Difference between revisions of "Mastocytosis"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(+cat.) |
|||
| (9 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
# | {{ Infobox diagnosis | ||
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | |||
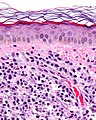
| Image = Mastocytosis_-_cropped_-_very_high_mag.jpg | |||
| Width = | |||
| Caption = Mastocytosis. [[H&E stain]]. | |||
| Synonyms = | |||
| Micro = mast cells (cells in the superficial/mid dermis that are: lymphocyte-like with more cytoplasm that is granular; cells may have spindled or stellate morphology); +/-eosinophils (common) | |||
| Subtypes = | |||
| LMDDx = [[intradermal nevus]] | |||
| Stains = [[Giemsa stain]] +ve | |||
| IHC = CD117 +ve, tryptase +ve | |||
| EM = | |||
| Molecular = | |||
| IF = | |||
| Gross = | |||
| Grossing = | |||
| Site = [[skin]] | |||
| Assdx = | |||
| Syndromes = | |||
| Clinicalhx = | |||
| Signs = | |||
| Symptoms = | |||
| Prevalence = not very common | |||
| Bloodwork = | |||
| Rads = | |||
| Endoscopy = | |||
| Prognosis = dependent on underlying cause | |||
| Other = | |||
| ClinDDx = | |||
| Tx = dependent on underlying cause | |||
}} | |||
'''Mastocytosis''' is the abundance of [[mast cells]]. It can be due to a number of causes. | |||
==General== | |||
*Abundance of [[mast cell]]s. | |||
Classification:<ref name=pmid21083038>{{Cite journal | last1 = Arock | first1 = M. | last2 = Valent | first2 = P. | title = Pathogenesis, classification and treatment of mastocytosis: state of the art in 2010 and future perspectives. | journal = Expert Rev Hematol | volume = 3 | issue = 4 | pages = 497-516 | month = Aug | year = 2010 | doi = 10.1586/ehm.10.42 | PMID = 21083038 }}</ref> | |||
#Cutaneous (only) - usually children. | |||
#*Urticaria pigmentosa. | |||
#*Others. | |||
#Systemic - usually adults. | |||
#*Indolent subvariant. | |||
#*Aggressive subvariant. | |||
#*Leukemic subvariant. | |||
==Microscopic== | |||
Features:<ref name=Ref_PBoD8|1185>{{Ref PBoD8|1185}}</ref> | |||
*Cells in the superficial/mid dermis that are: | |||
**Lymphocyte-like with more cytoplasm that is granular. | |||
***Cells may have spindled or stellate morphology. | |||
***Tend to be more abundant around vessels. | |||
*+/-Eosinophils (common). | |||
*+/-Edema - often prominent; gives cells a white halo. | |||
Notes: | |||
*Lymphocyte versus mast cell: | |||
**Lymphocytes = round; mast cells = ovoid. | |||
DDx: | |||
*[[Intradermal nevus]]. | |||
*[[Pleomorphic undifferentiated sarcoma]], [[Langerhans cell histiocytosis]] and other [[pleomorphic tumours]] - for ''aggressive systemic mastocytosis''. | |||
===Images=== | |||
www: | |||
*[http://www.jameswpattersonmd.com/case_studies/index.cfm?CFID=387434 Mastocytosis - low res. (jameswpattersonmd.com)]. | |||
*[http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case366.html Mastocytosis - bone marrow - several images (upmc.edu)]. | |||
*[http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case409.html Systemic mastocytosis - several images (upmc.edu)]. | |||
<gallery> | |||
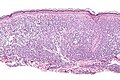
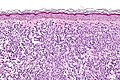
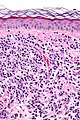
Image:Mastocytosis - intermed mag.jpg | Mastocytosis - intermed. mag. (WC) | |||
Image:Mastocytosis_-_high_mag.jpg | Mastocytosis - high mag. (WC) | |||
Image:Mastocytosis_-_very_high_mag.jpg | Mastocytosis - very high mag. (WC) | |||
