Difference between revisions of "Thymoma"
(split out) |
|||
| (8 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ Infobox diagnosis | |||
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | |||
| Image = Thymoma type B1 -- intermed mag.jpg | |||
| Width = | |||
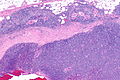
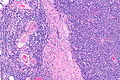
| Caption = Thymoma (right of image) and remnant of normal thymus (left of image). [[H&E stain]]. (WC) | |||
| Synonyms = | |||
| Micro = | |||
| Subtypes = A, AB, B1, B2, B3 | |||
| LMDDx = [[lymphoma]], [[squamous cell carcinoma]] (esp. [[squamous cell carcinoma of the lung]], [[head and neck squamous cell carcinoma]]), [[follicular dendritic cell sarcoma]] | |||
| Stains = | |||
| IHC = | |||
| EM = | |||
| Molecular = | |||
| IF = | |||
| Gross = light brown/tan, usually encapsulated | |||
| Grossing = | |||
| Staging = [[thymus staging]] | |||
| Site = [[thymus]] | |||
| Assdx = myasthenia gravis | |||
| Syndromes = | |||
| Clinicalhx = | |||
| Signs = | |||
| Symptoms = | |||
| Prevalence = uncommon overall, common for thymic tumours | |||
| Bloodwork = | |||
| Rads = | |||
| Endoscopy = | |||
| Prognosis = benign | |||
| Other = | |||
| ClinDDx = [[mediastinum|mediastinal mass]] | |||
| Tx = excision | |||
}} | |||
'''Thymoma''' is a common tumour of the [[thymus]]. | '''Thymoma''' is a common tumour of the [[thymus]]. | ||
| Line 43: | Line 75: | ||
Note: | Note: | ||
*Neoplastic cells derived from the thymus with cytologic features of malignancy are [[thymic carcinoma]]s. | *Neoplastic cells derived from the thymus with cytologic features of malignancy are [[thymic carcinoma]]s. | ||
