Difference between revisions of "Mammary myofibroblastoma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→IHC) |
|||
| Line 72: | Line 72: | ||
*CD34 +ve.<ref name=pmid11474286/> | *CD34 +ve.<ref name=pmid11474286/> | ||
*Desmin +ve.<ref name=pmid11474286/> | *Desmin +ve.<ref name=pmid11474286/> | ||
*Actin +ve. | *Actin +ve. | ||
*Vimentin +ve. | *Vimentin +ve. | ||
Others: | |||
* | *S-100 -ve.<ref name=pmid24298520/> | ||
*Beta-catenin -ve. | *Beta-catenin -ve.{{fact}} | ||
*H-caldesmon -ve.<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Mnif | first1 = H. | last2 = Charfi | first2 = S. | last3 = Abid | first3 = N. | last4 = Sallemi-Boudawara | first4 = T. | title = Mammary myofibroblastoma with leiomyomatous differentiation: case report and literature review. | journal = Pathologica | volume = 105 | issue = 4 | pages = 142-5 | month = Aug | year = 2013 | doi = | PMID = 24466766 }}</ref>{{fact}} | |||
*CK7 -ve.<ref name=pmid24298520>{{Cite journal | last1 = Shivali | first1 = B. | last2 = S | first2 = K. | last3 = Chandramouleeswari | first3 = K. | last4 = Anita | first4 = S. | title = Myofibroblastoma breast with unusual morphological features. Cytohistopathogical diagnostic pitfalls and role of immunohistochemistry-review of literature. | journal = J Clin Diagn Res | volume = 7 | issue = 10 | pages = 2323-5 | month = Oct | year = 2013 | doi = 10.7860/JCDR/2013/5281.3515 | PMID = 24298520 }}</ref> | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
Revision as of 04:15, 16 February 2014
| Mammary myofibroblastoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
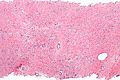
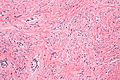
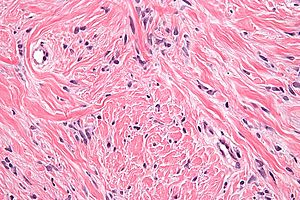 Mammary myofibroblastoma. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | well-circumscribed lesion, wpindle cells without nuclear atypia arranged in fascicles, interspersed thick bundles of collagen. |
| LM DDx | metaplastic breast carcinoma, fibromatosis, leiomyoma of the breast, nodular fasciitis, phyllodes tumour, spindle cell lipoma |
| IHC | CD34 +ve, desmin +ve, H-caldesmon +ve, actin +ve, vimentin +ve, S100 -ve, beta-catenin -ve |
| Site | breast |
|
| |
| Clinical history | postmenopausal female or older male |
| Prevalence | rare |
| Prognosis | benign |
| Treatment | excision |
Mammary myofibroblastoma is a rare benign pathology of the breast.
General
Note:
- In extra-mammary sites the tumour is known as a mammary-type myofibroblastoma may immunohistochemically and histomorphologically overlap with spindle cell lipoma.[3]
Microscopic
Features:[4]
- Well-circumscribed lesion.
- Spindle cells without nuclear atypia arranged in fascicles.
- Interspersed thick bundles of collagen.
Notes:
- No calcifications.
- No necrosis.
- No hemorrhage.
DDx:
- Metaplastic breast carcinoma.
- Fibromatosis.
- Leiomyoma of the breast.
- Nodular fasciitis.
- Phyllodes tumour.
- Spindle cell lipoma.
Images
www:
IHC
Features:[2]
Others:
- S-100 -ve.[5]
- Beta-catenin -ve.[citation needed]
- H-caldesmon -ve.[6][citation needed]
- CK7 -ve.[5]
See also
References
- ↑ Qureshi, A.; Kayani, N.. "Myofibroblastoma of breast.". Indian J Pathol Microbiol 51 (3): 395-6. PMID 18723968.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Mele, M.; Jensen, V.; Wronecki, A.; Lelkaitis, G. (2011). "Myofibroblastoma of the breast: Case report and literature review.". Int J Surg Case Rep 2 (6): 93-6. doi:10.1016/j.ijscr.2011.02.006. PMC 3199680. PMID 22096693. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3199680/. Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name "pmid22096693" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 McMenamin, ME.; Fletcher, CD. (Aug 2001). "Mammary-type myofibroblastoma of soft tissue: a tumor closely related to spindle cell lipoma.". Am J Surg Pathol 25 (8): 1022-9. PMID 11474286.
- ↑ O'Malley, Frances P.; Pinder, Sarah E. (2006). Breast Pathology: A Volume in Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology series (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 131. ISBN 978-0443066801.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Shivali, B.; S, K.; Chandramouleeswari, K.; Anita, S. (Oct 2013). "Myofibroblastoma breast with unusual morphological features. Cytohistopathogical diagnostic pitfalls and role of immunohistochemistry-review of literature.". J Clin Diagn Res 7 (10): 2323-5. doi:10.7860/JCDR/2013/5281.3515. PMID 24298520.
- ↑ Mnif, H.; Charfi, S.; Abid, N.; Sallemi-Boudawara, T. (Aug 2013). "Mammary myofibroblastoma with leiomyomatous differentiation: case report and literature review.". Pathologica 105 (4): 142-5. PMID 24466766.