Image:Mastocytosis_-_cropped_-_very_high_mag.jpg | Mastocytosis - very high mag. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
==Stains== | |||
*[[Toluidine blue stain|Toluidine blue]] -- highlights the granules. | |||
*[[Giemsa stain]] +ve | |||
==IHC== | |||
*CD117 +ve. | |||
*Tryptase +ve.<ref name=pmid21866466>{{Cite journal | last1 = Rudzki | first1 = Z. | last2 = Sotlar | first2 = K. | last3 = Kudela | first3 = A. | last4 = Starzak-Gwóźdź | first4 = J. | last5 = Horny | first5 = HP. | title = Systemic mastocytosis (SM) and associated malignant bone marrow histiocytosis - a hitherto undescribed form of SM-AHNMD. | journal = Pol J Pathol | volume = 62 | issue = 2 | pages = 101-4 | month = | year = 2011 | doi = | PMID = 21866466 }} | |||
</ref> | |||
==See also== | |||
*[[Non-malignant skin disease]]. | |||
*[[Mast cell]]. | |||
==References== | |||
{{Reflist|2}} | |||
[[Category:Diagnosis]] | [[Category:Diagnosis]] | ||
[[Category:Non-malignant skin disease]] | |||
Latest revision as of 03:19, 20 March 2018
| Mastocytosis | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
 Mastocytosis. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | mast cells (cells in the superficial/mid dermis that are: lymphocyte-like with more cytoplasm that is granular; cells may have spindled or stellate morphology); +/-eosinophils (common) |
| LM DDx | intradermal nevus |
| Stains | Giemsa stain +ve |
| IHC | CD117 +ve, tryptase +ve |
| Site | skin |
|
| |
| Prevalence | not very common |
| Prognosis | dependent on underlying cause |
| Treatment | dependent on underlying cause |
Mastocytosis is the abundance of mast cells. It can be due to a number of causes.
General
- Abundance of mast cells.
Classification:[1]
- Cutaneous (only) - usually children.
- Urticaria pigmentosa.
- Others.
- Systemic - usually adults.
- Indolent subvariant.
- Aggressive subvariant.
- Leukemic subvariant.
Microscopic
Features:[2]
- Cells in the superficial/mid dermis that are:
- Lymphocyte-like with more cytoplasm that is granular.
- Cells may have spindled or stellate morphology.
- Tend to be more abundant around vessels.
- Lymphocyte-like with more cytoplasm that is granular.
- +/-Eosinophils (common).
- +/-Edema - often prominent; gives cells a white halo.
Notes:
- Lymphocyte versus mast cell:
- Lymphocytes = round; mast cells = ovoid.
DDx:
- Intradermal nevus.
- Pleomorphic undifferentiated sarcoma, Langerhans cell histiocytosis and other pleomorphic tumours - for aggressive systemic mastocytosis.
Images
www:
- Mastocytosis - low res. (jameswpattersonmd.com).
- Mastocytosis - bone marrow - several images (upmc.edu).
- Systemic mastocytosis - several images (upmc.edu).
Stains
- Toluidine blue -- highlights the granules.
- Giemsa stain +ve
IHC
- CD117 +ve.
- Tryptase +ve.[3]
See also
References
- ↑ Arock, M.; Valent, P. (Aug 2010). "Pathogenesis, classification and treatment of mastocytosis: state of the art in 2010 and future perspectives.". Expert Rev Hematol 3 (4): 497-516. doi:10.1586/ehm.10.42. PMID 21083038.
- ↑ Kumar, Vinay; Abbas, Abul K.; Fausto, Nelson; Aster, Jon (2009). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 1185. ISBN 978-1416031215.
- ↑ Rudzki, Z.; Sotlar, K.; Kudela, A.; Starzak-Gwóźdź, J.; Horny, HP. (2011). "Systemic mastocytosis (SM) and associated malignant bone marrow histiocytosis - a hitherto undescribed form of SM-AHNMD.". Pol J Pathol 62 (2): 101-4. PMID 21866466.