==Gross== | ==Gross== | ||
| Line 57: | Line 82: | ||
Image: | Image: | ||
*[http://www.sciencephoto.com/media/253251/enlarge Thymoma (sciencephoto.com)]. | *[http://www.sciencephoto.com/media/253251/enlarge Thymoma (sciencephoto.com)]. | ||
Note: | |||
*The line between ''thymoma'' and ''persistent normal thymus in the adult'' is not well-defined in the radiologic context.<ref name=pmid25925358>{{Cite journal | last1 = Araki | first1 = T. | last2 = Nishino | first2 = M. | last3 = Gao | first3 = W. | last4 = Dupuis | first4 = J. | last5 = Hunninghake | first5 = GM. | last6 = Murakami | first6 = T. | last7 = Washko | first7 = GR. | last8 = O'Connor | first8 = GT. | last9 = Hatabu | first9 = H. | title = Normal thymus in adults: appearance on CT and associations with age, sex, BMI and smoking. | journal = Eur Radiol | volume = 26 | issue = 1 | pages = 15-24 | month = Jan | year = 2016 | doi = 10.1007/s00330-015-3796-y | PMID = 25925358 }}</ref> | |||
==Microscopic== | ==Microscopic== | ||
| Line 68: | Line 96: | ||
*[[Squamous cell carcinoma]]. | *[[Squamous cell carcinoma]]. | ||
*[[Lymphoma]]. | *[[Lymphoma]]. | ||
*[[Follicular dendritic cell sarcoma]]. | |||
*Normal persistent [[thymus]]. | |||
===Images=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
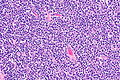
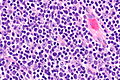
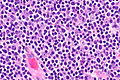
Image:Thymoma_type_B1_(1).JPG | Thymoma Type B1. (WC/KGH) | |||
