Difference between revisions of "Hyaline globules"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(make image larger) |
Jensflorian (talk | contribs) m (→Tumours: add secretory meningioma) |
||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
*[[Renal cell carcinoma]].<ref name=pmid11026104/> | *[[Renal cell carcinoma]].<ref name=pmid11026104/> | ||
*[[Kaposi sarcoma]] (KS). | *[[Kaposi sarcoma]] (KS). | ||
* Secretory [[Meningioma]].<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Budka | first1 = H. | title = Hyaline inclusions (Pseudopsammoma bodies) in meningiomas: immunocytochemical demonstration of epithel-like secretion of secretory component and immunoglobulins A and M. | journal = Acta Neuropathol | volume = 56 | issue = 4 | pages = 294-8 | month = | year = 1982 | doi = | PMID = 6283779 }}</ref> | |||
===Images=== | ===Images=== | ||
| Line 30: | Line 32: | ||
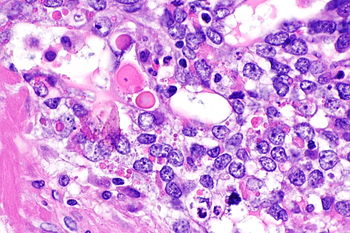
Image:Kaposi_sarcoma_high_mag.jpg | Hyaline globules in KS - high mag. (WC) | Image:Kaposi_sarcoma_high_mag.jpg | Hyaline globules in KS - high mag. (WC) | ||
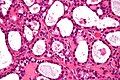
Image:Solid_pseudopapillary_tumour_-_very_high_mag.jpg | Hyaline globules in solid pseudopapillary tumour - very high mag. (WC) | Image:Solid_pseudopapillary_tumour_-_very_high_mag.jpg | Hyaline globules in solid pseudopapillary tumour - very high mag. (WC) | ||
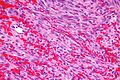
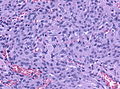
File:Secretory meningioma HE x200.jpg | Hyaline globules (pseudopsammoma bodies) in secretory meningioma (WC/jensflorian) | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Revision as of 08:34, 13 April 2015
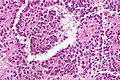
Hyaline globules, also hyaline bodies, are a common non-specific histomorphologic feature that can be useful in formulating a differential diagnosis.
They can be seen in benign and malignant tissue.
Microscopic
Features:
- Eosinophilic (pink) round bodies ~ typically 4-10 micrometers in diameter.
Benign
- Ectopic decidua.[1]
Tumours
Gynecologic:
- Clear cell carcinoma (CCC).
- Yolk sac tumour, hepatoid pattern.[2]
Gastrointestinal:
- Solid pseudopapillary tumour.[3]
- Pancreatic endocrine tumour.[3]
- Hepatocellular carcinoma - very common.[4]
Other:
- Renal cell carcinoma.[4]
- Kaposi sarcoma (KS).
- Secretory Meningioma.[5]
Images
See also
References
- ↑ Dharan M (September 2009). "Hyaline globules in ectopic decidua in a pregnant woman with cervical squamous cell carcinoma". Diagn. Cytopathol. 37 (9): 696–8. doi:10.1002/dc.21113. PMID 19526574.
- ↑ URL: http://webpathology.com/image.asp?case=34&n=6. Accessed on: March 8, 2010.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Serra S, Chetty R (November 2008). "Revision 2: an immunohistochemical approach and evaluation of solid pseudopapillary tumour of the pancreas". J. Clin. Pathol. 61 (11): 1153–9. doi:10.1136/jcp.2008.057828. PMID 18708424. http://jcp.bmj.com/content/61/11/1153.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Nayar, R.; Bourtsos, E.; DeFrias, DV. (Oct 2000). "Hyaline globules in renal cell carcinoma and hepatocellular carcinoma. A clue or a diagnostic pitfall on fine-needle aspiration?". Am J Clin Pathol 114 (4): 576-82. doi:10.1309/F4TU-6AFE-R7NU-39Y3. PMID 11026104.
- ↑ Budka, H. (1982). "Hyaline inclusions (Pseudopsammoma bodies) in meningiomas: immunocytochemical demonstration of epithel-like secretion of secretory component and immunoglobulins A and M.". Acta Neuropathol 56 (4): 294-8. PMID 6283779.