involving the synovium.
This article deal with nonspecific causes of acute synovitis (acute nonspecific synovitis).
General
- Cultures negative - by definition.
- Nonspecific finding.
- May form a tumour-like mass.[1]
Microscopic
Features:
- Synovium with abundant neutrophils.
- No significant number of plasma cells.
DDx:
- Infectious synovitis.
- Rheumatoid arthritis - should have plasma cells.
Images
Sign out
SYNOVIUM, LEFT FIFTH FINGER, EXCISION: - ACUTE SYNOVITIS WITH FOCAL HEMOSIDERIN-LADEN MACROPHAGES AND FIBROVASCULAR TISSUE. - NO SIGNIFICANT NUMBER OF PLASMA CELLS ARE IDENTIFIED. - NO MICROORGANISMS APPARENT WITH ROUTINE STAINS, SEE COMMENT. - NO EVIDENCE OF MALIGNANCY. COMMENT: Correlation with microbiology is suggested.
SYNOVIUM, RIGHT ELBOW, BIOPSY: - ACUTE SYNOVITIS. - NO MICROORGANISMS IDENTIFIED WITH ROUTINE STAINS. - NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY. COMMENT: Correlation with microbiology is suggested.
See also
References
- ↑ Prosser, GH.; Sterne, GD.; Nancarrow, JD. (Jan 2002). "Intratendinous rupture of flexor digitorum profundus caused by non-specific synovitis.". Br J Plast Surg 55 (1): 77-9. doi:10.1054/bjps.2001.3726. PMID 11783976.