Image:Thymoma_B1_(2).JPG | Thymoma Type B1. (WC/KGH) | |||
Image:Thymoma_B1_(3)_CK_CAM5-2.JPG | Thymoma Type B1 - CAM5.2. (WC/KGH) | |||
</gallery> | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image: Thymoma type B1 -- low mag.jpg | Thymoma B1 - low mag. | |||
Image: Thymoma type B1 -- intermed mag.jpg | Thymoma B1 - intermed. mag. | |||
Image: Thymoma type B1 -- high mag.jpg | Thymoma B1 - high mag. | |||
Image: Thymoma type B1 -- very high mag.jpg | Thymoma B1 - very high mag. | |||
Image: Thymoma type B1 - alt -- very high mag.jpg | Thymoma B1 - very high mag. | |||
</gallery> | |||
[[File:5 404717367 sl 1.png|Thymoma type B1]] | |||
[[File:5 404717367 sl 2.png|Thymoma type B1]] | |||
[[File:5 404717367 sl 3.png|Thymoma type B1]] | |||
[[File:5 404717367 sl 4.png|Thymoma type B1]] | |||
[[File:5 404717367 sl 5.png|Thymoma type B1]] | |||
[[File:5 404717367 sl 6.png|Thymoma type B1]] | |||
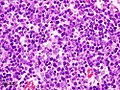
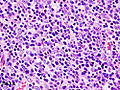
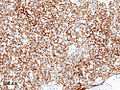
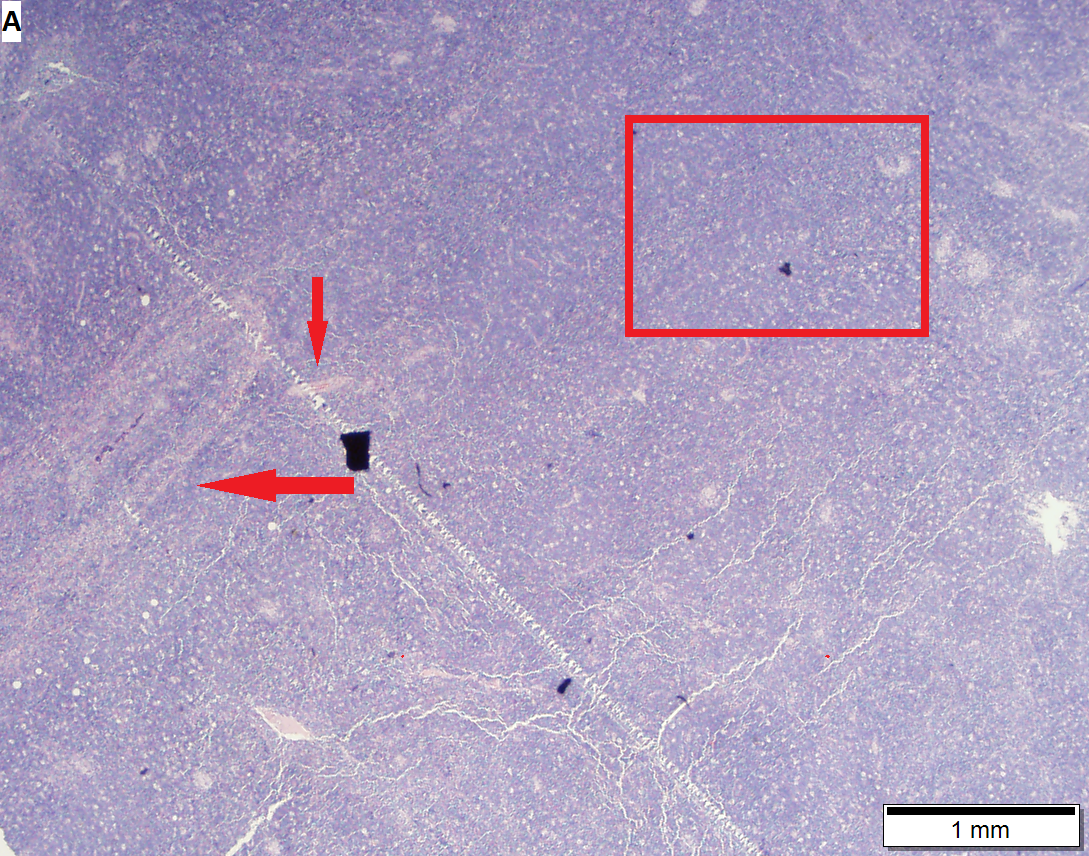
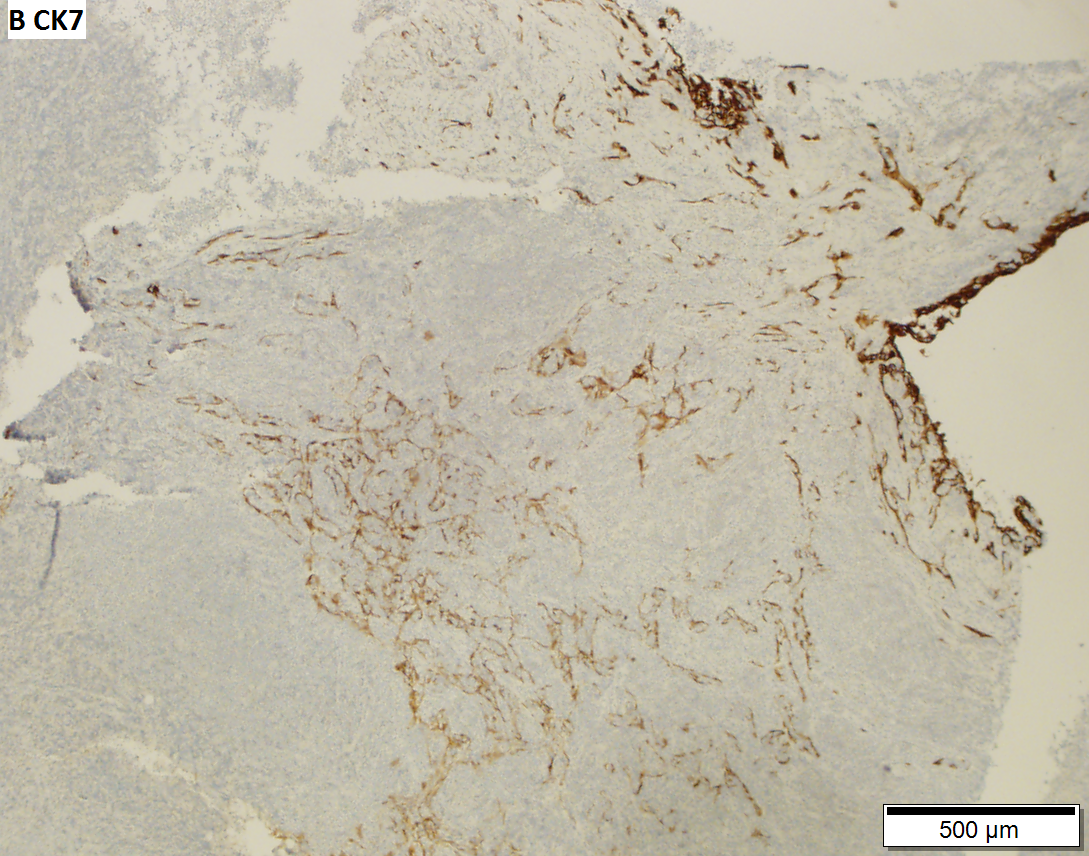
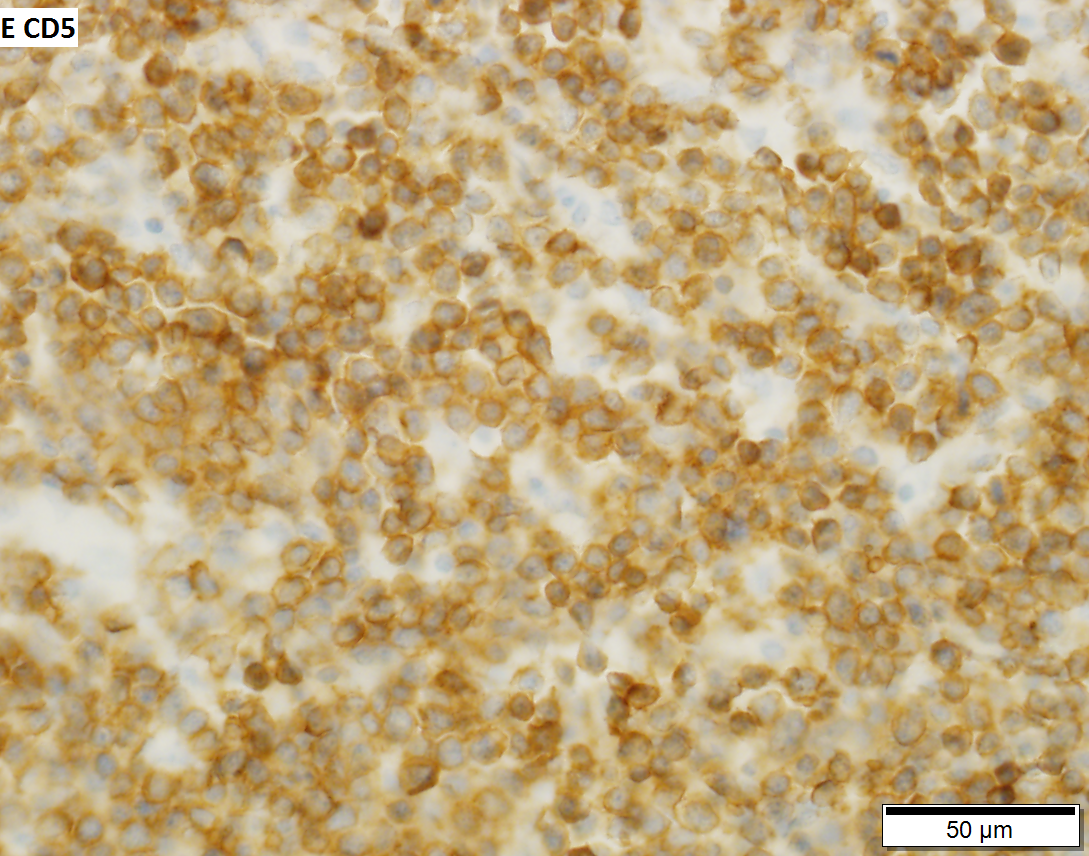
Thymoma type B1 in a 33 y man, 384 gram 9 x 10 x 8 cm. A. Blue tumor shows a starry sky pattern (red square), as well as occasional fibrous bands (red arrows). B. Epithelial component, impossible to see on H&E at lower power, is readily identified, here with immunostain for CK7. C. CK7 positivity favors B over type A. Note that where the nuclei are visible the tumor cells are round, proving type B. The predominance