Spindle cell lipoma
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Spindle cell lipoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
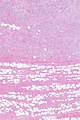
 Micrograph showing a spindle cell lipoma. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
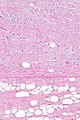
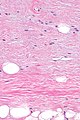
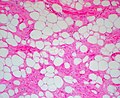
| LM | aligned bland spindled cells adjacent to fat, rope-like collagen bundles (key feature), +/-myxoid component, +/-staghorn-like vessels |
| LM DDx | neurofibroma, spindle cell liposarcoma, pleomorphic lipoma |
| IHC | CD34 +ve, MDM2 -ve |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
| Prognosis | benign |
Spindle cell lipoma is a rare benign adipocytic tumour.
General
- Rare.
- Predominantly men.[1]
Note:
- Spindle cell lipoma may immunohistochemically and histomorphologically overlap with mammary-type myofibroblastoma[2] - see: mammary myofibroblastoma.
Microscopic
Features:[1]
- Aligned bland spindled cells adjacent to fat.
- Rope-like collagen bundles - key feature.
- May be described as "shreaded wheat".
- +/-Myxoid component.
- +/-Staghorn-like vessels.
Notes:
- May overlap with pleomorphic lipoma.[3]
DDx:
- Neurofibroma.
- Spindle cell liposarcoma - extremely rare.[4]
Images
www
IHC
- CD34 +ve.[5]
- Desmin +ve.
- S100 -ve. (???)
Lipoma versus liposarcoma:
Molecular
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Murphey, MD.; Carroll, JF.; Flemming, DJ.; Pope, TL.; Gannon, FH.; Kransdorf, MJ.. "From the archives of the AFIP: benign musculoskeletal lipomatous lesions.". Radiographics 24 (5): 1433-66. doi:10.1148/rg.245045120. PMID 15371618.
- ↑ McMenamin, ME.; Fletcher, CD. (Aug 2001). "Mammary-type myofibroblastoma of soft tissue: a tumor closely related to spindle cell lipoma.". Am J Surg Pathol 25 (8): 1022-9. PMID 11474286.
- ↑ URL: http://surgpathcriteria.stanford.edu/softfat/spindle_cell_lipoma/. Accessed on: 4 December 2010.
- ↑ Dei Tos, AP.; Mentzel, T.; Newman, PL.; Fletcher, CD. (Sep 1994). "Spindle cell liposarcoma, a hitherto unrecognized variant of liposarcoma. Analysis of six cases.". Am J Surg Pathol 18 (9): 913-21. PMID 8067512.
- ↑ Wood, L.; Fountaine, TJ.; Rosamilia, L.; Helm, KF.; Clarke, LE. (Dec 2010). "Cutaneous CD34+ spindle cell neoplasms: Histopathologic features distinguish spindle cell lipoma, solitary fibrous tumor, and dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans.". Am J Dermatopathol 32 (8): 764-8. doi:10.1097/DAD.0b013e3181d0c587. PMID 20559119.
- ↑ Alshenawy, H. (Jun 2013). "Can HMGI-C be used as an aid with MDM2 and CDK4 to differentiate liposarcoma subtypes from their mimics?". J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 139 (6): 1073-81. doi:10.1007/s00432-013-1420-6. PMID 23529275.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Creytens, D.; van Gorp, J.; Savola, S.; Ferdinande, L.; Mentzel, T.; Libbrecht, L. (Jul 2014). "Atypical spindle cell lipoma: a clinicopathologic, immunohistochemical, and molecular study emphasizing its relationship to classical spindle cell lipoma.". Virchows Arch 465 (1): 97-108. doi:10.1007/s00428-014-1568-8. PMID 24659226.