Difference between revisions of "Pulmonary infarct"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(redirect) |
(split out) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Pulmonary infarct''' is the death of [[lung]] tissue due to oxygen deprivation. | |||
It is also known as a '''lung infarct''', '''lung infarction''', and '''pulmonary infarction'''. | |||
==General== | |||
*Uncommon because of the dual blood supply (systemic via the bronchial arteries, pulmonary via the pulmonary arteries). | |||
Common causes:<ref>URL: [http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/908045-overview http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/908045-overview]. Accessed on: 12 April 2012.</ref> | |||
*[[Pulmonary embolism]]. | |||
*[[Sickle cell disease]]. | |||
Less common causes: | |||
*Lymphoma, esp. [[acute promyelocytic leukemia]]. | |||
*Drugs, e.g. chemotherapy. | |||
*[[Vasculitis]]. | |||
*Others. | |||
==Gross== | |||
*Lung periphery, classically described as wedge-shaped. | |||
Note: | |||
*In a histologic section, the classic wedge-shaped infarct is triangular: | |||
**Base of triangle on the pleural aspect. | |||
**Point furthest from the pleura close to the compromised artery that lead to infarction. | |||
Image: | |||
*[http://www.sciencephoto.com/media/258474/enlarge Pulmonary infarct (sciencephoto.com)]. | |||
*[http://www.flickr.com/photos/pulmonary_pathology/3732297830/ Pulmonary infarct (flickr.com)] | |||
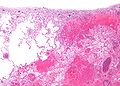
==Microscopic== | |||
Features: | |||
*[[Necrosis]] of alveolar walls - loss of nuclei. | |||
*Alveolar hemorrhage. | |||
===Image=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Pulmonary_infarct_intermed_mag.jpg | Pulmonary infarct - low mag. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
==See also== | |||
*[[Pulmonary pathology]]. | |||
==References== | |||
{{Reflist|2}} | |||
[[Category:Diagnosis]] | [[Category:Diagnosis]] | ||
[[Category:Pulmonary pathology]] | |||
Revision as of 01:28, 17 February 2014
Pulmonary infarct is the death of lung tissue due to oxygen deprivation.
It is also known as a lung infarct, lung infarction, and pulmonary infarction.
General
- Uncommon because of the dual blood supply (systemic via the bronchial arteries, pulmonary via the pulmonary arteries).
Common causes:[1]
Less common causes:
- Lymphoma, esp. acute promyelocytic leukemia.
- Drugs, e.g. chemotherapy.
- Vasculitis.
- Others.
Gross
- Lung periphery, classically described as wedge-shaped.
Note:
- In a histologic section, the classic wedge-shaped infarct is triangular:
- Base of triangle on the pleural aspect.
- Point furthest from the pleura close to the compromised artery that lead to infarction.
Image:
Microscopic
Features:
- Necrosis of alveolar walls - loss of nuclei.
- Alveolar hemorrhage.
Image
See also
References
- ↑ URL: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/908045-overview. Accessed on: 12 April 2012.