of lymphoid cells makes this tumor B1. D. Lymphoid cells are uniform and small. Arrows show the tangible body macrophages that gave the low power starry sky appearance. E. Lymphoid cells are CD5 positive. F. Lymphoid cells are TdT positive. | |||
===Staging=== | ===Staging=== | ||
{{Main|Thymic staging}} | |||
==IHC== | ==IHC== | ||
| Line 157: | Line 132: | ||
A panel: | A panel: | ||
*TdT, CD1a, CD3, CD5, CD20, Ki-67, CD117, p63, CK5/6. | *TdT, CD1a, CD3, CD5, CD20, Ki-67, CD117, [[p63]], [[CK5/6]]. | ||
==Sign out== | ==Sign out== | ||
| Line 174: | Line 149: | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
*[[Thymus]]. | *[[Thymus]]. | ||
*[[Thymus staging]]. | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Latest revision as of 18:29, 22 October 2019
| Thymoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
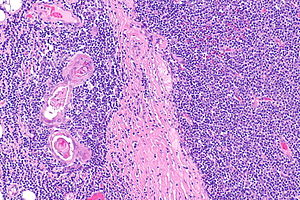 Thymoma (right of image) and remnant of normal thymus (left of image). H&E stain. (WC) | |
| Subtypes | A, AB, B1, B2, B3 |
| LM DDx | lymphoma, squamous cell carcinoma (esp. squamous cell carcinoma of the lung, head and neck squamous cell carcinoma), follicular dendritic cell sarcoma |
| Gross | light brown/tan, usually encapsulated |
| Staging | thymus staging |
| Site | thymus |
|
| |
| Associated Dx | myasthenia gravis |
| Prevalence | uncommon overall, common for thymic tumours |
| Prognosis | benign |
| Clin. DDx | mediastinal mass |
| Treatment | excision |
Thymoma is a common tumour of the thymus.
General
- Strong association with autoimmune disease, esp. myasthenia gravis.
