Rosai-Dorfman disease
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
The printable version is no longer supported and may have rendering errors. Please update your browser bookmarks and please use the default browser print function instead.
| Rosai-Dorfman disease | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
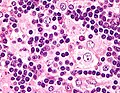
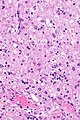
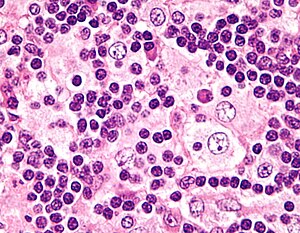 Rosai-Dorfman disease. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | sinus histiocytosis with histiocytes have a singular large round nucleus (~2x the size of a lymphocyte) with a prominent nucleolus (visible with 10x objective); emperipolesis |
| LM DDx | other specific histiocytoses (Langerhans cell histiocytosis, Erdheim-Chester disease), specific infections (rhinoscleroma, xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis), sinus histiocytosis |
| IHC | CD68 +ve, S-100 +ve, CD1a -ve |
| Gross | nodules (skin) |
| Site | skin, lymph nodes - see lymph node pathology |
|
| |
| Signs | fever, lymphadenopathy |
| Prevalence | rare |
| Blood work | leukocytosis with neurophilia |
| Prognosis | usually self-limited, benign |
| Clin. DDx | lymphoma, infections with lymphadenopathy |
Rosai-Dorfman disease, abbreviated RDD, is a rare lymph node pathology.
It is also known as sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy,[1] abbreviated SHML.
General
- Super rare.
- Prognosis - good, usually self-limited.[2]
- Fever.
- Leukocytosis with neutrophilia.
- Polyclonal gammaglobulinemia.
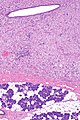
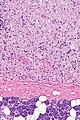
Gross
- Skin: nodules.[2]
Note:
- Reported at many sites.
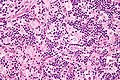
Microscopic
Features:
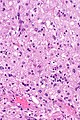
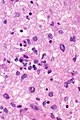
- Sinus histiocytosis:
- Histiocytes - abundant.
- Singular large round nuclei[4] ~2x the size of resting lymphocyte.
- Prominent nucleolus - visible with 10x objective.
- Abundant cytoplasm.
- Singular large round nuclei[4] ~2x the size of resting lymphocyte.
- Histiocytes - abundant.
- Emperipolesis (from Greek: em = inside, peri = around, polemai = wander about[5]):
DDx:
- Other specific histiocytoses:
- Infection, e.g. rhinoscleroma (nasopharynx), xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis.
- Sinus histiocytosis.
- Xanthomatous change.
Images
Case 1
Case 2
www
- RDD - case 1 - several images (upmc.edu).
- RDD - case 2 - several images of breast (upmc.edu).
- RDD - case 3 - several images (upmc.edu).
- RDD - case 4 - several images (upmc.edu).
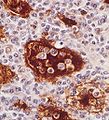
IHC
Features:[8]
- CD68 +ve.
- S-100 +ve.
- Useful for seeing emperipolesis.
- CD1a -ve.
- CD1a +ve in Langerhans cell histiocytosis.
Images
See also
References
- ↑ Agarwal A, Pathak S, Gujral S (October 2006). "Sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy--a review of seven cases". Indian J Pathol Microbiol 49 (4): 509–15. PMID 17183839.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Leal, PA.; Adriano, AL.; Breckenfeld, MP.; Costa, IS.; de Sousa, AR.; Gonçalves, Hde S.. "Rosai-Dorfman disease presenting with extensive cutaneous manifestation - case report.". An Bras Dermatol 88 (2): 256-9. doi:10.1590/S0365-05962013000200014. PMID 23739703.
- ↑ Landim, FM.; Rios, Hde O.; Costa, CO.; Feitosa, RG.; Rocha Filho, FD.; Costa, AA. (Jul 2009). "Cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman disease.". An Bras Dermatol 84 (3): 275-8. PMID 19668942.
- ↑ Bailey, D. 24 August 2010.
- ↑ Stedman's Medical Dictionary. 27th Ed.
- ↑ Viswanathan P, Raghunathan K, Majhi U, Pandit RV, Shanthi R, Rajkumar T (1997). Emperipolesis : an electron microscopic characteristic in RDD (Rosai-Dorfaman disease) : a case report. pp. 14-6. http://www.ijmpo.org/article.asp?issn=0971-5851;year=1997;volume=18;issue=1;spage=14;epage=16;aulast=Viswanathan;type=0.
- ↑ Lyons DJ, Gautam A, Clark J, et al. (January 1992). "Lymphocyte macrophage interactions: peripolesis of human alveolar macrophages". Eur. Respir. J. 5 (1): 59–66. PMID 1577151.
- ↑ Hartmann, S.; Kriener, S.; Hansmann, ML. (Jul 2008). "[Diagnostic spectrum of reactive lymph node changes].". Pathologe 29 (4): 253-63. doi:10.1007/s00292-008-1003-5. PMID 18504582.