Classification
The WHO published a widely used system - WHO classification:[1]
Type A
- AKA Spindle cell or medullary.
- Arise from medullary epithelial cells.
- Good prognosis.
IHC:
- Usu. keratin+.
Type AB
- Like Type A... but with foci of lymphocytes.
Type B1
- Near normal, expanded cortex.
Lesion consists of:
- >2/3 lymphocytes, <1/3 cortical epithelial cells.
Type B2
- Neoplastic cells with some resemblance to cortical epithelial cells.
- Epithelioid cells with distinct nucleoli.
- May be perivascular.
- Large population of lymphocytes.
Lesion consists of:
- <2/3 but >1/3 lymphocytes, >1/3 but <2/3 cortical epithelial cells.
Notes:
- Most common B type.
Type B3
- Neoplastic cells with some resemblance to cortical epithelial cells.
- Polygonal/round shape.
- Form sheets (of cells) - key feature.
- Lymphocytes - less than in Type B2.
- AKA well-differentiated thymic carcinoma.
Lesion consists of:
- <1/3 lymphocytes, >2/3 cortical epithelial cells.
Note:
- Neoplastic cells derived from the thymus with cytologic features of malignancy are thymic carcinomas.
Gross
- Light brown/tan.
- Encapsulated.
Image:
Note:
- The line between thymoma and persistent normal thymus in the adult is not well-defined in the radiologic context.[2]
Microscopic
Features:
- Lymphocytes.
- Epithelial cells.
- Spindle cells - Type A.
- Epithelioid cells - Type B.
DDx:
- Squamous cell carcinoma.
- Lymphoma.
- Follicular dendritic cell sarcoma.
- Normal persistent thymus.
Images
Thymoma type B1 in a 33 y man, 384 gram 9 x 10 x 8 cm. A. Blue tumor shows a starry sky pattern (red square), as well as occasional fibrous bands (red arrows). B. Epithelial component, impossible to see on H&E at lower power, is readily identified, here with immunostain for CK7. C. CK7 positivity favors B over type A. Note that where the nuclei are visible the tumor cells are round, proving type B. The predominance of lymphoid cells makes this tumor B1. D. Lymphoid cells are uniform and small. Arrows show the tangible body macrophages that gave the low power starry sky appearance. E. Lymphoid cells are CD5 positive. F. Lymphoid cells are TdT positive.
Staging
IHC
A panel:
Sign out
A. Lymph Node, Station 6, Lymphadenectomy: - One benign lymph node (0/1). B. Submitted as "Anterior Mediastinal Tumour (Thymus)", Excision: - Thymoma, WHO type B2. - Modified Masaoka stage IIa. - Three benign lymph nodes (0/3). - Rim of benign thymus. - Please see synoptic report.
See also
References
- ↑ Mills, Stacey E; Carter, Darryl; Greenson, Joel K; Oberman, Harold A; Reuter, Victor E (2004). Sternberg's Diagnostic Surgical Pathology (4th ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 1264. ISBN 978-0781740517.
- ↑ Araki, T.; Nishino, M.; Gao, W.; Dupuis, J.; Hunninghake, GM.; Murakami, T.; Washko, GR.; O'Connor, GT. et al. (Jan 2016). "Normal thymus in adults: appearance on CT and associations with age, sex, BMI and smoking.". Eur Radiol 26 (1): 15-24. doi:10.1007/s00330-015-3796-y. PMID 25925358.
- ↑ Adam P, Hakroush S, Hofmann I, Reidenbach S, Marx A, Ströbel P (June 2014). "Thymoma with loss of keratin expression (and giant cells): a potential diagnostic pitfall". Virchows Arch.. doi:10.1007/s00428-014-1606-6. PMID 24923897.
- ↑ Viti, A.; Bertolaccini, L.; Cavallo, A.; Fortunato, M.; Bianchi, A.; Terzi, A. (Sep 2014). "18-Fluorine fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography in the pretreatment evaluation of thymic epithelial neoplasms: a metabolic biopsy confirmed by Ki-67 expression.". Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 46 (3): 369-74; discussion 374. doi:10.1093/ejcts/ezu030. PMID 24585679.